Zyxel Firewall Flaws Exploited: Urgent Action Required
[Update] July 24, 2023: Threat actors are targeting several Zyxel devices with CVE-2023-28771. Fortinet has detected a significant rise in botnet attacks associated with this vulnerability. Added the subheading: “Increase in Botnet Attacks Targeting Zyxel Command Injection Vulnerability (CVE-2023-28771).”
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has added two recently discovered vulnerabilities in Zyxel firewalls to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog.
These vulnerabilities, known as CVE-2023-33009 and CVE-2023-33010, have been actively exploited and pose serious risks. They have a CVSS score of 9.8 assigned by Zyxel, indicating their criticality. However, NVD Analysts have not published a CVSS score for these CVEs at this time.
These vulnerabilities are buffer overflow flaws that allow unauthorized attackers to execute remote code and cause a Denial-of-Service (DoS).
What are CVE-2023-33009 & CVE-2023-33010?
The CVE-2023-33009 vulnerability relates to a buffer overflow issue present in the notification function of certain firewall versions.
CVE-2023-33010 pertains to a buffer overflow vulnerability in the ID processing function found in specific firewall versions.
Which Zyxel Versions Are Affected?
Zyxel released patches to address these security risks on May 24, 2023. The following Zyxel devices are affected by the vulnerabilities:
|
Affected Series |
Affected versions for CVE 2023 33009/CVE 2023 33010 |
Latest Firmware |
|
ATP |
ZLD V4.32 to V5.36 Patch 1 |
ZLD V5.36 Patch 2 |
|
USG FLEX |
ZLD V4.50 to V5.36 Patch 1 |
ZLD V5.36 Patch 2 |
|
USG FLEX50(W) / USG20(W)-VPN |
ZLD V4.25 to V5.36 Patch 1 |
ZLD V5.36 Patch 2 |
|
VPN |
ZLD V4.30 to V5.36 Patch 1 |
ZLD V5.36 Patch 2 |
|
ZyWALL/USG |
ZLD V4.25 to V4.73 Patch 1 |
ZLD V4.73 Patch 2 |
To ensure network security and protect against potential threats, Federal Civilian Executive Branch (FCEB) agencies are required to address these vulnerabilities by June 26, 2023.
Although the exact details of the attacks remain unknown, it is worth noting that the discovery of these vulnerabilities follows the exploitation of another flaw tracked as CVE-2023-28771, in Zyxel firewalls, which led to the compromise of susceptible devices through the Mirai botnet.
Increase in Botnet Attacks Targeting Zyxel Command Injection Vulnerability (CVE-2023-28771)
In June, Fortinet discovered the spread of several Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) botnets that exploit the Zyxel vulnerability, CVE-2023-28771 (CVSS score: 9.8, Critical).
CVE-2023-28771 is a remote unauthenticated command injection vulnerability. It resides in the Internet Key Exchange (IKE) packet decoder over UDP port 500 on the WAN interface of several Zyxel devices. Unauthorized attackers can exploit the vulnerability by sending a specially crafted packet to the targeted device and execute arbitrary code with root privileges on multiple firewall models. Furthermore, the affected devices are vulnerable in their default configuration.
The following devices are affected by CVE-2023-28771:
- ATP, versions 4.60 to 5.35
- USG FLEX, versions 4.60 to 5.35
- VPN, versions 4.60 to 5.35
- ZyWALL/USG, versions 4.60 to 4.73
Malicious activity has increased significantly since the exploit module was made available. FortiGuard Labs discovered several botnets, including Dark.IoT, a Mirai variant, as well as links to Rapperbot malware and the Katana botnet.
