
CISA Highlights Updates Addressing Adobe, Fortinet Vulnerabilities: CVE-2023-42789, CVE-2023-48788, CVE-2024-20756, CVE-2024-20767
[Update] April 16, 2024: “Novel Campaign ‘Connect:fun’ Exploits CVE-2023-48788”
[Update] April 9, 2024: “CVE-2023-48788 Vulnerability in FortiClient EMS Exploited in Targeted Campaign”
[Update] March 27, 2024: “Exploit Code Available for Adobe ColdFusion CVE-2024-20767 Vulnerability”
[Update] March 26, 2024: “Critical Vulnerability in FortiClient EMS Added to CISA’s KEV Catalog”
[Update] March 22, 2024: “PoC Exploit Available for Critical FortiClient EMS Vulnerability as Fortinet Confirms Exploitation”
In recent alerts, CISA has emphasized security updates released by Adobe and Fortinet to address multiple vulnerabilities.
The highlighted Fortinet advisories feature three critical severity vulnerabilities, which could result in arbitrary code or command execution. Meanwhile, Adobe advisories encompass numerous high-severity issues, notably including a Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability.
CISA warns that threat actors may exploit these vulnerabilities across various Adobe and Fortinet products to seize control of affected systems, underscoring the urgency for users and administrators to take immediate action.
In this blog post, we will outline the most critical vulnerabilities recently addressed by Adobe and Fortinet, which were subsequently highlighted by CISA.
Critical Vulnerabilities Affecting FortiOS, FortiProxy, and FortiClientEMS
CISA has spotlighted five Fortinet advisories, addressing vulnerabilities across various products including FortiOS and FortiProxy SSLVPN, FortiWLM MEA for FortiManager, and FortiClientEMS.
