
Critical Zero-Day Vulnerability in ‘libwebp’: CVE-2023-4863 Reassigned as CVE-2023-5129
[Update] October 18, 2023: See the subheading: “Fantom Foundation Breached: $550K Crypto Theft Linked to CVE-2023-4863.”
Google has issued a new CVE identifier for a critical zero-day vulnerability that is under active exploitation. The vulnerability, labeled CVE-2023-5129, was initially misidentified as a Chrome vulnerability (CVE-2023-4863). However, it has been revealed that the vulnerability affects the libwebp image library used for rendering images in WebP format, specifically stemming from the Huffman coding algorithm.
The libwebp image library is integrated into nearly every operating system and application, including those built on Electron. Consequently, the CVE-2023-5129 vulnerability does not solely impact web browsers but affects any software employing the libwebp library.
How Does the CVE-2023-5129 Vulnerability in libwebp Work?
An attacker can exploit the CVE-2023-5129 vulnerability in libwebp by using a specially crafted WebP lossless file, and cause it to write data beyond the heap boundaries.
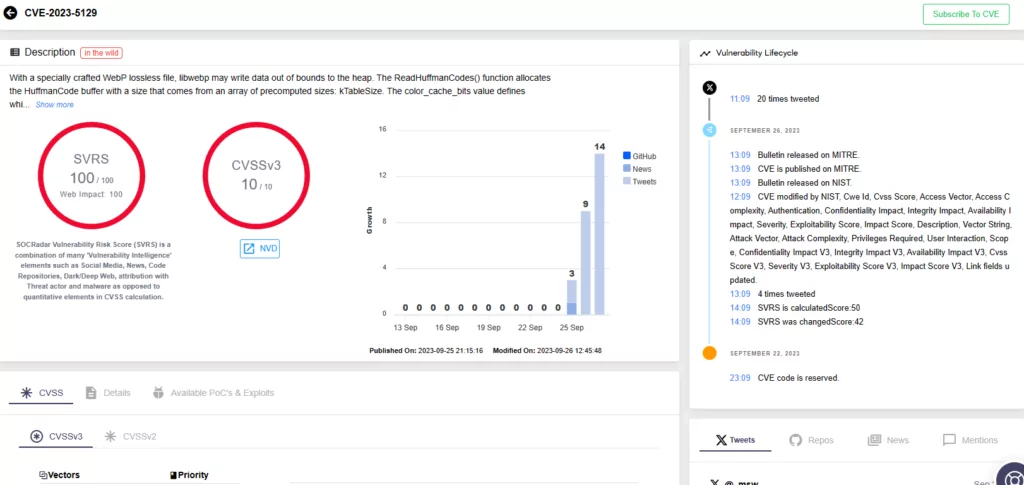
The allocation of the HuffmanCode buffer within the ReadHuffmanCodes() function causes this problem. The size of the buffer is determined by a precomputed array (kTableSize), which only considers sizes for 8-bit first-level table lookups. Because libwebp supports up to 15-bit codes, the issue arises when the BuildHuffmanTable() function tries to populate the second-level tables.
How Critical Is CVE-2023-5129?
The libwebp vulnerability is serious, with a maximum CVSS score of 10. The previous advisory with the identifier CVE-2023-4863 had a CVSS score of 8.8; because the wide availability of libwebp broadens the attack surface, the CVSS score has been updated as well.
Timely patch management is of paramount importance for organizations to avoid exploitation of vulnerabilities and maintain a secure environment. Google Chrome versions prior to 116.0.5845.187 are known to be vulnerable to exploitation. To ensure security, users should also confirm that their Electron versions are v22.3.24, v24.8.3, v25.8.1, or newer before using applications.
The Reclassifying of Chrome Vulnerability as a libwebp Issue
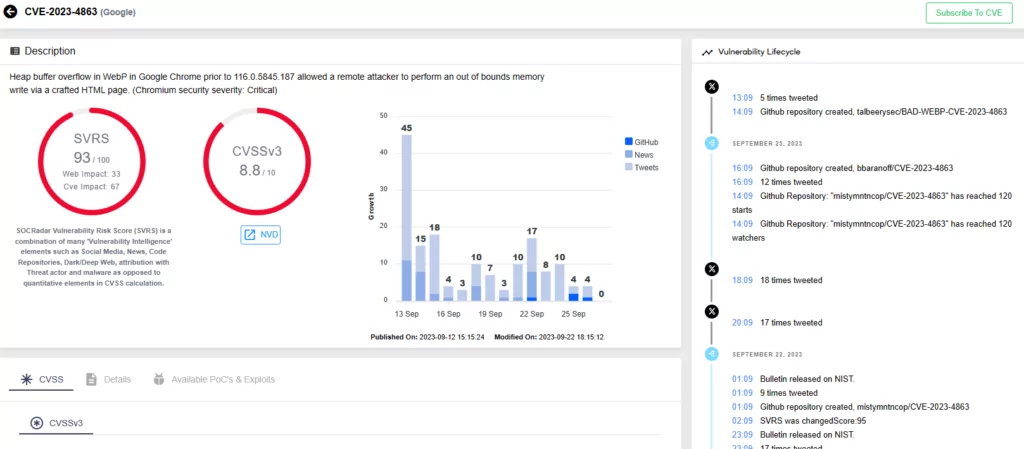
Google had initially issued a security advisory for CVE-2023-4863, which it described as a heap buffer overflow in WebP in Chrome, despite the fact that the vulnerability had a broader impact and affected any code that used libwebp.
