
The Role of Firewalls in Modern Computer Security
Firewalls are an essential part of modern computer security, acting as network protection’s first line of defense. Via regulating incoming and outgoing traffic, firewalls prevent unauthorized access and safeguard sensitive information. This blog will explore their role in network security, the types of firewalls available, how to set them up effectively.
Role of Firewalls in Network Security
Firewalls are pivotal in ensuring a secure computing environment. They monitor and control traffic based on predefined security rules, blocking malicious traffic while allowing legitimate communication. By acting as a barrier between your network and potential threats, firewalls help prevent cyberattacks such as malware infiltration, ransomware, and unauthorized data access. Beyond essential protection, firewalls provide the following benefits:
- Intrusion Prevention: Detect and block suspicious activities.
- Data Protection: Safeguard sensitive data from unauthorized access.
- Policy Enforcement: Enforce organizational security policies.
- Network Segmentation: Divide a network into segments to contain potential breaches.
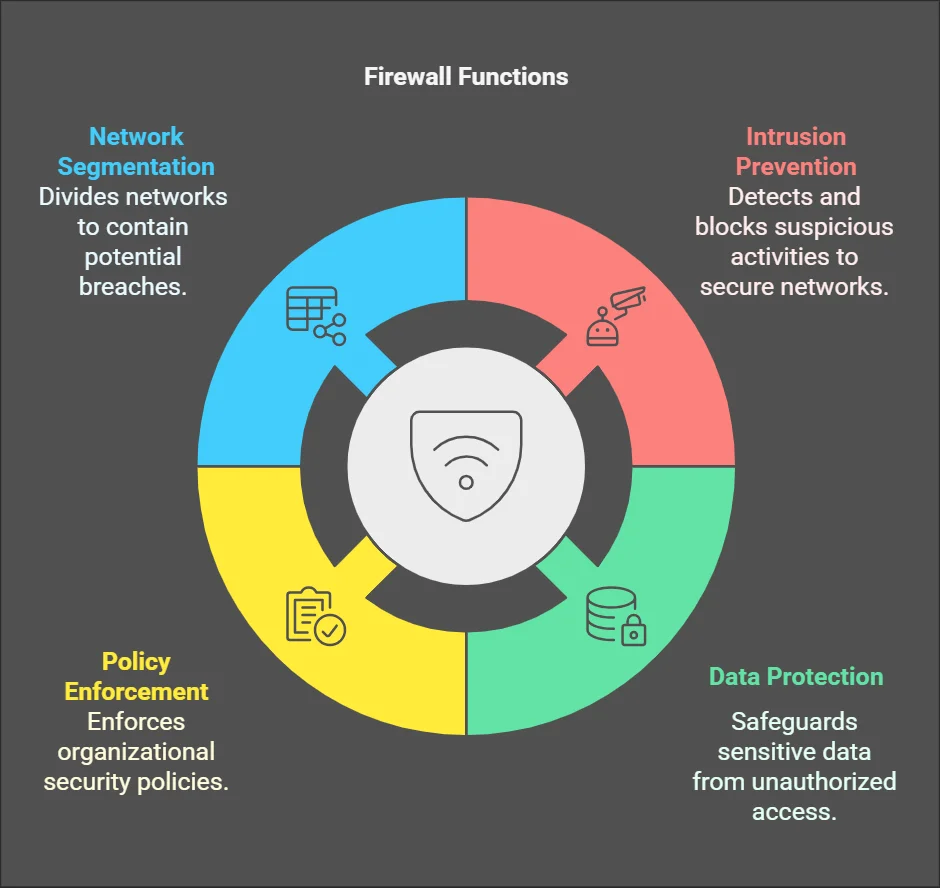
Beyond essentials, firewall functions (Napkin.ai)
Modern firewalls, often integrated with advanced features such as Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS), have become indispensable in a robust security strategy.
Types of Firewalls
Firewalls come in various forms, each suited to specific security needs. Below are the primary types:
- Packet-Filtering Firewalls: Analyze individual data packets, allowing or blocking them based on predefined rules. These are basic but effective for smaller networks.
- Stateful Inspection Firewalls: Monitor active connections and make decisions based on the state and context of network traffic.
- Proxy Firewalls: Act as intermediaries between users and the internet, inspecting all traffic before it reaches the internal network.
- Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFW): Combine traditional firewall capabilities with advanced features like application awareness, IDPS, and malware filtering.
- Cloud-Based Firewalls: Ideal for businesses leveraging cloud infrastructure, offering scalable and flexible protection.
- Hardware vs. Software Firewalls: Hardware firewalls are physical devices that protect entire networks, while software firewalls are installed on individual devices to provide localized security.
