
Dark Web Profile: INC Ransom
The digital world is constantly under the threat of cyber attacks, and the emergence of new ransomware groups only intensifies this peril. One such group that has recently come into the spotlight is INC Ransom. This group has quickly gained notoriety for its sophisticated attacks and elusive nature. In this article, we will delve into the details of INC Ransom, exploring who they are, how they operate, and the implications of their activities. We will also provide insights into the security measures that can be implemented to protect against such threats.

The threat actor card of INC Ransom
Who is INC Ransom?
INC. Ransomware is a relatively new but highly sophisticated cybercriminal group that has rapidly gained notoriety in the realm of digital extortion. Emerging onto the cybercrime scene, this group has distinguished itself through its targeted ransomware attacks, primarily focusing on corporate and organizational networks.

Illustration of INC Ransom (generated using DALL-E 3)
Unlike many opportunistic ransomware operators, INC. Ransomware appears to carefully select its targets, often aiming at entities with substantial financial resources and sensitive data, which makes the potential payoff from their ransom demands significantly higher.
The group’s modus operandi involves a combination of advanced techniques, including spear-phishing campaigns to gain initial access, exploitation of known vulnerabilities (such as CVE-2023-3519 in Citrix NetScaler), and the use of both Commercial Off-The-Shelf (COTS) softwares and legitimate system tools (LOLBINs) for reconnaissance and lateral movement within a network. This approach not only demonstrates their technical prowess but also their ability to stay under the radar, making detection and prevention more challenging.
INC. Ransomware’s attacks are not just limited to encryption and locking of data; they also involve data theft and threats of public release, a tactic known as double extortion. This method adds an additional layer of pressure on the victims to comply with the ransom demands, as it puts at risk not just the accessibility of the data but also its confidentiality.
How does INC Ransom attack?
INC. Ransom employs a sophisticated and multi-staged approach to infiltrate and compromise target systems. Their attack methodology combines initial access through spear-phishing or exploiting vulnerabilities, such as CVE-2023-3519 in Citrix NetScaler, with a series of calculated steps to establish control and execute their ransomware. Here’s an overview of their attack process:
Initial Access and Reconnaissance: The group begins by gaining initial access, either through spear-phishing emails or by targeting vulnerable services. Once inside, they use a variety of tools for internal reconnaissance and lateral movement. These tools include NETSCAN.EXE for network scanning, MEGAsyncSetup64.EXE for file sharing and synchronization, ESENTUTL.EXE for database management, and AnyDesk.exe for remote desktop control.
Exploiting Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP): INC. Ransom frequently uses compromised credentials to access systems via RDP. During these sessions, they perform enumeration activities such as scanning for domain admins and testing network connections. This phase often involves brief connections to multiple servers, indicating a search for vulnerable points within the network.
Data Collection and Staging: Over the course of their attack, they abused legitimate software to collect and stage data for exfiltration. This involves using 7-Zip archival commands to gather data and employing native tools like Wordpad, Notepad, and MSPaint to inspect the contents of documents and images. They also install MEGASync on servers, presumably to facilitate the transfer of stolen data.
Lateral Movement and Credential Access: The attackers move laterally across the network, accessing multiple servers. They use tools like Advanced IP Scanner and Internet Explorer to explore the network and identify additional targets. During this phase, they also run credential access commands, indicative of using tools like lsassy.py, to extract login credentials from the systems.
File Encryption and Deployment: The final stage involves deploying the ransomware. They use a combination of wmic.exe and PSExec (disguised as winupd) to launch the file encryption executable across multiple endpoints. This phase is characterized by rapid command execution, indicating the use of batch files or scripts to automate the encryption process.
Troubleshooting and Adaptation: Interestingly, there are instances where the attackers encounter difficulties, such as the inability to run the encryption executable on certain servers. This is evidenced by multiple attempts to execute the ransomware with debug commands, showcasing their adaptability and persistence in overcoming challenges.
