
Microsoft’s June 2024 Patch Tuesday Highlights KeyTrap Zero-Day, Critical MSMQ Flaw; Windows LPE Exploit
[Update] December 24, 2024: “CVE-2024-30085 PoC Exploit Released, Immediate Action Required to Patch Windows Vulnerability”
[Update] December 17, 2024: “CVE-2024-35250 Has Been Added to CISA KEV Catalog”
[Update] October 15, 2024: “PoC Exploit Released for CVE-2024-35250”
[Update] October 14, 2024: “OilRig Exploits Windows Kernel Vulnerability (CVE-2024-30088) in Espionage Campaign”
Microsoft has released the June 2024 Patch Tuesday updates, aiming to fortify Microsoft products against various security threats, providing necessary patches and security enhancements. The update addressed 49 security vulnerabilities, one of which is classified as critical and another as a zero-day vulnerability.
The June 2024 Patch Tuesday focuses on addressing the following types of vulnerabilities:
- 24 Elevation of Privilege (EoP) Vulnerabilities
- 18 Remote Code Execution (RCE) Vulnerabilities
- 4 Denial of Service (DoS) Vulnerabilities
- 3 Information Disclosure Vulnerabilities
In the sections that follow, we will look into the specifics of the vulnerabilities addressed, the nature of the zero-day exploit, and the critical patches that have been deployed.
The Zero-Day of June 2024 Patch Tuesday, CVE-2023-50868
The June 2024 Patch Tuesday update addresses one zero-day vulnerability, which, although not yet exploited, was publicly disclosed before a fix was available.
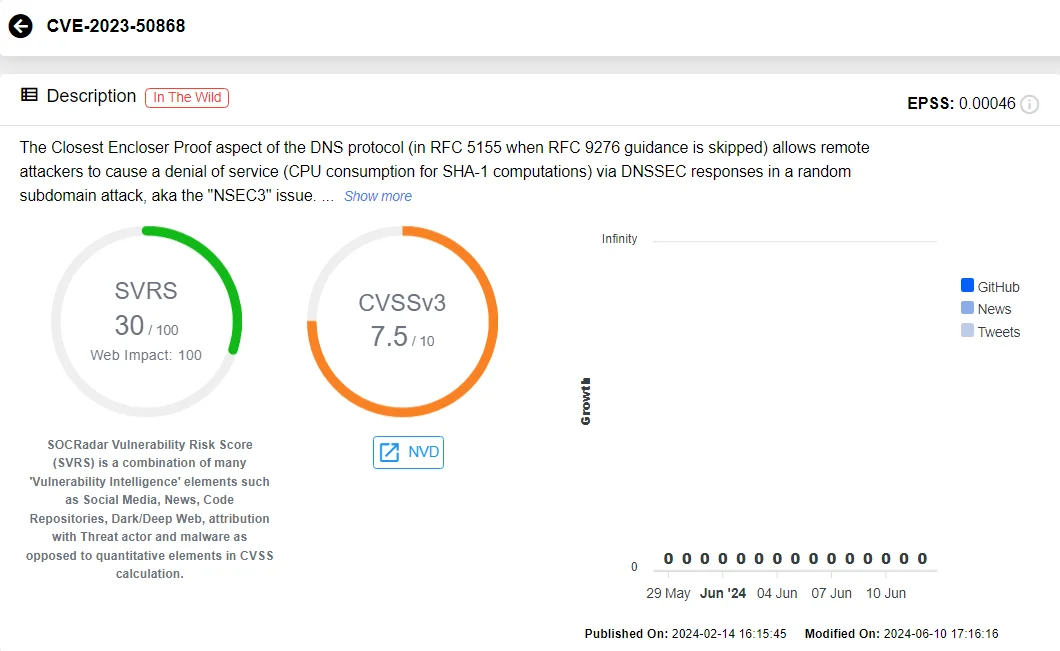
Tracked as CVE-2023-50868, this vulnerability was listed by the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) as early as February 14, 2024. The vulnerability could lead to what is referred to as a ‘KeyTrap’ attack. It has since been patched in various DNS implementations, including BIND and PowerDNS.
