
Exploited PAN-OS Zero-Days Threaten Thousands of Firewalls (CVE-2024-0012 and CVE-2024-9474)
[Update] December 25, 2024: “CVE-2024-9474 Used to Deploy Advanced Backdoor on Palo Alto Firewalls”
[Update] November 22, 2024: “Growing Exploitation of Palo Alto Networks PAN-OS Vulnerabilities”
Palo Alto Networks recently disclosed two zero-day vulnerabilities affecting their PAN-OS devices, actively exploited in the wild. These flaws, CVE-2024-0012 and CVE-2024-9474, exploit weaknesses in the management web interface, with one allowing attackers to bypass authentication and gain administrator privileges without user interaction.
While the company reports only limited exposure, thousands of potentially vulnerable systems have been identified globally, raising concerns about the broader impact.
CVE-2024-0012: Authentication Bypass Explained
CVE-2024-0012 is a critical vulnerability (CVSS 9.3) affecting the PAN-OS management web interface. Palo Alto Networks updated its advisory for the vulnerability yesterday, reclassifying it as an authentication bypass after it had previously been identified as a remote command execution.
This flaw allows unauthenticated attackers to bypass security measures and gain full administrative access to affected systems. Exploiting this issue requires no user interaction, making it particularly dangerous for internet-exposed interfaces.
Once exploited, attackers can manipulate system configurations, compromise sensitive data, or launch additional attacks.
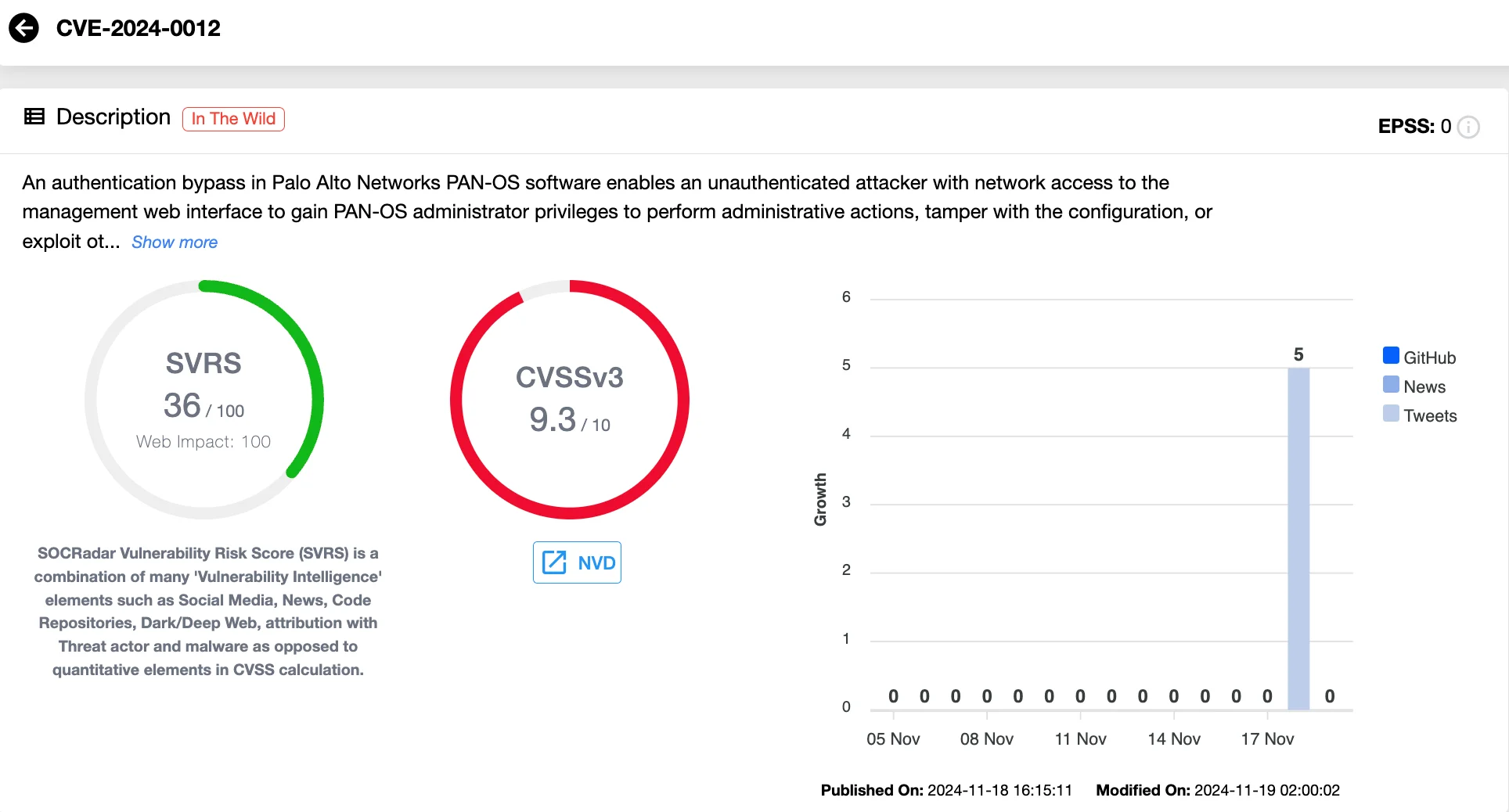
Details of CVE-2024-0012 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Palo Alto Networks has emphasized that the vulnerability’s impact can be significantly reduced by limiting access to the management interface to trusted internal networks.