The most notable Fortinet vulnerabilities addressed throughout these advisories are:
CVE-2023-42789 (CVSS: 9.8) and CVE-2023-42790 (CVSS: 8.1)
CVE-2023-42789 is classified as an Out-of-Bounds Write vulnerability, while CVE-2023-42790 is a Stack-based Buffer Overflow. Both vulnerabilities, addressed within a single advisory, pose severe risks.
Exploitation of these vulnerabilities could allow internal attackers with access to the captive portal to execute unauthorized code or commands through specially crafted HTTP requests.
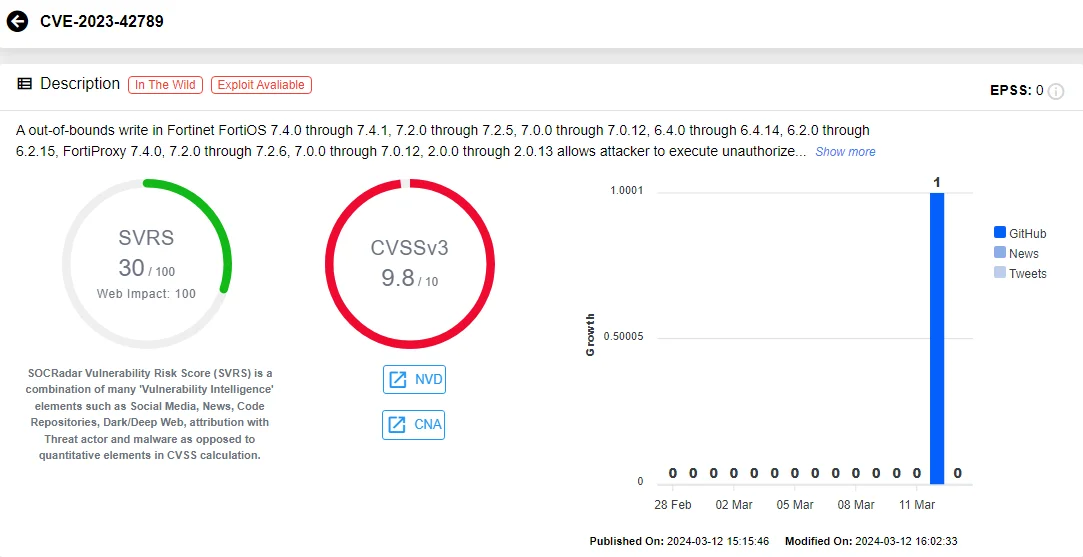
CVE-2023-42789 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence Module)
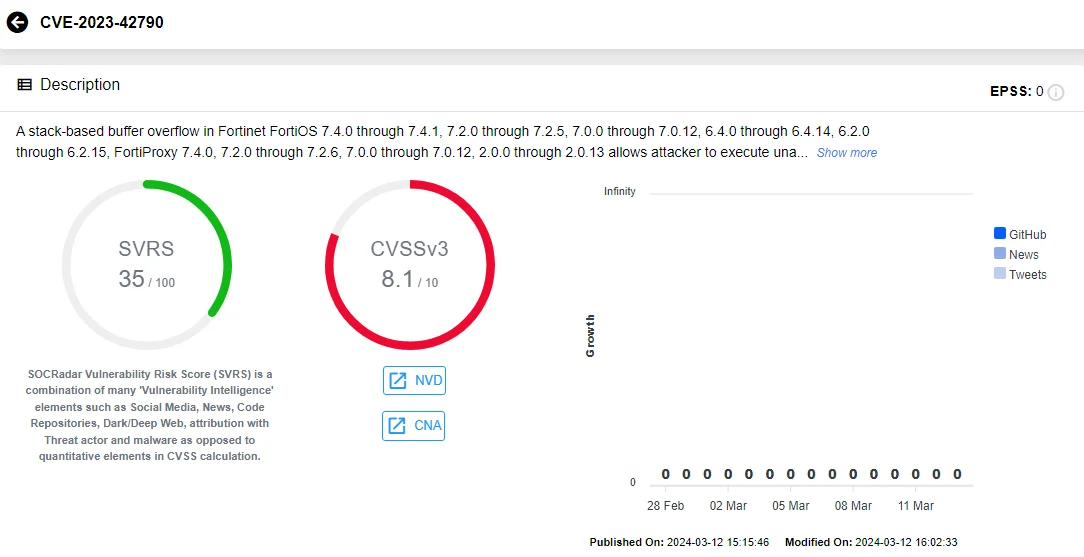
CVE-2023-42790 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence Module)
These vulnerabilities affect several versions of Fortinet FortiOS and FortiProxy:
- FortiOS: 7.4.0 through 7.4.1, 7.2.0 through 7.2.5, 7.0.0 through 7.0.12, 6.4.0 through 6.4.14, and 6.2.0 through 6.2.15.
- FortiProxy: 7.4.0, 7.2.0 through 7.2.6, 7.0.0 through 7.0.12, and 2.0.0 through 2.0.13.
Workaround Available for Fortinet’s CVE-2023-42789 and CVE-2023-42790
Fortinet has provided a workaround for CVE-2023-42789 and CVE-2023-42790 in its advisory, involving the configuration of a non-form-based authentication scheme. Users can implement this workaround by setting the authentication scheme method as detailed in the advisory.
Also, there are two severe vulnerabilities in FortiClientEMS.
CVE-2023-48788 (CVSS: 9.3) and CVE-2023-47534 (CVSS: 8.7)
CVE-2023-48788 involves an SQL Injection, and its exploitation may allow an unauthenticated attacker to execute unauthorized code or commands via specially crafted requests.