Vulnerability card for CVE-2023-50868 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
CVE-2023-50868 is a security vulnerability in the Closest Encloser Proof aspect of the DNS protocol. It allows remote attackers to cause a Denial-of-Service (DoS) by exploiting CPU consumption for SHA-1 computations via DNSSEC responses in a random subdomain attack.
According to Microsoft’s advisory, this vulnerability in DNSSEC validation could be exploited by attackers using standard DNSSEC protocols intended for DNS integrity. By consuming excessive resources on a resolver, the attacker can cause a DoS for legitimate users.
The CVE-2023-50868 vulnerability is now fixed with Microsoft’s latest Patch Tuesday updates, ensuring that DNSSEC validation and resource consumption are appropriately managed to prevent potential DoS attacks.
Critical RCE in MSMQ: CVE-2024-30080
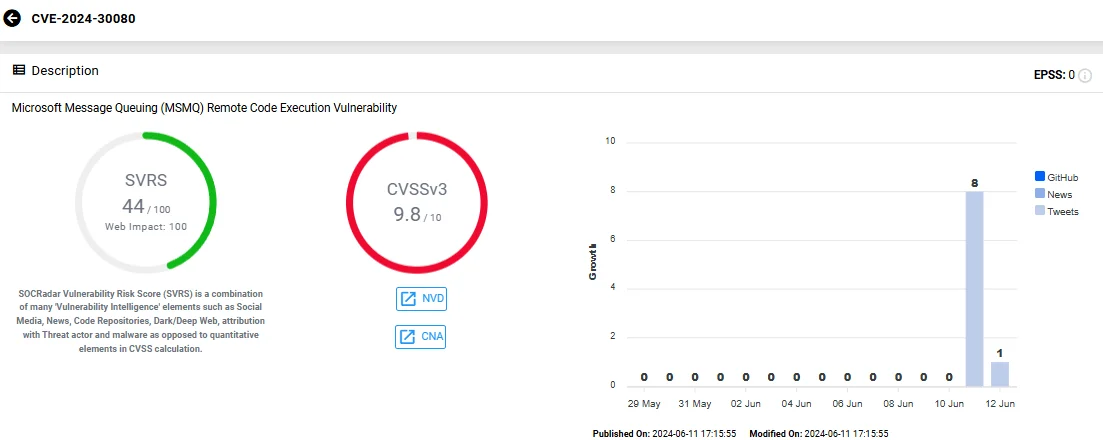
In the June 2024 Patch Tuesday update, Microsoft addresses one CVE with a maximum severity rating of ‘Critical.’ This vulnerability is identified as CVE-2024-30080, a server-side Remote Code Execution (RCE) issue in Microsoft Message Queuing (MSMQ) with a severity score of 9.8.
CVE-2024-30080 arises from a Use-After-Free vulnerability. An attacker can exploit this vulnerability by sending a specially crafted malicious MSMQ packet to an MSMQ server. This could potentially allow the attacker to execute arbitrary code on the affected system.
Vulnerability card for CVE-2024-30080 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Microsoft stresses that the MSMQ service, which is a Windows component, needs to be enabled for a system to be exploitable by this vulnerability. This feature can be added via the Control Panel. You can also check to see if there is a service running named Message Queuing and TCP port 1801 is listening on the machine, as listed in the mitigation section.
According to Shodan, there are over 988,000 machines online that are accessible via port 1801.
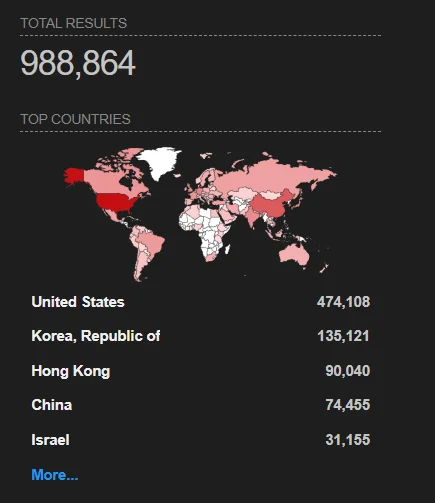
Shodan search results for the TCP port 1801
Microsoft clarifies that for this vulnerability to be exploitable, the MSMQ service must be enabled. MSMQ is a Windows component that can be added through the Control Panel.
