
March 2025 Patch Tuesday: Microsoft Fixes 6 Critical & 6 Exploited Security Vulnerabilities
[Update] April 18, 2025: “CVE-2025-24054 Actively Exploited in Phishing Campaigns”
Microsoft has released its highly anticipated March 2025 Patch Tuesday update, tackling a staggering 57 security flaws. Among these, six vulnerabilities are deemed critical, while six have already fallen into the hands of threat actors. With active exploitation in the wild, organizations must waste no time in applying these patches to defend their networks from imminent threats.
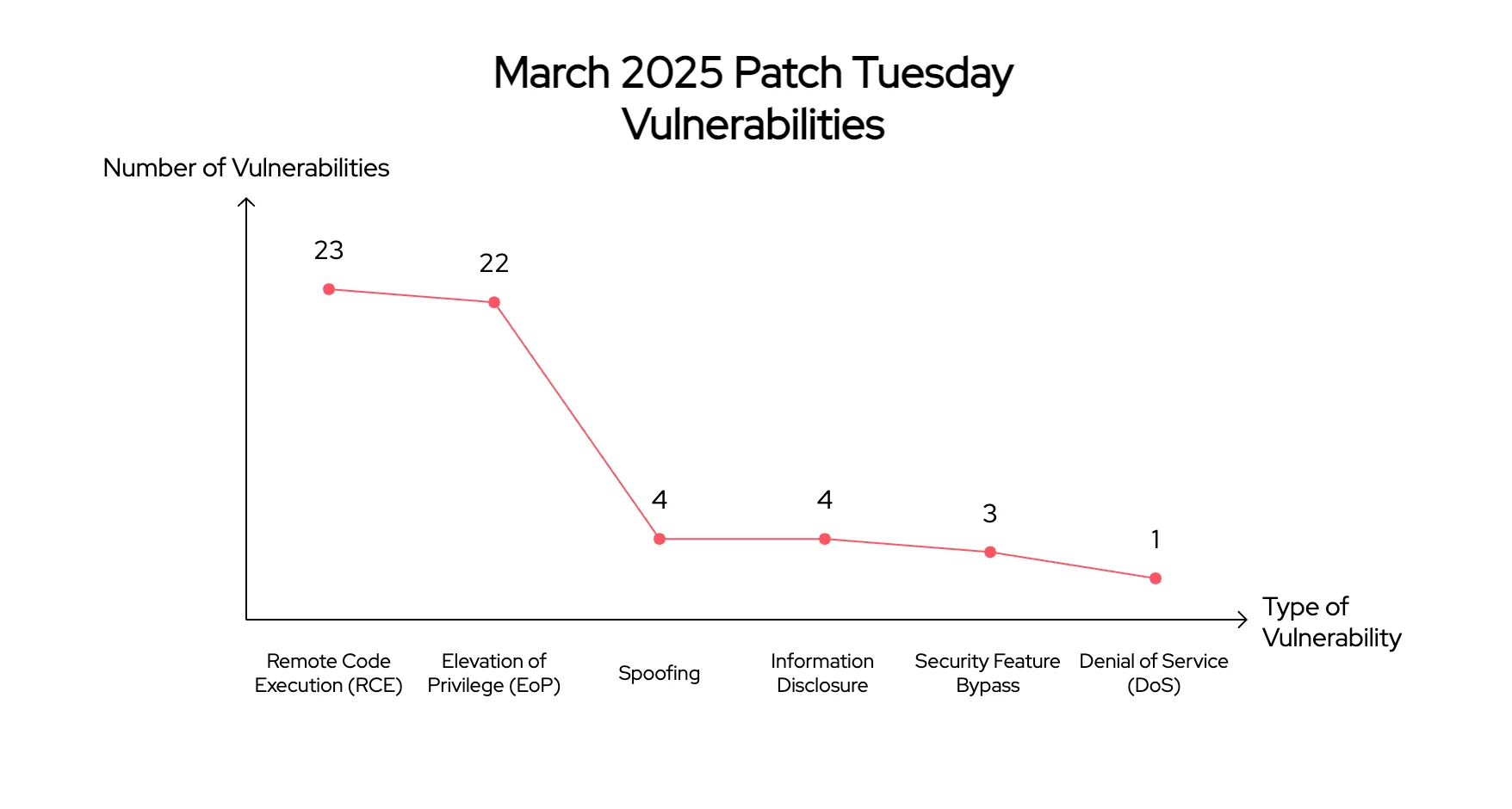
Here’s a quick breakdown of the March 2025 Patch Tuesday vulnerabilities:
- 23 Remote Code Execution (RCE) Vulnerabilities
- 22 Elevation of Privilege (EoP) Vulnerabilities
- 4 Spoofing Vulnerabilities
- 4 Information Disclosure Vulnerability
- 3 Security Feature Bypass Vulnerabilities
- 1 Denial of Service (DoS) Vulnerability
March 2025 Patch Tuesday Vulnerabilities
From actively exploited zero-days to high-severity security gaps, this Patch Tuesday presents both immediate threats and critical fixes that demand swift attention. Let’s shine a light on the vulnerabilities making headlines this month.