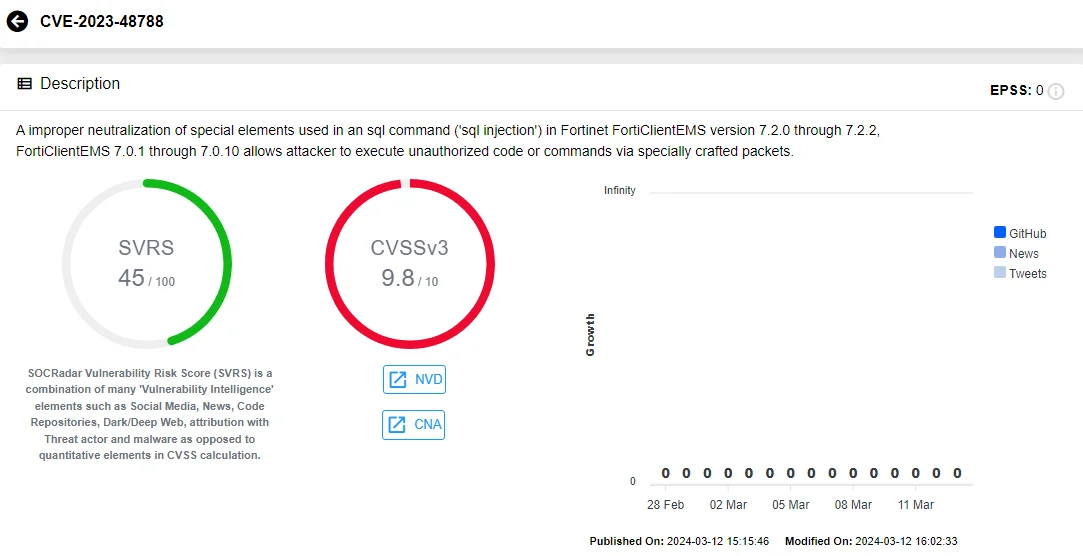
CVE-2023-48788 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence Module)
CVE-2023-47534, the second vulnerability in FortiClientEMS, involves the improper neutralization of formula elements in a CSV file. Exploiting this vulnerability, a remote and unauthenticated attacker could execute arbitrary commands on the admin workstation by creating malicious log entries with crafted requests to the server.
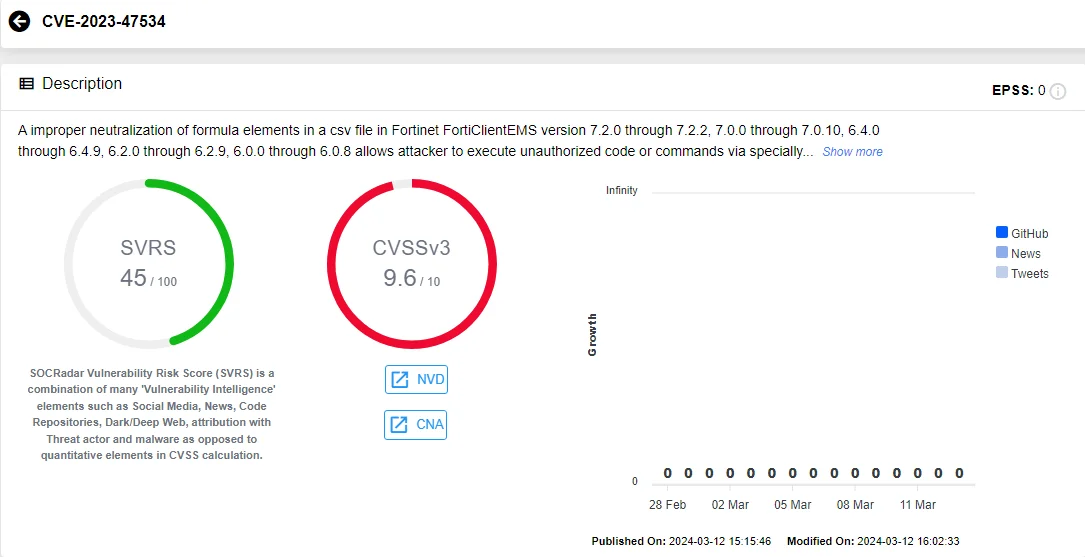
CVE-2023-47534 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence Module)
FortiClientEMS versions 7.2.0 through 7.2.2 and 7.0.1 through 7.0.10 are affected by both vulnerabilities.
CVE-2023-47534 additionally affects all versions under the 6.4, 6.2, and 6.0 branches. Fortinet customers using versions under these branches are advised to migrate to a fixed release.