To determine if a system is vulnerable, administrators should check if the Message Queuing service is running and if TCP port 1801 is listening on the machine, as detailed in the mitigation section of the advisory.
Exploit for a Previous Windows Flaw is Circulating the Hacker Channels (CVE-2024-26229)
In further developments, SOCRadar has detected threat actors sharing an exploit for a Microsoft vulnerability patched in the April 2024 Patch Tuesday updates.
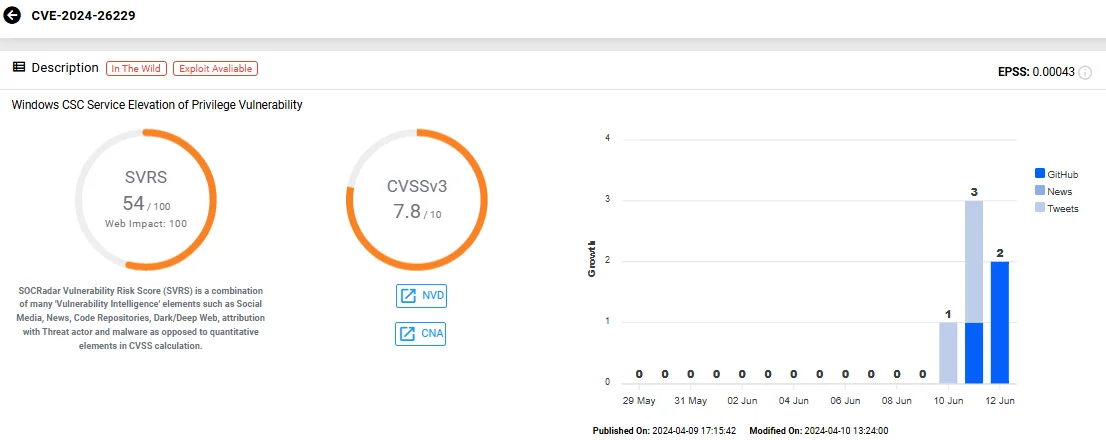
The specific vulnerability, CVE-2024-26229, is a high-severity local privilege escalation (LPE) flaw with a CVSS score of 7.8, affecting the Windows CSC Service.
Vulnerability card for CVE-2024-26229 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
The threat actors provided brief information about the vulnerability, along with a link to the exploit hosted on GitHub. The shared details mention slight adjustments to the original exploit, indicating potential enhancements by the attackers.
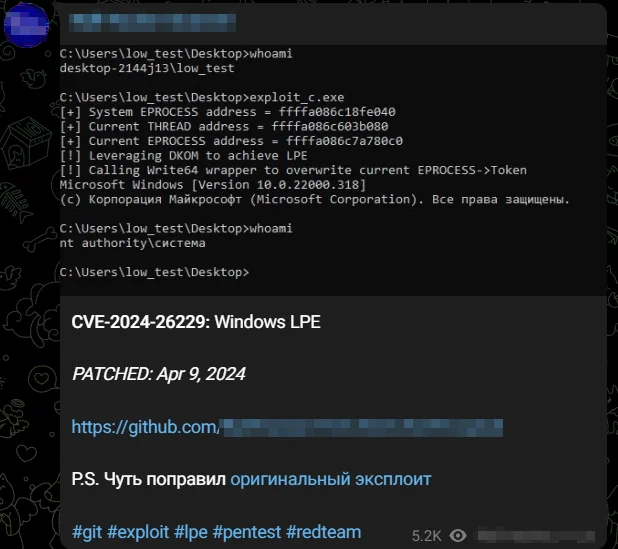
Threat actors shared an exploit for CVE-2024-26229 on Telegram
The exploitation of this vulnerability could allow attackers to gain SYSTEM privileges on the affected systems, posing significant risks to users and organizations.
SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence feature helps organizations stay ahead of potential breaches by monitoring new exploits and their developments across various platforms. It provides an in-depth view of identified security vulnerabilities, offering real-time alerts and comprehensive insights into emerging threats.