Actively Exploited Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
Cybercriminals are always on the lookout for unpatched systems, and the March 2025 Patch Tuesday update includes six vulnerabilities that are already being exploited in real-world attacks. Below, we break down these critical zero-days and their potential impact.
CVE-2025-24993 (CVSS 7.8) – NTFS Heap-Based Buffer Overflow
This flaw exists within the NTFS file system and affects Windows Server 2008 and later, including Windows 10 and 11. Although categorized as an RCE, exploitation requires local user interaction – an attacker must convince a victim to mount a malicious Virtual Hard Disk (VHD) image.
Once triggered, the vulnerability allows arbitrary code execution, making it a high-priority patching concern.
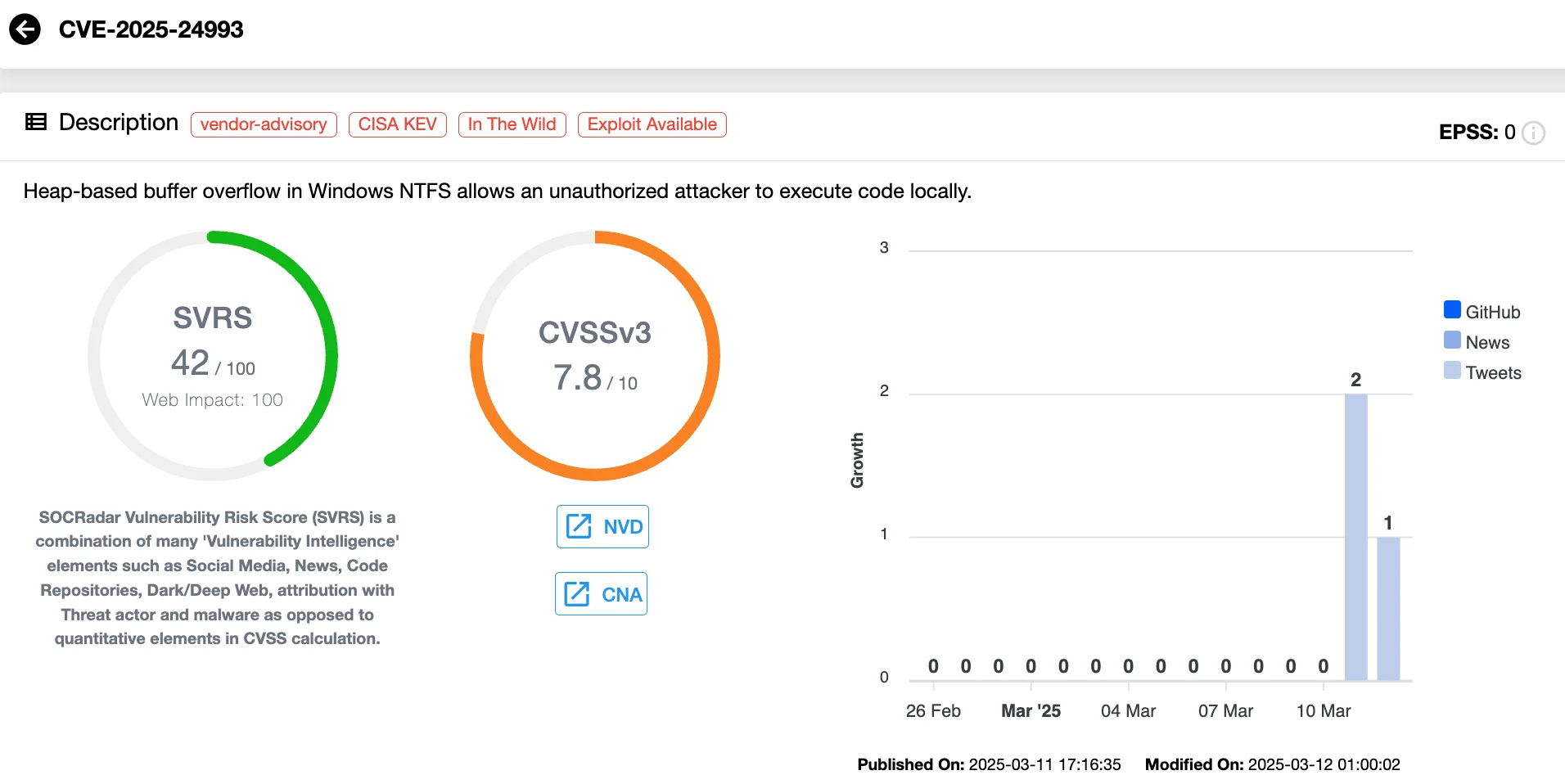
Vulnerability card of CVE-2025-24993 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
CVE-2025-24985 (CVSS 7.8) – Windows Fast FAT File System RCE
Similarly to CVE-2025-24993, this Fast FAT File System flaw enables attackers to execute code by manipulating a crafted VHD file.
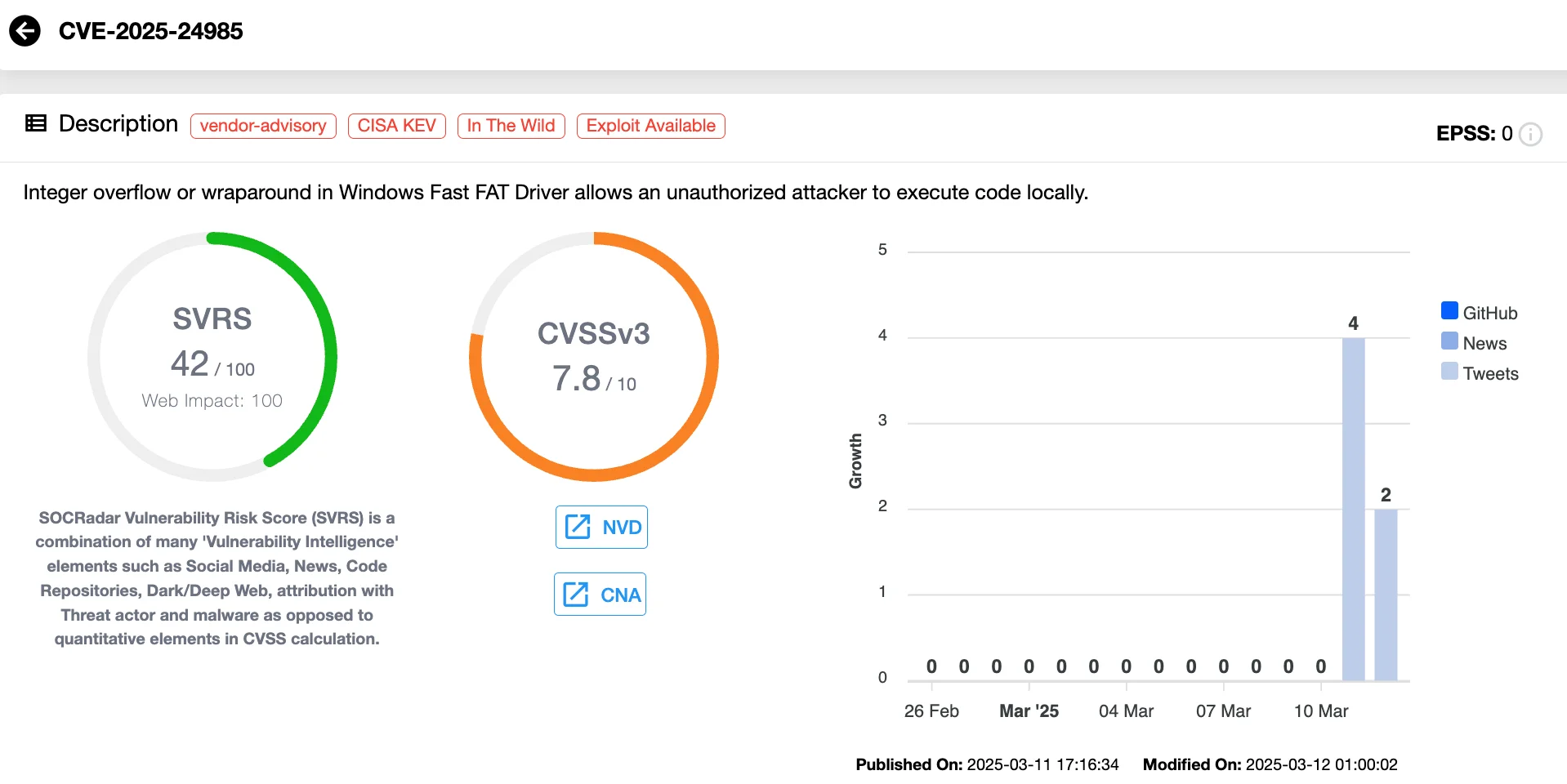
