
How to Spot and Avoid Malicious Apps on App Stores
The increasing integration of mobile applications into daily life has created significant security challenges that affect individuals, organizations, and the broader digital ecosystem. This rapid proliferation of mobile applications has fundamentally transformed how we interact with technology. With over 5 million apps available across major platforms and the global mobile app market expanding every year, the scale of this ecosystem presents an expansive attack surface for malicious actors.
The mobile threats have grown increasingly sophisticated. Malicious applications have evolved from simple scams to complex operations that can compromise personal data, financial information, and corporate networks. These mobile threats often exploit the trust users place in official app stores and legitimate brands.
Malicious apps on an app store, Source: SOCRadar Dark Web Intelligence
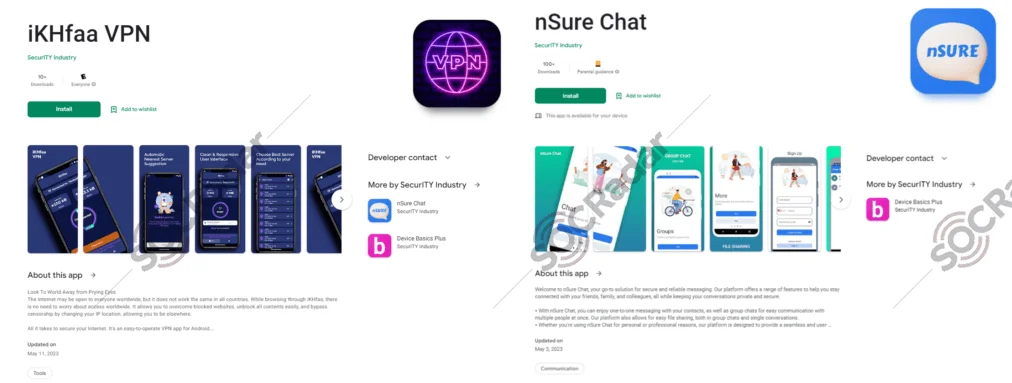
Previously, researchers have reported allegations of an espionage campaign targeting individuals in Pakistan, allegedly orchestrated by the threat actor group known as DoNot Team. Also tracked as APT-C-35 and Viceroy Tiger, this group is said to exploit rogue Android applications available on the Google Play Store to deceive unsuspecting victims.
According to the allegations, the malicious apps, named iKHfaa VPN and nSure Chat, have been designed to exploit users’ trust in the Google Play Store as an official and secure platform. These applications reportedly use advanced social engineering techniques to manipulate users into granting extensive permissions. Once granted, these permissions allegedly enable access to victims’ contact lists and precise location data.
Spotting Malicious Apps
The first line of defense against malicious applications is knowing their telltale signs. Cybercriminals often leave traces that can alert observant users to potential mobile threats:
- Enable Google Play Protect: Activate Google Play Protect on your device to automatically scan apps for harmful behavior and block potential threats.
- Download Numbers: Compare download counts with similar apps in the category. If a “popular” banking app has only a few thousand downloads while competitors have millions, this disparity deserves scrutiny.
- Check Reviews and Ratings: While high ratings can be manipulated, the content of reviews often reveals the truth. Look for detailed, specific reviews rather than generic praise. Multiple reviews mentioning security issues or unexpected behavior are major red flags.
- Analyze the App Description: Look for poorly written or overly generic app descriptions, as these can indicate a lack of credibility or an attempt to hide malicious intent.
- Check Permission Requirements: Be suspicious of apps requesting excessive permissions. A simple flashlight app shouldn’t need access to your contacts, location, or camera. Each permission request should logically align with the app’s core functionality.
- Verify App Age: Check the app’s release date and update history. Older, well-maintained apps are often more trustworthy than newly released ones with minimal activity.
- Developer Credibility: Examine the developer’s profile carefully. Legitimate developers typically have an established history, contact information and/or professional website, and other published apps. Be wary of new developer accounts with no track record.
Avoiding Fake Applications
Malicious apps often masquerade as legitimate services, but you can protect yourself by following these essential practices:
- Verify the Publisher: Double-check the exact name of the app publisher. Scammers often use names very similar to legitimate companies, like “Googel” instead of “Google” or “WhatsAp” instead of “WhatsApp Inc.”
- Cross-Reference Links: Only download apps through links from the official company website. If you’re downloading a banking app, visit your bank’s official website first and follow their provided app store link.
- Check Branding Elements: Examine app icons, screenshots, and promotional images carefully. Legitimate apps maintain consistent, high-quality branding. Poor image quality, misaligned logos, or obvious design inconsistencies often indicate malicious apps.
- Watch for Time Stamps: Recently published versions of supposedly established apps should raise concerns. Popular applications typically have version histories spanning months or years.
