
Mitel MiCollab PoC Exploit Links CVE-2024-41713 and Zero-Day, Exposing Sensitive Files
[Update] January 8, 2025: “CISA Adds Mitel MiCollab Vulnerabilities to KEV Catalog”
Cyberattacks targeting VoIP and communication systems have become increasingly common, highlighting the vulnerabilities of these critical infrastructures. VoIP platforms, which bridge traditional telephony and digital communication, present attackers with opportunities to disrupt operations and exfiltrate valuable data.
One such platform is Mitel MiCollab, a widely adopted solution that integrates chat, voice, video, and SMS capabilities into a single ecosystem. While its features aid enterprise communications, recent research has pointed out significant vulnerabilities that could leave organizations exposed to serious security risks.
In this blog post, we’ll outline two important vulnerabilities affecting Mitel MiCollab: CVE-2024-41713, a high-impact authentication bypass, and an arbitrary file read zero-day. A recently released Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit demonstrates how attackers can chain these vulnerabilities to compromise systems, steal sensitive data, and disrupt enterprise operations.
How Mitel Micollab Vulnerabilities Expose a Critical Exploit Chain
Recent investigations into the Mitel MiCollab platform uncovered multiple vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit in sequence, creating a powerful exploit chain.
CVE-2024-35286: The Initial Discovery
The research began with CVE-2024-35286 (CVSS 9.8), a critical pre-auth SQL injection vulnerability in the NuPoint Unified Messaging (NPM) component of Mitel MiCollab. This flaw enables attackers to perform unauthorized database operations, and compromise sensitive information. While CVE-2024-35286 was patched in May 2024 with the release of MiCollab version 9.8 SP1, its discovery laid the foundation for uncovering a related, equally concerning vulnerability.
The Path to CVE-2024-41713
During efforts to reproduce the SQL injection flaw, researchers identified CVE-2024-41713 (CVSS 7.5), an authentication bypass vulnerability with far-reaching implications.
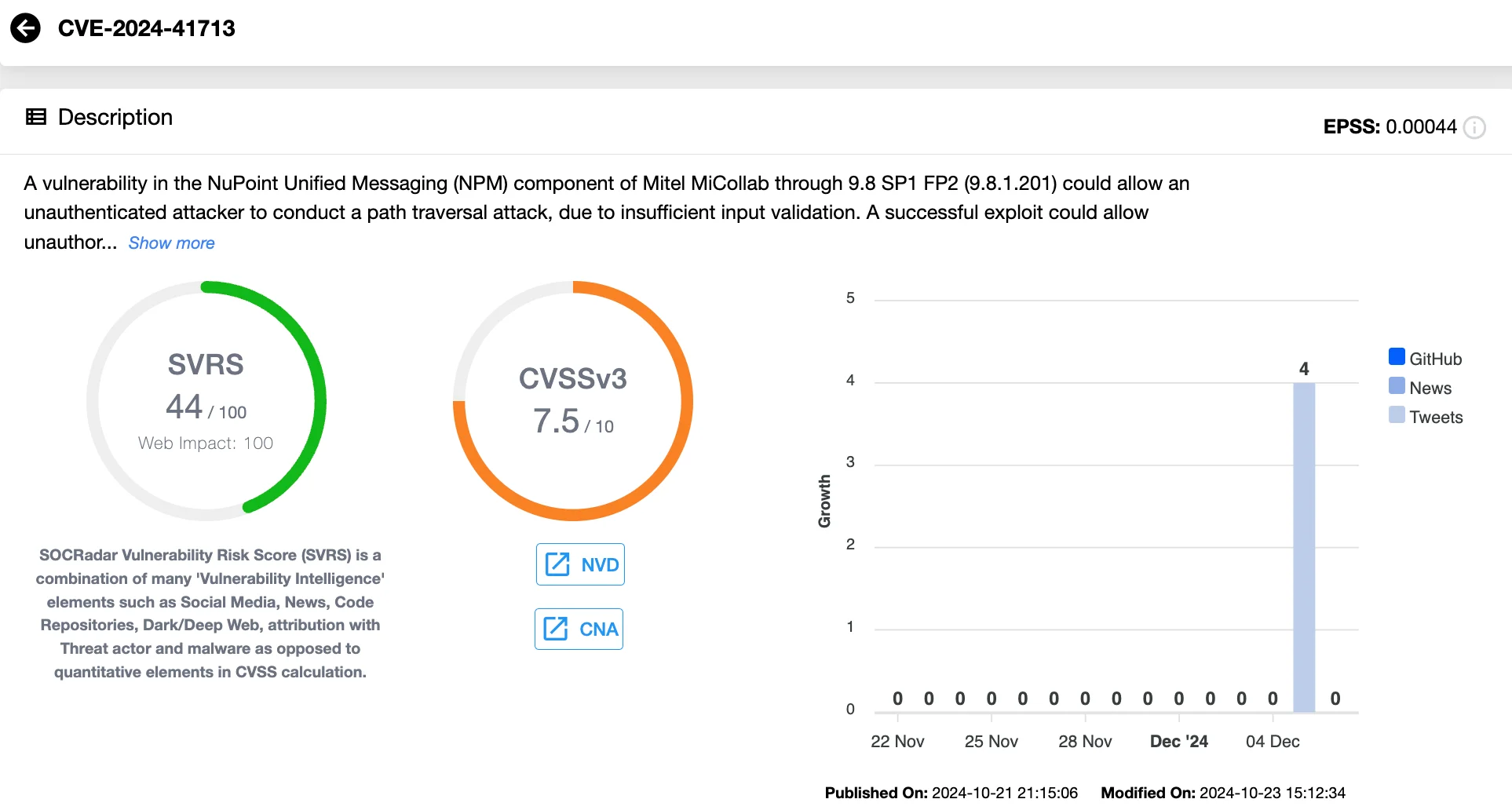
Details of CVE-2024-41713 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
