
February 2025 Patch Tuesday: Microsoft Fixes 63 Vulnerabilities, Including Two Actively Exploited Zero-Days
Microsoft’s latest Patch Tuesday update for February 2025 delivers important security fixes, addressing 63 vulnerabilities across various products. Among them, four are classified as critical, while two have been actively exploited as zero-day vulnerabilities.
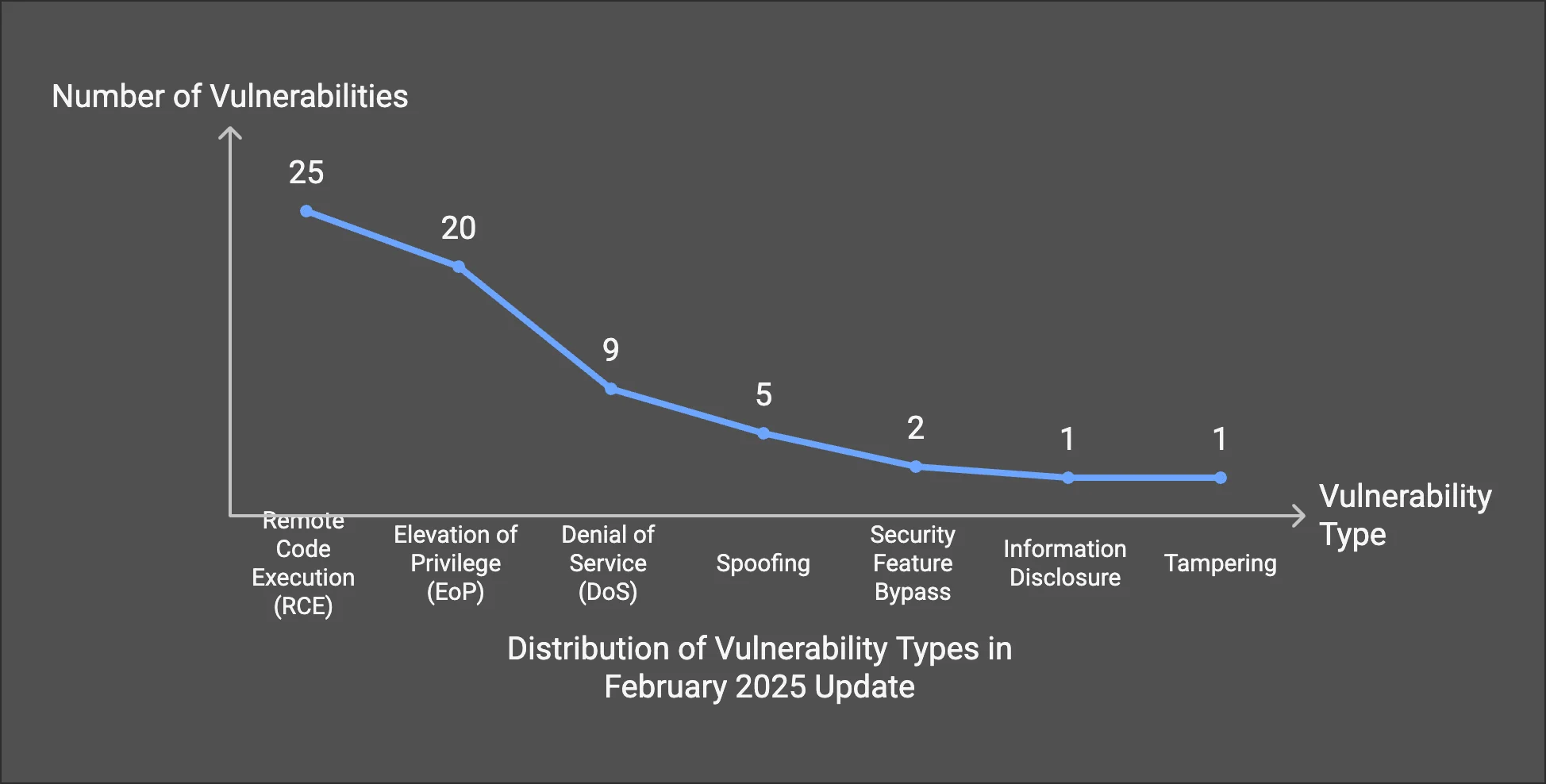
This month’s security patches cover a broad spectrum of vulnerability types:
- 25 Remote Code Execution (RCE) Vulnerabilities
- 20 Elevation of Privilege (EoP) Vulnerabilities
- 9 Denial of Service (DoS) Vulnerabilities
- 5 Spoofing Vulnerabilities
- 2 Security Feature Bypass Vulnerabilities
- 1 Information Disclosure Vulnerability
- 1 Tampering Vulnerability
Breakdown of February 2025 Patch Tuesday vulnerabilities
Let’s take a closer look at the actively exploited zero-day vulnerabilities and other critical risks addressed in this update.