PoC Exploit Available for Critical FortiClient EMS Vulnerability as Fortinet Confirms Exploitation
Security researchers have published a Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit for the critical vulnerability in FortiClient EMS, CVE-2023-48788.
Furthermore, Fortinet reported that the vulnerability has been exploited in the wild. According to a Shodan search, there are more than 450 FortiClient EMS instances exposed on the internet, indicating vulnerable systems.
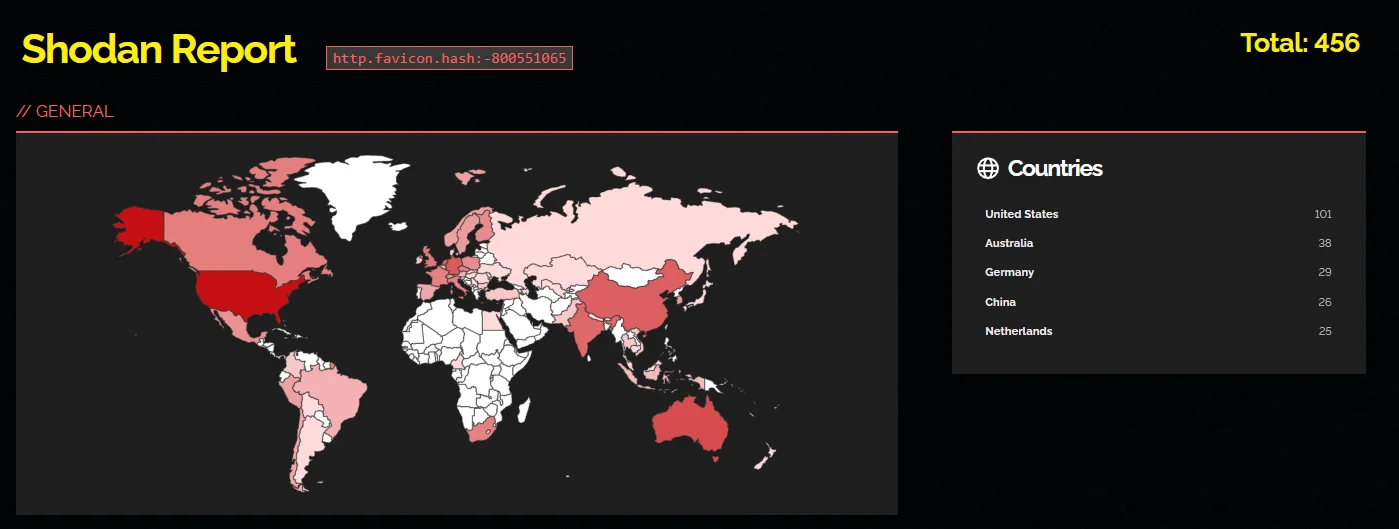
Shodan search for FortiClient EMS instances
Horizon3 published the PoC exploit along with an extensive technical analysis. Notably, while this PoC is unable to execute Remote Code Execution (RCE), it can effectively determine whether a system is vulnerable to CVE-2023-48788 via a simple SQL injection. The researchers stated that in order to enable RCE, the exploit they provided must be modified.
The researchers converted the SQL injection to RCE by leveraging Microsoft SQL Server’s xp_cmdshell functionality. Additionally, they emphasized that FortiClient EMS users can examine the C:Program Files (x86)FortinetFortiClientEMSlogs directory for unusual connections and malicious activity traces.
Analysis of MS SQL logs is also important for detecting xp_cmdshell usage. However, keep in mind that attackers might employ diverse techniques or erase evidence from logs post-exploitation.
Critical Vulnerability in FortiClient EMS Added to CISA’s KEV Catalog
On March 25, 2024, CISA added the critical CVE-2023-48788 vulnerability in Fortinet’s FortiClient EMS to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog. Organizations and federal agencies are urged to address CVE-2023-7101 by the deadline of April 15, 2024, to mitigate the risk of exploitation.
