
Phishing Attack Compromises Cyberhaven’s Chrome Extension, Impacts Thousands – What You Need to Know
[Update] January 2, 2025: “New Details on the Chrome Extension Phishing Attack”
A significant cyber attack struck just recently, when Cyberhaven, a well-known cybersecurity firm, disclosed that its Chrome extension had been compromised. This breach, which affected thousands of users, is part of a broader, ongoing campaign that targeted a variety of Chrome extensions from different developers.
The attackers injected malicious code into legitimate extensions, using them to steal sensitive information, including cookies and access tokens. As the investigation unfolds, new extensions are being uncovered as part of this large-scale attack.
In this post, we will examine the details of the Cyberhaven Chrome extension breach, the broader implications of the attack, and recommendations.
What Happened?
On December 24, 2024, a phishing attack targeting a Cyberhaven employee’s credentials led to the compromise of the company’s Chrome extension. The attacker gained access to the Google Chrome Web Store, using the employee’s credentials to publish a malicious update to the extension. This version (24.10.4) was active for less than 24 hours, between December 25 and 26, 2024.
The malicious code allowed the attacker to exfiltrate cookies and authentication tokens for certain social media and AI platforms from users running the compromised extension. Only those whose browsers had auto-updated to this version during the affected period were impacted.
The company’s swift action included notifying affected users, removing the malicious extension, and publishing a secure update. The company also engaged an external incident response team and started working with federal law enforcement to investigate the attack.
Details of the Cyberhaven Phishing Attack
The attack was made possible by a highly targeted phishing email that mimicked official communication from the Google Chrome Web Store Developer Support team. The email falsely claimed that an extension was at risk of removal for policy violations, urging the recipient to click on a link to accept the policies.
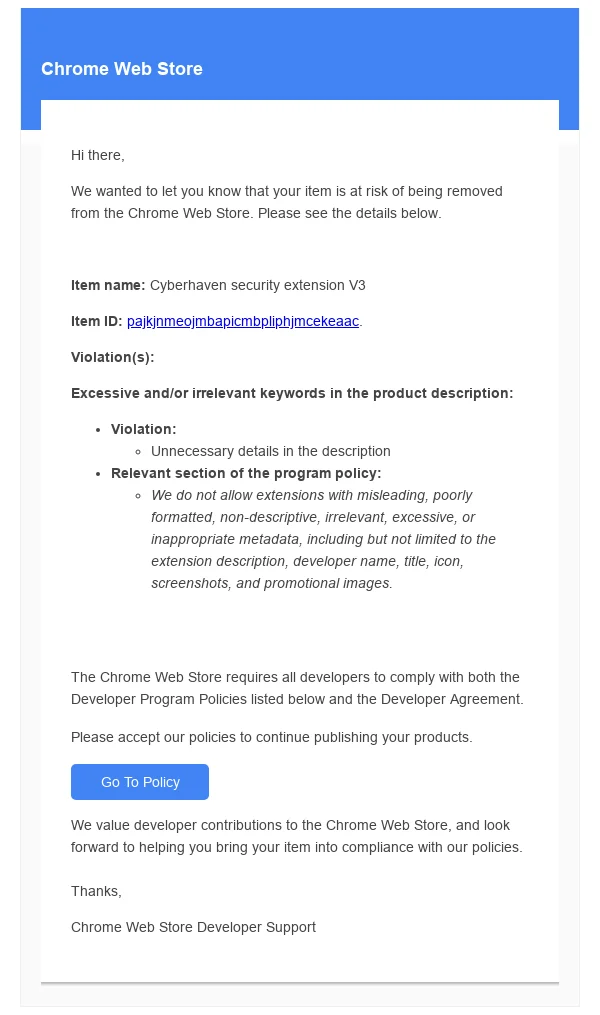
Chrome Web Store phishing email (Image Source: Cyberhaven)
The link redirected the recipient to a malicious OAuth application named “Privacy Policy Extension,” which granted the attacker access to the extension developer’s credentials. After gaining access, the attacker published the malicious update, which bypassed the usual Chrome Web Store security review process.
Stolen data, including credentials and access, is often sold on the dark web. If compromised, it can cause massive harm to your organization. SOCRadar’s Dark Web Monitoring module tracks and alerts you about your exposed data, including any sensitive information being traded on hidden forums and marketplaces.
Our platform continuously scans Dark Web sources for mentions of your organization’s credentials, ensuring that you are alerted before attackers can misuse stolen data. With real-time alerts, you can take action to protect your brand and customers.
Who Was Affected? Scope and Impact of the Breach
Although Cyberhaven was the first to report the attack, security researchers quickly identified other affected extensions. The malicious code from Cyberhaven’s extension, which had over 400,000 users, was also found in several widely used browser extensions, including VPNs, reward-based services, and AI assistants.
Other extensions that were compromised notably included VPNCity (50,000 users), Uvoice (40,000 users), and Internxt VPN (10,000 users). It is estimated that at least 600,000 users were impacted by this attack, considering both Cyberhaven and the other compromised extensions.
The attack is believed to be part of a larger phishing campaign that may have begun as early as April 2023, with some evidence pointing to even earlier compromises.
Browser extensions, requiring broad permissions to access sensitive data, are a prime target for attackers seeking to steal personal or organizational information. For more details on other compromised extensions and insights from researchers, you can refer toSecure Annex’s analysis.
Phishing remains one of the most common entry points for cyberattacks. SOCRadar’s Email Analyzer scans incoming emails to detect malicious attachments and phishing attempts before they can cause harm. It is a free tool, available on SOCRadar LABS, alongside other SOC tools.

