
Understanding the Components of Information Security Risk Management
Information Security Risk Management (ISRM) plays a critical role in safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring that risks are identified, assessed, and managed effectively. ISRM is a structured, continuous process aimed at protecting the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information, while adapting to an evolving threat landscape.
What is Information Security Risk Management?
Information Security Risk Management (ISRM) is a critical process that identifies, assesses, and mitigates risks associated with the use of information technology to safeguard an organization’s information assets. This process ensures data confidentiality, integrity, and availability, all of which are required to maintain operational efficiency and protect sensitive information from potential threats.

AI illustration of Information Security Risk Management
Information Security Risk Management is an ongoing effort that requires continuous risk monitoring and reassessment in order to adapt to the ever-changing cyber threat landscape. ISRM’s ultimate goal is to manage risks in line with an organization’s overall risk tolerance, ensuring that the measures taken are proportional to the potential impact of the risks.
Cybersecurity Risk Management Frameworks
To effectively manage risks, organizations often adopt cybersecurity risk management frameworks. These frameworks provide structured guidelines for assessing and managing risks related to information security. Common frameworks include the NIST Cybersecurity Framework and ISO/IEC 27001/27005, which offer a set of best practices for identifying risks, implementing controls, and continuously monitoring for potential threats.
These frameworks help organizations create a formalized approach to information security risk management, ensuring that they remain resilient against evolving cyber threats while maintaining compliance with industry regulations.
NIST
Cybersecurity Risk Management Frameworks (RMFs) provide a structured approach for managing security and privacy risks within organizations. The framework outlined in the NIST SP 800-37 Rev. 2 takes a system life cycle approach and integrates both security and privacy considerations throughout.

NIST logo
Key updates to this framework include aligning it with the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, incorporating privacy risk management processes, and integrating supply chain risk management. The RMF provides steps such as categorizing information, selecting and implementing controls, continuous monitoring, and authorizing systems to ensure risks to organizational assets, operations, and individuals are managed effectively.
The goal of the RMF is to offer a flexible and repeatable process to help organizations reduce risks while supporting their missions and business processes. Continuous monitoring and real-time risk management are critical to ensure risks are addressed promptly as the environment or system changes. It also emphasizes organizational-wide preparation for risk management, ensuring that system-level activities are aligned with broader mission goals.
ISO/IEC 27001/27005
Provides a framework for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an Information Security Management System (ISMS). The standard integrates risk management as a key component of managing cybersecurity.
ISO/IEC 27001:2022
Cybersecurity Risk Management:
- Risk Assessment: In ISO/IEC 27001:2022 risk assessment process involves defining and applying criteria to systematically identify and evaluate information security risks. Organizations must establish risk acceptance criteria and ensure that risk assessments produce consistent, reliable results. The process begins with identifying risks related to the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information, followed by assessing the potential consequences and likelihood of these risks. Based on this analysis, risks are evaluated and prioritized for treatment according to their severity. Documented information must be retained to ensure that the process is transparent and verifiable.
- Risk Treatment: The risk treatment process involves selecting appropriate options to address the identified risks. Organizations must choose treatment actions based on the results of the risk assessment, which can include mitigating, avoiding, transferring, or accepting risks. Necessary controls are determined and compared with those listed in a provided table in the document, to ensure none are omitted. The organization must produce a Statement of Applicability, outlining the necessary controls, their implementation status, and justifications for any exclusions. A risk treatment plan is formulated, and approval from risk owners is required for both the plan and any residual risks.
ISO/IEC 27005:2022
ISO/IEC 27005:2022 introduces several improvements and additions to enhance guidance for managing information security risks in alignment with ISO/IEC 27001. This edition aligns more closely with ISO 31000:2018, ensuring that terminology and structure are consistent across risk management standards. Notable improvements include the introduction of risk scenario concepts, offering organizations new ways to model and anticipate security risks based on sequences of events. Additionally, the standard contrasts event-based approaches with asset-based approaches to risk identification, giving organizations flexibility in how they approach risk management.
The document also consolidates the tables into a single, streamlined table, providing more cohesive guidance on supporting techniques for risk assessment processes. This version emphasizes the iterative nature of risk assessment and treatment, promoting cycles of reassessment to ensure that risks remain properly managed in evolving contexts. These changes enhance the alignment between ISO/IEC 27005 and ISO/IEC 27001, ensuring more effective implementation of risk management processes.
Importance of Continuous Monitoring in Information Security Risk Management
Continuous monitoring is an essential component of effective Information Security Risk Management (ISRM), ensuring that organizations are alert to emerging threats and vulnerabilities. In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, where cyber threats evolve quickly, static security measures are no longer adequate.
Continuous monitoring allows organizations to detect and respond to potential security incidents in real time, providing valuable insights into unusual activity and potential breaches. Organizations that consistently track network behavior, system vulnerabilities, and data access can quickly mitigate risks, avoid data breaches, and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
SOCRadar’s advanced monitoring solutions take this concept to a new level. SOCRadar’s offerings include Brand Protection, Vulnerability Intelligence, Threat Detection and Response, Attack Surface Management, and Dark Web Monitoring, giving organizations 24/7 visibility into potential risks.