CVE-2024-41713 is a high-severity vulnerability that allows attackers to bypass authentication mechanisms on the Mitel MiCollab platform. This flaw leverages a path traversal technique using the “..;/” input in HTTP requests.
This vulnerability affects MiCollab versions 9.8 SP1 FP2 (9.8.1.201) and earlier. The exploit is particularly concerning due to its ability to bypass authentication, enabling attackers to launch further attacks or combine it with other vulnerabilities for more devastating consequences.
Mitel addressed this flaw in October 2024 with the release of MiCollab version 9.8 SP2.
The Arbitrary File Read Zero-Day
Researchers have released a Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit that chains CVE-2024-41713 with a post-authentication Arbitrary File Read zero-day vulnerability. While a CVE is reserved for the zero-day flaw, it is yet to be patched at the time of writing.
Although the zero-day may seem less severe due to its post-authentication requirement, chaining it with CVE-2024-41713 effectively removes this limitation, amplifying the risks to affected systems.
Every unmonitored endpoint or overlooked configuration can open the door to attackers. SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) module offers an advanced solution to proactively secure your organization. It enables you to:
- Identify and monitor exposed digital assets across your infrastructure.
- Continuously assess potential vulnerabilities and misconfigurations in real-time.
- Gain actionable insights into potential threats targeting your enterprise systems.
By integrating advanced threat intelligence and continuous testing, SOCRadar ASM ensures you remain one step ahead.
Protect your organization’s digital perimeter with SOCRadar ASM, because knowing your attack surface is the first step to securing it.
The Bigger Picture – Lessons from the PoC Exploit
Researchers showcased the PoC exploit by successfully dumping the /etc/passwd file, highlighting how these flaws can compromise sensitive system information. This exploit chain underscores the dangers of vulnerabilities that may seem limited in isolation but, when combined, allow attackers to bypass security layers, steal data, and disrupt operations.