Zero-Days in February 2025 Patch Tuesday
Microsoft has fixed two vulnerabilities that are actively being exploited in the wild, making them immediate threats. Additionally, other zero-day vulnerabilities have been publicly disclosed, meaning they are known to attackers and could be leveraged at any time.

Prioritize your security measures based on zero-days’ status
Actively Exploited: CVE-2025-21391 & CVE-2025-21418
One of the most concerning vulnerabilities patched this month is CVE-2025-21391 (CVSS 7.1), an elevation of privilege flaw in Windows Storage. If exploited, an attacker could delete critical system files, potentially leading to data loss and service disruptions.
Microsoft has clarified that this vulnerability does not enable unauthorized access to confidential data, but the ability to remove essential files could severely impact system availability.
The second actively exploited zero-day vulnerability, CVE-2025-21418 (CVSS 7.8), affects the Ancillary Function Driver for Windows Sockets (WinSock). This flaw allows attackers to escalate privileges, potentially gaining SYSTEM-level access on a compromised machine.
At this time, details regarding how attackers have exploited these flaws remain undisclosed.
Publicly Disclosed: CVE-2025-21194 & CVE-2025-21377
In addition to the actively exploited vulnerabilities, Microsoft has addressed publicly disclosed zero-day flaws that, while not yet exploited, still pose significant security risks:
CVE-2025-21194 (CVSS 7.1) is linked to a hypervisor flaw affecting UEFI-based virtual machines, potentially compromising the secure kernel. Security researchers speculate that it might be connected to the PixieFail vulnerabilities, a set of flaws affecting the IPv6 network protocol stack used in Microsoft Surface and hypervisor products.
In parallel, CVE-2025-21377 (CVSS 6.5) could allow an attacker to obtain NTLM hashes simply by tricking a user into interacting with a malicious file. Even without opening the file, minimal interaction such as selecting or inspecting it could trigger NTLM authentication, enabling attackers to collect credentials for further attacks.
SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence: Track the newest CVEs, hacker trends, updates, and exploits
SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence provides insights into the latest threats and vulnerabilities. By tracking risks and offering detailed intelligence, it helps your security team prioritize patching and reduce exposure.
Which Critical Vulnerabilities Were Addressed?
The vulnerabilities deemed critical in their maximum severity in Microsoft’s advisories are as follows:
- CVE-2025-21376 (CVSS 8.1) – Windows Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) RCE:
An out-of-bounds write vulnerability caused by a race condition in LDAP, leading to possible arbitrary code execution within the Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS). - CVE-2025-21177 (CVSS 8.7) – Microsoft Dynamics 365 SSRF Privilege Escalation:
A Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) vulnerability in Dynamics 365 Sales CRM could allow privilege escalation over a network. - CVE-2025-21379 (CVSS 7.1) – DHCP Client Service RCE:
An attacker on the same network could exploit this flaw to execute arbitrary code on affected systems. - CVE-2025-21381 (CVSS 7.8) – Microsoft Excel RCE:
This vulnerability allows remote code execution and can be triggered through the preview pane without opening a file.