CVE-2024-9474: Privilege Escalation Risks
CVE-2024-9474 is a medium-severity vulnerability (CVSS 6.9) that allows malicious administrators to escalate their privileges to root level on affected PAN-OS systems. Unlike CVE-2024-0012, this flaw requires existing administrative access, making it less critical but still a significant concern for organizations.
When exploited, this vulnerability enables attackers to perform actions with full system control, potentially leading to severe consequences, such as disabling security features or launching further attacks.
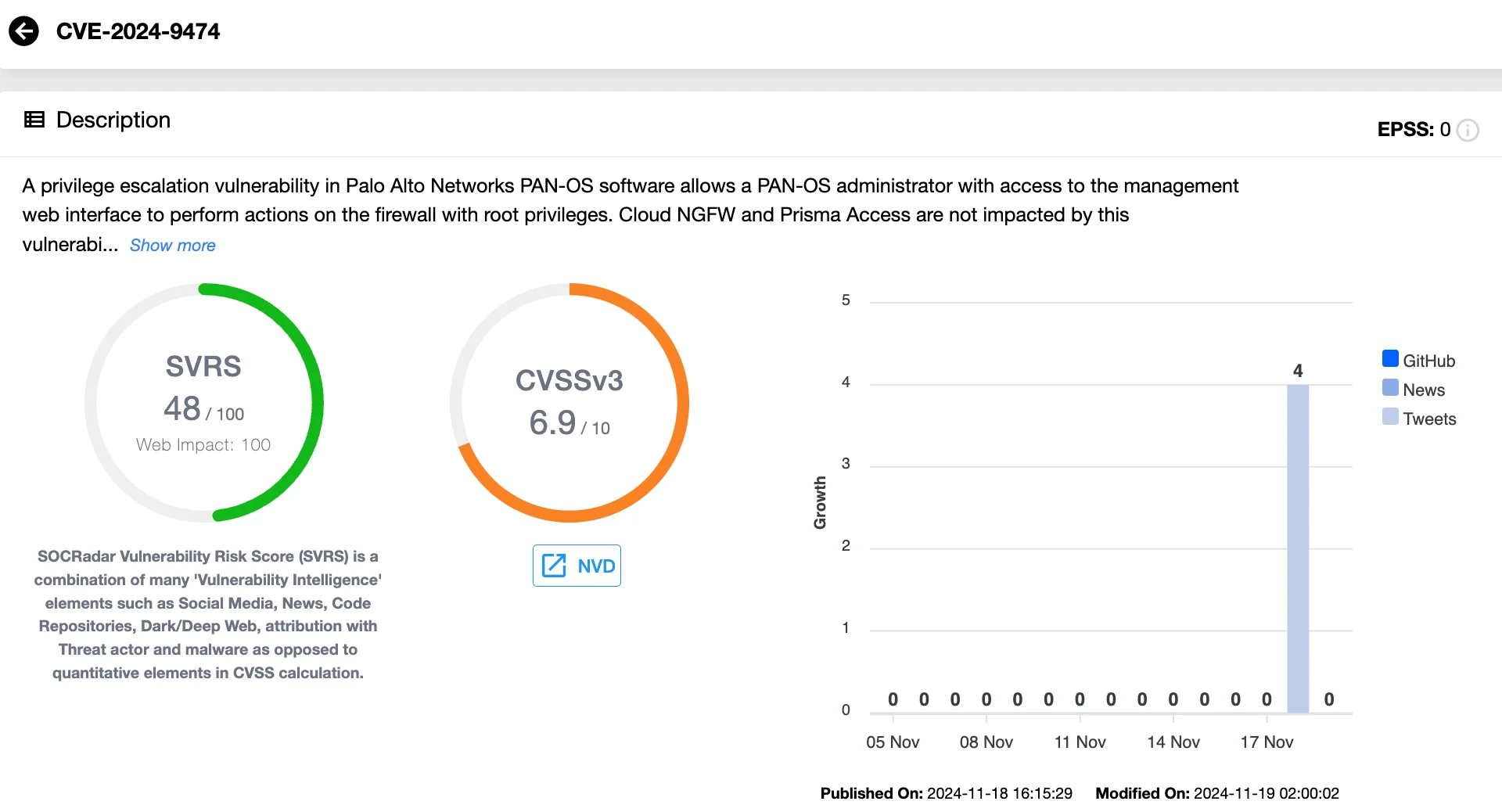
Details of CVE-2024-9474 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
While it poses a lower risk compared to CVE-2024-0012, its potential impact on compromised systems underlines the importance of immediate patching and strict access controls.
Affected PAN-OS Versions
Both CVE-2024-0012 and CVE-2024-9474 impact multiple versions of PAN-OS; the affected versions for each vulnerability are outlined below:
- CVE-2024-0012:
Affects PAN-OS 10.2 to 11.2 (versions before: 10.2.12-h2, 11.0.6-h1, 11.1.5-h1, 11.2.4-h1). - CVE-2024-9474:
Affects PAN-OS 10.1 to 11.2 (versions before: 10.1.14-h6, 10.2.12-h2, 11.0.6-h1, 11.1.5-h1, 11.2.4-h1).
Upgrading to later versions secures your systems against these vulnerabilities, reducing exposure to potential exploitation.
How Were the Vulnerabilities Exploited – Operation Lunar Peek