In addition to CVE-2023-48788, the KEV Catalog now includes two other critical vulnerabilities: command injections in Ivanti EPM Cloud Services Appliance (CVE-2021-44529) and Linear eMerge E3-Series, used for access control (CVE-2019-7256).
CVE-2023-48788 Vulnerability in FortiClient EMS Exploited in Targeted Campaign
Researchers have discovered a campaign targeting the CVE-2023-48788 vulnerability in FortiClient EMS. In the campaign, attackers initiated each intrusion with external network connections targeting the FCMdaemon process, leading to SQL injection.
Exploiting this vulnerability, attackers activate xp_cmdshell via SQL statements, enabling the execution of arbitrary commands using cmd[.]exe and granting SYSTEM-level permissions.
Attackers then deploy legitimate Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) tools (such as Atera and ScreenConnect) or PowerShell-based backdoors, gaining complete control over compromised systems.
If patching immediately is not possible, organizations can use several strategies to detect malicious activity, as recommended by the researchers. These strategies include monitoring inbound network connections to FCMdaemon[.]exe, particularly from unknown IP addresses.
Researchers also advise to keep an eye out for unusual PowerShell processes, particularly those that spawn from cmd.exe with sqlservr[.]exe as a parent process, and to be wary of using the Invoke-WebRequest cmdlet to download.msi files from external sources.
Another security strategy is to constantly monitor RMM tools; using allowlists for such tools within the network can significantly reduce risks.
Novel Campaign ‘Connect:fun’ Exploits CVE-2023-48788
A new campaign, dubbed Connect:fun, has emerged, exploiting the critical Fortinet vulnerability, CVE-2023-48788, to infiltrate media companies.
In an observed incident, initial attempts on March 21 were unsuccessful due to syntax errors. However, the attackers persisted, and two days into the attack, they successfully deployed both the ScreenConnect remote management tool and a script based on Powerfun, allowing them to execute arbitrary commands on the victim system.
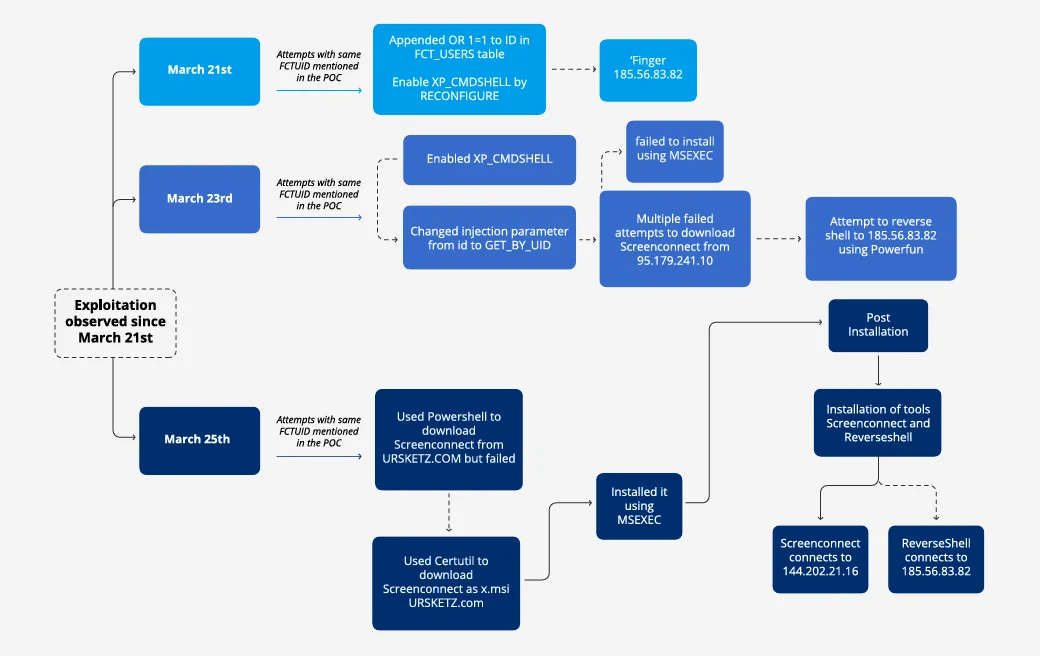
Connect:fun attack scheme (Forescout)
Furthermore, the threat actors employed the domain ‘ursketz[.]com’ in their attacks, utilizing multiple SQL statements to fetch ScreenConnect from it. Researchers observed that ScreenConnect connections were directed to 144[.]202[.]21[.]16, marking the sole instance of connections to/from ScreenConnect. Unfortunately, they were unable to access the ScreenConnect logs to ascertain further actions.
