
New Ivanti CSA Zero-Days Under Active Exploitation; Critical RCE in Connect Secure & Policy Secure
[UPDATE] October 14, 2024: “Nation-State Attack Exploits Ivanti CSA Vulnerabilities, More Details Are Revealed”
Ivanti has alerted its customers to three newly discovered zero-day vulnerabilities in its Cloud Service Appliance (CSA), which are currently under active exploitation. These flaws, tracked as CVE-2024-9379, CVE-2024-9380, and CVE-2024-9381, enable threat actors to execute SQL injection, command injection, and path traversal attacks, posing serious risks if left unaddressed.
In a recent advisory, the company acknowledged that several customers using older versions of CSA have already been targeted by chaining these zero-days with a previously identified vulnerability, CVE-2024-8963.
Among the latest Ivanti patches is also a critical Remote Code Execution (RCE) flaw, impacting Connect Secure and Policy Secure. What’s more concerning is that the technical and exploitation details for this vulnerability are also available, escalating the urgency for organizations to update their systems immediately.
What Happened?
In September, Ivanti released patches for CVE-2024-8190, a critical RCE vulnerability in Ivanti CSA. Shortly after the patch, it was discovered that attackers were chaining this vulnerability with CVE-2024-8963 to bypass authentication and enable remote code execution.
Most recently, the company disclosed that CVE-2024-8963 has also been chained with additional Ivanti CSA vulnerabilities to target a limited number of customers. However, while Ivanti’s notice mentions three new flaws (CVE-2024-9379, CVE-2024-9380, and CVE-2024-9381) being combined with CVE-2024-8963, their advisory only confirms use of CVE-2024-9379 and CVE-2024-9380 in exploit chains.
Details of New Ivanti CSA Zero-Day Vulnerabilities: CVE-2024-9379, CVE-2024-9380, CVE-2024-9381
Ivanti discovered the new vulnerabilities (CVE-2024-9379, CVE-2024-9380, and CVE-2024-9381) while investigating previous exploits of CVE-2024-8963 and CVE-2024-8190. These new vulnerabilities, exploited as zero-days, are described below:
- CVE-2024-9379 (CVSS: 6.5) is an SQL injection vulnerability in the admin web console of Ivanti CSA, allowing an authenticated attacker with admin privileges to run arbitrary SQL commands.