Palo Alto Networks linked the exploitation of the critical vulnerability to a campaign they named Operation Lunar Peek. Attackers targeted exposed PAN-OS management interfaces, using CVE-2024-0012 to bypass authentication and gain administrative access. While CVE-2024-9474 has been exploited in follow-up attacks, researchers have not directly tied it to this operation.
Security researcher Yutaka Sejiyama reported on X that they discovered 15,429 public-facing servers globally running Palo Alto Networks’ management interface via Shodan. Among these, 11,180 were confirmed as active, indicating a widespread risk. The United States had the highest number of exposed instances among the affected countries.
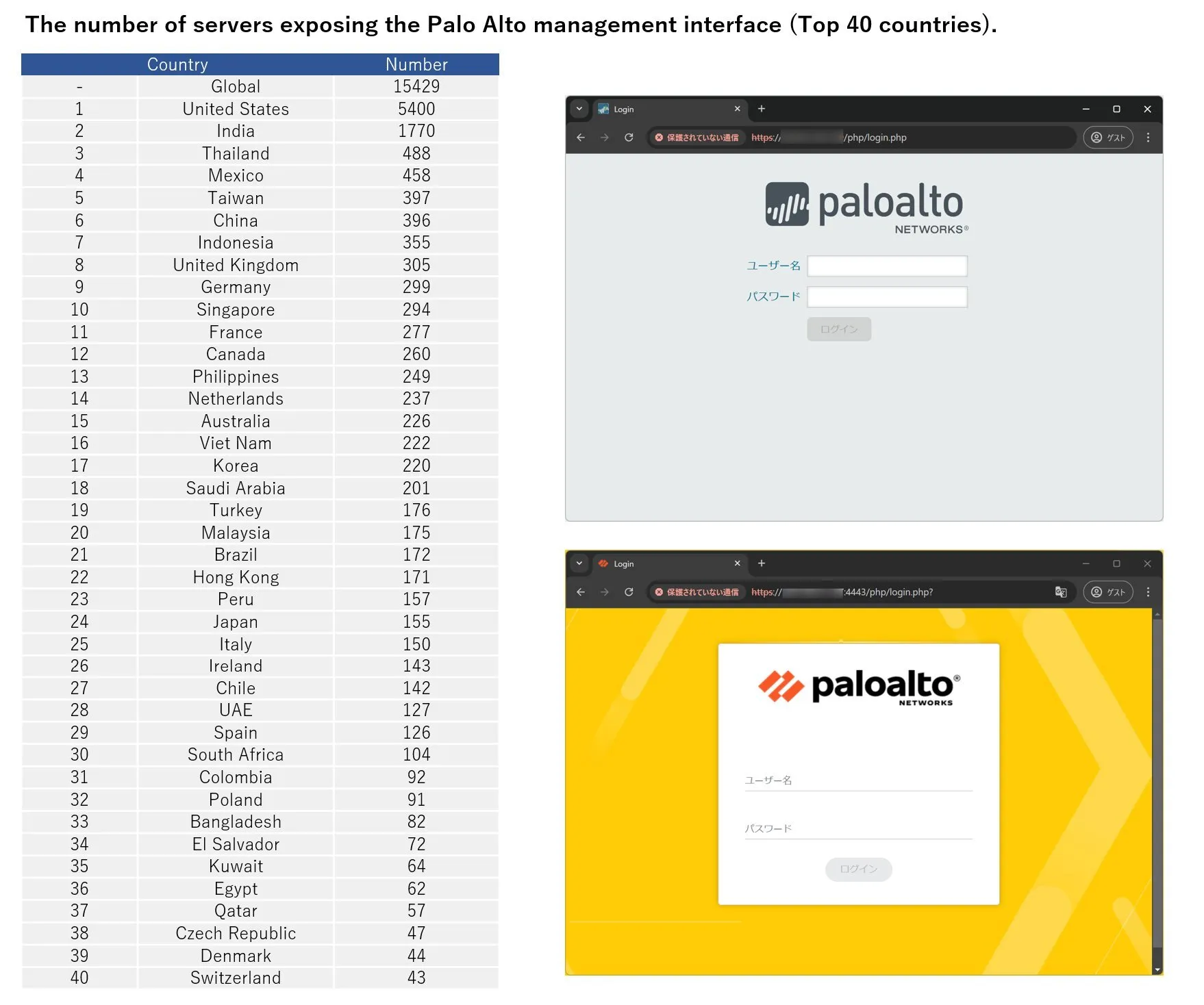
The number of servers exposing Palo Alto management interface (Source: X)
Growing Exploitation of Palo Alto Networks PAN-OS Vulnerabilities
Palo Alto Networks continues its investigation into the exploitation of CVE-2024-0012 and CVE-2024-9474. Initial malicious activity, observed on November 18, 2024, was traced to IP addresses linked to anonymous VPN services, complicating efforts to pinpoint the attackers.
Palo Alto’s Unit 42 now assesses with moderate to high confidence that a functional exploit chaining these vulnerabilities is publicly available, potentially enabling attackers to escalate their activities and target more systems. Meanwhile, Shadowserver reported that it identified over 2,000 compromised PAN-OS devices worldwide as a result of the exploitation of CVE-2024-0012 and CVE-2024-9474.
