
New Zero-Day Vulnerability in Windows Themes Threatens NTLM Security
A newly discovered zero-day vulnerability in Windows Themes files exposes users’ NTLM credentials, posing serious risks for remote credential theft. Despite Microsoft’s recent efforts to address similar vulnerabilities in theme files, a security gap remains, allowing attackers to cause credential leaks simply by viewing a malicious theme file in Windows Explorer. Researchers at ACROS Security reported this vulnerability, which highlights the ongoing risk that Windows users face from NTLM-related exploits.
New Bypass Detected by ACROS Security
While Microsoft initially patched CVE-2024-21320 in January to address NTLM leaks, Akamai researcher Tomer Peled discovered that attackers could still bypass the patch, resulting in CVE-2024-38030. Malicious theme files can use this vulnerability to send network requests containing NTLM credentials to remote attackers without requiring user interaction.
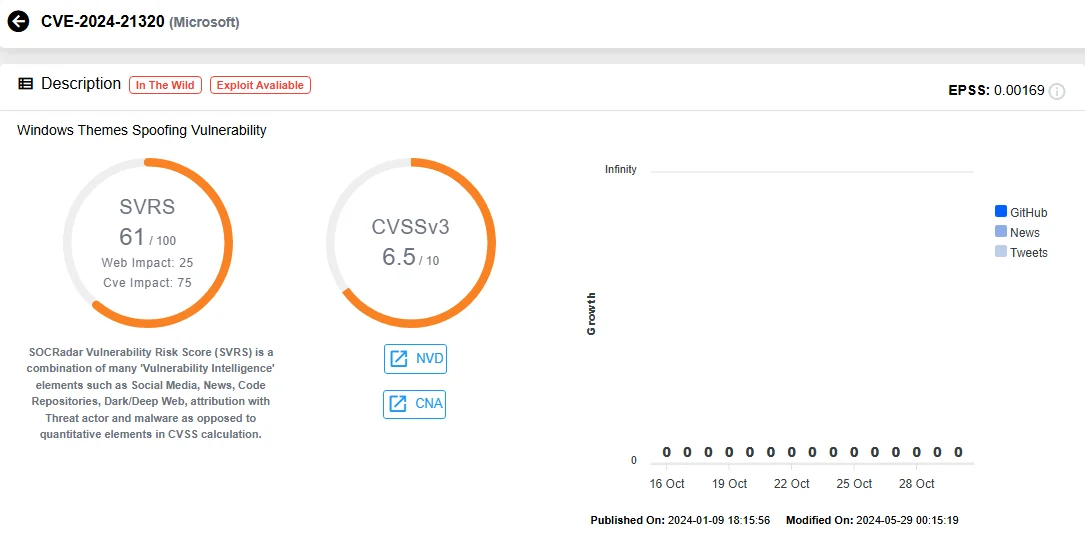
Details of CVE-2024-21320 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
ACROS Security discovered yet another bypass of Microsoft’s patch that affects fully updated Windows systems, including Windows 11 24H2. As a solution, ACROS Security has released a temporary micropatch through their 0patch service, allowing users to secure their systems until an official patch is available. This vulnerability affects both legacy and supported versions of Windows Workstation.
How the Zero-Day Attack Works
Malicious theme files that include a network path for properties such as BrandImage and Wallpaper cause Windows to send NTLM authentication requests to remote hosts, even if the theme file is only displayed in Explorer. This NTLM leak occurs in multiple Windows versions, from Windows 7 to Windows 11 24H2, and attackers can use it to perform NTLM relay and pass-the-hash attacks, allowing for lateral movement across compromised networks.
ACROS Security’s temporary patch resolves the issue by ensuring that Windows systems correctly detect network paths within theme files, thereby preventing NTLM leaks.
How the Micropatch Works
In response to the Windows Themes zero-day vulnerability, ACROS Security provided a micropatch that effectively prevents NTLM credential leaks caused by malicious Windows theme files. This micropatch targets specific paths in Windows Explorer that would normally send a network request to an attacker’s machine when viewing a compromised theme file. By correctly identifying network paths in theme files, the patch prevents NTLM credential sharing, ensuring that no unauthorized connections are initiated.
In this YouTube video, the vulnerability is tested on two fully updated Windows 11 24H2 computers. The first PC creates a malicious theme file and sends it to the second, unpatched PC. Simply copying this file to the unpatched PC’s desktop initiates a network connection and sends NTLM credentials to the attacker’s machine with no further action required.
