
Critical Auth Bypass in GitHub Enterprise Server, CVE-2024-4985; PoC Available for QNAP QTS’ CVE-2024-27130
The vulnerability landscape continues to grow, introducing critical risks that can enable malicious actions if not promptly addressed. Recently, significant vulnerabilities have come to light, targeting widely used technologies: GitHub Enterprise Server and QNAP QTS.
GitHub Enterprise Server has been identified with a severe vulnerability, and it has been assigned the highest possible CVSS score of 10.0.
In parallel, QNAP QTS, QNAP’s operating system for Network-Attached Storage (NAS) devices, has been found to contain 11 unpatched vulnerabilities. Alarmingly, one of these vulnerabilities has already received an exploit. Security researchers have developed and published a Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit, demonstrating the practical dangers and exploitability of the security vulnerability.
What is CVE-2024-4985? Details of the Critical Auth Bypass in GitHub Enterprise Server
GitHub recently announced the discovery of a severe security vulnerability within its GitHub Enterprise Server (GHES), a version of GitHub designed for self-hosting on organizations’ own servers or private cloud environments.
This vulnerability, identified as CVE-2024-4985, has been reported through GitHub’s Bug Bounty program and is considered extremely critical, with a CVSS score of 10.0.
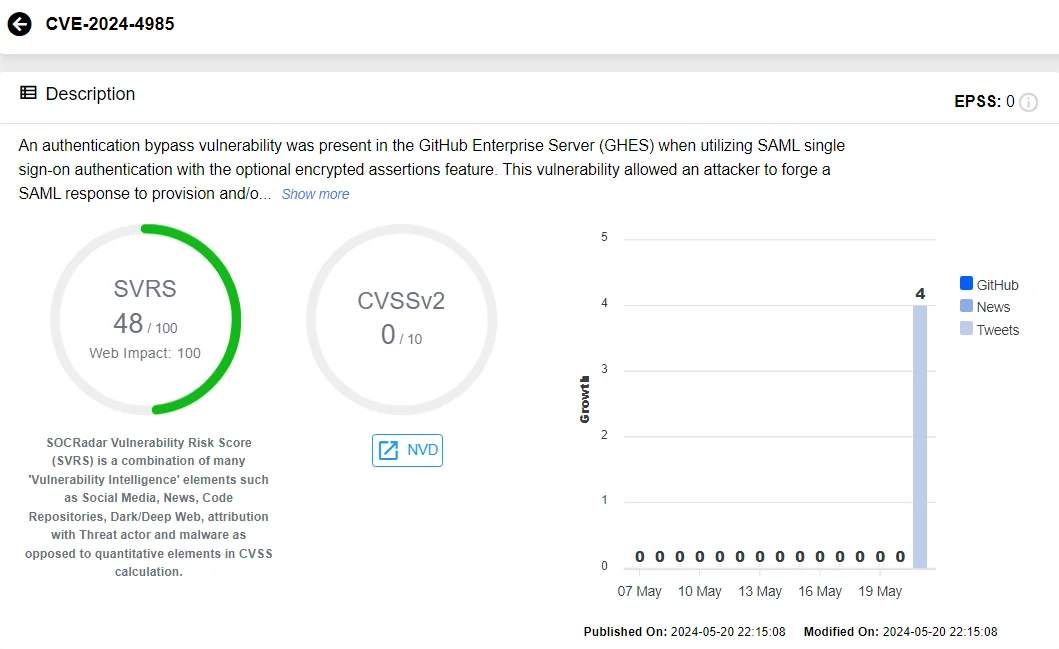
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-4985 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
What is the impact of CVE-2024-4985 on GitHub Enterprise Server?
CVE-2024-4985 presents a significant security threat, enabling an attacker to bypass authentication mechanisms. It targets a specific component within the GitHub Enterprise Server (GHES) – the encrypted assertions feature of its SAML Single Sign-On (SSO) authentication mechanism.
Designed to bolster security by encrypting SAML assertions, this feature inadvertently introduced a critical vulnerability. Attackers can exploit this flaw by forging a SAML response, which allows them to impersonate legitimate users, potentially even gaining administrative privileges.
This vulnerability specifically affects GHES instances where SAML SSO is configured with encrypted assertions. It is important to note that this configuration is not the default setting; therefore, GHES deployments that do not use this configuration remain unaffected by CVE-2024-4985.