Threat actors have been observed executing commands and deploying malware, including web shells, on compromised firewalls. Palo Alto is actively analyzing and categorizing this post-exploitation behavior to understand its broader impact.
On an additional note, Palo Alto Networks has recently updated its advisories for CVE-2024-0012 and CVE-2024-9474 to clarify their impact on the following product lines:
- PA-Series, VM-Series, and CN-Series firewalls, along with Panorama (virtual and M-Series).
- For CVE-2024-9474, WildFire appliances are also now listed as affected.
Users are encouraged to review the updated advisories for detailed guidance and remediation steps, and remain vigilant for any signs of malicious activity.
Vulnerability management and attack surface monitoring often become overwhelming with the sheer number of alerts and exposed assets. SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence and Attack Surface Management (ASM) modules work together to cut through the noise, prioritizing vulnerabilities and exposed entry points based on risk factors specific to your environment.
What Does SOCRadar Provide?
- Real-time alerts on high-impact vulnerabilities like CVE-2024-0012.
- Detailed exploit analysis and threat actor behaviors.
- Insights to patch, secure exposed assets, and mitigate risks promptly.
By leveraging SOCRadar’s platform, you can track vulnerabilities tied to your digital assets, ensuring immediate action when necessary. Stay one step ahead of attackers by turning threat insights into proactive defense strategies.