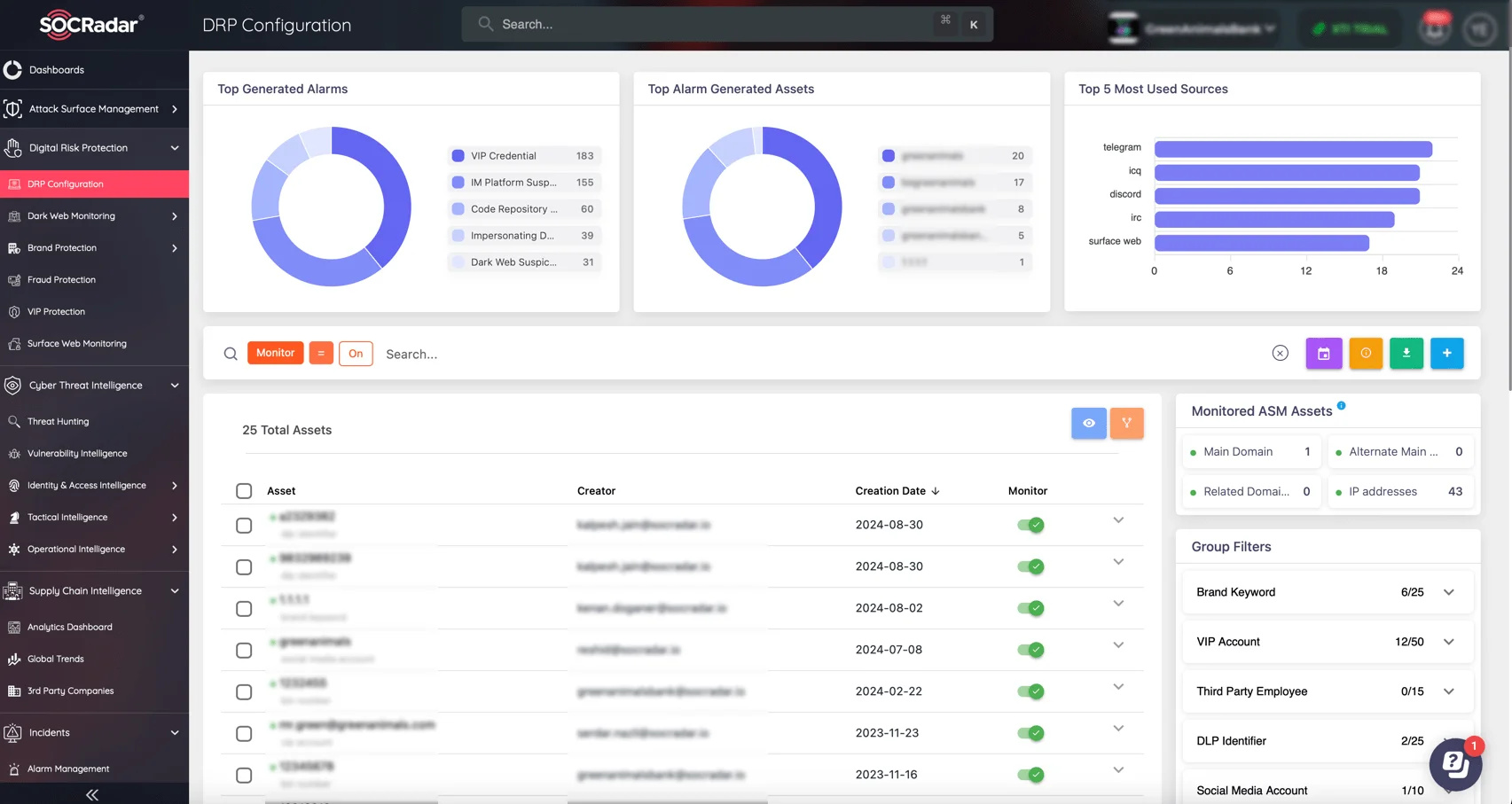
SOCRadar’s Digital Risk Protection real time monitoring
These tools provide real-time alerts for emerging threats, allowing businesses to stay ahead of cybercriminals while ensuring comprehensive security across all digital assets. SOCRadar keeps businesses up to date on their ever-changing security landscape by monitoring brand misuse, detecting threats on the dark web, and managing attack surfaces.
Conclusion
Information Security Risk Management (ISRM) is a continuous process that helps organizations navigate the complex and changing landscape of cyber threats. By constantly monitoring for new risks, reassessing existing vulnerabilities, and adapting security strategies, ISRM enables businesses to proactively defend their most valuable assets—data and systems.
Implementing established frameworks such as NIST and ISO/IEC 27001/27005 provides a systematic approach to identifying and managing risks while adhering to industry standards. These frameworks, when combined with continuous monitoring tools like SOCRadar, help organizations remain resilient to emerging threats, allowing them to protect their operations and achieve long-term business objectives.
ISRM’s strength lies in its ability to align with organizational goals, creating a secure environment that promotes growth, innovation, and operational continuity in a rapidly changing digital world.




































