What are CVSS Scores?
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (also known as CVSS) assigns a number value (0-10) to the severity of a security vulnerability. CVSS scores are often used by security professionals as part of a vulnerability management program to compare and prioritize the process of remediation.
Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS)
A CVSS score can alternatively be represented as a vector string, which is a compressed textual representation of the values used to calculate it. As a result, CVSS is a good fit as a standard measuring system for enterprises, organizations, and governments that require precise and consistent vulnerability severity scores.
Since 2005, CVSS scoring algorithms have undergone three major updates and several minor revisions. The shift from CVSSv2 to CVSSv3, with CVSSv3.1 being the most recent revision, was the most recent revision. The security community believes that CVSSv3, which was created to address the vulnerabilities in v2, has addressed some, but not all, of the vulnerabilities in v2.
When mapped onto a qualitative scale, CVSSv3 scores look like this:
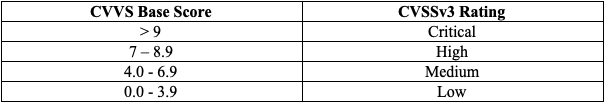
For reducing the security risks, many organizations, for example, prioritize and fix “critical” vulnerabilities within seven business days, while “medium” ones are patched within 30 days. PCI DSS standards also suggest that medium to critical level vulnerabilities should be remediated rapidly.
Why is CVSS crucial for Vulnerability Management?
Since it is an open platform, companies have complete access to the parameters used to calculate ratings, allowing everyone to understand the reasoning and differences behind any vulnerability scores. This makes it easier for security teams to assess the severity of vulnerabilities on their systems and prioritize which ones should be addressed first.
CVSS is an essential part of the overall vulnerability context scheme; however, it should be used with other vital components such as asset exposure level, potential business impact, and threat context.
Threat context typically represents the perspective of external threat intelligence, measuring the risk of exploiting this specific flaw by collecting and analyzing data from a broad range of data sources, including honeypots, deep web black markets, and dark web forums where recent activities of threat actors can be monitored.
Considering all these components holistically is essential for effective vulnerability management and intelligence program.
Using CVSS only for prioritization without considering the organization’s business risks and threat model can cause failures. Recently discovered Log4j 2 vulnerabilities revealed how important it is to have a holistic perspective while assessing the vulnerabilities for prioritization.
What are Vulnerability Metrics?
There are three types of metrics in CVSS: Base, Temporal, and Environmental. The Base metrics generate a score between 0 and 10, which can subsequently be adjusted by scoring the Temporal and Environmental measurements.

First, the vulnerability’s features are represented by the metric base group. Second, temporal metrics describe a vulnerability’s characteristics as they evolve. However, it fails to account for the various user environments. On the other hand, environmental metrics indicate the features of a vulnerability while considering the user’s surroundings.
The Organizations Calculating CVSS Scores
CVSS scores for practically all known vulnerabilities may be found in the National Vulnerability Database (NVD), maintained by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
The NVD gives CVSS base scores, which indicate each vulnerability’s inherent properties. Currently, the NVD does not offer “temporal scores” or “environmental scores.” However, the NVD provides CVSS calculators that can be used to incorporate temporal and environmental score data.
Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE)
CVE is another standard that vulnerability management professionals must understand to manage and assess vulnerabilities efficiently. The various technologies identifying vulnerabilities use CVE IDs, a unique identifier to reference newly discovered issues and further investigate the risk.
The Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) program is a glossary or dictionary of security vulnerabilities in specific codebases, such as software applications or open libraries. This list lets interested parties obtain information on vulnerabilities by referring to the CVE ID, a unique identifier.
CVE was created in 1999 and is handled and maintained by the MITRE Corporation’s (National Cybersecurity FFRDC (Federally Funded Research and Development Center). The US Department of Homeland Security (DHS) and the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) contribute operating funds to CVE, which the US Federal Government funds. CVE is a public database that anyone can access and use for free.



