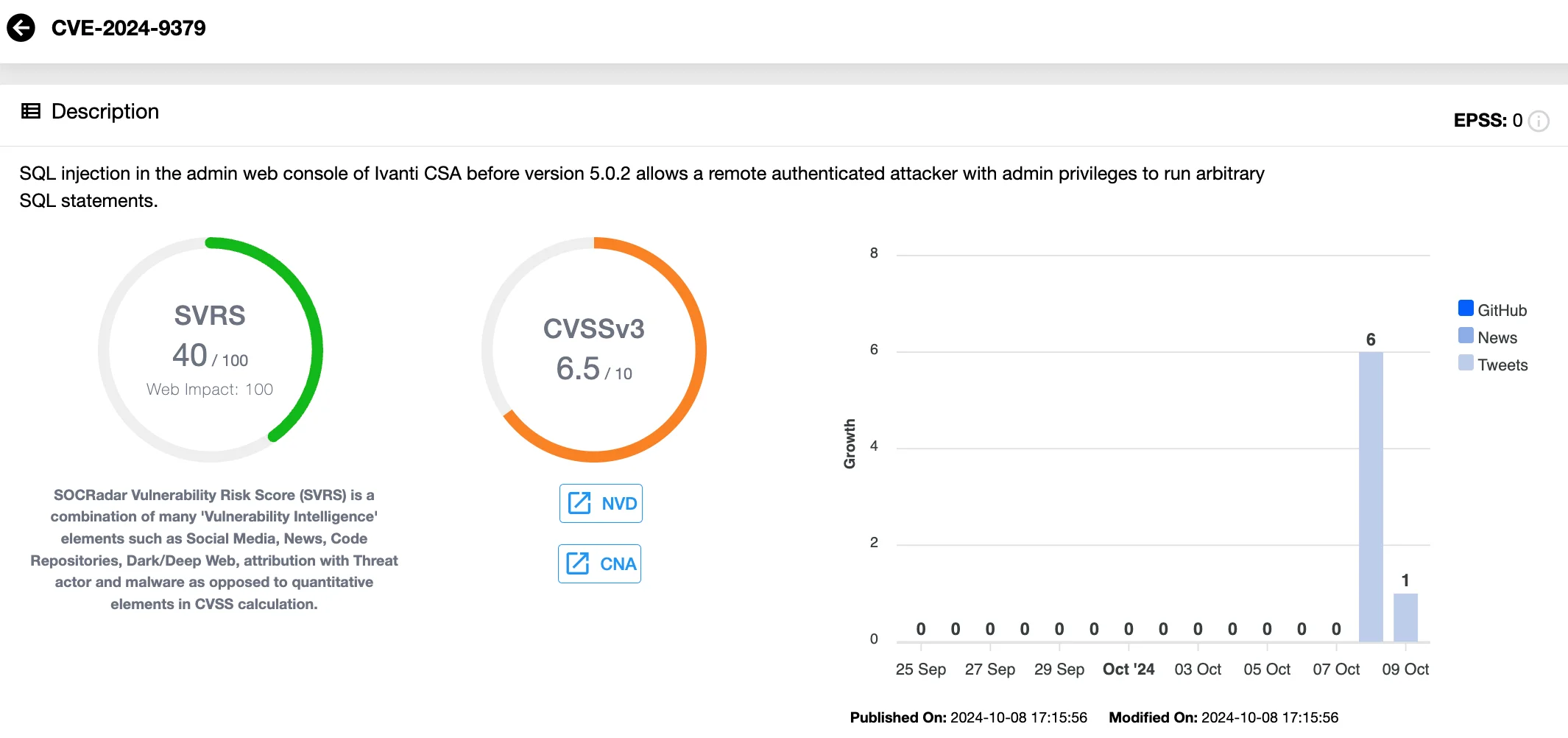
Details of CVE-2024-9379 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
- CVE-2024-9380 (CVSS: 7.2) is an OS command injection flaw that enables authenticated attackers to execute remote code on vulnerable systems, provided they have admin privileges.
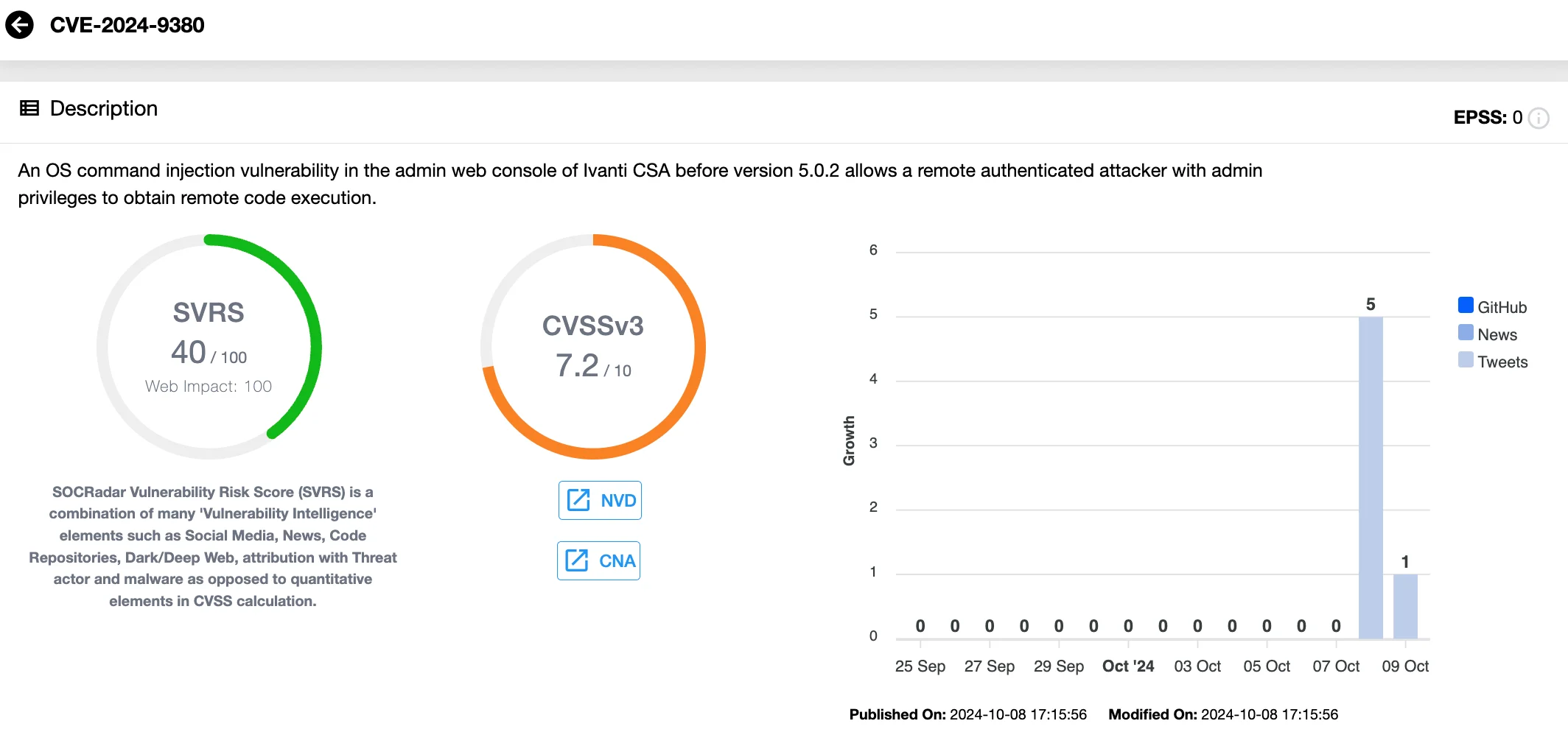
Details of CVE-2024-9380 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
- CVE-2024-9381 (CVSS: 7.2) is a path traversal vulnerability that allows remote attackers with admin privileges to bypass security restrictions.
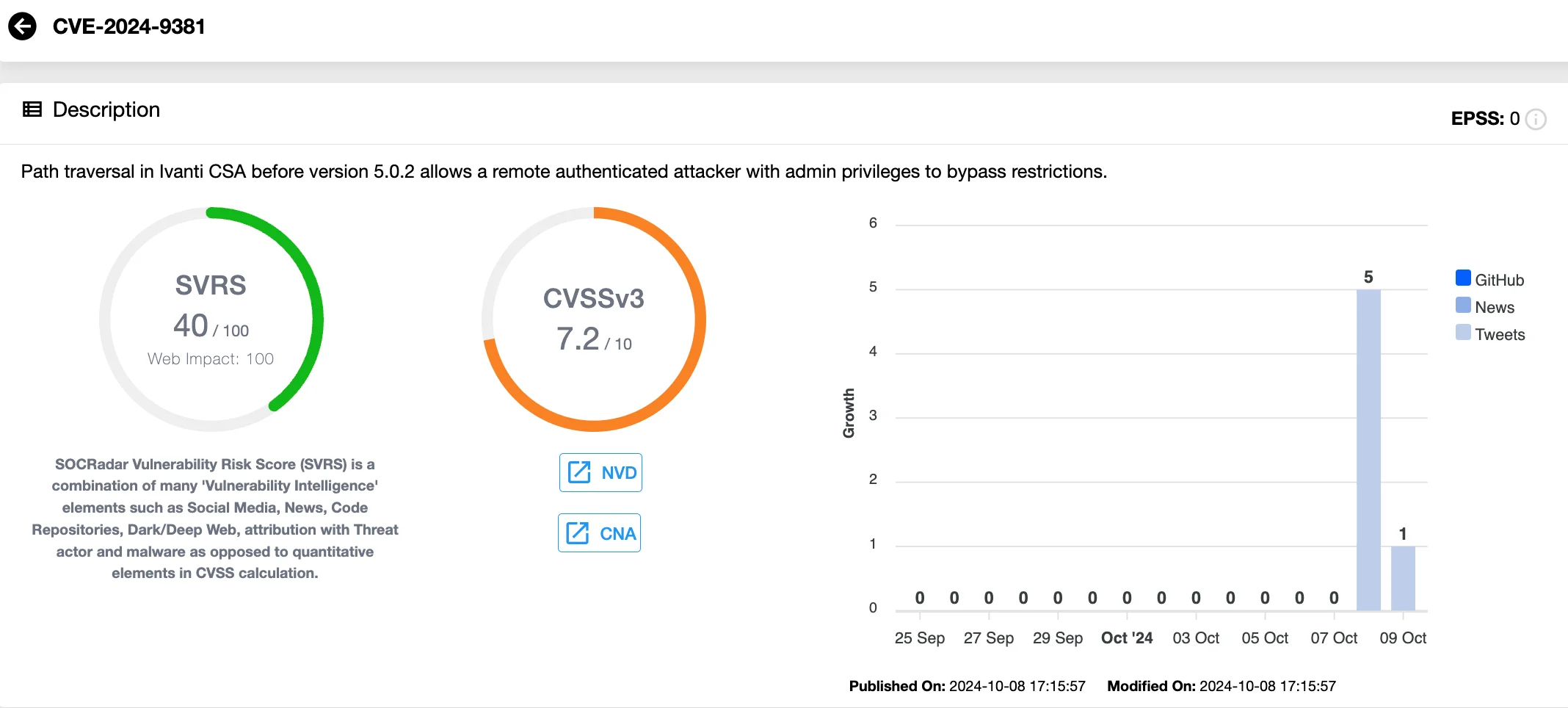
Details of CVE-2024-9381 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Though these vulnerabilities were discovered in CSA 4.6, Ivanti confirmed that they also exist in CSA 5.0, but have not yet been exploited. The company reported exploitation attempts on a limited number of customers using CSA 4.6 patch 518 or earlier, where attackers chained these flaws with CVE-2024-8963.
Which Ivanti CSA Versions Are Affected?
Ivanti has confirmed that these vulnerabilities affect Ivanti CSA versions 5.0.1 and earlier, with a particular focus on CSA version 4.6 patch 518 and below, allowing unauthenticated remote code execution.
Threat actors appear to be chaining CVE-2024-8963 with CVE-2024-9379 OR CVE-2024-9380 in each attack, as Ivanti states, rather than exploiting them all simultaneously. Ivanti has also clarified that there is currently no evidence of exploitation in environments running CSA 5.0.
Update Ivanti CSA to 5.0.2 to Prevent Exploitation
Ivanti urges all users to update their Cloud Service Appliance (CSA) to version 5.0.2 to protect against these vulnerabilities. Users should also check for signs of compromise, such as newly added or modified administrative accounts, and monitor for alerts from Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools.
For more details, visit Ivanti’s official security advisory.
In today’s fast-moving threat landscape, attackers are quick to exploit vulnerabilities, as seen in recent Ivanti CSA attacks. Staying updated on the latest risks is vital to prevent being caught off guard. SOCRadar offers real-time alerts and detailed analysis on vulnerabilities, helping organizations prioritize patches and mitigate risks effectively before they can be exploited.
