
Cerberus Unchained: The Multi-Stage Trojan Banking Campaign Targeting Android Devices
The Cerberus Android banking trojan has reemerged in a sophisticated multi-stage attack campaign targeting banking credentials, SMS data, and contact lists of Android users. Known for its stealthy overlay attacks, the campaign mimics legitimate apps, tricking users into providing sensitive information on screens that look identical to trusted apps.

Illustration of the Cerberus Android banking trojan, generated by DALL-E
First detected in 2019, the trojan has since evolved to gain advanced capabilities, including keylogging, remote access, and, most recently, Domain Generation Algorithms (DGAs) for dynamic Command and Control (C2) communications.
The Cerberus malware campaign, also known as ErrorFather, reveals adaptability as it repurposes core functions through a series of droppers, native libraries, and encrypted payloads, effectively bypassing Android’s security defenses. Distributed through Google Play and third-party app stores, Cerberus remains a persistent threat across a broad range of sectors.
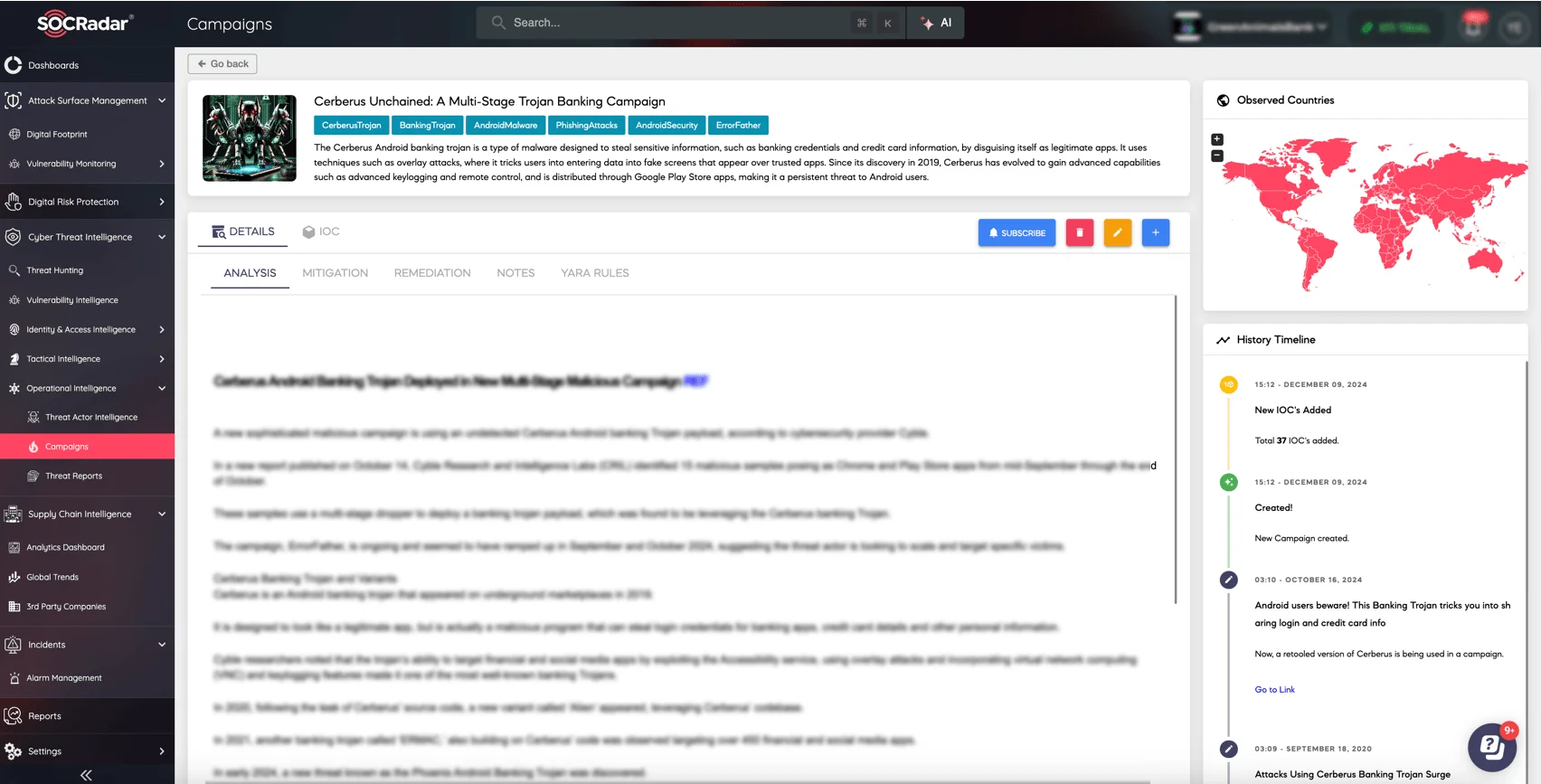
The campaign page for Cerberus on SOCRadar XTI platform
Explore information about the campaign and related threats by going to the Campaigns section under SOCRadar LABS. You can also find out how SOCRadar’s XTI platform can improve your proactive security tactics.