High-Risk Vulnerabilities, Likely to be Exploited by Attackers
There are several security vulnerabilities that also demand immediate attention due to their high exploitability and the absence of available workarounds. Organizations should act swiftly to apply the necessary fixes as outlined in the February 2025 Patch Tuesday release to mitigate potential risks.
These vulnerabilities include the critical CVE-2025-21376 vulnerability and the disclosed CVE-2025-21377 zero-day mentioned earlier, as well as the following:
- CVE-2025-21400 (8.0) – Microsoft Office SharePoint
- CVE-2025-21420 (7.8) – Windows Disk Cleanup Tool
- CVE-2025-21358 (7.8) – Windows CoreMessaging
- CVE-2025-21367 (7.8) – Windows Win32 Kernel Subsystem
- CVE-2025-21419 (7.1) – Windows Setup Files Cleanup
- CVE-2025-21414 (7.0) – Windows DWM Core Library
- CVE-2025-21184 (7.0) – Windows CoreMessaging
With two actively exploited zero-days and a range of critical vulnerabilities, the February 2025 Patch Tuesday update serves as a reminder for organizations to prioritize cybersecurity patching. Given the potential for attacks like privilege escalation, Remote Code Execution (RCE), and Denial of Service (DoS), applying these updates promptly is vital in reducing exposure to threats.
System administrators should assess the impact of these vulnerabilities on their environments and deploy patches accordingly to safeguard their networks from potential exploitation.
To support ongoing defense efforts, SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) module continuously monitors your digital assets and vulnerabilities, helping you identify risks and vulnerabilities such as those seen in the latest Patch Tuesday release.
SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management module, Company Vulnerabilities
With real-time insights, automated alerts, and complete visibility, SOCRadar ASM ensures your security team is ahead of emerging threats. By tracking and prioritizing these risks, your organization can take the necessary steps to reduce exposure and bolster your cybersecurity posture.
For a full list of fixed vulnerabilities and further details, refer to Microsoft’s official Release Note for the February 2025 Patch Tuesday update.
SAP’s February 2025 Security Patches Address Critical Flaws