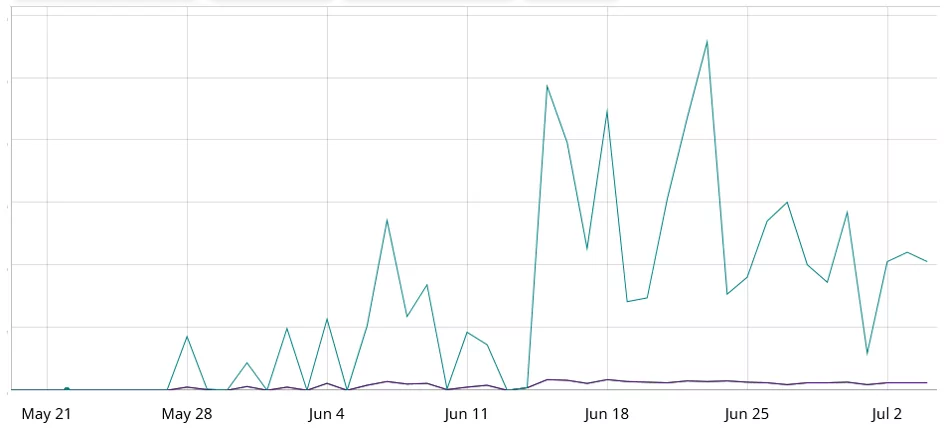
The researchers traced the attack source IP address using exploit traffic analysis, revealing attacks in Central America, North America, East Asia, and South Asia. Distinct IP addresses, namely 193[.]32[.]162[.]190, 109[.]205[.]213[.]30, 109[.]207[.]200[.]42, 109[.]207[.]200[.]47, and 109[.]207[.]200[.]44, serve as the origins of these attacks.
The primary focus of these attacks is the command injection vulnerability on Zyxel devices. The attackers employ tools like curl or wget to download scripts for executing further malicious actions.
According to Fortinet, the acquired script files are exclusively designed for the MIPS processor architecture, indicating a highly specific target, and the campaign employs multiple servers for launching attacks and quickly updates itself to maximize Zyxel device compromise within a few days.
For Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) and technical analysis of the botnet variants used in attacks, refer to Fortinet’s research.
Mitigations for Zyxel Vulnerabilities
Taking immediate action to patch the Zyxel firewall vulnerabilities is crucial to protect networks from exploitation. By prioritizing security measures and following Zyxel’s guidance, organizations can safeguard their infrastructure from potential cyber threats and maintain the integrity of their operations.
To mitigate potential risks and enhance network security, Zyxel has issued the following guidance to its customers:
- Disable HTTP/HTTPS services from the Wide Area Network (WAN) unless absolutely necessary.
- Disable UDP Port 500 and Port 4500 if you do not require the use of the IPSec VPN function.
Other Vulnerabilities Added to CISA’s KEV Catalog
In addition to the Zyxel vulnerabilities, other critical vulnerabilities from different vendors have been added to CISA’s KEV catalog. Here are some notable vulnerabilities:
- Huawei EMUI: A lack of length check vulnerability in the HW_KEYMASTER module could lead to an out-of-bounds read. This vulnerability, assigned CVE-2021-46887, has a CVSS score of 9.8.
- Microsoft Windows 10: A remote code execution vulnerability in the Windows Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) has been identified. Assigned CVE-2022-35744, this vulnerability has a CVSS score of 9.8.
- AudioCodes Device Manager Express: Multiple vulnerabilities have been discovered, including an unauthenticated SQL injection (CVE-2022-24627) and a directory traversal leading to remote code execution (CVE-2022-24629). Both vulnerabilities have a CVSS score of 9.8.
- Samsung Galaxy Store: Several vulnerabilities have been found, including improper scheme validation vulnerability (CVE-2023-21514) with CVSS score of 9.8, XSS vulnerability (CVE-2023-21516) with CVSS score of 9.6, and Improper scheme validation vulnerability (CVE-2023-21515) with CVSS score of 8.8. These vulnerabilities have the potential to allow JavaScript API execution, enabling the installation of APK files from the Galaxy Store.
- Additional Microsoft vulnerabilities: Windows systems are affected by multiple vulnerabilities, such as the Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP) Remote Code Execution vulnerabilities (CVE-2022-35753 and CVE-2022-35745) with CVSS scores of 8.1.
Make sure to stay updated with the published information and apply necessary patches to mitigate these risks.
Stay Informed with SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence
SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence provides in-depth information about vulnerabilities, allowing you to stay informed about the latest trends in exploitation.
By having visibility into vulnerabilities within your organization, you can prioritize patching efforts and enhance the overall security posture of your organization.