Email Analyzer tool on SOCRadar LABS
Response and Mitigation – How to Prevent Further Risks
In response to the attack, Cyberhaven promptly notified affected customers and released a clean version of the extension (24.10.5) after December 26. The company confirmed that no other systems, including CI/CD processes or code signing keys, were compromised.
They also recommended precautionary measures for users, such as revoking non-FIDOv2 passwords, rotating API tokens, and reviewing browser logs for any suspicious activity. Additionally, the company engaged with federal law enforcement and brought in an external incident response firm for forensic analysis.
As the investigation continues, researchers are examining more compromised extensions, and users are advised to uninstall potentially risky extensions or ensure they have upgraded to a secure version.
For users who installed the compromised extension, Cyberhaven has recommended several immediate actions:
- Update to the latest version (24.10.5 or newer)
- Revoke or rotate all passwords, especially for platforms not using FIDOv2
- Review browser logs for any suspicious activity
For a detailed look at the compromise, including some technical insights, you can refer to Cyberhaven’s preliminary analysis.
New Details on the Chrome Extension Phishing Attack
Investigations have revealed additional details about the phishing campaign targeting Chrome extensions and their developers, showing that it is more extensive than previously recognized. Here are the newest clarifications:
- Initially, Cyberhaven’s security extension was the first to attract media attention, but further analysis has revealed that at least 36 extensions have been compromised. It is estimated that approximately 2.6 million users have been impacted.
- The campaign is believed to have started around December 5, 2024, although earlier indicators of malicious activity can be traced back to March 2024, with Command and Control (C2) subdomains identified.
- Multiple domains were utilized throughout the phishing campaign, including supportchromestore[.]com, forextensions[.]com, and chromeforextension[.]com, as reported by BleepingComputer.
- Victims were redirected to a malicious OAuth application hosted on a legitimate Google domain, which was disguised as part of the standard Google authorization process. Once users granted permissions, attackers gained control over the developers’ Chrome Web Store extensions, allowing them to modify or release new versions. MFA proved ineffective as the OAuth flow relied on user comprehension of permissions without additional verification steps.
- In addition to compromising extensions, attackers targeted Facebook accounts associated with the affected extensions, stealing sensitive user data such as account details, advertising information, and business accounts. The malicious code also attempted to bypass two-factor authentication (2FA) by searching for QR codes linked to Facebook’s security protocols.
- The extensive list of Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) suggests that the number of affected extensions could exceed 36, as pre-registered domains for other extensions were also found. VirusTotal confirmed that attackers had set up domains intended to exploit potential victims, even if those victims were not ultimately compromised.
Protect Yourself and Your Organization
The recent Chrome extension breach is a reminder of the vulnerabilities that can exist in our everyday tools. While browser extensions offer convenience and enhanced functionality, they also pose significant risks if not properly secured.
Organizations should take immediate action to assess the security of their extensions, educate employees about phishing tricks, and ensure their response protocols are swift and effective.
In light of this breach, it is critical to adopt stronger security practices for browser extensions:
- Review Installed Extensions: Periodically check which extensions are installed on your browser and ensure they are from trusted publishers.
- Keep Extensions Updated: Ensure your extensions are always updated to the latest and fixed versions to avoid security vulnerabilities.
- Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement FIDO2-compliant MFA for all sensitive accounts to protect against credential theft.
- Regularly Monitor Activity: Review browser logs for any signs of suspicious activity, especially if you have used affected extensions.
With increasing threats targeting digital assets, knowing your exposure is essential. SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) module provides continuous monitoring of your entire digital footprint, identifying potential vulnerabilities across your extensions, web applications, and connected systems.
SOCRadar’s ASM module, Digital Footprint
Proactively discover unknown risks, manage assets, and minimize your attack surface to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. ASM ensures that your digital environment stays secure by identifying and addressing weaknesses before they can be exploited.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
The compromise of Cyberhaven’s Chrome extension (version 24.10.4) can be identified through specific Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) tied to the malicious activity. These IOCs serve as critical clues for identifying whether a device has been compromised and if sensitive data has been exfiltrated.
Extension Version and File Hashes:
- Malicious version: 24.10.4
- Unique file hash for the extension: DDF8C9C72B1B1061221A597168f9BB2C2BA09D38D7B3405E1DACE37AF1587944
JavaScript Files:
- The malicious content.js file contains the hash: AC5CC8BCC05AC27A8F189134C2E3300863B317FB
- worker.js file: 0B871BDEE9D8302A48D6D6511228CAF67A08EC60
Local Storage Keys:
- cyberhavenext_ext_manage: Indicates the presence of a configuration payload downloaded by the extension.
- cyberhaven_ext_log: Present only if data has been exfiltrated to the command-and-control (C&C) server.
Network Traffic (Communication with suspicious C&C servers):
- cyberhavenext[.]pro
- api.cyberhaven[.]pro
- IP addresses: 149.28.124[.]84 and 149.248.2[.]160
Users can also check for potential compromise by accessing the Developer Console in Chrome.
- Open a tab (e.g., mail.google.com).
- Navigate to the Console tab and select Cyberhaven in the list of sources.
- Run the command await chrome.storage.local.get(null).
If results include cyberhavenext_ext_manage and cyberhavenext_ext_log, data may have been exfiltrated.
A more extensive list of IOCs is available here.



