TOR Site of INC Ransom
The first thing that caught our attention when we visited INC. Ransom’s TOR site was the dark and light modes:
INC Ransom TOR site in dark mode (Source: X)
Looking at the site in general, there is a section on the left side that leads to Leaks, a “Submit a Feedback” section, and a Twitter icon where “INC Ransom” is searched on Twitter when clicked. The rest of the page contains announcements made by INC. Ransom:
INC Ransom’s TOR site
Clicking on any leak announcement, a short description, the domain address of the victim organization, and proofs of the data leak, if any, can be found on the detail page.
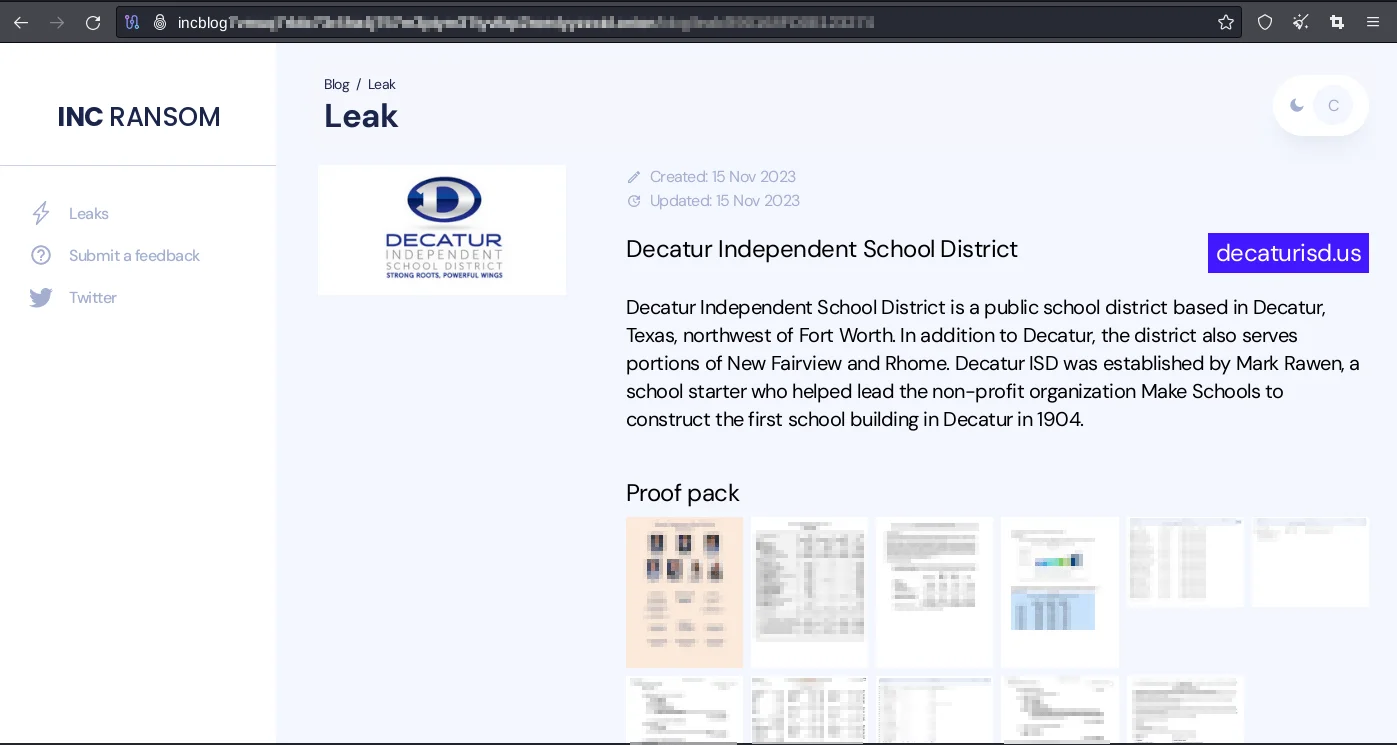
Decatur’s, one of the INC. Ransom’s victim, detailed Leak page
Additionally, the incapt[.]blog page that INC. Ransom has recently included on its page and where current leak announcements can be followed on the surface web:
INC Ransom’s Leak Announcements
What are the targets of INC Ransom?