The evidence from the campaign suggests the presence of a potentially active threat actor dating back to at least 2022, with a focus on targeting Fortinet appliances. Moreover, their infrastructure indicates proficiency in Vietnamese and German languages.
It is also important to highlight that similar tactics observed against systems vulnerable to CVE-2023-48788 have been detected targeting other organizations. This underscores the widespread nature of the Connect:fun campaign.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) Related to the Connect:fun Campaign
IP Addresses:
- 141[.]136[.]43[.]188 (IPv4) / 2a02:4780:a:952:0:1e10:e79b:1 (IPv6)
- 144[.]202[.]21[.]16
- 185[.]56[.]83[.]82
- 95[.]179[.]241[.]10
- 45[.]77[.]160[.]195
- 216[.]245[.]184[.]86
URLs/Domains:
- mci11[.]raow[.]fun
- hxxp[:]//45.227.255[.]213:20201
- hxxp[:]//68[.]178.202.116
- jxqmwbgxygkyftpxykdk8cfkq1hy371pz.oast[.]fun
Hostnames:
- “VULTR-GUEST”
Continuous Vulnerability Monitoring with SOCRadar
Use SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) module to proactively monitor emerging vulnerabilities in your digital assets. Receive timely threat alerts and effectively manage patching efforts to mitigate potential impacts.
Attack Surface Management module, Company Vulnerabilities page (SOCRadar)
Adobe Fixed Vulnerabilities in ColdFusion, Bridge, Lightroom, and Other Products
CISA has brought attention to six Adobe advisories targeting various products:
- Adobe Experience Manager
- Adobe Premiere Pro
- Adobe ColdFusion
- Adobe Bridge
- Adobe Lightroom
- Adobe Animate
The vulnerabilities marked as ‘Critical’ by Adobe were found in Adobe ColdFusion, Adobe Bridge, and Adobe Lightroom.
Adobe Bridge Affected by a Severe Vulnerability: CVE-2024-20756
An Adobe Bridge vulnerability, CVE-2024-20756, carries the highest CVSS score among the vulnerabilities (CVSS: 8.6) and presents a risk of arbitrary code execution stemming from an out-of-bounds write.
Other notable vulnerabilities affecting Adobe Bridge include CVE-2024-20752 and CVE-2024-20755, both with CVSS scores of 7.8, also posing a risk of arbitrary code execution.
These Adobe Bridge vulnerabilities impact versions 13.0.5 and earlier, as well as 14.0.1 and earlier, across Windows and macOS platforms.
New High Severity Vulnerability in Adobe ColdFusion: CVE-2024-20767
The second most severe vulnerability addressed by Adobe in the recent updates is CVE-2024-20767(CVSS 8.2), affecting ColdFusion.
ColdFusion, a rapid web application development platform, utilizes ColdFusion Markup Language (CFML) and offers built-in functions for commonly used tools to create modern websites.
CVE-2024-20767 stems from improper access control and could result in arbitrary file system read. According to Adobe’s advisory, it affects ColdFusion updates 6, 12, and earlier versions across all platforms.
Another significant vulnerability addressed by Adobe impacts Lightroom, exclusively on the macOS platform. However, there is limited detail about the vulnerability in its advisory at the time of writing, although it is deemed ‘Critical’. It could lead to arbitrary code execution due to an untrusted search path.