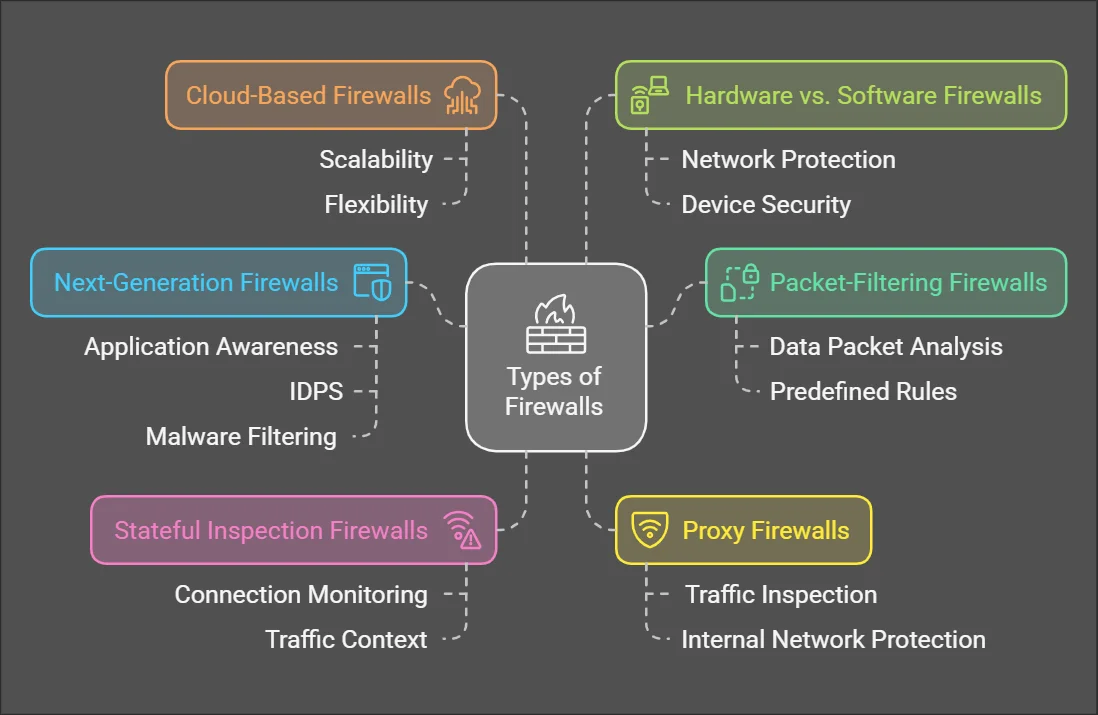
Primary types of Firewall (Napkin.ai)
How Firewalls Work
Firewalls operate by establishing a set of rules to control traffic. These rules are based on IP addresses, domain names, protocols, and ports. Here’s a simplified overview of their operation:
- Packet Filtering: Firewalls analyze data packets and decide whether to permit or block them based on security rules.
- Stateful Inspection: They assess the state of active connections to ensure that traffic matches expected patterns.
- Deep Packet Inspection (DPI): Advanced firewalls inspect packets’ content to identify hidden threats like malware.
How to Set Up Firewalls
Setting up a firewall requires careful planning to ensure optimal security without disrupting legitimate network activities. Here are the steps to follow:
- Identify Security Needs: Assess the specific requirements of your network to determine the most suitable type of firewall.
- Choose the Right Firewall: Choose a firewall that aligns with your organization’s needs, whether hardware, software, or a cloud-based solution.
- Define Rules and Policies: Establish clear rules to govern traffic, specifying what to allow and block.
- Configure the Firewall: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to install and configure it, tailoring it to your network structure.
- Test and Monitor: Regularly test the firewall’s effectiveness and monitor traffic logs to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
- Update and Maintain: Keep the firewall updated to address new threats and ensure continued protection.
Common Firewall Misconfigurations and How to Avoid Them
Despite their importance, firewalls can be rendered ineffective by common misconfigurations. Here are some pitfalls to avoid:
- Overly Permissive Rules: Allowing too much traffic can expose your network to threats.
- Unnecessary Open Ports: Ensure only necessary ports are open to reduce potential attack vectors.
- Outdated Firmware: Regularly update firmware to fix vulnerabilities.
- Lack of Monitoring: Continuously monitor firewall logs for suspicious activities.
Addressing these issues ensures that your firewall operates at peak efficiency.
Advanced Features of Modern Firewalls
Modern firewalls come equipped with advanced functionalities that enhance their effectiveness:
- Threat Intelligence Integration: Leverage real-time threat data to block emerging risks.
- VPN Support: Secure remote connections for employees working outside the office.
- Content Filtering: Restrict access to malicious or inappropriate websites.
- Application Control: Manage and monitor the use of specific applications on the network.
These features make firewalls an integral part of a comprehensive security strategy.
Summary
Firewalls are a cornerstone of modern computer security, providing vital protection against cyber threats. Organizations can significantly enhance their network defense by understanding their role, choosing the right type, and setting them up correctly. Regular maintenance and leveraging advanced features further strengthen their effectiveness. In today’s digital landscape, investing in a robust firewall solution is not just an option—it’s necessary to safeguard your digital assets.




