Targeted Sectors
Looking at the industries in which INC. Ransom’s victim organizations work, the majority are in Professional Services, Manufacturing and Construction:
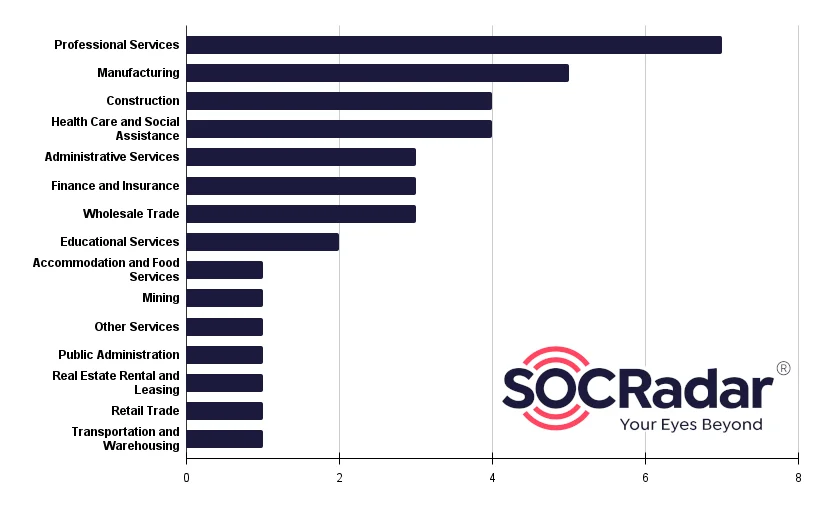
INC. Ransom’s Targeted Sectors
Targeted Countries
The majority of the organizations targeted by “INC. Ransom” are based in North America and Europe:
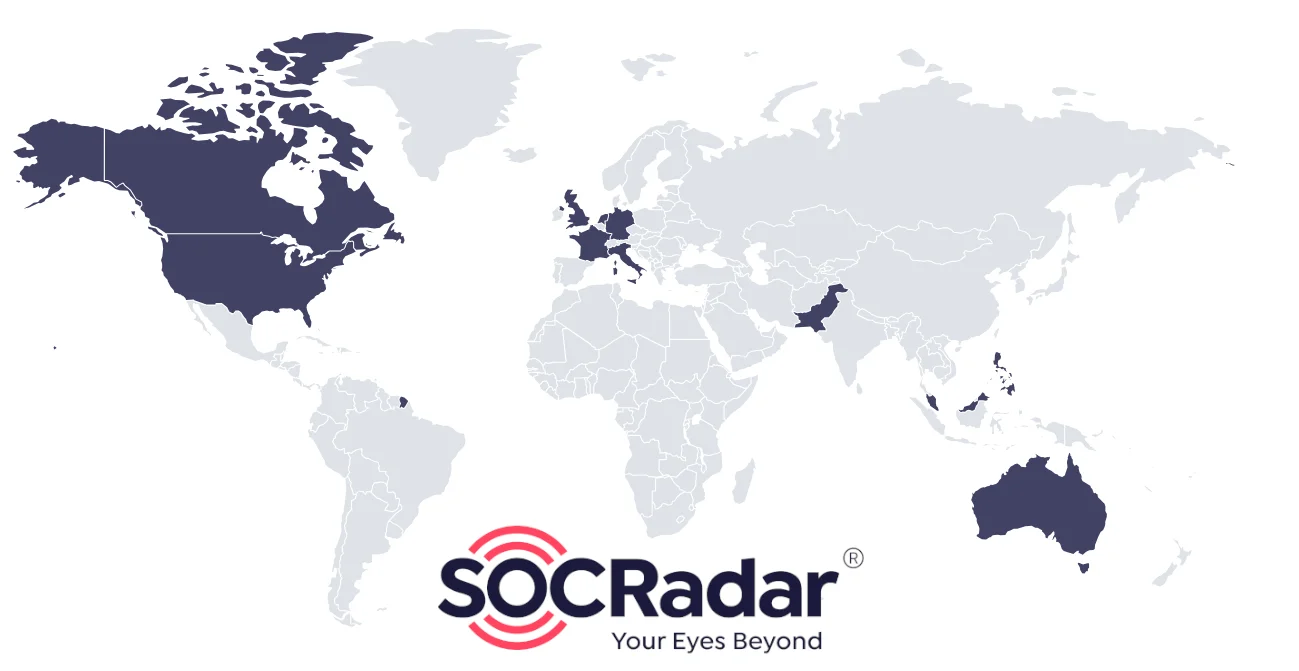
