
Vulnerability Management Best Practices
Every day, new vulnerabilities emerge, and multiplying proliferating vulnerabilities throughout today’s complex technology contexts yield a never-ending risk hamster wheel. That’s why vulnerability management has been a crucial component of any organization’s security program for many years. It identifies potential weaknesses inside your network and provides a method to prioritize potential threats and reduce your attack surface. In several cases, compliance rules even mandate these programs.
What is Vulnerability Management?

Vulnerability management means continually discovering, analyzing, and resolving security flaws in technological systems. Vulnerability management is a crucial aspect of security maintenance.
Cybercriminals might exploit an organization’s internal controls vulnerabilities to access critical company data or disrupt systems.
Due to the rise in cyberattacks, organizations must control vulnerabilities. Every day, organizations identify millions of vulnerabilities, requiring them to prioritize by severity, patch software, and adjust network security settings.
Managing vulnerabilities also helps firms comply with legislation and standards, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) currently in effect in the European Union and the United Kingdom.
Most Common Forms of Vulnerabilities
- Network vulnerabilities: To obtain access to a network, malicious actors exploit holes in hardware, software, or operational procedures, such as out-of-date firewall settings and improperly configured Wi-Fi access points.
- Operating system vulnerabilities: Malicious actors use these flaws in operating system software to gain access to other sections of a network or asset and do harm.
- Vulnerabilities in apps: Cybercriminals use these defects to breach an application’s security, putting users at risk.
- Configuration vulnerabilities: Cybercriminals use these vulnerabilities to target networks and devices. These problems result from incomplete installs, poorly conducted system updates, and default deployments.
What Challenges Does Vulnerability Management Face?
To remain ahead of threat actors, enterprises must comprehend the complexities of vulnerability management. Include the following:
Improper prioritization of vulnerabilities: Since security teams cannot fix every flaw, the list of vulnerabilities grows with each new scan. Large businesses may have hundreds of defects at any one moment, making it challenging to choose which to prioritize and correct promptly.
Vulnerability scanners overlook specific vulnerabilities and cause false positives, requiring the security team to act, analyze the data, and assess the actual security state of a business.
An excessive number of vulnerabilities in reports: Vulnerability scan reports may be lengthy and comprehensive. Each piece contains tens of thousands of errors and false positives. As a result, a security team cannot handle all of the report’s action items, compromising the organization’s capacity to maintain its systems patched.
What are Vulnerability Management Best Practices?
Vulnerability management is a defined and tested procedure that ensures people and technology collaborate and communicate effectively. This approach should be undertaken routinely to report software vulnerabilities and, ultimately, to limit risk.
If you want to restore your security posture with an improved vulnerability management program, consider the following recommended practices:
- Plan in advance and determine KPIs: As with any other company endeavor, you must first define Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). These will direct your security personnel and provide attainable objectives. Vulnerability coverage, scan frequency, and patching time are all valuable KPIs.
- Recognize your attack surface: All parts of your attack surface must be included in your vulnerability management program. In addition to conventional network assets, this consists of online apps, cloud instances, mobile devices, IoT devices, etc. Machine learning and real-time dashboards can allow you to gain insight into your attack surface effortlessly.
- Expand your database: Relying on overlapping tools or spreadsheet lists may make proper asset tracking challenging, particularly in an IT environment that is constantly evolving. Identify and map all your digital assets to collect data about your network architecture. These assets may then be categorized and prioritized to match your business and operational priorities.
- Leverage automation: It is crucial to use automation capabilities wherever feasible to meet the ever-increasing complexity of the security environment. For instance, automated asset management frameworks that increase organization-wide connectedness and comprehension or risk-scoring systems that automate prioritizing. Automation will raise compliance, eliminate human error, and improve the efficiency of your program.
- Effective record-keeping: Your vulnerability assessment is null and void if you cannot provide efficient and timely reports that allow team members to make prompt corrections. How information is presented and shared determines how quickly and effectively system deficiencies are corrected. You need a system that lets you notify the correct individuals with the right information quickly and without friction.
- Prioritization: This cannot be negotiated. Utilize your threat intelligence database and KPIs to develop individualized priority metrics. Prioritize remediation operations based on additional business information (such as the sensitivity of assets) to provide faster risk deferral and extra assessment capabilities.
- Responsibility and repairing: Everything is useless without adequate patching mechanisms and accountability procedures. Reevaluate recently patched systems or segments to confirm that vulnerabilities have been eliminated.
How Can SOCRadar Help with Vulnerability Management?
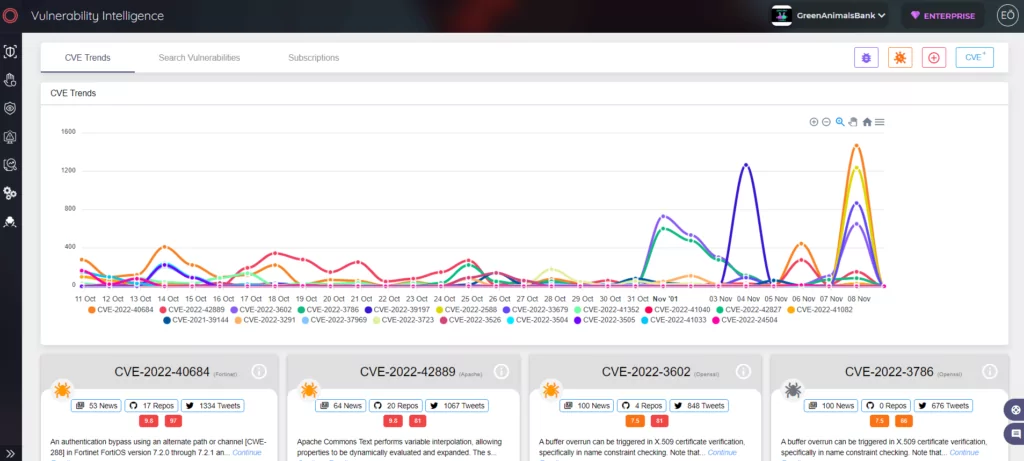
SOCRadar can assist vulnerability teams in maintaining an accurate inventory of externally-facing assets. To complete the life cycle of a vulnerability threat, the platform is equipped with additional capabilities to scan these assets and discover new critical vulnerabilities continually. SOCRadar offers worldwide monitoring of the surface, deep, and dark web to uncover vulnerabilities exploited by adversaries or in the wild.



































