
Critical SAP NetWeaver Vulnerability (CVE-2025-31324) Allows Unauthorized Upload of Malicious Executables
In a critical security alert, SAP has released an emergency patch for CVE-2025-31324 — a severe, unauthenticated file upload vulnerability affecting SAP NetWeaver Visual Composer. With a perfect CVSS score of 10.0 and confirmed active exploitation in the wild, this flaw allows attackers to remotely execute code and potentially take full control of SAP systems. Organizations running SAP NetWeaver must act quickly to understand the risk, implement mitigations, and apply patches to protect sensitive business data and operations.
What Is CVE-2025-31324?
A critical vulnerability in the Metadata Uploader of SAP NetWeaver Visual Composer (CVSS score: 10.0) permits unauthenticated agents to upload potentially malicious executable binaries. A successful exploitation could seriously harm the host system.
Attackers have been able to take control of SAP servers by uploading files without authorization. The vulnerability has been exploited as a zero-day.

Vulnerability card of CVE-2025-31324 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Which SAP NetWeaver Versions Are Affected?
The vulnerability specifically impacts the Visual Composer Framework version 7.50.
It is crucial to remember that systems that have been patched with SAP’s normal April 8, 2025, update remain vulnerable. To fix this issue, an emergency patch was later made available.
Exploitation Mechanics: How Attackers Leverage the Vulnerability?
ReliaQuest linked the exploitation of CVE-2025-31324 to the /developmentserver/metadatauploader endpoint in SAP NetWeaver Visual Composer. Attackers exploited this endpoint to upload JSP webshells directly into publicly accessible directories on target servers without requiring authentication.
Once uploaded, the webshells enabled remote code execution through simple browser-based GET requests. This allowed adversaries to execute system commands, upload or download files, and maintain control over compromised systems with ease.
Post-Exploitation Activity
After gaining initial access, attackers escalated their operations using various tools:
- Brute Ratel: A red-teaming toolkit deployed for command and control (C2) and post-exploitation.
- Heaven’s Gate: An evasion method used to bypass security controls in 64-bit environments.
- MSBuild DLL injection: Malicious code was compiled and injected into dllhost.exe, making it harder to detect malicious processes.
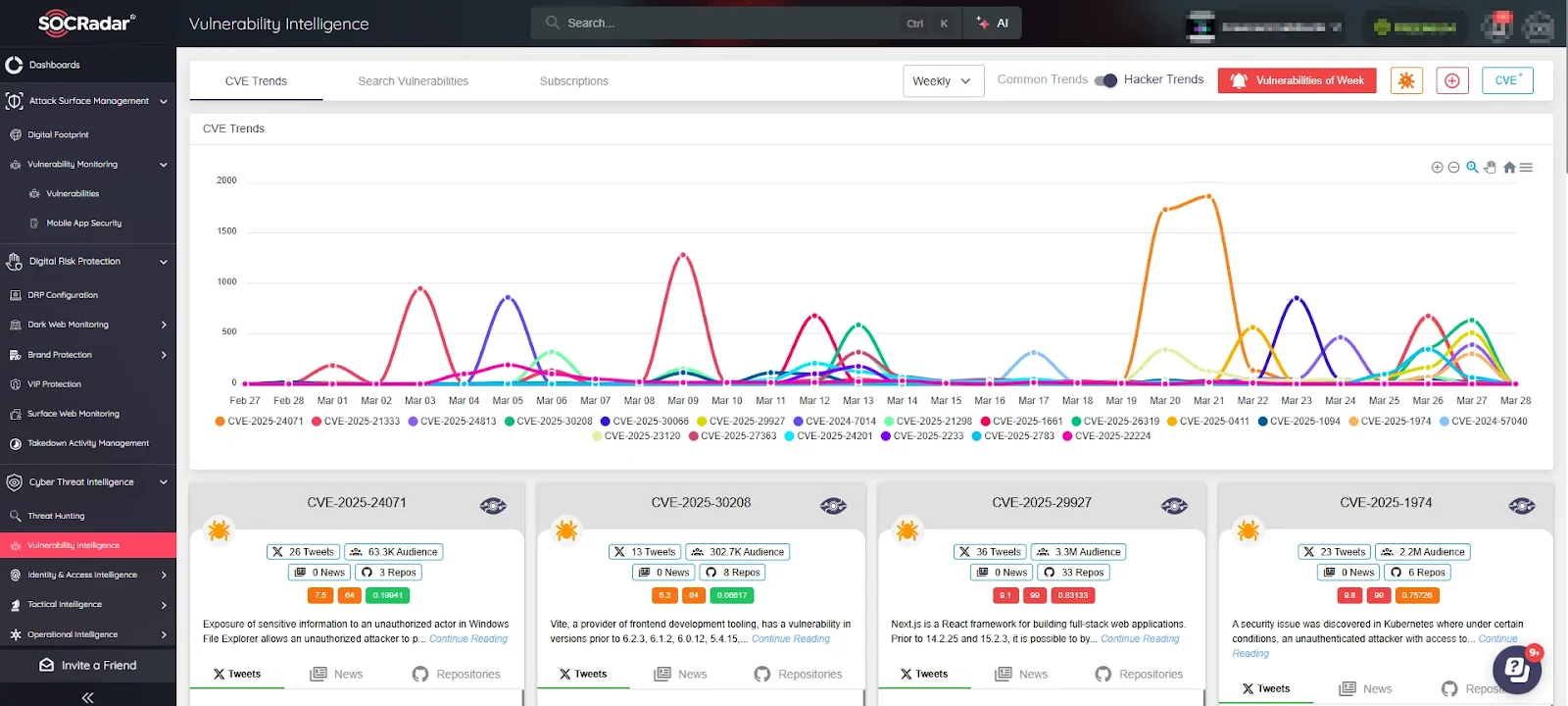
SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence
Real-World Risk: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability at Stake
Exploitation of CVE-2025-31324 can lead to full remote code execution and total system compromise, posing risks such as:
- Unauthorized access to sensitive SAP business data and processes
- Potential ransomware deployment
- Lateral movement across network environments
- Long-term persistence via planted webshells
Given SAP’s prevalence in government and large enterprise environments globally, successful exploitation could have widespread and serious consequences.