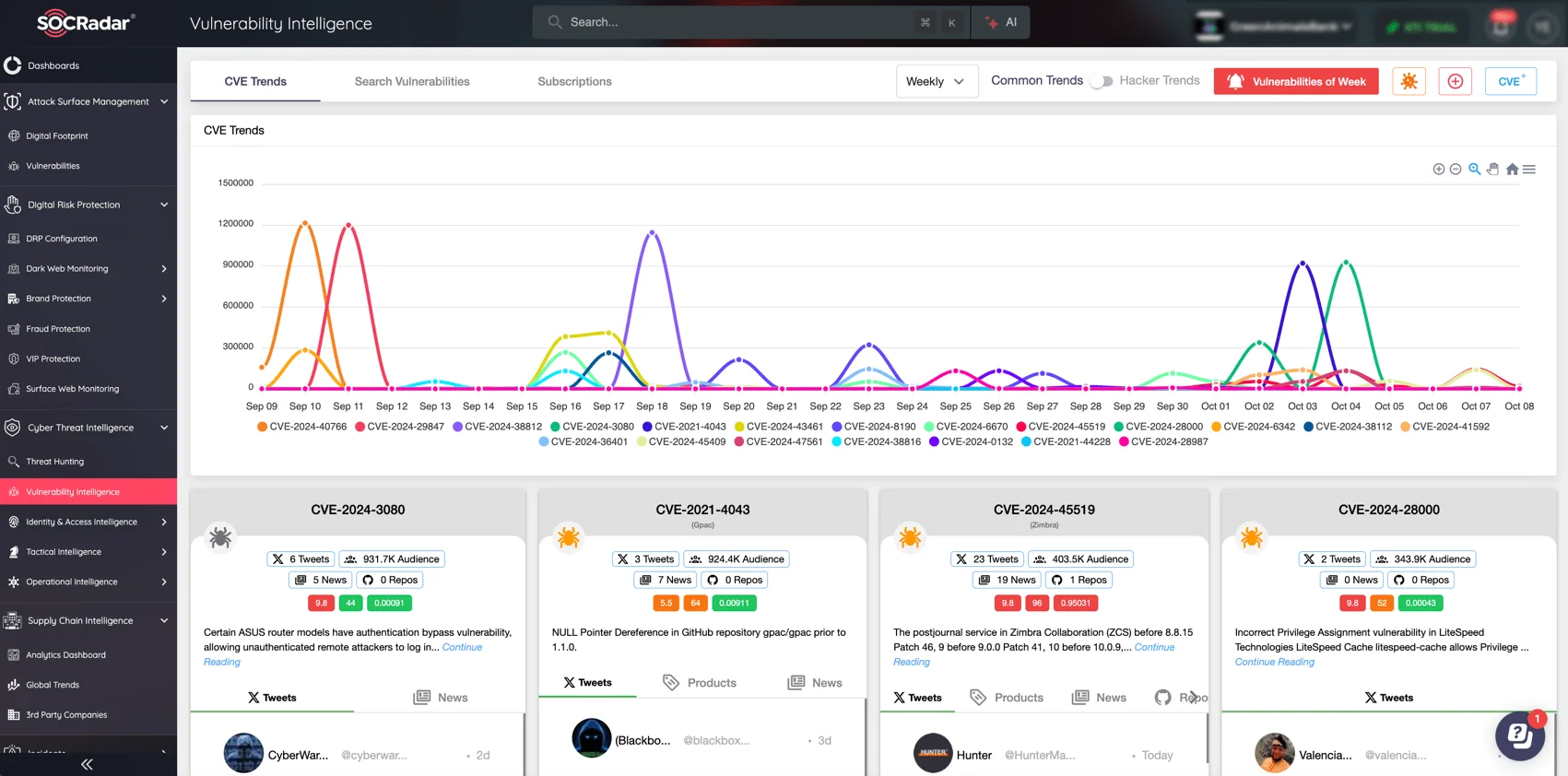
Get real-time alerts, in-depth analysis, and actionable insights with Vulnerability Intelligence to prioritize patches and mitigate risks before attackers can exploit them.