Failure to accurately identify the nature of a vulnerability can lead to delays in patching, thereby granting attackers an extended window of opportunity for exploitation. In the context of Google’s situation, where the vulnerability involved a zero-day within a widely utilized library, this raised significant concerns.
In the most recent Google disclosure, the vulnerability is identified as CVE-2023-5129, which correctly identifies libwebp as the affected vendor and software.
CVE-2023-4863 Linked to Apple’s CVE-2023-41064
Following the release of CVE-2023-4863, there were speculations of it being linked to the CVE-2023-41064 vulnerability affecting Apple products, due to both being the same issue with BuildHuffmanTable.
CVE-2023-41064 was discovered by Citizen Lab in connection with a zero-click iMessage exploit, which was employed to disseminate the Pegasus spyware from the NSO group. Researchers named this attack “BLASTPASS”, emphasizing how the attackers bypassed Apple’s iMessage sandbox, BlastDoor.
Ben Hawkes, a security expert, has released detailed information about the connections between two vulnerabilities and a Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit in a blog.
The expert suggested that bundling a malicious image within a PassKit attachment could exploit the vulnerability, as observed in Apple’s initial CVE, CVE-2023-41061. However, exploiting this vulnerability required an image exploit, leading to the discovery of CVE-2023-41064, a buffer overflow vulnerability in Apple’s ImageIO framework. Notably, ImageIO had recently added support for WebP files.
Adding to the intrigue, Apple reported a WebP vulnerability to Chrome, which Google promptly patched and classified as “exploited in the wild.” According to the expert, this strengthens the implication that BLASTPASS (CVE-2023-41064) and CVE-2023-4863 are likely the same bug.
Fantom Foundation Breached: $550K Crypto Theft Linked to CVE-2023-4863
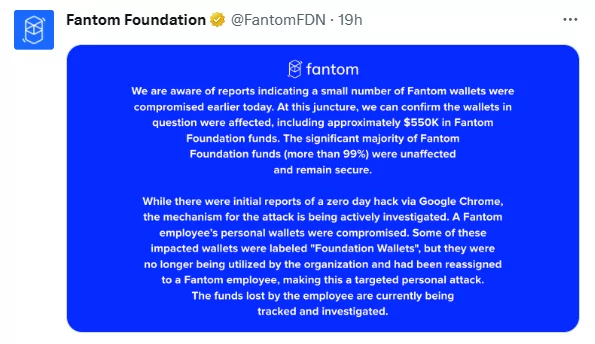
The Fantom Foundation, a non-profit organization supporting the Fantom blockchain network, experienced a security breach. While details about the breach are limited, discussions suggest a connection to the libwebp vulnerability, CVE-2023-4863.
The Fantom Foundation revealed that only a small number of wallets were compromised, and more than 99% of its funds remain secure. According to the disclosure, the primary target of the attack was an employee, making it a ‘targeted personal attack’.
Attackers exploited CVE-2023-4863 and gained access to private keys to the Fantom Foundation’s wallets, subsequently stealing over $550,000 in cryptocurrency.
Better Vulnerability Management with SOCRadar
The SOCRadar XTI platform offers comprehensive solutions that enable you to easily detect, assess, and remediate vulnerabilities in real-time. With its Vulnerability Intelligence module, the platform continuously monitors vulnerabilities. Using the module, you can search for vulnerabilities, access detailed information and related activities about them, and track hacker trends.
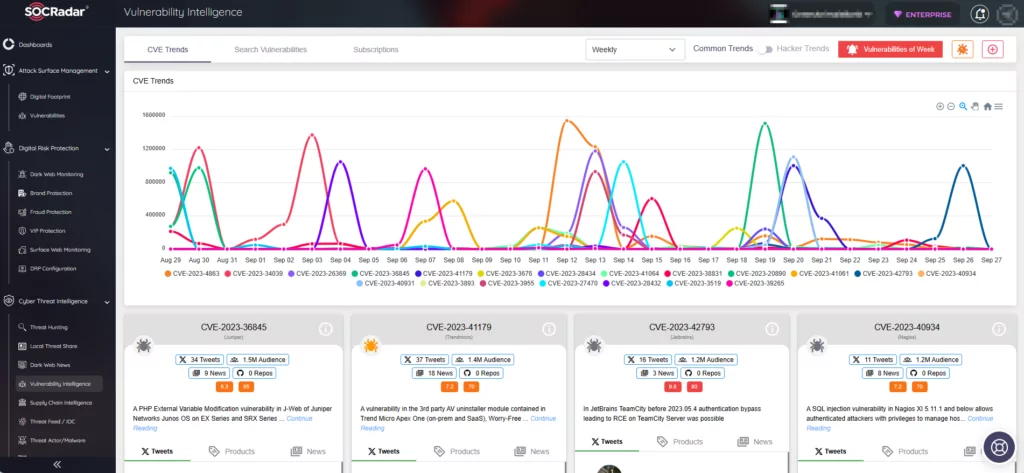
Additionally, the Attack Surface Management (ASM) module enables secure monitoring of asset status and notifies you of emerging vulnerabilities, empowering you to better prioritize patches.
By signing up for the Free Edition, you can seamlessly integrate SOCRadar into your security strategy, fortifying your defenses and proactively addressing emerging threats.


