Alongside Microsoft’s Patch Tuesday updates, SAP has also rolled out security patches, addressing 19 newly discovered vulnerabilities and updating two previously released Security Notes. These fixes address critical security risks, including an authorization flaw in SAP BusinessObjects Business Intelligence that could allow an attacker to impersonate users.
The most severe issue, CVE-2025-0064 (CVSS 8.7), grants admin-level attackers the ability to assume any user’s identity, potentially exposing sensitive data and system controls. SAP strongly urges organizations to prioritize patching this vulnerability.
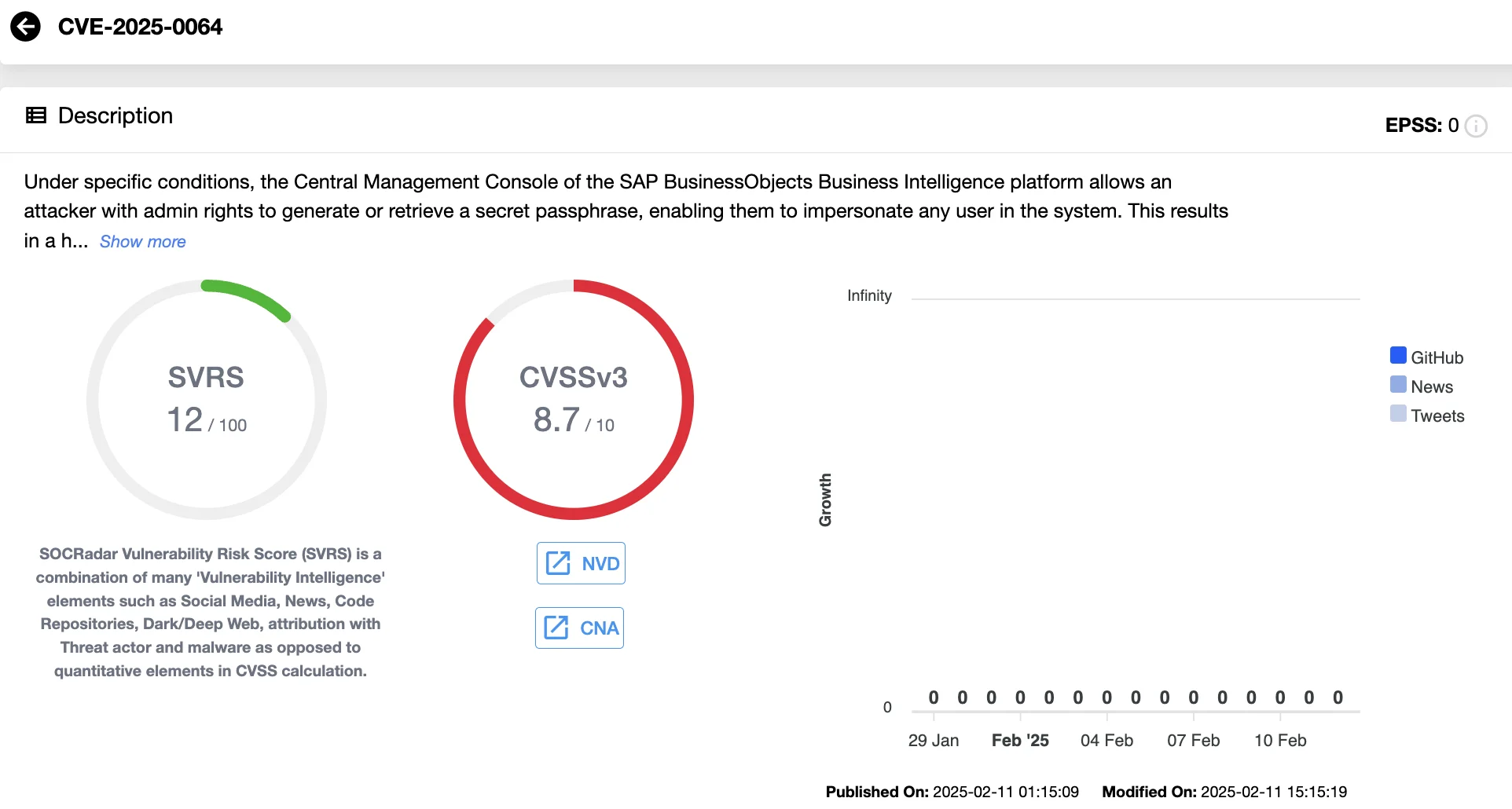
Vulnerability card of CVE-2025-0064 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Additional high-severity vulnerabilities include:
- CVE-2025-25243 (CVSS 8.6) – SAP Supplier Relationship Management Path Traversal:
Allows unauthorized file downloads, posing a risk of sensitive data leaks. - CVE-2025-24876 (CVSS 8.1) – SAP Approuter Authentication Bypass:
Could let attackers hijack user sessions and access applications without authorization. - CVE-2024-38819 (CVSS 7.5) Multiple vulnerabilities in SAP Enterprise Project Connection: Threaten unauthorized access to project data and potential operational disruption.
Organizations relying on SAP products should review and apply the latest security patches immediately. For the full list of fixes and technical details, refer to SAP’s official February 2025 Patch Day Bulletin.
Critical OS Command Injection in Ivanti CSA: CVE-2024-47908
Moreover, Ivanti has released an important security update for its Cloud Services Application (CSA), fixing two significant vulnerabilities.
The most critical, CVE-2024-47908 (CVSS 9.1), allows a remote authenticated attacker with admin privileges to execute arbitrary commands on the system due to an OS command injection flaw. Meanwhile, a less severe flaw, CVE-2024-11771 (CVSS 5.3), enables an unauthenticated remote attacker to access restricted functionality via a path traversal vulnerability.
Although Ivanti has reported no active exploitation of these vulnerabilities at the time of disclosure, organizations using CSA versions 5.0.4 and earlier should immediately upgrade to CSA 5.0.5 to mitigate the risks.
For more details and patch instructions, refer to Ivanti’s official security advisory.



