Check out SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence module to easily keep track of newly identified vulnerabilities and related threat activity in real time.
Nation-State Attack Exploits Ivanti CSA Vulnerabilities, More Details Are Revealed
Fortinet’s FortiGuard Labs has released new details about the exploitation of Ivanti Cloud Services Appliance (CSA) vulnerabilities. In their investigation, they uncovered that a nation-state adversary exploited CVE-2024-8190 alongside two previously undisclosed vulnerabilities
The attack, detected in September 2024, began with the exploitation of a path traversal vulnerability in the /client/index.php resource, enabling unauthorized access to sensitive information. This was followed by leveraging the command injection vulnerability in /gsb/reports.php to establish persistent access and execute arbitrary commands on the CSA appliance.
In addition to exploiting these vulnerabilities, the attackers also demonstrated sophisticated tactics by patching the same flaws they used, preventing other actors or researchers from accessing the compromised systems. Lateral movement within the victim’s network occurred through further exploitation of a SQL injection vulnerability (CVE-2024-29824) on Ivanti’s backend database server, allowing the attackers to gain remote code execution.
For further details and Indicators of Compromise (IOCs), you can read the full research article here.
Ivanti Fixes Critical RCE Vulnerability in Connect Secure and Policy Secure (CVE-2024-37404)
Ivanti has also patched a critical Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability, CVE-2024-37404, affecting Ivanti Connect Secure and Policy Secure products. With a CVSS score of 9.1, this flaw poses a serious risk to users.
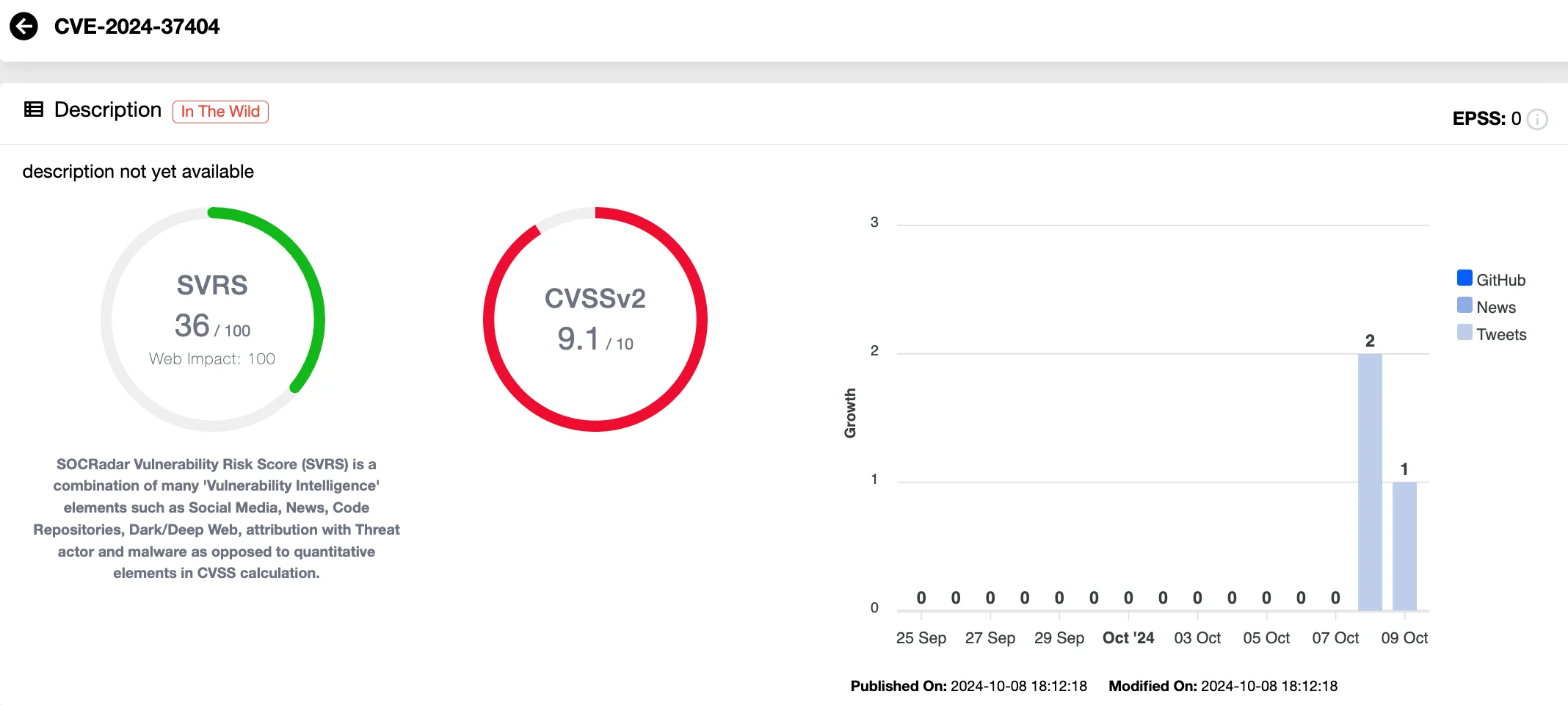
RCE in Ivanti Connect Secure and Policy Secure, CVE-2024-37404 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
The affected versions include Ivanti Connect Secure (all versions prior to 22.7R2.1) and Ivanti Policy Secure (all versions prior to 22.7R1.1).
In the past years, these products have been frequent targets for attackers. Previously, exploits have led to webshell deployments, and even the Mirai botnet leveraged two zero-days in Ivanti Connect Secure for propagation. For more details on these exploitation cases, read ourarticle here.
Details and PoC of CVE-2024-37404
