
Revealing Critical SAP Vulnerabilities and Proof-of-Concept Exploit
In the world of cybersecurity, staying informed about the latest vulnerabilities is crucial for organizations, especially when it comes to business-critical applications like SAP’s Application Server for ABAP.
Recently, researchers from SEC Consult uncovered a PoC (Proof-of-Concept) exploit that takes advantage of four previously discovered critical vulnerabilities in SAP’s NetWeaver Application Server ABAP and ABAP platform, exposing potential risks for organizations. While patches have been released for three of the bugs, the availability of technical details and PoC code raises concerns about targeted attacks. In this article, we will delve into the details of these vulnerabilities and discuss their potential impact on SAP systems.
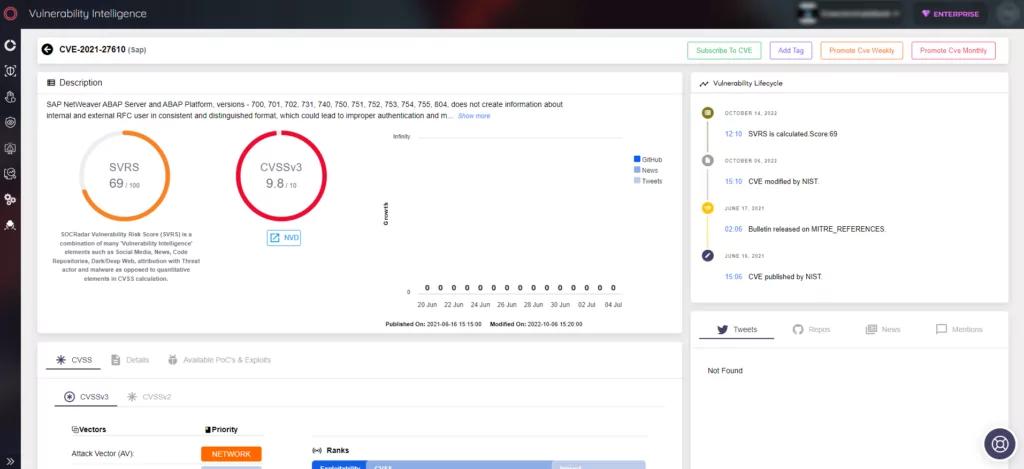
CVE-2021-27610 – Authentication Bypass and Privilege Escalation
One of the identified vulnerabilities allows adversaries to bypass authentication and escalate privileges on affected systems. By exploiting this flaw, attackers can establish their own communication with a vulnerable system, reuse leaked credentials, and impersonate user accounts, ultimately leading to a full system compromise. SAP has addressed this issue with a patch (SAP Security Note 3007182), and affected users are advised to implement the necessary corrections promptly.
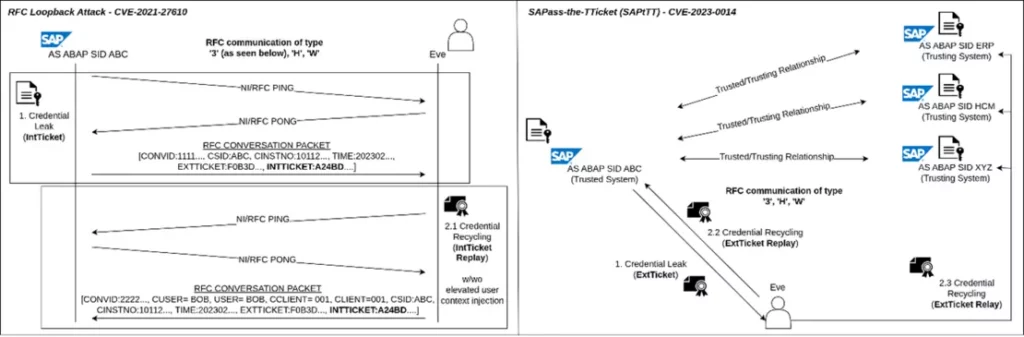
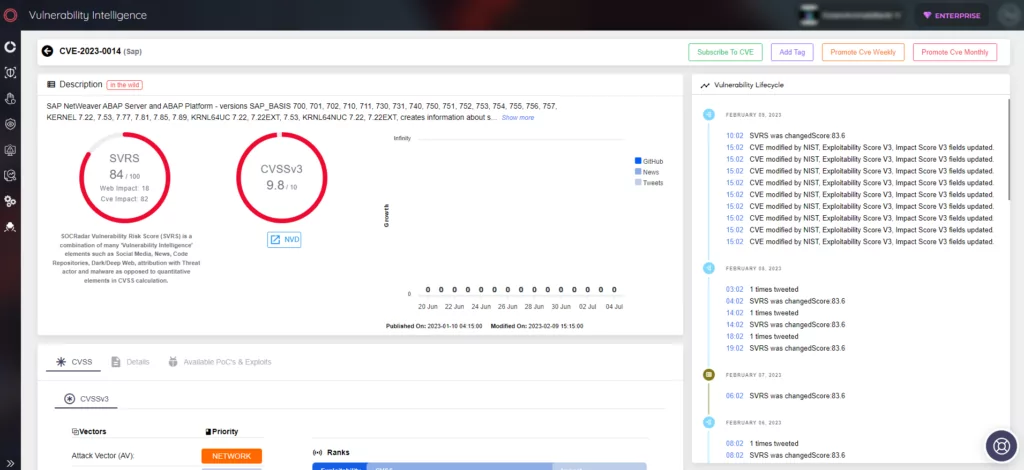
CVE-2023-0014 – Design Issue Enabling Lateral Movement
The second vulnerability discovered in SAP systems revolves around a design flaw in the trusted/trusting architecture, enabling remote attackers to gain illegitimate access to vulnerable systems and move laterally within SAP system landscapes. This flaw, known as “SAPass-the-TTicket,” allows adversaries to claim a trusted identity by reusing leaked logon material, leading to potential system compromise. SAP has released a patch (SAP Security Note 3089413) to address this vulnerability, and organizations are encouraged to follow the provided correction instructions.