INC. Ransom Targeted Countries
In terms of distribution, it is observed that “INC. Ransom” mostly targets organizations operating in the United States(57.9%):
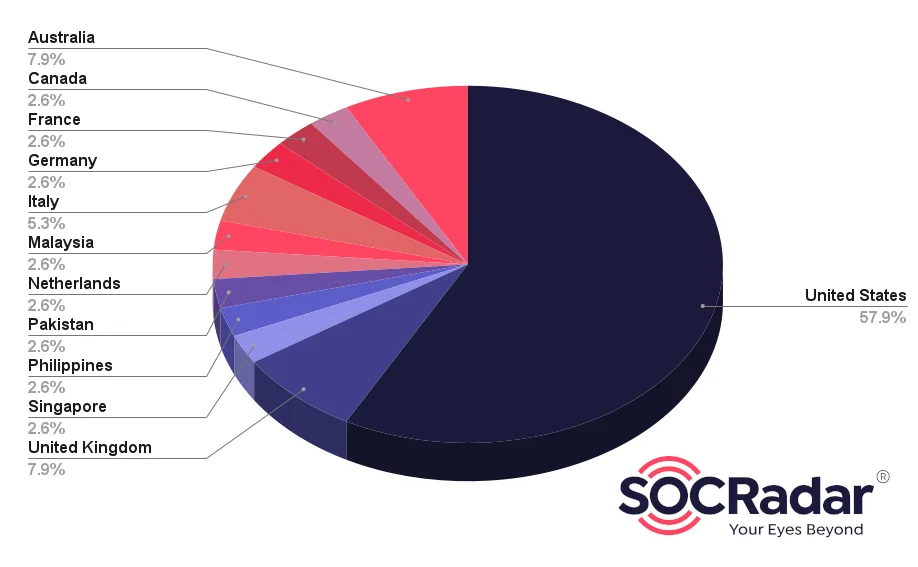
Targets Distribution
Latest Activities of INC Ransomware
Trylon:
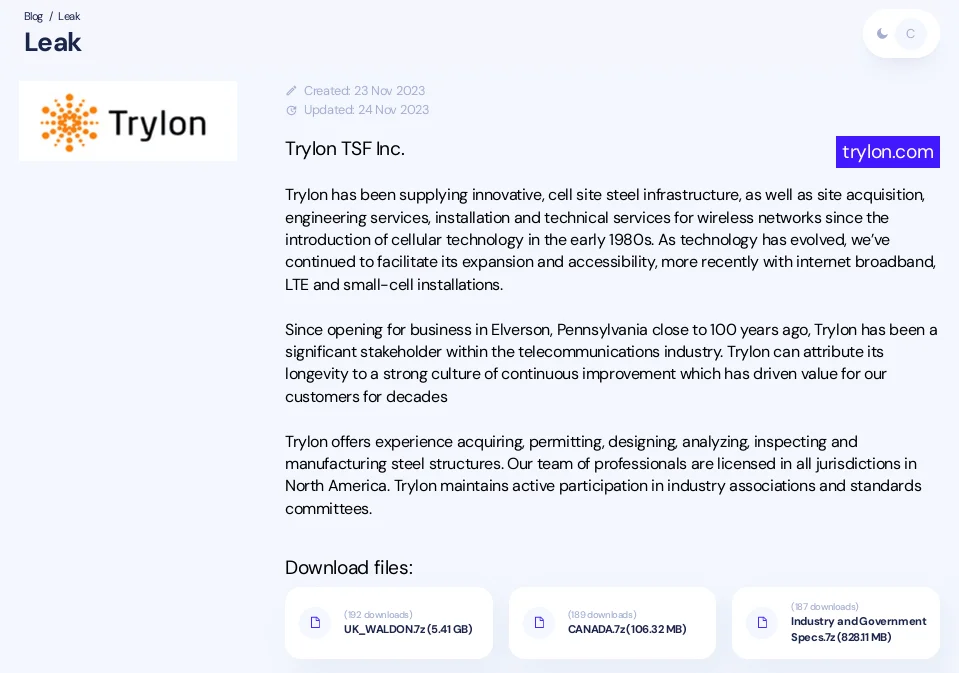
Trylon
Springfield:
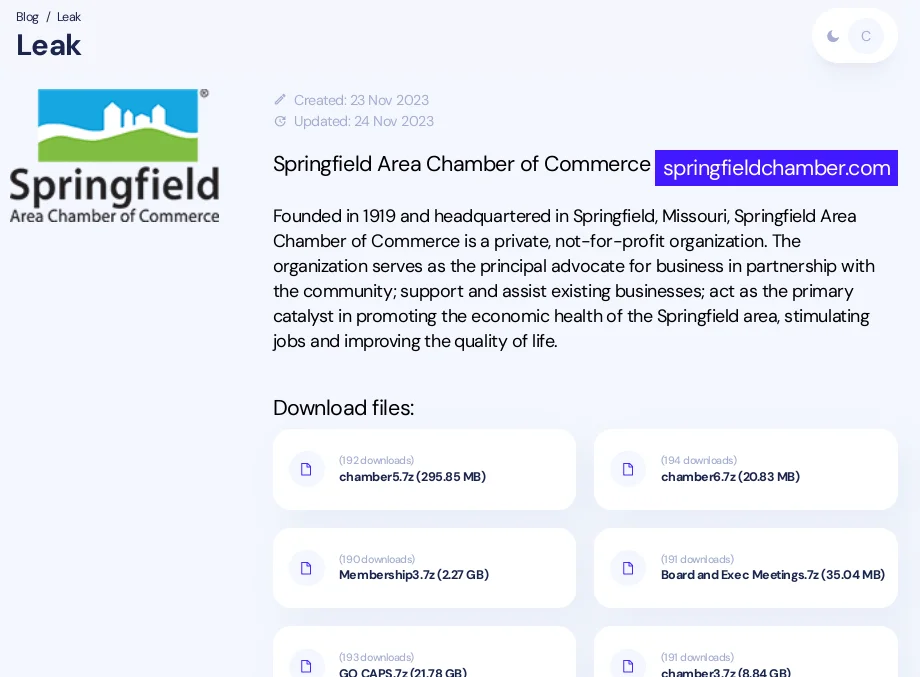
Springfield
Conclusion
The emergence and activities of the INC. Ransom group represent a significant threat in the cybersecurity landscape. Their sophisticated and multi-layered attack methodology, which includes exploiting vulnerabilities, using a mix of commercial and legitimate tools for reconnaissance and lateral movement, and executing a carefully planned ransomware deployment, highlights the evolving nature of cyber threats.