Vulnerability card of CVE-2025-24985 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
CVE-2025-24983 (CVSS 7.0) – Win32 Kernel Subsystem Privilege Escalation
Exploitable only by authenticated users, this flaw allows attackers to gain SYSTEM-level privileges by executing a specially crafted program.
CVE-2025-26633 (CVSS 7.0) – Microsoft Management Console (MMC) Security Bypass
This flaw in Microsoft Management Console (MMC) lets attackers trick users into opening malicious MSC files, bypassing security protections and executing code in the user’s context.
According to a Zero Day Initiative (ZDI) report, the EncryptHub (a.k.a. Larva-208) threat group has exploited this vulnerability; moreover, this threat group has affected over 600 organizations, making it a serious risk. Immediate patching is crucial to prevent further compromises.
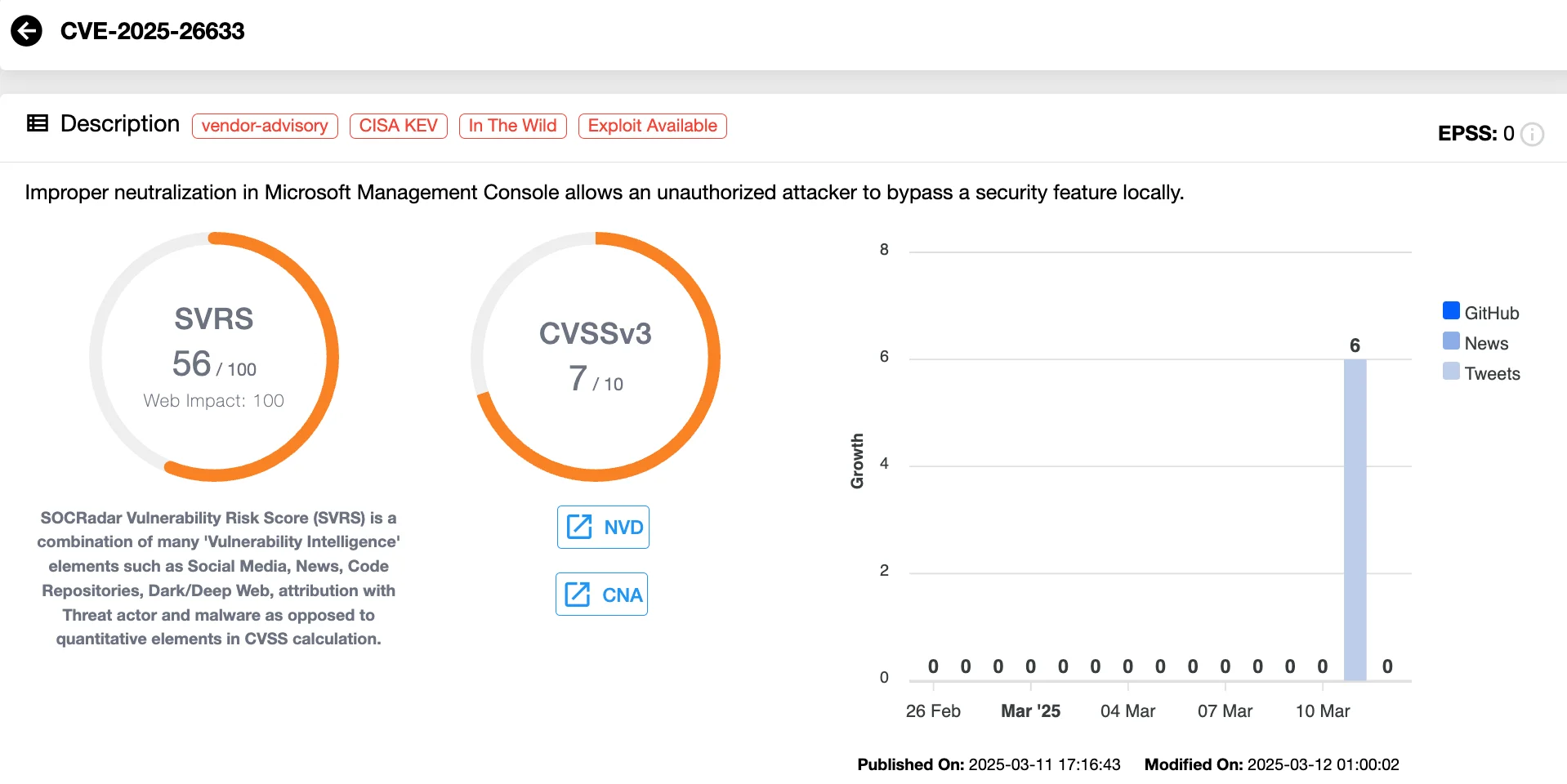
Vulnerability card of CVE-2025-26633 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
CVE-2025-24991 (CVSS 5.5) – NTFS Information Disclosure