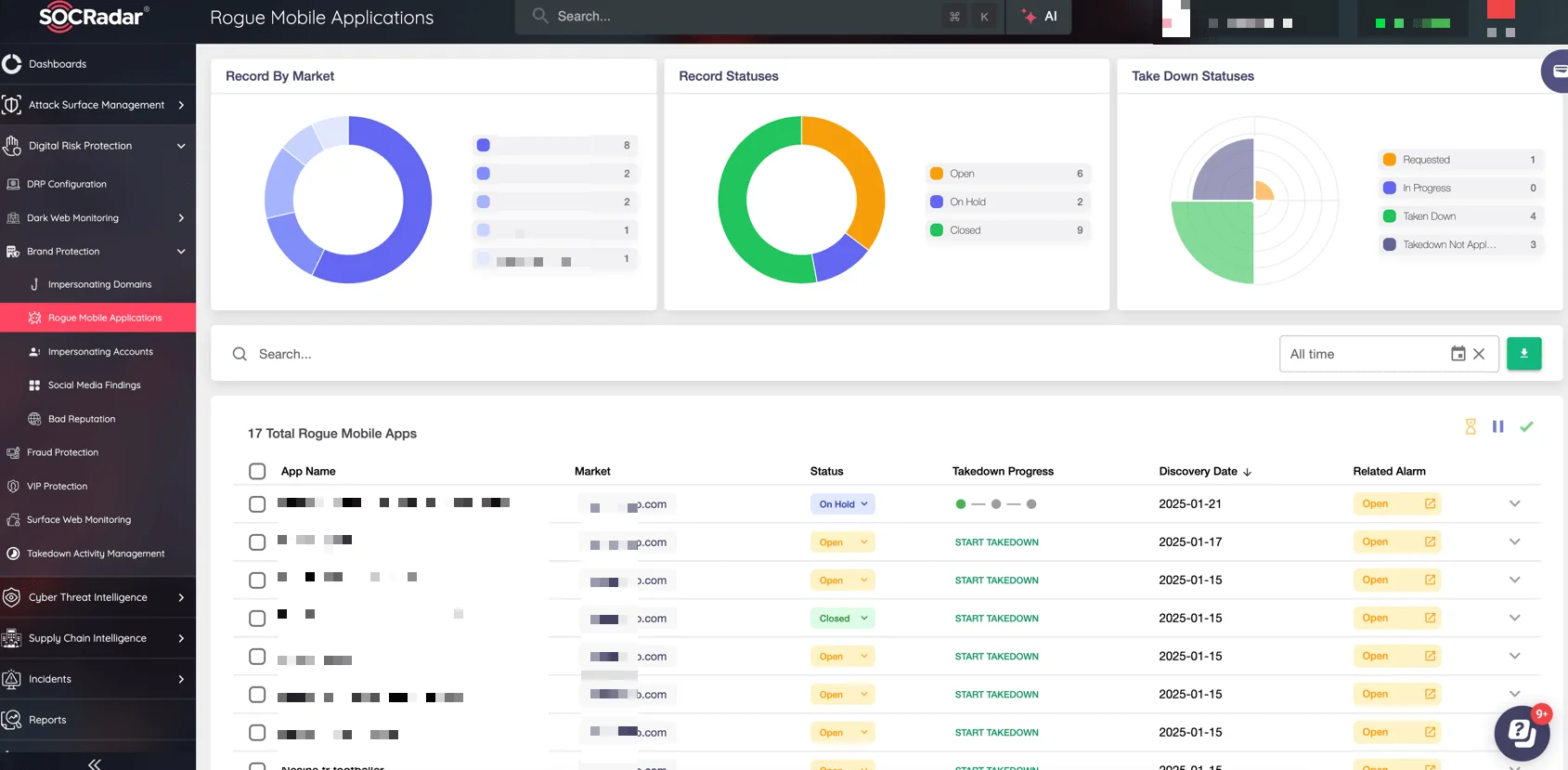
Rogue Mobile Applications (SOCRadar MAS module)
With SOCRadar Brand Protection’s Mobile App Security (MAS) module, you gain comprehensive protection for your organization’s mobile apps, preventing potential damage caused by malicious apps. Here’s how the Mobile App Security (MAS) module enhances your security:
Malicious App Detection: Quickly identify malicious apps similar to your own in app stores using the APK code.
Behavior Monitoring: Get instant notifications of any unusual app behavior in real time, enabling you to take timely action.
App Ecosystem Insights: Gain awareness of potential mobile threats in other apps that your app interacts with.
Continuous Security Checks: Stay ahead of threat actors by performing regular security checks and staying updated on the latest risks.
Tools to Verify App Safety
Several tools and resources can help verify an application’s legitimacy:
- Built-in Store Protection: Both Google Play Protect and Apple’s App Store review process provide baseline security. However, they shouldn’t be your only line of defense.
- Third-Party Security Apps: Mobile security solutions (anti-virus applications) from reputable cybersecurity companies can scan apps for malicious code. Consider tools like:
- Online Verification Tools: Services like VirusTotal can analyze apps by checking their signatures against multiple antivirus databases. While not foolproof, these tools provide additional validation layers.
Conclusion
Recommendations for Spotting and Avoiding Malicious Apps
For Users
- Download apps only from trusted sources.
- Scrutinize app permissions and deny excessive access.
- Regularly update apps and the operating system.
- Use mobile security apps for added protection.
- Pay attention to non-technical signs like generic developer names, vague app descriptions, or suspicious app update frequencies.
For Developers
- Follow secure coding standards and integrate security testing during development.
- Stay informed about emerging mobile threats and implement proactive defenses.
- Report vulnerabilities in third-party libraries or SDKs.
- Collaborate with threat intelligence teams or analysts to compile a list of security tools and techniques for scanning apps
The best protection comes from personal oversight. Stay informed about current mobile threats, maintain healthy skepticism toward unfamiliar apps, and regularly review your installed applications.
Remember that cybercriminals constantly evolve their tactics, so maintaining awareness of new threat patterns is crucial. When in doubt, delay installation until you can verify an app’s legitimacy through multiple sources.



