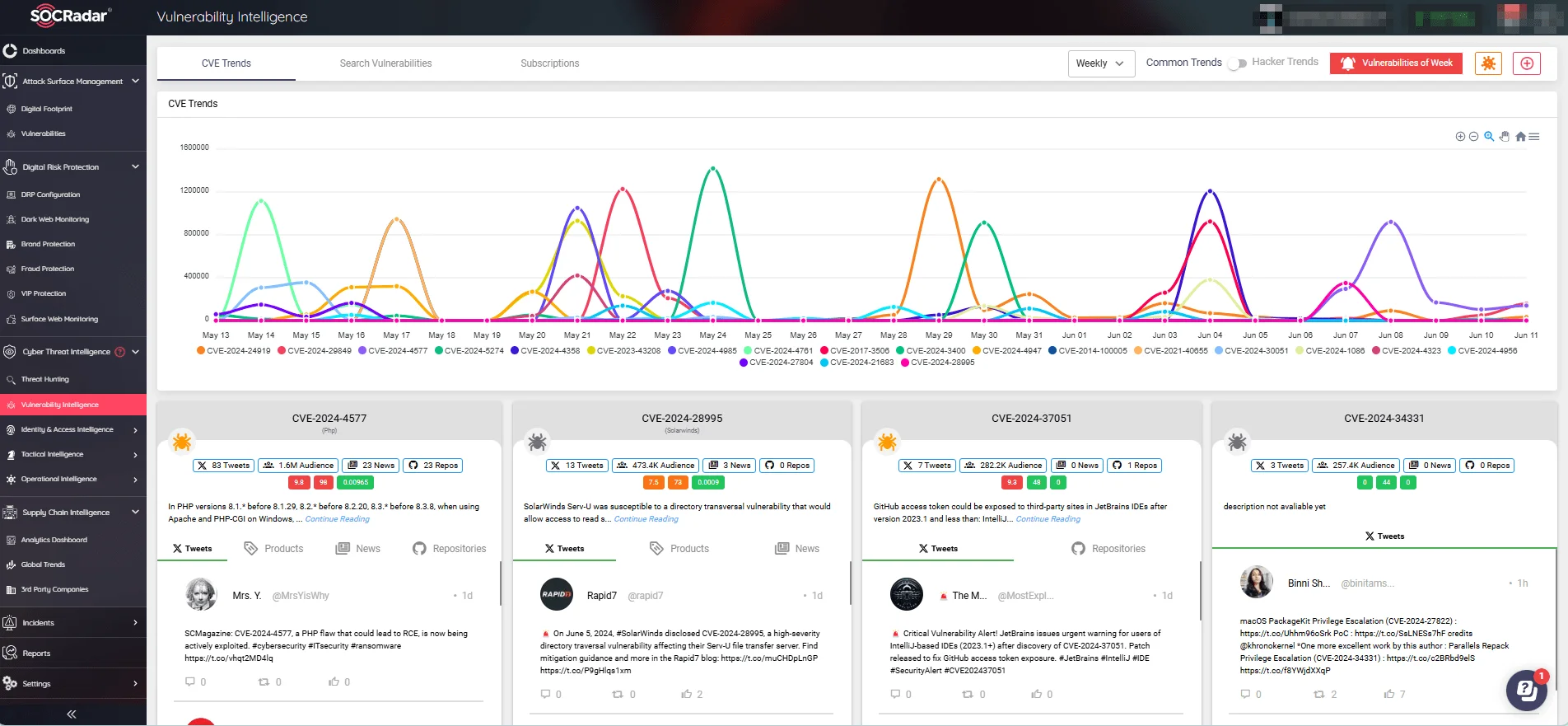
SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence
High-Risk Vulnerabilities in June 2024 Patch Tuesday
The June 2024 Patch Tuesday update addressed several high-severity vulnerabilities that are more likely to be exploited.
Unfortunately, there are no workarounds available for these issues, highlighting the urgency of applying the official patches to prevent exploitation.
