
Cisco Fixes Numerous DoS Vulnerabilities in IOS, IOS XE, and Access Point Software
Cisco recently addressed multiple Denial-of-Service (DoS) vulnerabilities across its product range, including Cisco IOS, IOS XE, and Access Point software.
CISA has issued an alert emphasizing the severity of these vulnerabilities, urging users to patch their systems accordingly to prevent potential disruption by threat actors. In this article, we will outline these vulnerabilities, allowing for a better understanding of the most recent security threats.
The Latest Cisco IOS, IOS XE Vulnerabilities: CVE-2024-20308, CVE-2024-20311, CVE-2024-20259, CVE-2024-20314
Cisco’s semiannual Cisco IOS and IOS XE software security advisory included 13 advisories that addressed 14 vulnerabilities. In particular, eight of these advisories are given a ‘high’ security impact rating, and four vulnerabilities have high CVSS scores of 8.6.
Interestingly, all of the high-severity issues described in these advisories are Denial-of-Service (DoS) vulnerabilities. Below, we provide an overview of each vulnerability:
CVE-2024-20308:
CVE-2024-20308 presents a vulnerability in the IKEv1 fragmentation code of Cisco IOS Software and Cisco IOS XE Software.
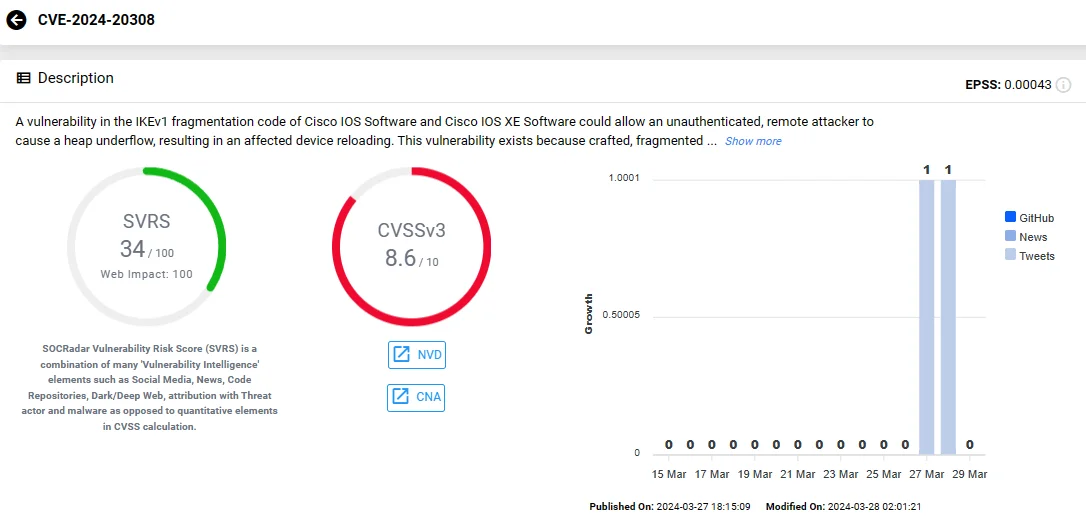
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-20308 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
The security vulnerability occurs due to crafted, fragmented IKEv1 packets not being properly reassembled; its exploitation involves sending crafted UDP packets to a vulnerable system.
If exploited, CVE-2024-20308 could permit an unauthenticated, remote attacker to trigger a heap underflow, leading to the reloading of the affected device.
Cisco highlights that only the IPv4/IPv6 traffic directed to the affected system can exploit this vulnerability.
In addition to the patch, Cisco offers a workaround for CVE-2024-20308: disabling IKEv1 fragmentation using the commands below.
Router#configureterminal
Router(config)#nocryptoisakmpfragmentation
Router(config)#end
Router#
CVE-2024-20311:
It is a vulnerability in the Locator ID Separation Protocol (LISP) feature of Cisco IOS Software and Cisco IOS XE Software, arising from mishandling LISP packets. Similarly to CVE-2024-20308, this vulnerability could also allow a remote attacker to force a device reload.