Recommended Actions for SAP Customers
- Immediately apply the emergency patch provided by SAP.
- If the patch cannot be applied right away:
- Limit access to the endpoint /developmentserver/metadatauploader.
- If Visual Composer is not being used, disable it.
- Send logs to a SIEM, and scan for unauthorized files under servlet paths.
- Before implementing additional mitigations, perform deep environment scans to find and remove any unauthorized webshells.
For businesses relying on web applications, tools like SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence and Attack Surface Management (ASM) can help identify and monitor vulnerable software versions across your infrastructure.
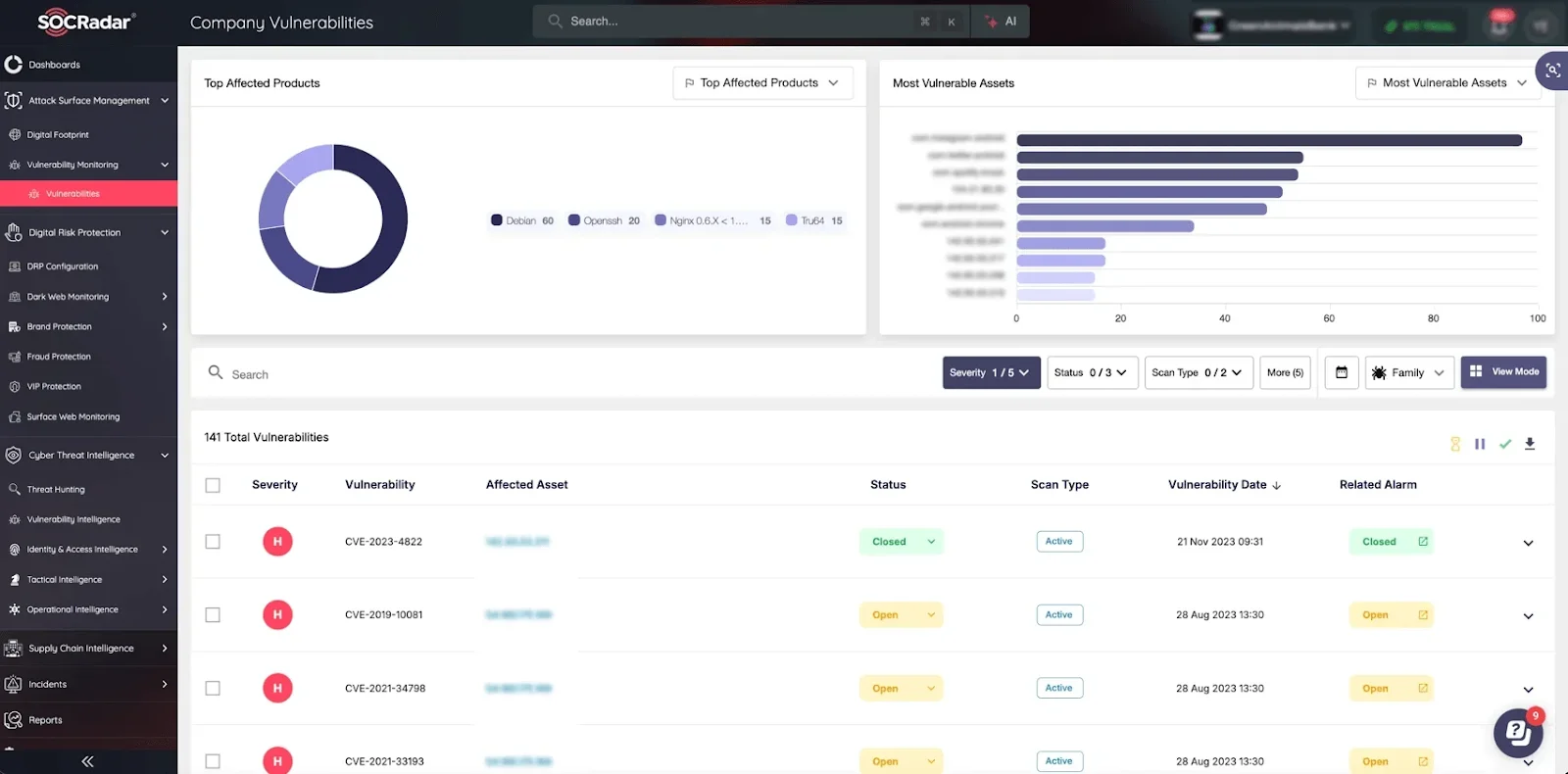
Proactively detect and remediate vulnerabilities, ensuring attackers cannot exploit them before action is taken. (SOCRadar’s ASM)
Proactively detect exposed vulnerabilities and prioritize remediation efforts to minimize the risk of exploitation. By leveraging SOCRadar’s ASM, security teams can gain continuous visibility into outdated software, misconfigurations, and unpatched systems, enabling a more proactive defense against evolving threats.



