INC. Ransom’s ability to adapt and troubleshoot during their attacks, as well as their strategic use of tools for data collection, staging, and encryption, demonstrate a high level of technical expertise and planning.
SOCRadar Dark Web News
Security Recommendations Against INC Ransom
To defend against the sophisticated tactics of INC. Ransom, organizations need to adopt a multi-layered security approach. Here are some key recommendations to enhance cybersecurity defenses against such ransomware threats:
Regularly Update and Patch Systems: Ensure that all software, especially critical and widely-used applications like Citrix NetScaler, are regularly updated and patched. This helps to close vulnerabilities that could be exploited by ransomware groups.
Enhanced Email Security: Since spear-phishing is a common initial access vector, implement advanced email security solutions. These should include phishing detection, sandboxing for email attachments, and user training to recognize and report suspicious emails.
Robust Endpoint Protection: Deploy advanced Endpoint Protection Platforms (EPP) that can detect, prevent, and respond to threats using techniques like behavioral analysis and machine learning.
Network Segmentation and Monitoring: Segment your network to limit lateral movement by attackers. Use Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) to monitor network traffic for suspicious activities.
Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security for accessing sensitive systems and data, making it harder for attackers to gain access even if they have compromised credentials.
Regular Backups and Data Encryption: Regularly back up critical data and ensure it’s stored securely, preferably off site or in the cloud. Encrypt sensitive data to add an additional layer of protection.
Incident Response Planning: Have a well-defined incident response plan that includes procedures for isolating affected systems, eradicating the ransomware, and restoring data from backups.
Employee Awareness and Training: Regularly train employees on cybersecurity best practices, including how to recognize phishing attempts and the importance of using strong, unique passwords.
Use of Advanced Threat Intelligence: Stay informed about the latest ransomware tactics and Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) through threat intelligence feeds and cybersecurity reports.
Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Assessments: Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and mitigate potential security gaps in your network and systems.
MITRE ATT&CK TTPs of INC Ransom
| Tactic | Technique | Technique ID | Tool/Procedure | Notes |
| Initial Access | Spear-Phishing | T1566 | Spear-Phishing Emails | Gains initial access through targeted emails. |
| Exploitation of Public-Facing Application | T1190 | CVE-2023-3519 | Exploiting known vulnerabilities in public-facing applications. | |
| Execution | Command and Scripting Interpreter | T1059 | Wmic.exe, PSExec | Uses command-line tools to execute scripts for ransomware deployment. |
| Persistence | Valid Accounts | T1078 | RDP with Compromised Credentials | Maintains access using Remote Desktop Protocol with stolen credentials. |
| Privilege Escalation | Exploitation for Privilege Escalation | T1068 | RDP | Escalates privileges through compromised Remote Desktop Protocol connections. |
| Defense Evasion | Obfuscated Files or Information | T1027 | PSExec disguised as winupd | Hides its activities by disguising tools and commands. |
| Credential Access | Credential Dumping | T1003 | Lsassy.py | Extracts credentials from the systems they compromise. |
| Discovery | System Network Configuration Discovery | T1016 | NETSCAN.EXE, Advanced IP Scanner | Scans the network to discover configurations and connected systems. |
| Lateral Movement | Remote Services: Remote Desktop Protocol | T1021.001 | AnyDesk.exe | Moves within the network, often using remote desktop software. |
| Collection | Data Staged | T1074 | 7-Zip, MEGASync | Collects and stages data for exfiltration using archival and file transfer tools. |
| Exfiltration | Data Encrypted for Impact | T1486 | Custom Ransomware | Encrypts files for ransom, and may exfiltrate data for double extortion. |
| Command and Control | Ingress Tool Transfer | T1105 | MEGASync, AnyDesk.exe | Uses legitimate tools for command and control activities. |
| Impact | Data Destruction | T1485 | Custom Ransomware | Destroys or encrypts data, rendering it inaccessible. |




































