
Critical Vulnerabilities in Progress WhatsUp Gold, Jenkins Could Lead to RCE Attacks (CVE-2024-4885, CVE-2024-43044)
A critical vulnerability in Progress WhatsUp Gold, recently patched, has been actively exploited since early August. Identified as CVE-2024-4885, this flaw can lead to Remote Code Execution (RCE) and carries a critical severity rating.
WhatsUp Gold, a network monitoring tool developed by Progress, provides comprehensive visibility into network-connected devices. Due to Progress’s prominence in the business sector, attackers could leverage this vulnerability to infiltrate organizational networks. Therefore, addressing and mitigating such security flaws promptly is essential to minimize potential damage.
Additionally, the popular automation server Jenkins has patched an RCE vulnerability in its latest security update.
What Is CVE-2024-4885?
CVE-2024-4885 (CVSS: 9.8) is an unauthenticated Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability located in the function ‘WhatsUp.ExportUtilities.Export.GetFileWithoutZip’. This flaw enables threat actors to gain the privileges of ‘iisapppoolnmconsole’.
Although ‘iisapppoolnmconsole’ is not an administrator user, it possesses elevated privileges within WhatsUp Gold, allowing the execution of commands.
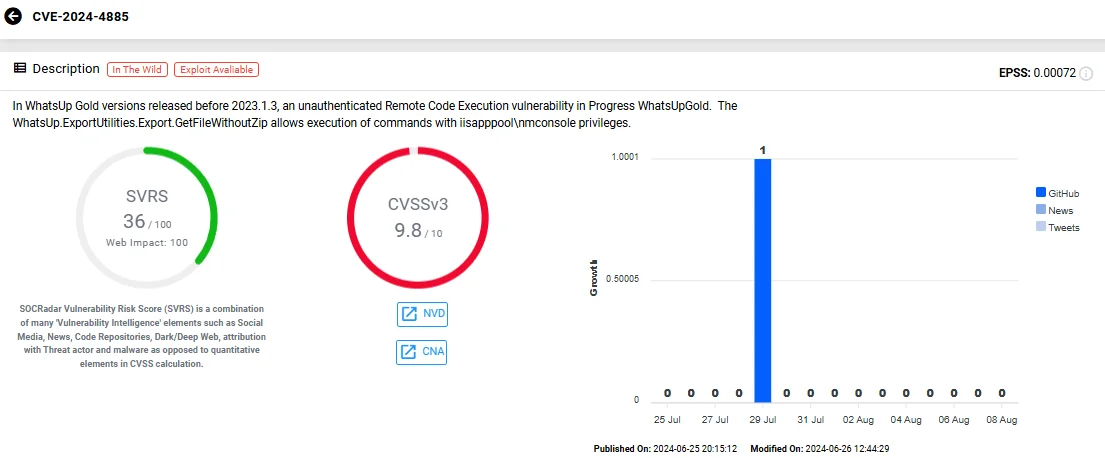
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-4885 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Security researcher Sina Kheirkhah (@SinSinology) was credited for the discovery of this vulnerability and has also shared the related technical details.
Which Versions of Progress WhatsUp Gold Are Affected?
The CVE-2024-4885 vulnerability affects Progress WhatsUp Gold version 23.1.2 and all earlier versions.
PoC Exploit and Active Exploitation Attempts
Security researcher Sina Kheirkhah, who discovered the CVE-2024-4885 vulnerability, provided a Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit to demonstrate the flaw.
The exploit targets an exposed endpoint, ‘/NmAPI/RecurringReport’. Shadowserver reported observing exploitation attempts against this endpoint starting from August 1, originating from six distinct IP addresses.