SOCRadar Attack Surface Management (ASM) module, Company Vulnerabilities page
CISA Adds Palo Alto Zero-Days (CVE-2024-0012 and CVE-2024-9474) to the KEV Catalog
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has added the Palo Alto Networks vulnerabilities, CVE-2024-0012 and CVE-2024-9474, to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog. Federal agencies have been instructed to prioritize patching affected systems by December 9, 2024, ensuring compliance with CISA’s directive.
Alongside these vulnerabilities, CISA added another high-risk issue to the KEV catalog: CVE-2024-1212, a command injection vulnerability in Progress Kemp LoadMaster with a maximum CVSS score of 10.
Organizations are encouraged to review and address all vulnerabilities in the catalog to strengthen their defenses.
CVE-2024-9474 Used to Deploy Advanced Backdoor on Palo Alto Firewalls
A sophisticated backdoor named LITTLELAMB.WOOLTEA has been identified, targeting Palo Alto Networks firewalls through the exploitation of CVE-2024-9474. Researchers uncovered the backdoor during a forensic investigation following the compromise of a device. Once the attackers exploited the vulnerability, they deployed a malicious script, bwmupdate, which installed the backdoor on the compromised system.
The backdoor, designed for stealth and persistence, disguises itself as the legitimate logd service. It ensures long-term survival by modifying system configurations, such as the rc.local file and RedHat package manager settings, allowing it to persist through system upgrades. Additionally, LITTLELAMB.WOOLTEA injects a dynamic library into the nginx process, enabling attackers to use a 48-byte magic knock for covert communication over existing open ports, eliminating the need to open new ports.
Key features of the backdoor include remote shell access, the ability to read and write files, and the establishment of secure network tunnels. It also supports a SOCKS5 proxy for covert data transfer, making it a versatile tool for attackers. The malware enables the creation of a command-and-control network, with each infected device capable of interacting with others in a hierarchical manner.
Although attribution remains unconfirmed, the complexity and stealth of the attack suggest that it may be the work of a nation-state actor, especially as the exploitation occurred shortly after CVE-2024-9474 was publicly disclosed.
For a detailed breakdown of the LITTLELAMB.WOOLTEA backdoor, check out its write-up.
Secure Your PAN-OS Device: Recommendations
To mitigate the risks posed by CVE-2024-0012 and CVE-2024-9474, implement the following measures:
- Patch immediately
Upgrade to the latest secure PAN-OS versions to address these vulnerabilities. Detailed guidance and updated versions can be found in Palo Alto’s advisories:
Technical details have also been made available; for a detailed breakdown of the vulnerabilities, visit this research blog. To give administrators time to patch, researchers have decided not to release a Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit just yet. Instead, they have provided a Nuclei template for CVE-2024-0012 to help identify affected hosts. You can access the template here.
- Secure management interfaces
- Restrict access to management interfaces to trusted internal networks or through a secure jump box. Doing this reduces exploitation risks, lowering the severity of CVE-2024-0012 to CVSS 5.9 by requiring privileged access from approved IP addresses.
- Block all internet-facing access to management interfaces to prevent unauthorized exploitation.
- Use the Palo Alto Networks support portal (Products → Assets → All Assets → Remediation Required) to identify exposed assets tagged with PAN-SA-2024-0015.
- Monitor Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) to identify potential attacks
Threat actor IPs actively scanning or connecting to vulnerable interfaces:
- 91.208.197[.]167
- 136.144.17[.]146
- 136.144.17[.]149
- 136.144.17[.]154
- 136.144.17[.]161
- 136.144.17[.]164
- 136.144.17[.]166
- 136.144.17[.]167
- 136.144.17[.]170
- 136.144.17[.]176
- 136.144.17[.]177
- 136.144.17[.]178
- 136.144.17[.]180
- 173.239.218[.]251
- 209.200.246[.]173
- 209.200.246[.]184
- 216.73.162[.]69
- 216.73.162[.]71
- 216.73.162[.]73
- 216.73.162[.]74
Post-Exploitation Payload (SHA256 Hash):
- 3C5F9034C86CB1952AA5BB07B4F77CE7D8BB5CC9FE5C029A32C72ADC7E814668
User-Agent String:
- User-Agent:Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.3; Trident/7.0; rv 11.0) like Gecko
For a complete list of IOCs, visit this GitHub page.




































