Everything You Need To Know About AI Agents: Is It Hype or Reality?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) agents have become one of the hottest topics in the tech world. Every passing day, new articles, podcasts, and product launches claim that AI agents will transform the way we work and live.
But what is real, and what is just hype? In this Q&A-style blog post, we’ll break down everything you need to know, with simple examples from real life and cybersecurity.
Q1: What is the current hype around AI agents? Is it justified?
AI agents are being discussed as the next big leap in automation — systems that can not only follow commands but also think, decide, and act independently to achieve goals. The hype is based on rapid advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4 and Claude, which can process vast amounts of information and make human-like decisions.
Real-life example: A recent article showed an AI agent, UI-TARS autonomously searching for flight tickets, comparing prices, and helping users to find flights.
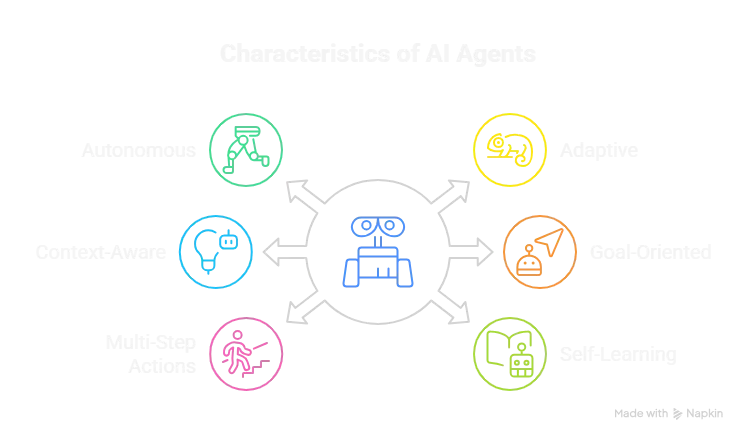
Q2: What exactly is an AI agent?
An AI agent is a software entity capable of making decisions and taking actions toward achieving a goal, often without continuous human guidance. It observes its environment, interprets data, and adapts its actions.
Example: A cybersecurity AI agent that monitors for suspicious IP addresses, automatically blocks them, and notifies the security team. So, cybersecurity professionals already are familiar with working with agents.
Check out our Ultimate Guide: Using Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity
Q3: Where are AI agents commonly used?
- Customer Support: Automating responses and handling simple inquiries are one of the leading uses of AI agents currently.
- Example: ChatGPT-based bots helping customers troubleshoot common issues, commonly used in Airlines companies.
- Cybersecurity: Real-time monitoring, alerting, and automatic remediation.