In addition to the critical CVE-2024-30080, other notable high-risk vulnerabilities that were addressed are:
- CVE-2024-30082 (CVSS: 7.8) – Windows Win32K – GRFX
- CVE-2024-30085 (CVSS: 7.8) – Windows Cloud Files Mini Filter Driver
- CVE-2024-30086 (CVSS: 7.8) – Windows Win32 Kernel Subsystem
- CVE-2024-30087 (CVSS: 7.8) – Windows Win32K – GRFX
- CVE-2024-30089 (CVSS: 7.8) – Microsoft Streaming Service
- CVE-2024-30091 (CVSS: 7.8) – Windows Win32K – GRFX
- CVE-2024-35250 (CVSS: 7.8) – Windows Kernel-Mode Drivers
- CVE-2024-30084 (CVSS: 7.0) – Windows Kernel-Mode Drivers
- CVE-2024-30088 (CVSS: 7.0) – Windows NT OS Kernel
- CVE-2024-30099 (CVSS: 7.0) – Windows NT OS Kernel
It is highly recommended that you apply the patches as soon as possible in order to secure your system. Refer to Microsoft’s Release Note for more specific details on the vulnerabilities fixed in the June 2024 Patch Tuesday update.
OilRig Exploits Windows Kernel Vulnerability (CVE-2024-30088) in Espionage Campaign
The Iranian threat actor OilRig (APT34) has been exploiting CVE-2024-30088 in a cyber espionage campaign targeting the U.A.E. and the Gulf region.
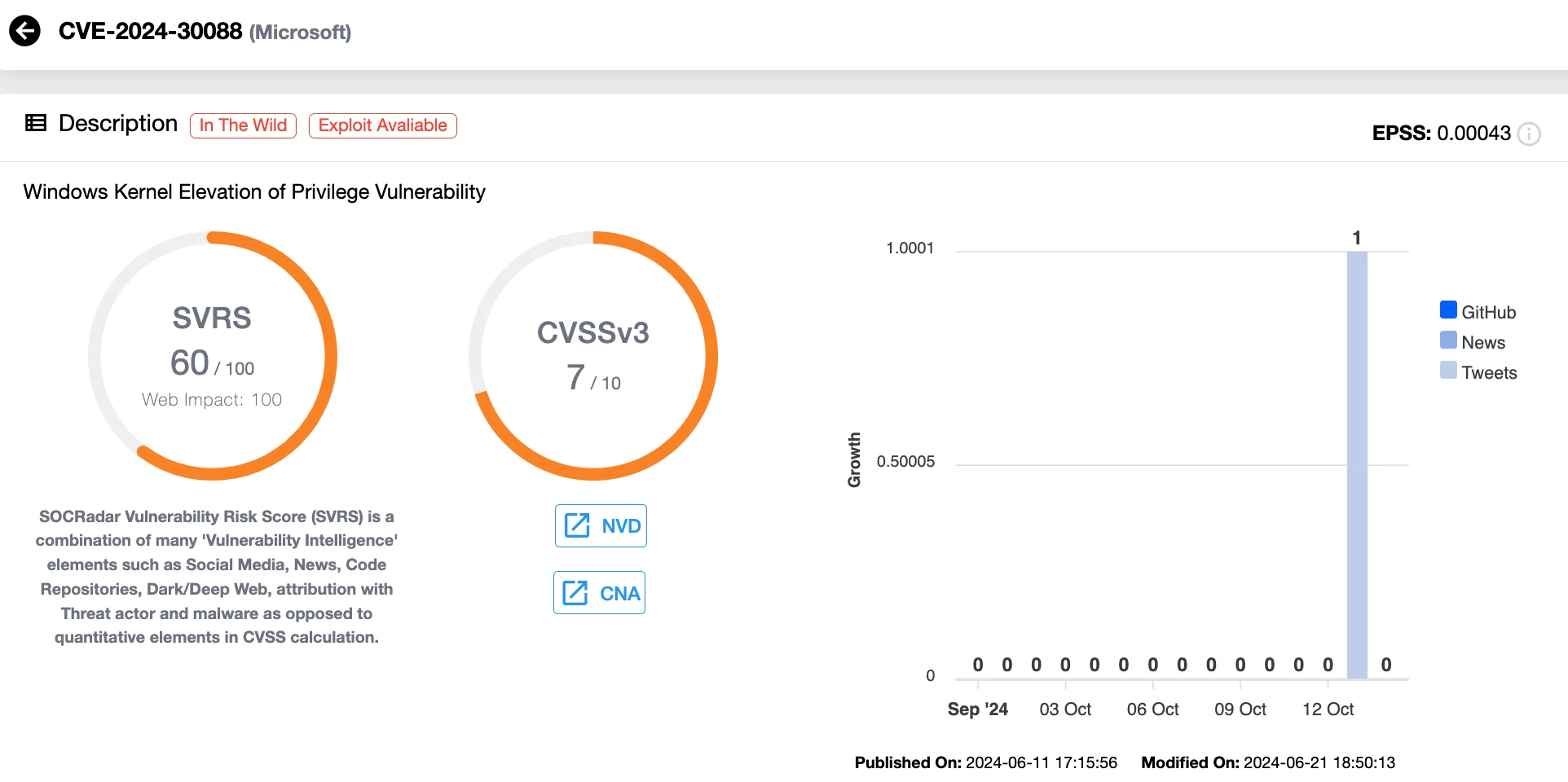
Windows Kernel privilege escalation flaw, CVE-2024-30088 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
The campaign involves deploying a backdoor called STEALHOOK, which exfiltrates credentials through Microsoft Exchange servers. OilRig also leverages the psgfilter[.]dll to extract sensitive domain credentials, enabling remote access and further lateral movement. This highlights the group’s continued focus on abusing vulnerabilities in key regional infrastructure.