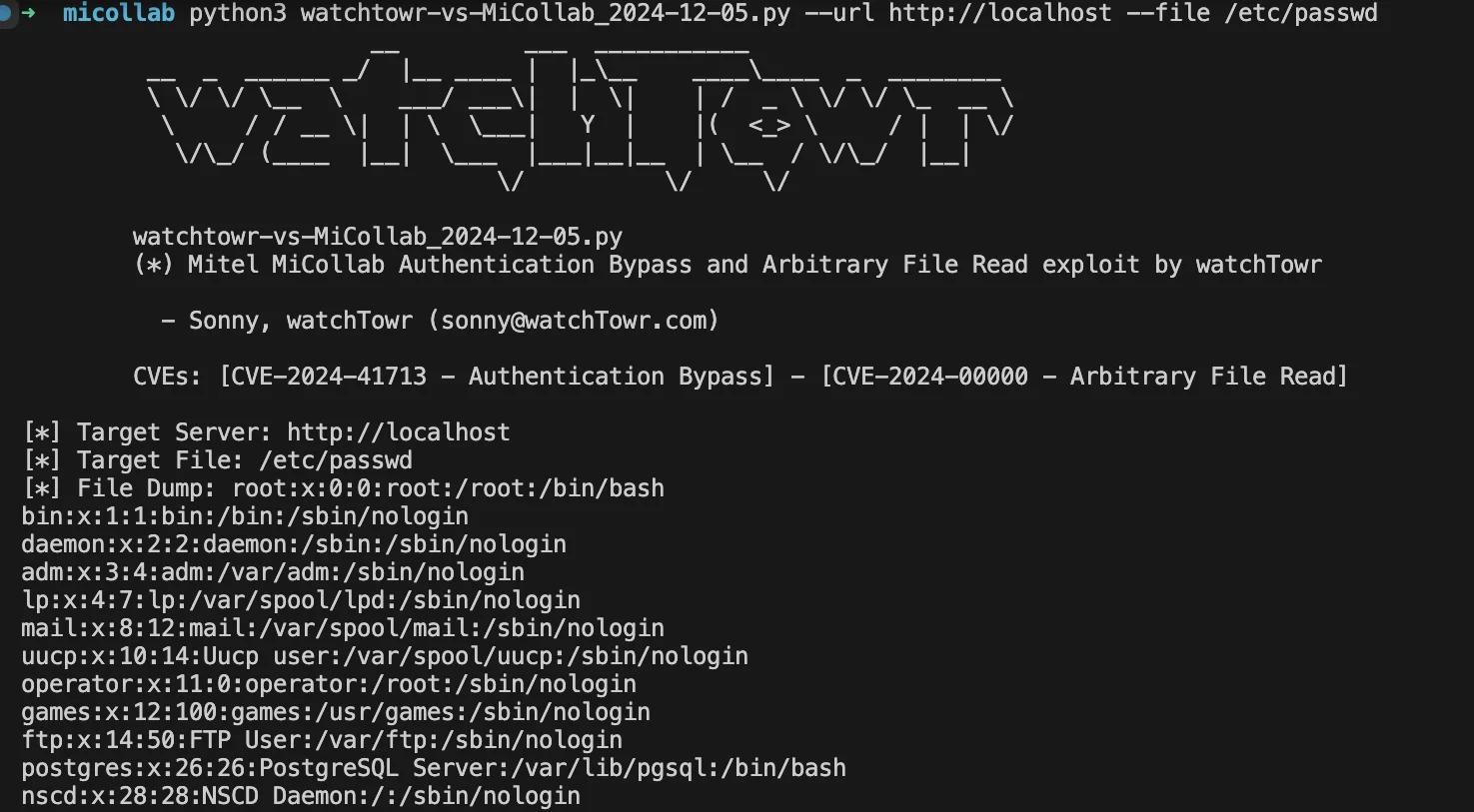
The PoC combining CVE-2024-41713 and the Arbitrary File Read zero-day (watchTowr)
VoIP systems like Mitel MiCollab represent attractive targets for attackers due to their important role in enterprise communication. With expanding attack surfaces, these platforms often house sensitive data, including call records and user credentials, making them high-value assets for cybercriminals.
While the availability of technical details and a PoC provides defenders with critical insights, threat actors can potentially weaponize these in real world attacks.
Organizations using Mitel MiCollab are strongly advised to patch their systems and implement proactive measures to mitigate risks. For additional guidance, refer to Mitel’s official security advisory: MISA-2024-0029.
CISA Adds Mitel MiCollab Vulnerabilities to KEV Catalog
CISA has recently added CVE-2024-41713 and CVE-2024-55550 to the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog. While CVE-2024-41713 was previously mentioned, the addition of CVE-2024-55550 (CVSS 4.4) further highlights the risk. Importantly, CVE-2024-41713 can be chained with CVE-2024-55550, enabling an unauthenticated, remote attacker to read arbitrary files on the server.
The due date for addressing these vulnerabilities is January 28, 2025. For more details, refer to the full CISA alert.
Vulnerabilities don’t wait, and neither should your organization. A delayed response can lead to exploitation, data breaches, or operational disruptions.
SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence module enables organizations to detect and prioritize vulnerabilities, including high-risk flaws like CVE-2024-41713.
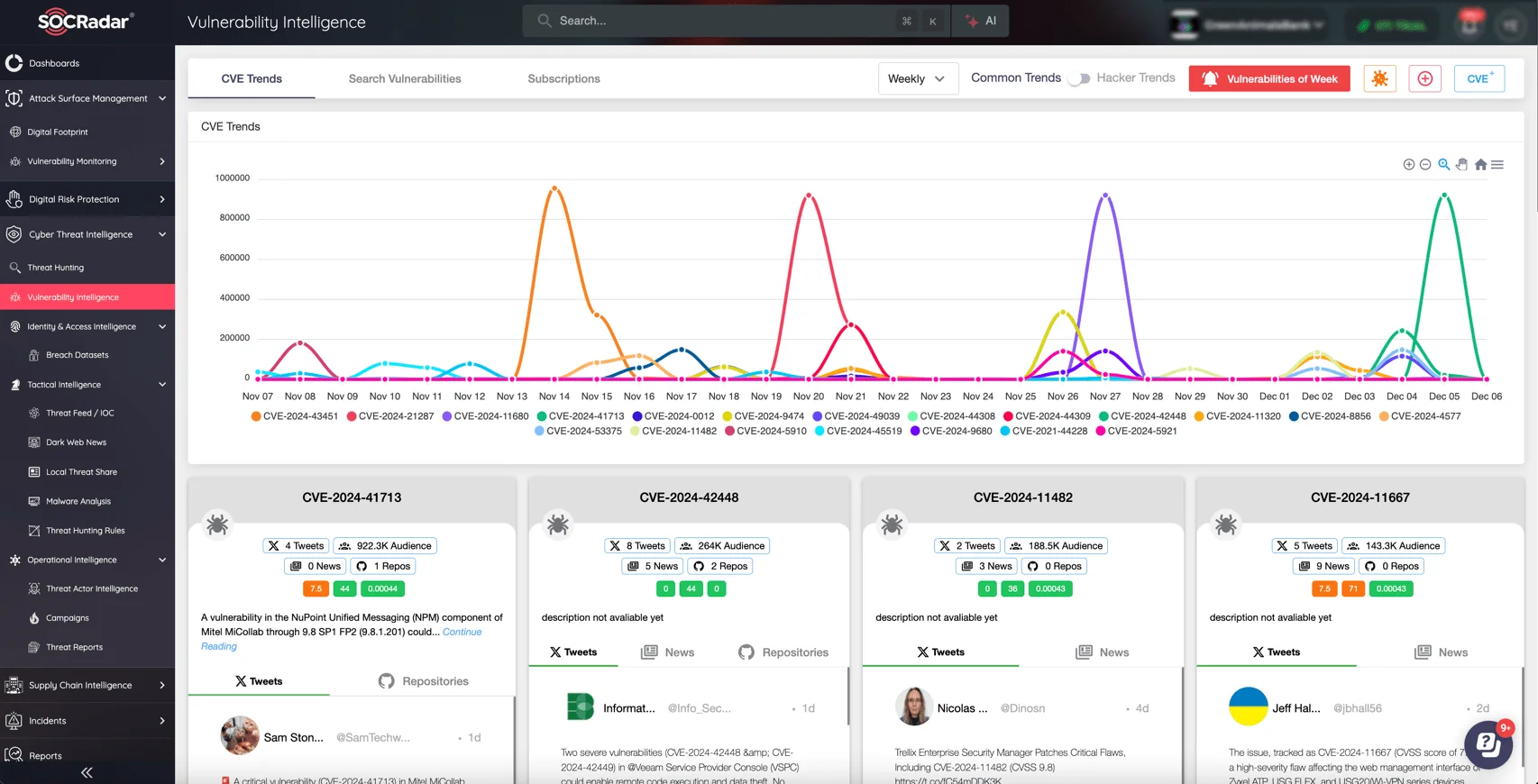
Monitor the newest CVEs and exploitation trends with SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence
The module provides real-time threat insights, offering a clear view of which vulnerabilities pose immediate risks. This enables you to focus on what matters most—mitigating the vulnerabilities that attackers are actively exploiting.


