Exploit Code Available for Adobe ColdFusion CVE-2024-20767 Vulnerability
Security researchers recently published a Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit for Adobe ColdFusion’s high-severity vulnerability, CVE-2024-20767.
A technical analysis of the vulnerability outlines how its exploit leverages bytecode manipulation to gain unauthorized access and read sensitive files. It involves manipulating servlet UUIDs and exploiting file logging and heap_dump functionalities.
The PoC script, available on GitHub, simplifies fetching the UUID from the server, necessary for accessing the vulnerable endpoint; using this UUID, the script constructs a request to read the specified file. Upon success, it displays the file’s contents.
A Shodan search indicates over 190 exposed Adobe ColdFusion instances, highlighting potentially vulnerable endpoints. Conversely, FOFA lists nearly 473,000 assets related to Adobe ColdFusion.
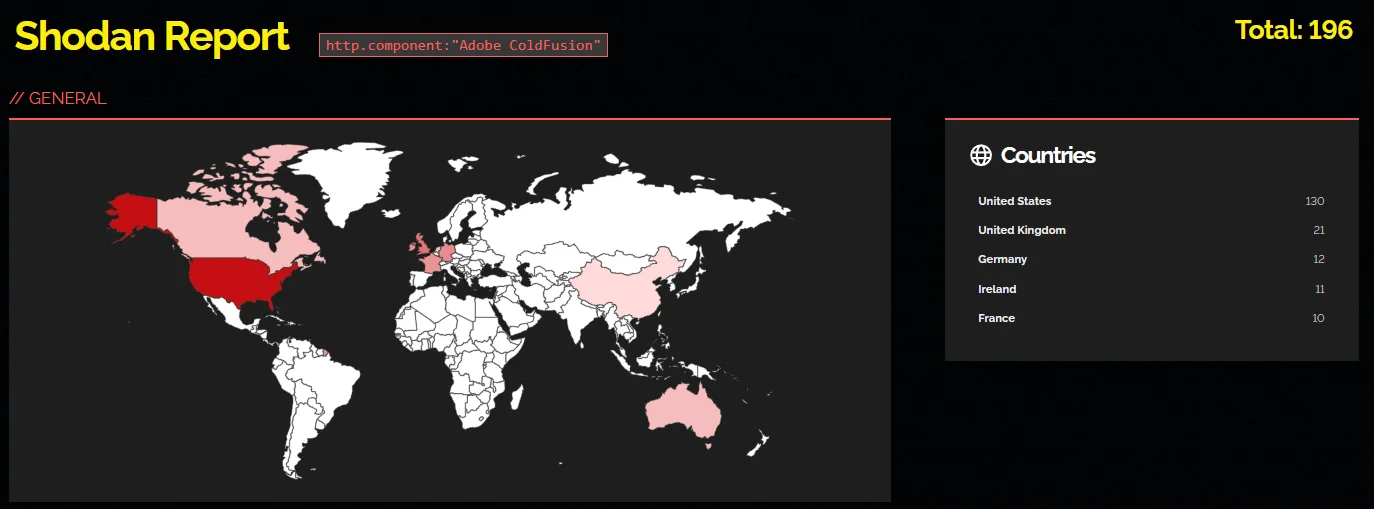
Shodan search results for Adobe ColdFusion instances
Though there have not been reports of exploitation yet, the availability of exploit code suggests potential threats. Applying patches to address this vulnerability is strongly recommended, as attackers may attempt to weaponize the PoC exploit in the near future.
Track CVE Trends, Exploits, and Vulnerability Updates Easily with SOCRadar
Gain comprehensive insights into vulnerabilities using SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence feature. Vulnerability Intelligence allows you to easily follow CVE trends and provides detailed information on a vulnerability’s exploitability, available exploits, repositories, and updates, aiding you in bolstering your security posture.
Cyber Threat Intelligence module, Vulnerability Intelligence page (SOCRadar)




