This vulnerability enables out-of-bounds reads, potentially exposing sensitive data on the system. Like CVE-2025-24993, exploitation depends on a victim mounting a crafted VHD file, emphasizing the importance of user awareness and strict file-handling policies.
CVE-2025-24984 (CVSS 4.6) – NTFS Log File Information Leak
This flaw allows attackers with physical access to a vulnerable device to insert sensitive information into log files. Though rated lower in severity, it can still be a stepping stone for further attacks.
It is important to note that these vulnerabilities have been added to CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog, with a remediation due date of April 1, 2025. Federal agencies and organizations subject to compliance must apply these patches immediately to meet security requirements and reduce exposure.
Vulnerability Intelligence, SOCRadar XTI
Easily track cyber threats with SOCRadar’s Cyber Threat Intelligence module. Our platform, with its Vulnerability Intelligence feature, continuously monitors the latest security risks, providing real-time insights and detailed intelligence to help your security team prioritize patching and reduce exposure.
With automated alerts and in-depth threat tracking, SOCRadar ensures you’re always ahead of attackers.
Critical Vulnerabilities Addressed in March 2025 Patch Tuesday
This month’s Patch Tuesday introduces multiple critical vulnerabilities that pose significant threats to enterprise security. If exploited, these flaws could allow attackers to execute remote code, escalate privileges, or compromise sensitive data, making immediate patching a top priority.
- CVE-2025-26645 (CVSS 8.8) – Remote Desktop Client RCE:
A relative path traversal flaw allowing network-based code execution. - CVE-2025-24084 (CVSS 8.4) – Windows Subsystem for Linux RCE:
A pointer dereference vulnerability allowing unauthorized code execution locally. - CVE-2025-24064 (CVSS 8.1) – Windows DNS Server RCE:
A use-after-free vulnerability facilitating remote attacks. - CVE-2025-24035 (CVSS 8.1) – Windows Remote Desktop Services RCE:
Exploits improperly locked memory, leading to network-based RCE. - CVE-2025-24045 (CVSS 8.1) – Windows Remote Desktop Services RCE:
Another Remote Desktop Services flaw exploiting sensitive data storage issues. - CVE-2025-24057 (CVSS 7.8) – Microsoft Office RCE:
A heap-based buffer overflow enabling local code execution.