Successful exploitation of CVE-2024-4985 could lead to several high-risk scenarios, including the theft of sensitive source code, breaches of confidential data, and substantial disruption to development operations, posing a substantial risk to organizational security and integrity.
A ZoomEye search shows over 76,000 potentially exposed instances. These instances are primarily located in the United States, Japan, and Ireland, among other countries. These instances indicate the potential attack surface and may become targeted by attackers.
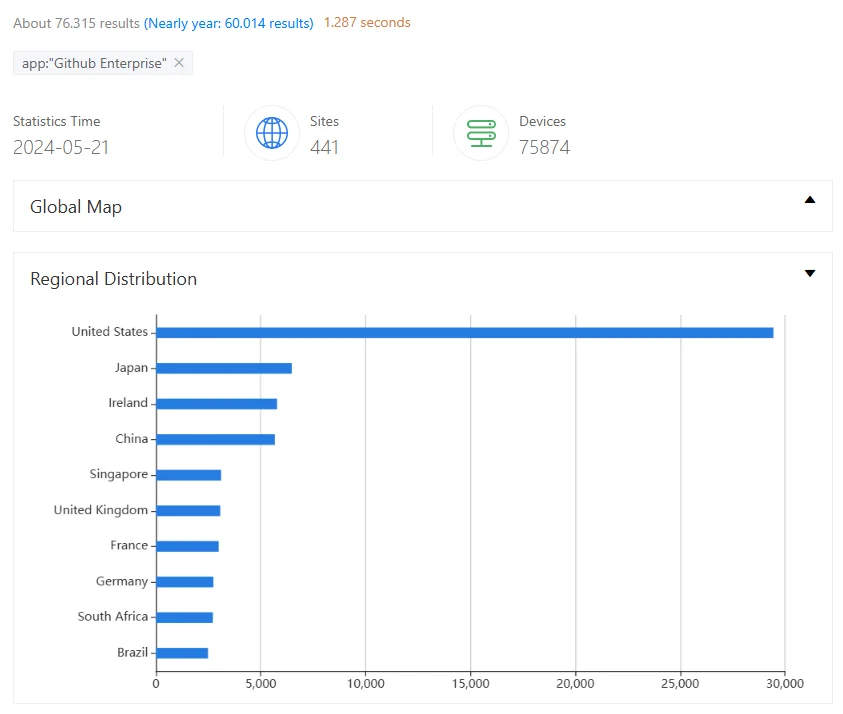
ZoomEye search results for GitHub Enterprise instances
How to secure GitHub Enterprise Server? Are patches available for CVE-2024-4985?
In response to the discovery of CVE-2024-4985, GitHub has promptly issued patches to address the vulnerability. The specific versions receiving these critical updates are:
Administrators managing GitHub Enterprise Servers are strongly advised to apply these updates to avoid exploitation.
Stay up to date on cybersecurity trends and respond quickly to new vulnerabilities to keep your systems and data secure. SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) module protects your digital assets by continuously monitoring them, providing timely threat alerts, and allowing for effective preemptive actions to improve your cybersecurity posture.
Monitor organizational digital assets and CVEs, take quick actions (SOCRadar ASM)
QNAP QTS Vulnerabilities: PoC Made Available for CVE-2024-27130
QNAP’s QTS, the proprietary operating system used in its Network Attached Storage (NAS) devices, along with its variants QuTScloud and QTS hero, has recently been spotlighted due to multiple security vulnerabilities.
Since December 2023, 15 vulnerabilities were reported, out of which 11 remain unresolved due to delays in the patching process.
Among these vulnerabilities, one notably critical issue, CVE-2024-27130, which enables Remote Code Execution (RCE), has escalated concerns due to the availability of a Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit. Its exploit demonstrates the vulnerability’s practical application, highlighting its potential for abuse by malicious actors.