Attack Techniques Used by Cerberus
Cerberus’s multi-stage approach relies on several tactics to infiltrate and control devices. The trojan often masquerades as trusted applications like Google Play or Chrome, capturing sensitive data through overlay screens and keylogging. Once deployed, it performs extensive reconnaissance by identifying installed applications, accessing system information, and capturing screen and audio data. The malware’s dynamic C2 communications are encrypted, making detection even more challenging.
Mitigation Measures
Mitigating the Cerberus malware campaign requires comprehensive defense measures, including app verification, endpoint security, and user training. The following are recommended mitigation strategies against known techniques used by the campaign.
| ID | Technique | Description |
| T1660 | Phishing | Implement email filtering, advanced threat detection, regular phishing awareness training, and enforce multi-factor authentication. |
| T1575 | Native API Execution | Use application whitelisting to prevent unauthorized use of APIs; monitor API calls for abnormal activity. |
| T1655.001 | Masquerading: Match Legitimate Name/Location | Enforce app verification and app store policies; monitor for unusual app behaviors and permissions. |
| T1418 | Application Discovery | Block suspicious app discovery activities through endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions. |
| T1516 | Input Injection | Monitor for unusual input behaviors; enforce app sandboxing to restrict permissions and ensure regular patching. |
| T1417.001 | Input Capture: Keylogging | Use anti-keylogging measures and audit permissions for apps accessing sensitive data. |
| T1521.001 | Encrypted Channel: Symmetric Cryptography | Deploy IDS/IPS solutions to detect encrypted anomalies in C2 communication. |
| T1637.001 | Dynamic Resolution: Domain Generation Algorithm | Use DNS filtering and network monitoring to block suspicious domain generation activity. |
Remediation Steps
To remediate devices affected by Cerberus, organizations should deploy tools and policies to monitor and eliminate the malware’s persistent components. Below are key detection and remediation tactics.
| ID | Data Source | Data Component | Detection and Remediation Method |
| DS0017 | Command | Command Execution | Monitor command-line activities for unauthorized scripts that perform API calls or network commands. |
| DS0009 | Process | OS API Execution | Track unusual API activities, especially commands tied to screen capturing and keylogging on Android devices. |
| DS0022 | File | File Modification | Analyze app installation sources for unusual modifications, especially in high-sensitivity folders. |
| DS0024 | Windows Registry | Registry Key Creation | Monitor for registry modifications that add Cerberus or ErrorFather as startup applications, ensuring persistence. |
| DS0011 | Module | Module Load | Observe for unauthorized module loads, particularly those accessing critical Android system functionalities. |
| DS0029 | Network Traffic | Network Connection Creation | Use network analysis to detect irregular, encrypted traffic indicative of the campaign’s command-and-control communications. |
Indicators of Compromise (IoCs)
The following IoCs help security teams detect devices compromised by Cerberus. Implement these in threat intelligence feeds to enhance detection and protection.
| Category | Indicator | Description |
| Hashes | c67b03c0a91eaefffd2f2c79b5c26a2648b8d3c19a22cadf35453455ff08ead0 | Known hash associated with the campaign’s malicious payload. |
| 880c9f65c5e2007bfed3a2179e64e36854266023a00e1a7066cbcf8ee6c93cbc | Hash indicative of overlay screens use | |
| 9d966baefa96213861756fde502569d7bba9c755d13e586e7aaca3d0949cbdc3 | Associated with ErrorFather’s remote control component. | |
| File Paths | %APPDATA%LocalTempCerberus* | Temporary files tied to the campaign’s Android deployment. |
| Registry Keys | HKCUSoftwareGooglePlayUpdateService | Registry entry ensuring malware persistence. |
| IP Addresses | 104.218.176.22 | IP address associated with the campaign C2 operations. |
Conclusion
The Cerberus malware campaign highlights the ever-evolving threat posed by mobile banking trojans. Through advanced techniques such as overlay attacks, keylogging, and encrypted C2 communication, Cerberus presents a persistent danger to Android devices globally. Combatting such sophisticated threats requires a proactive security approach, focusing on multi-layered endpoint protection, app whitelisting, and user training to recognize phishing attempts.
The SOCRadar Extended Threat Intelligence (XTI) platform provides real-time insights into emerging mobile threats, such as Cerberus, allowing for early detection and remediation. Organizations can stay informed and improve their defenses by visiting the Campaigns section under SOCRadar LABS for a thorough overview of current campaigns.



