CVE-2024-37404 allows attackers with admin access to execute arbitrary code on vulnerable Ivanti Connect Secure and Policy Secure systems. This flaw, caused by improper input validation in the admin portal, can be exploited during the Certificate Signing Request (CSR) process.
Researchers detailed in a blog, which also involves a Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit, that by injecting CRLF characters into the CSR form at ‘/dana-admin/cert/admincertnewcsr.cgi’, attackers can bypass validation and manipulate the OpenSSL configuration file. Exploiting this, attackers can upload a fake client log via Ivanti’s Client Log Upload feature, storing a malicious payload on the server and referencing it in the OpenSSL config file, leading to full system compromise.
Mitigations for Ivanti Connect Secure and Policy Secure Vulnerability
Ivanti states that they are not aware of any exploitation of CVE-2024-37404 at the time of disclosure. Still, it is strongly advised that users apply the updates immediately, as there is a possibility attackers could start weaponizing the exploit.
The vulnerability can be mitigated by updating Ivanti Connect Secure to versions 22.7R2.1, 22.7R2.2, or 9.1R18.9 which is set for release on October 15. Also, update Ivanti Policy Secure to version 22.7R1.1.
For those unable to update right away, Ivanti recommends restricting admin access to the management interface, which should be connected to a private, isolated network. Strengthening access controls with strong passwords, password rotation, vaults, and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is also advised, along with enabling admin logging to monitor any suspicious activity.
For more information on CVE-2024-37404, and update guidance, refer to Ivanti’s advisory.
With a growing number of vulnerabilities being discovered across various products, having full visibility into your attack surface is vital to prevent security gaps from going unnoticed, whether the flaws are actively exploited or not.
SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) continuously monitors your organization’s external assets, identifying potential vulnerabilities and risks before they can be exploited.
With SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) module, you can access detailed status insights into your external assets and potential vulnerabilities, helping you proactively address security issues and minimize exposure across your entire digital footprint.




