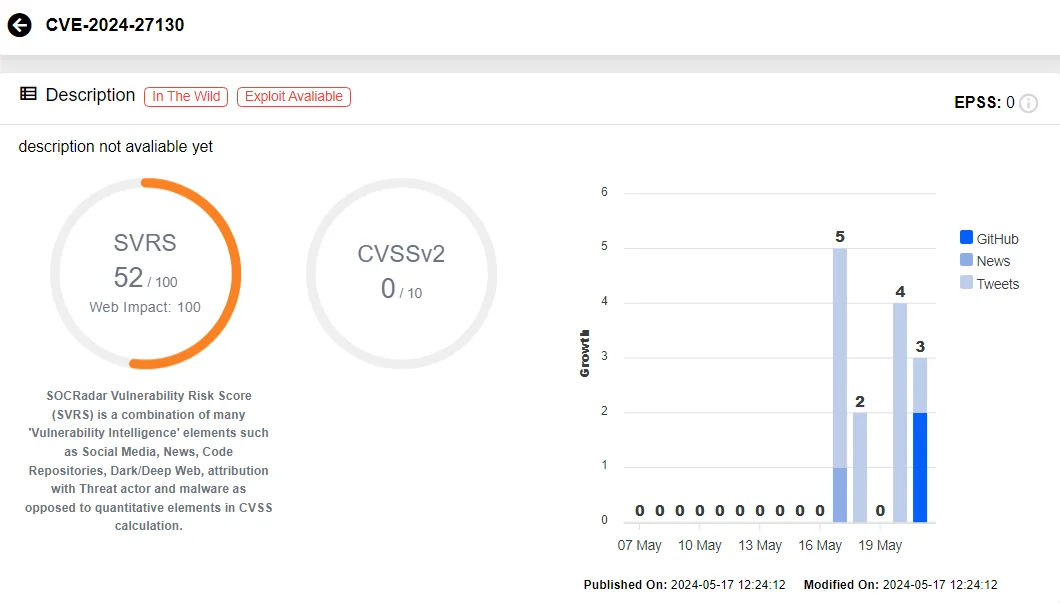
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-27130 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
The RCE vulnerability can allow attackers to execute arbitrary code remotely on affected QNAP NAS devices. The affected range of products includes QTS, QuTScloud, and QTS hero.
PoC Exploit for CVE-2024-27130: A Critical RCE Flaw Turned Into Zero-Day
CVE-2024-27130, identified within QNAP’s QTS operating system, has been classified as a zero-day as it has an exploit, yet is still unpatched.
Researchers released a detailed blog post on May 17, 2024, highlighting the critical nature of the CVE-2024-27130 vulnerability affecting QNAP QTS. This post included a Proof of Concept (PoC) exploit, providing a clear demonstration of how the vulnerability could be exploited to execute code remotely on affected devices.
CVE-2024-27130 results from the unsafe use of the ‘strcpy’ function within ‘No_Support_ACL’, which is accessible by the ‘get_file_size’ request of the ‘share.cgi’ script. A maliciously crafted ‘name’ parameter in a request can cause a buffer overflow, subsequently leading to RCE.
However, to successfully exploit this vulnerability, an attacker would need to obtain a valid ‘ssid’ parameter, which is generated whenever a NAS user shares a file from their QNAP device. This ‘ssid’ parameter is part of the URL in the ‘share’ link created by the device, meaning that an attacker would likely need to employ social engineering tactics to gain access to this sensitive information.
The PoC exploit devised by the researchers utilizes a crafted payload that creates a ‘watchtowr’ user account on the targeted QNAP device and grants it elevated privileges by adding it to the sudo list.
For those interested in understanding the technical specifics, the PoC exploit is available on GitHub.
QNAP QTS Vulnerabilities Await Patches
The vulnerabilities identified within QNAP QTS involve a variety of risks, from code execution to authentication bypass, and Cross-site Scripting (XSS). On the other hand, as a mitigating factor, many of them require specific conditions to be exploited.
Amidst these vulnerabilities, a subset of four has received patches:
- CVE-2023-50361 — Buffer Overflow due to unsafe use of the sprintf function.
- CVE-2023-50362 — SQL injection due to unsafe usage of SQLite functions
- CVE-2023-50363 — Improper Authorization, permits disabling 2FA (Two-Factor Authentication)
- CVE-2023-50364 — Heap Overflow, potentially leading to Denial-of-Service (DoS) and Code Execution
The patches for these vulnerabilities are included in the following QNAP updates:
- QTS 5.1.6.2722 build 20240402 and later
- QuTS hero h5.1.6.2734 build 20240414 and later
Users of QNAP devices are urged to apply these updates immediately to protect their devices from potential security breaches and ensure that their systems are safeguarded against these specific vulnerabilities.
With SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence module, organizations can search for and monitor vulnerabilities, accessing detailed insights into each one while also easily tracking related activities such as exploitation and current hacker trends.
Latest security vulnerabilities, mentions, and exploitation trends (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)




