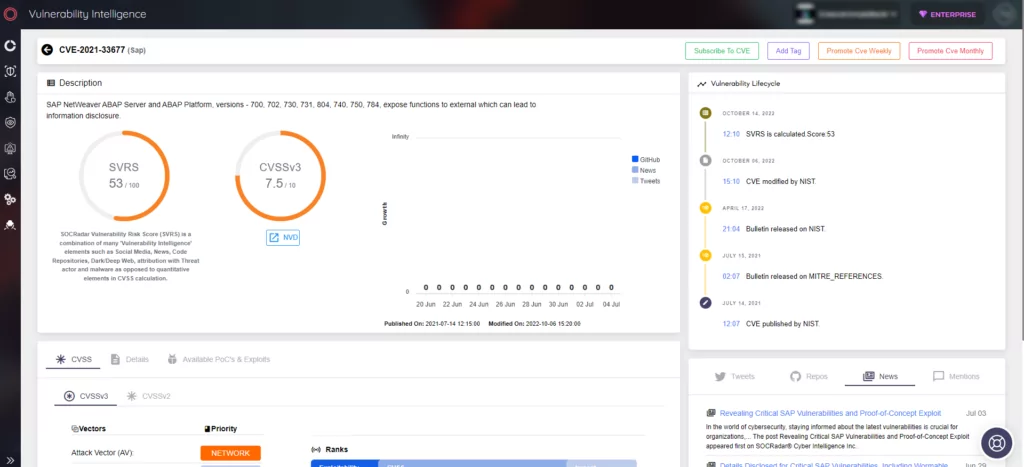
CVE-2021-33677 – Information Disclosure in AutoABAP/bgRFC Interface
Dialog instances of the AS ABAP provide the RFC Gateway service, which has been found to expose specific functions to authenticated yet unauthorized users. Exploiting this vulnerability, adversaries can remotely enumerate valid user accounts, perform requests to targeted hosts and ports, and combine the obtained information with other vulnerabilities to orchestrate further attacks. SAP has issued a patch (SAP Security Note 3044754) to mitigate this risk, and users should ensure they apply the necessary fixes.
CVE-2021-33684 – Out-of-Bounds Write and Memory Corruption
The fourth vulnerability affects the AS ABAP’s RFC Gateway service, where a memory corruption bug can be triggered by specially crafted RFC packets containing malformed logon material. Exploiting this flaw, attackers can remotely crash processes, corrupt authentication data integrity, and potentially gain code execution. SAP has released a patch (SAP Security Note 3032624) to address this vulnerability, and organizations should promptly implement the recommended fixes.
Mitigation and Countermeasures:
These vulnerabilities pose significant risks to organizations utilizing SAP’s ABAP technology stack across various business-critical products. Attackers can remotely execute arbitrary code, access critical data, move laterally within SAP systems, and execute malicious actions. SAP has released patches for the identified vulnerabilities, and organizations are strongly advised to apply them promptly. Additionally, the following measures are recommended to enhance system security:
- Upgrade affected software components and follow post-installation steps recommended by SAP.
- Limit network-wise access (RFC/HTTP) to vulnerable servers to minimize the attack surface.
- Enforce encrypted server-to-server communications using HTTPS and SNC.
- Reduce authorization distributions and restrict function calls to minimize potential risks.
- Follow the guidelines provided by SAP in their security notes and FAQs.
While the availability of technical details and PoC code increases the likelihood of targeted attacks, organizations should also consider additional security measures. Limiting network-wise access to vulnerable servers, enforcing encrypted server-to-server communications, and reducing authorization distributions can help minimize the attack surface. Moreover, monitoring function calls and implementing the recommended measures outlined in the corresponding SAP notes and FAQs will enhance system security.
The discovery of these critical vulnerabilities in SAP systems highlights the importance of timely patching and proactive security measures. Organizations must take immediate action to protect their business-critical applications and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their data. By staying vigilant and implementing the necessary mitigations, organizations can mitigate the risks associated with these SAP vulnerabilities.


