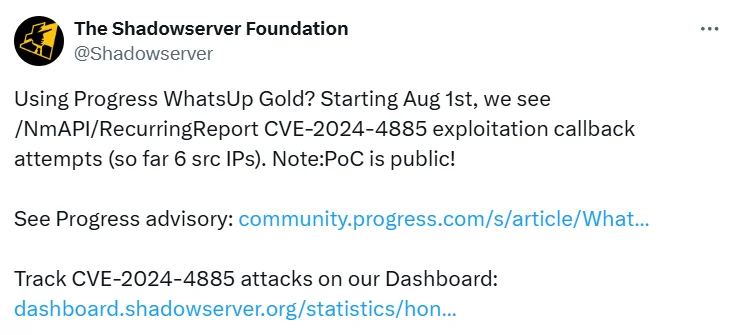
Shadowserver’s tweet (X)
The exploit involves sending a ‘TestRecurringReport’ to the endpoint, which includes a specially crafted configuration pointing to the attacker’s server. The targeted server responds with a user ID, which it should relay back to the attacker’s server.
When the targeted server responds, it includes the username and encrypted password associated with the user ID. The researcher devised the exploit to also be able to make additional requests on the targeted server, achieving file writing capabilities and Remote Code Execution (RCE).
See the full PoC here.
How Can You Fix CVE-2024-4885?
Progress released updates for CVE-2024-4885 and other critical vulnerabilities in its June 2024 security bulletin. Aside from CVE-2024-4885, the most severe ones include:
- CVE-2024-4883 (CVSS: 9.8)
- CVE-2024-4884 (CVSS: 9.8)
- CVE-2024-5008 (CVSS: 8.8)
These three vulnerabilities can also lead to Remote Code Execution (RCE) in Progress WhatsUp Gold. Progress advises users to update to version 23.1.3 to mitigate the risk of exploitation.
For those unable to update immediately:
- Monitor for exploitation attempts at the endpoint ‘/NmAPI/RecurringReport’.
- Implement protections such as firewalls and access restrictions.
- Allow only trusted IP addresses on ports 9642 and 9643, as the NmApi.exe process listens on these ports.
For more information and update guidance, visit the official Progress advisory.
With SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence module, you can monitor CVEs and exploitation trends, accessing a comprehensive database of the latest security vulnerabilities. The module helps organizations stay informed about new threats, enabling security teams to quickly identify relevant vulnerabilities and understand their potential impact.
By using Vulnerability Intelligence, your security team can stay ahead of emerging threats and effectively protect your organization.
Critical Jenkins Vulnerability (CVE-2024-43044) Could Allow RCE
Jenkins has recently fixed two vulnerabilities, one of which poses a critical risk and could lead to Remote Code Execution (RCE).
Tracked as CVE-2024-43044 (CVSS: 9.0), this critical vulnerability is an arbitrary file read issue through agent connections, potentially granting access to sensitive configuration data, credentials, or source code.
The flaw originates from the Remoting library, used for communication between Jenkins controllers and agents. Exploiting this vulnerability could lead to RCE on Jenkins controllers and enable complete control over a Jenkins instance.
CVE-2024-43045 (CVSS: 5.4) is the second, less severe vulnerability allows unauthorized access to the My Views dashboard on Jenkins. This could expose some information and allow changes to dashboard settings.
For both vulnerabilities, it is crucial to update Jenkins to the latest version to mitigate these risks.
Which Jenkins Versions Are Affected By These Vulnerabilities?
The following Jenkins versions are affected by CVE-2024-43044 and CVE-2024-43045 vulnerabilities:
- Jenkins weekly up to and including 2.470
- Jenkins LTS up to and including 2.452.3
Update Jenkins
To reduce the risk of exploitation, Jenkins users are urged to update without delay.
- Jenkins weekly should be updated to version 2.471
- Jenkins LTS should be updated to version 2.452.4 or 2.462.1
For more information, visit the official Jenkins security advisory.
Follow cybersecurity trends and respond swiftly to new vulnerabilities with SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) module.
SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) module
ASM protects your digital assets by continuously monitoring them, providing timely threat alerts, and enabling effective preemptive actions to enhance your cybersecurity strategy.



