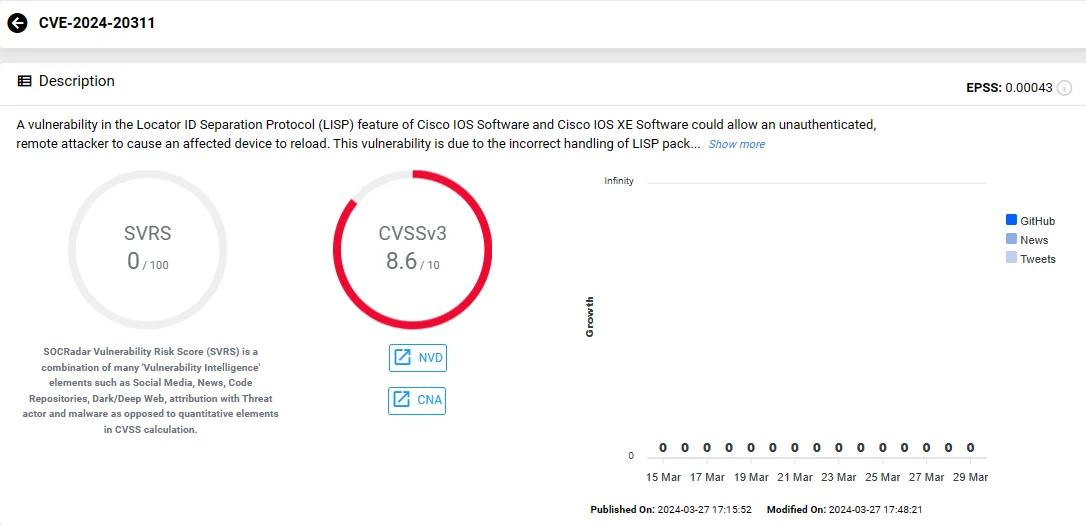
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-20311 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Attackers can exploit CVE-2024-20311 by sending a crafted LISP packet, leading to a DoS situation. Cisco warns that this vulnerability applies to both IPv4 and IPv6 transport, with no available workarounds.
CVE-2024-20259:
Residing in Cisco IOS XE Software’s DHCP snooping feature, CVE-2024-20259 could let an unauthenticated remote attacker force an unexpected device to reload, causing a Denial-of-Service.
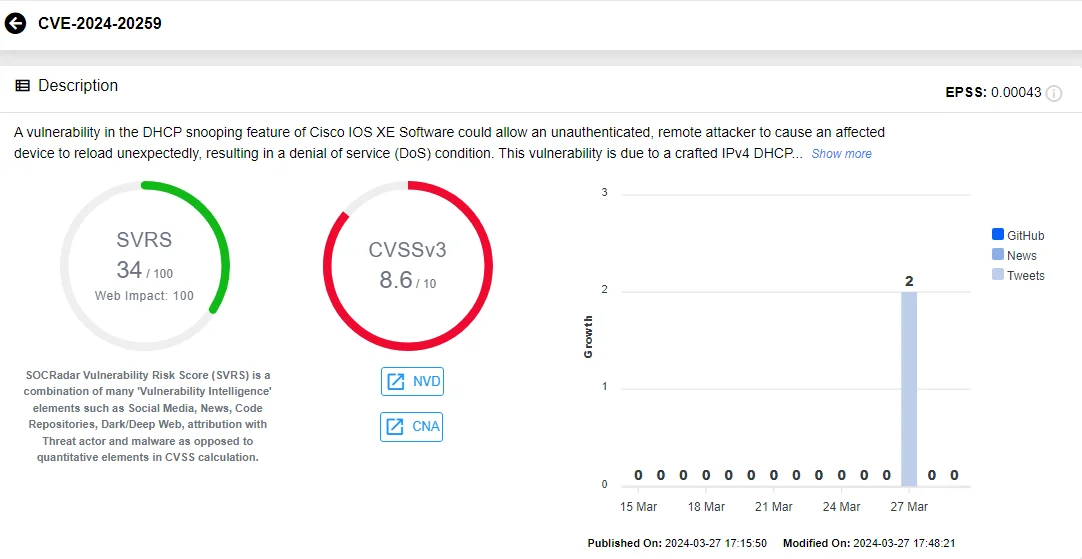
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-20259 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
The issue stems from mishandling crafted IPv4 DHCP request packets when endpoint analytics are activated.
Potential threat actors can exploit CVE-2024-20259 by sending a crafted DHCP request. According to Cisco, a DHCP relay anywhere on the network allows exploitation from networks that are not adjacent.
CVE-2024-20314:
The vulnerability affects the IPv4 Software-Defined Access (SD-Access) fabric edge node feature of Cisco IOS XE Software and could let a remote attacker cause high CPU utilization and halt traffic processing, resulting in a DoS condition.