High-Risk Security Gaps, Likely Targets for Exploitation
Although these vulnerabilities are not yet being actively exploited, they present a high risk due to their exploitability and lack of workarounds. These vulnerabilities include the critical CVE-2025-24035 and CVE-2025-24045 flaws, along with several others. Here’s the full list:
- CVE-2025-24035 (8.1) – Windows Remote Desktop Services
- CVE-2025-24045 (8.1) – Windows Remote Desktop Services
- CVE-2025-21180 (7.8) – Windows exFAT File System
- CVE-2025-24044 (7.8) – Windows Win32 Kernel Subsystem
- CVE-2025-24061 (7.8) – Windows Mark of the Web (MOTW)
- CVE-2025-24066 (7.8) – Windows Kernel-Mode Drivers
- CVE-2025-24067 (7.8) – Microsoft Streaming Service
- CVE-2025-24995 (7.8) – Kernel Streaming WOW Thunk Service Driver
- CVE-2025-24992 (5.5) – Windows NTFS
- CVE-2025-21247 (4.3) – Windows MapUrlToZone
CVE-2025-24054 Actively Exploited in Phishing Campaigns
A newly discovered Windows vulnerability, CVE-2025-24054 (CVSS 6.5), is being actively exploited in phishing attacks targeting government and private organizations. Initially considered a lower-risk flaw, this vulnerability allows attackers to capture NTLM hashes by exploiting .library-ms files. Although patched in March 2025’s Patch Tuesday, researchers observed active exploitation within days of the patch’s release.
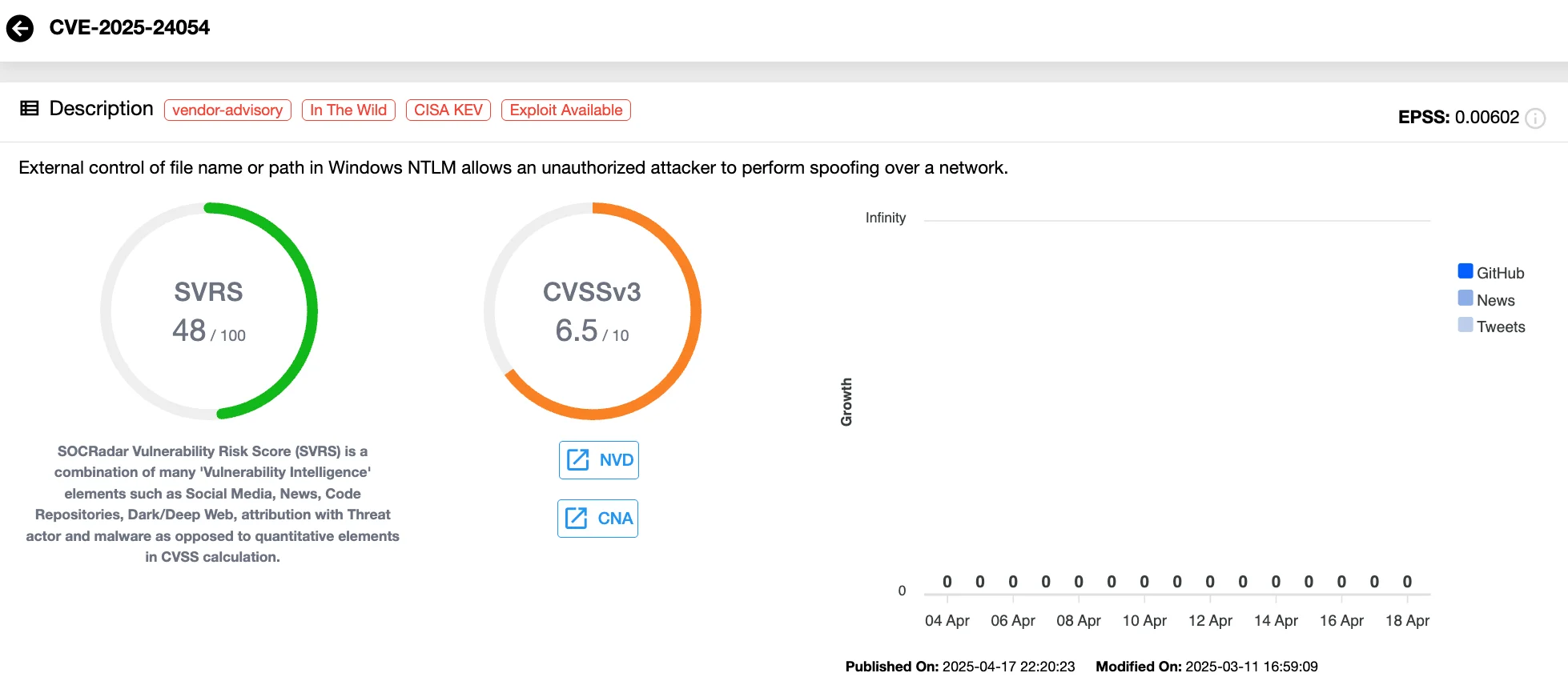
Vulnerability card of CVE-2025-24054 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
The vulnerability triggers when users interact with a malicious .library-ms file, which automatically establishes an SMB connection to an attacker-controlled server, enabling NTLM authentication and hash capture. In follow-up campaigns, attackers distributed these files without the need for a ZIP archive, reducing the interaction required to exploit the flaw.
While classified as medium severity, the potential for privilege escalation and authentication bypass makes this a high-risk issue. Organizations are urged to apply the latest updates, disable NTLM authentication when possible, and educate users about phishing threats to mitigate the risk.
Act Now to Secure Your Attack Surface