- Example: Microsoft Sentinel using AI agents for automatic threat detection and incident response.
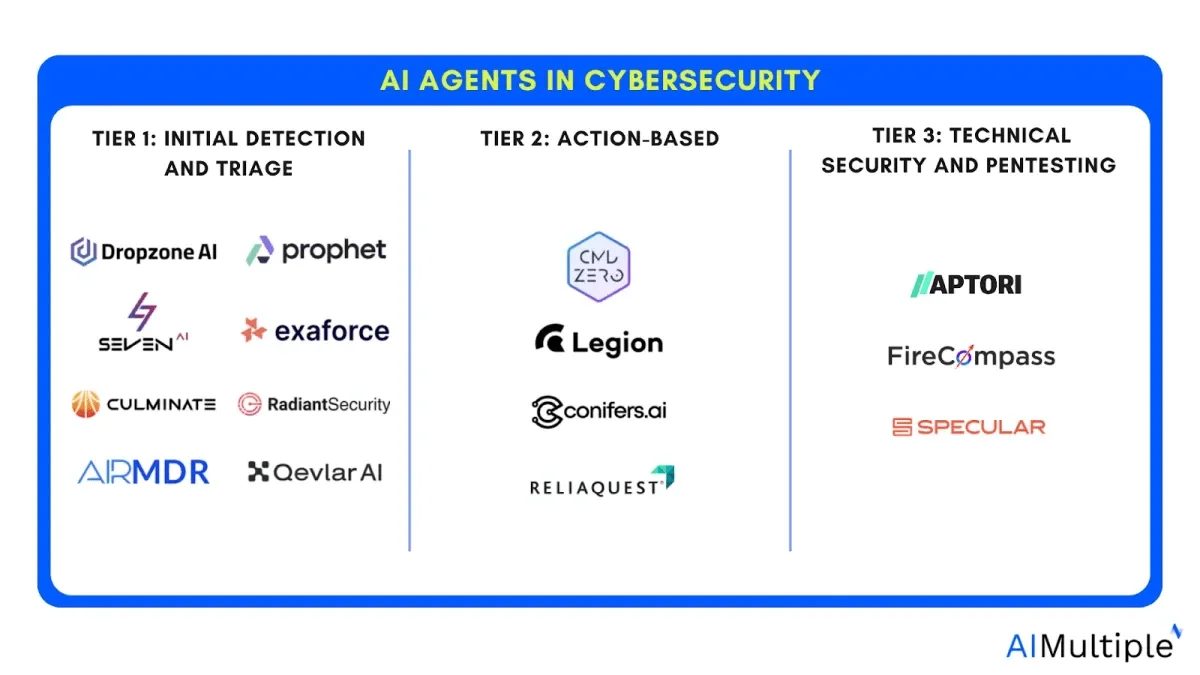
AI Agents in Cybersecurity (AIMultiple)
- E-commerce: Price comparisons and personalized recommendations. Example: An AI agent on Amazon suggesting deals based on browsing behavior.
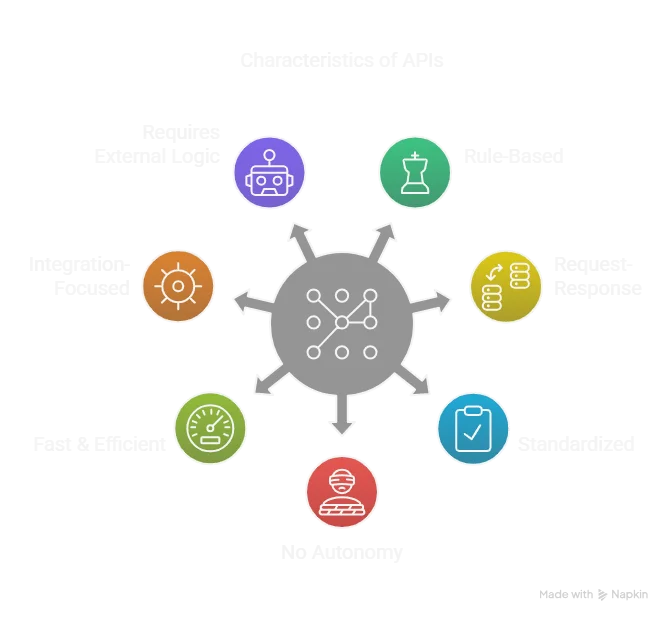
Q4: How do AI agents differ from APIs?
An API is a communication tool between two software systems. An AI agent, on the other hand, makes decisions and initiates actions on its own, often using APIs as part of its toolkit.
Example: An API can tell you the current weather, but an AI agent can check the weather and proactively reschedule your outdoor meetings.
Q5: How do AI agents differ from tools like Zapier or SOAR products?
It’s mostly about decision logic and capability.
- Zapier automates repetitive workflows but only performs tasks you’ve defined.
- SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) automates cybersecurity processes based on pre-set rules.
- AI Agents go a step further — they can learn, adapt, and make decisions when conditions change.
Example: Zapier might move new Gmail attachments to Dropbox, but an AI agent could decide which files are critical, label them, and notify relevant team members.
Q6: Why is everyone suddenly talking about AI agents?
Because large language models, advanced APIs, and orchestration engines now allow autonomous agents to handle complex tasks. Organizations like OpenAI, AutoGPT, and Cognosys have demonstrated prototypes that achieve multi-step goals.
Example: AutoGPT completing a project planning task by finding resources, creating schedules, and summarizing results in a report.
Q7: What is a workflow in this context?
A business process can be broken down into a workflow, which is a series of automated steps that lead to a desired outcome.
Example: Order placement → inventory check → payment processing → shipping confirmation.