For more detailed insights, refer to the full analysis here.
*On October 15, 2024, CISA added the Windows Kernel privilege escalation vulnerability, CVE-2024-30088, to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog due to evidence of active exploitation. Organizations are urged to patch by November 5, 2024, to mitigate potential risks.
PoC Exploit Released for CVE-2024-35250
A Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit has recently been made available on GitHub, demonstrating how CVE-2024-35250 (CVSS: 7.8) can be exploited to perform arbitrary IOCTL calls, leading to privilege escalation. Organizations are strongly advised to apply the patches to mitigate exploitation risks.
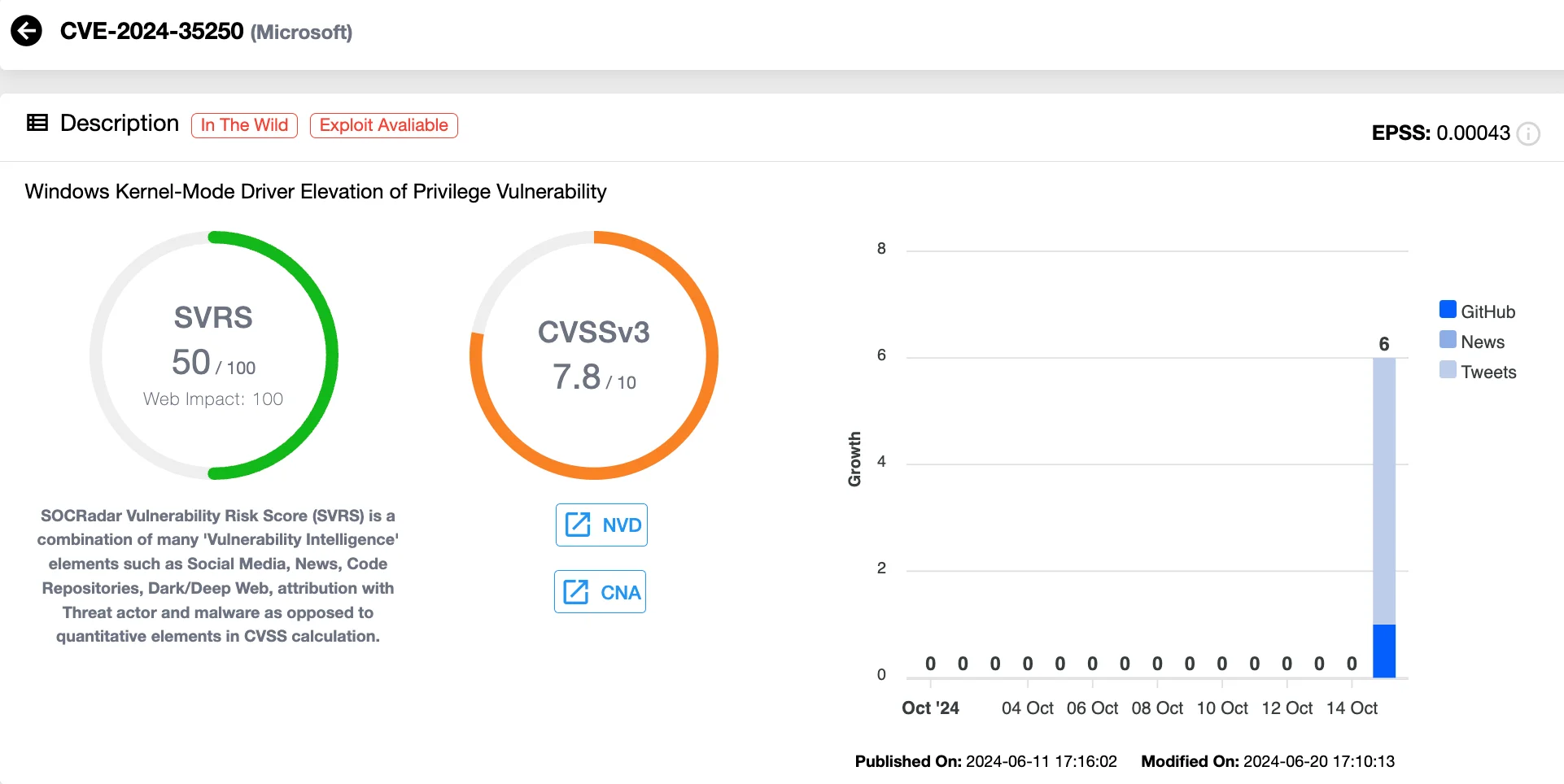
Details of CVE-2024-35250 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
CVE-2024-35250, a high-severity vulnerability in Windows Kernel-Mode Drivers, was initially exploited during the Pwn2Own Vancouver 2024 competition. According to an August analysis, the flaw is tied to improper handling of IOCTL_KS_PROPERTY requests in the Kernel Streaming driver (ks.sys), which attackers can exploit to escalate privileges.
CVE-2024-35250 Has Been Added to CISA KEV Catalog
CISA has included CVE-2024-35250 in its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog. This high-severity vulnerability in Windows Kernel-Mode Drivers was first exploited during the Pwn2Own Vancouver 2024 competition, and a PoC exploit became publicly available in October 2024.
The vulnerability allows attackers to perform untrusted pointer dereferencing, which can lead to remote code execution and further compromise systems.
Federal agencies must patch their systems by January 6, 2025, to protect against this risk.
CVE-2024-30085 PoC Exploit Released, Immediate Action Required to Patch Windows Vulnerability
A proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit for CVE-2024-30085 (CVSS 7.8), affecting the Windows Cloud Files Mini Filter Driver, has been released. Security researcher Alex Birnberg disclosed the flaw’s technical details, revealing how it allows local attackers to escalate privileges to the SYSTEM level.
The vulnerability arises from improper validation in the Cloud Files Mini Filter Driver (cldflt) within the HsmIBitmapNORMALOpen function. By exploiting this issue, attackers can bypass security checks and execute arbitrary code with SYSTEM-level privileges, enabling them to install malware, modify system files, or access restricted data.
Birnberg initially demonstrated the PoC exploit during the TyphoonPWN 2024 competition. For further details, you can check the advisory here.
The release of a PoC exploit and detailed technical information increases the risk of CVE-2024-30085 being weaponized by threat actors. With the ability to replicate the attack, cybercriminals can quickly develop automated exploits. As such, it’s critical for organizations to prioritize this vulnerability and ensure their systems are patched to prevent potential exploitation.
Improve Your Vulnerability Management Strategy with SOCRadar
SOCRadar offers two critical services to strengthen your vulnerability management strategy: Vulnerability Intelligence and the Attack Surface Management (ASM) module.
While the Vulnerability Intelligence module continuously tracks security vulnerabilities, providing real-time alerts and comprehensive insights into emerging threats, the Attack Surface Management (ASM) module equips organizations with tools to quickly identify, assess, and mitigate vulnerabilities.
With ASM, you can easily monitor your digital assets and receive alarms regarding security issues, enabling quick responses to potential threats. This comprehensive approach, supported with actionable insights, ensures that your organization can effectively address security concerns and protect system integrity.
SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) module, Company Vulnerabilities page


