The March 2025 Patch Tuesday underscores the ongoing risks posed by Remote Code Execution (RCE) and Elevation of Privilege (EoP) vulnerabilities, among other threats, some of which are already being exploited by cybercriminals. The active targeting of NTFS and Fast FAT File System flaws, along with Remote Desktop Services vulnerabilities, highlights the urgent need for swift mitigation. If left unpatched, these vulnerabilities could enable full system compromise, unauthorized data access, and lateral movement within networks.
With six actively exploited zero-days and six critical vulnerabilities, system administrators must prioritize patching to prevent potential breaches. Organizations should assess their attack surface, apply updates without delay, and reinforce their cyber resilience against these growing threats.
Company Vulnerabilities (ASM module), SOCRadar XTI
SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) module offers continuous monitoring of digital assets and vulnerabilities, helping organizations detect and mitigate risks, such as those addressed in the March 2025 Patch Tuesday update.
With real-time insights, automated alerts, and full visibility, SOCRadar ASM empowers security teams. By tracking, prioritizing, and addressing vulnerabilities proactively, organizations can minimize exposure and enhance their cybersecurity posture.
For a complete list of patched vulnerabilities and further details, refer to Microsoft’s official March 2025 Patch Tuesday release notes.
Apple Patches Actively Exploited WebKit Zero-Day: CVE-2025-24201
Aside from Microsoft’s Patch Tuesday updates this month, Apple has also issued an urgent security patch, for a WebKit zero-day that was recently exploited in “extremely sophisticated” attacks. Tracked as CVE-2025-24201, this out-of-bounds write flaw allows attackers to escape the Web Content sandbox using malicious web content.
The bug was previously mitigated in iOS 17.2, but Apple now confirms it was still exploited in targeted attacks on older iOS versions. To address the risk, Apple has issued patches for:
- iPhone XS and later
- iPad Pro, iPad Air, iPad mini, and iPad (7th gen and later)
- Macs running macOS Sequoia
- Apple Vision Pro
The fix is available in iOS/iPadOS 18.3.2, macOS Sequoia 15.3.2, visionOS 2.3.2, and Safari 18.3.1. While Apple has not shared attack details, the nature of the exploit suggests a highly advanced threat actor. Users should update immediately to prevent possible threats.



