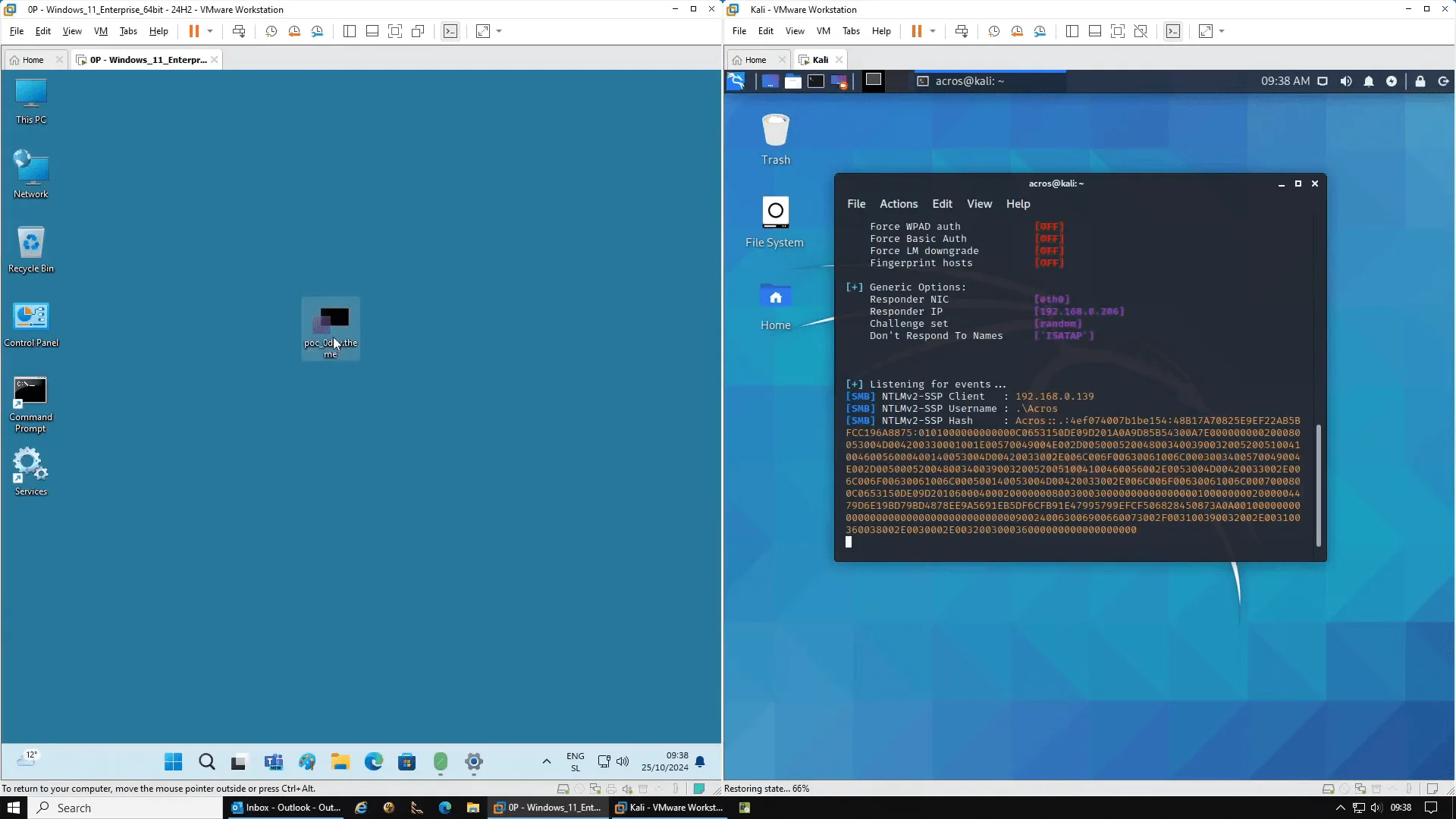
A showcase of the sent NTLM credentials as presented on the right monitor
With the 0patch micropatch installed, the same file transfer no longer results in a connection. Instead, the micropatch recognizes and blocks the network path within the theme file, ensuring that no credentials are compromised. This demonstration demonstrates the efficacy of 0patch’s solution by demonstrating how their real-time, targeted patch can mitigate the vulnerability even before Microsoft issues an official fix.
Stay Ahead with SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence
With new vulnerabilities emerging every day, proactive measures are critical for securing your organization’s digital environment. SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence provides the tools you need to stay ahead of potential threats. This feature assists you in identifying and prioritizing critical vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them by providing real-time alerts and detailed, actionable insights.
SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence Module
This module also ensures that your resources are focused on the most critical vulnerabilities, allowing for faster patching and assisting you in maintaining robust security. With SOCRadar, you’ll always be one step ahead, protecting your organization from the latest threats.
Conclusion
The recently discovered zero-day vulnerability in Windows Themes files highlights the risks associated with legacy authentication methods such as NTLM. With the growing complexity of NTLM-based attacks, this vulnerability emphasizes the need for better security patching practices. To reduce the risk of credential exposure, organizations and individuals using Windows should apply ACROS Security’s temporary patch and stay up to date on Microsoft’s official patch release.



