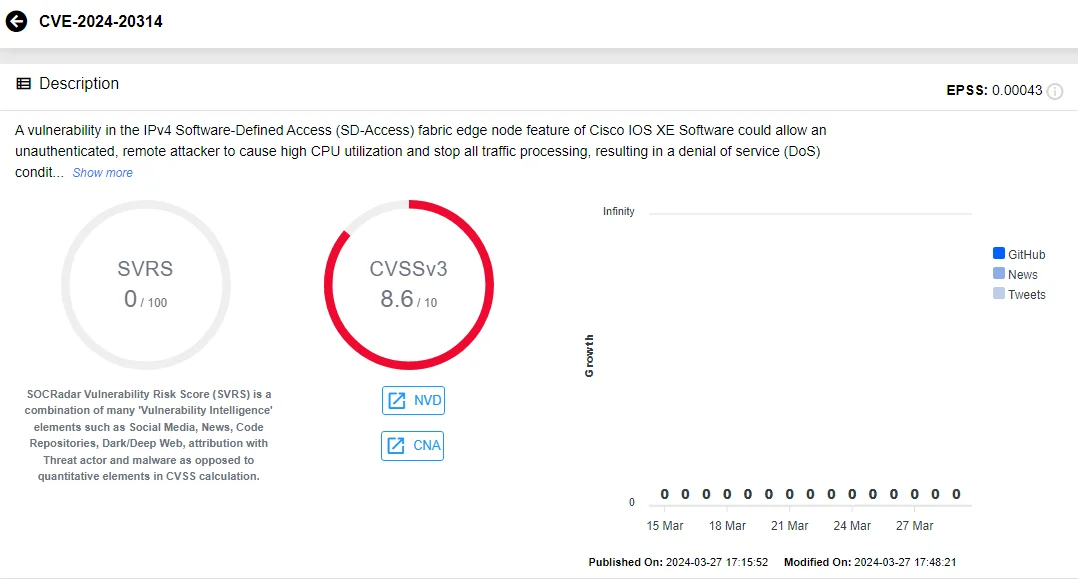
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-20314 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
The vulnerability arises from improper handling of certain IPv4 packets. It is exploitable by sending specific IPv4 packets, exhausting the device’s CPU resources.
Boost your organization’s defenses against Denial-of-Service (DoS) threats using SOCRadar Labs’ DoS Resilience module. Evaluate your domain’s or subnet’s capacity to withstand DoS attacks.

SOCRadar Labs, DoS Resilience
Cisco Access Point Software Affected by DoS and Secure Boot Bypass Vulnerabilities: CVE-2024-20271, CVE-2024-20265
In addition to the vulnerabilities affecting Cisco IOS and IOS XE, two severe vulnerabilities were patched in the Access Point (AP) Software, as highlighted in the CISA alert.
One of the vulnerabilities, CVE-2024-20271, is yet another Denial-of-Service (DoS) threat. It occurs due to insufficient input validation of certain IPv4 packets. An attacker could exploit this security vulnerability remotely, causing affected devices to unexpectedly reload.
It is noted in the advisory that exploiting this vulnerability does not require association with the affected AP, and it does not affect IPv6 packets.
The second AP Software vulnerability, CVE-2024-20265, involves a secure boot bypass, enabling a physical attacker to circumvent Cisco Secure Boot functionality. By executing specific commands at the physical console, the attacker can load a tampered software image onto the device.
This vulnerability arises from unnecessary commands available during boot time. Although this exploit allows the attacker to load the image once, it does not permanently compromise Cisco Secure Boot.
CVE-2024-20271 has a CVSS score of 8.6, while CVE-2024-20265 has a medium score of 5.9.
Track Hacker Trends and Vulnerability Exploits with SOCRadar
SOCRadar offers advanced Vulnerability Intelligence, delivering the latest insights on known vulnerabilities. These include exploits, repositories, and emerging hacker trends.
Armed with such insights, organizations can proactively safeguard against potential threats and enhance their vulnerability management.
SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence
Additionally, with SOCRadar’s vulnerability detection capabilities, organizations can find and evaluate vulnerabilities in their systems. The platform alerts users in real time to critical vulnerabilities or exploits affecting their defined product components and digital technologies.
SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management
Experience the full potential of the SOCRadar XTI platform with a Free Edition:



