Q8: What’s the difference between workflow automation and AI agents?
Workflow automation follows pre-defined rules and steps. AI agents dynamically make decisions along the way. Essentially reducing the need for human involvement.
Example: A workflow might automatically email invoices, but an AI agent could decide whether to send reminders, escalate to sales, or offer discounts based on client history.
Q9: What is no-code, and how does it connect to AI agents?
No-code tools allow non-developers to build workflows and apps visually. AI agents can be embedded in no-code platforms to make those workflows smarter.
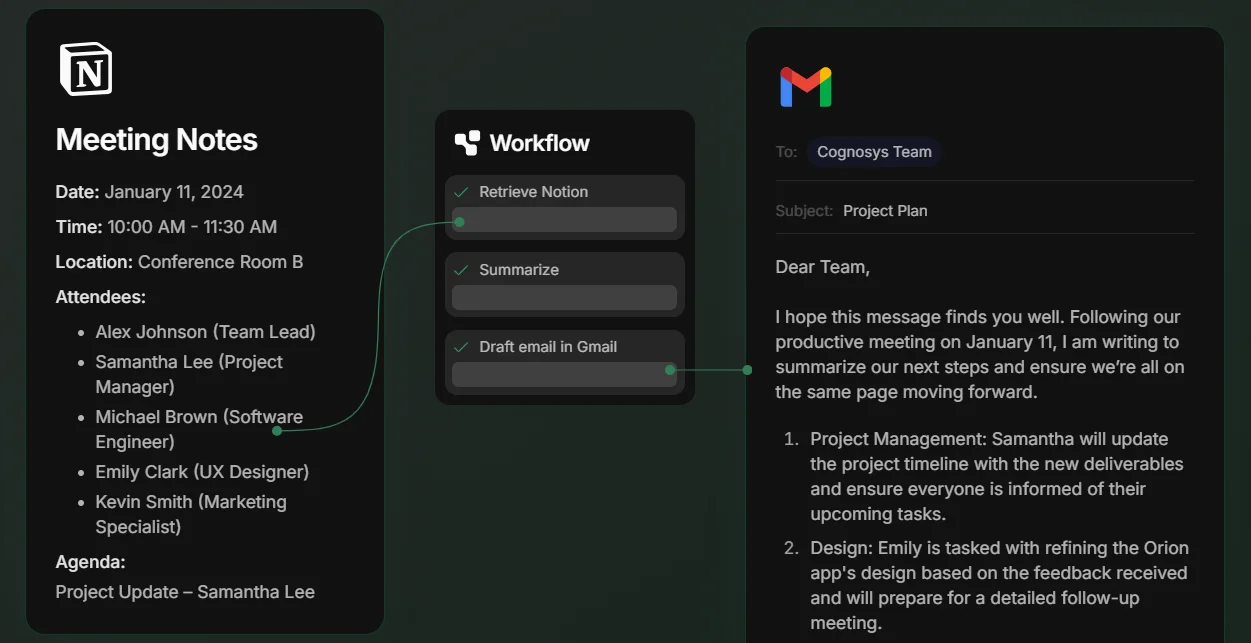
No coding is required, but an underlying algorithm is still in place. Instead of using strings and values, it relies on visual building blocks that streamline processes and enhance accessibility. (Image: Cognosys)
Example: A marketing manager using a no-code tool to automate email campaigns, with an AI agent adjusting email frequency based on engagement data.
Q10: What is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI refers to AI systems designed to independently pursue goals, make decisions and adapt actions as they learn.
Example: Self-driving cars making split-second decisions on the road.
Q11: What are some AI agent use cases in cybersecurity?
- Automatic threat detection and isolation.
- Incident response playbook execution.
- Vulnerability scanning and patch recommendations.
Example: CrowdStrike’s Falcon platform using AI agents to automatically quarantine infected machines.
To learn how SOCRadar uses AI agents, check out our relevant article.
Q12: What is MCP (Multi-Agent Collaboration Platforms)? Why is it being talked about so much?
MCP stands for Multi-Agent Collaboration Platforms. These are systems where multiple AI agents interact with each other to achieve more complex goals.
Example: Imagine one agent is responsible for collecting threat intelligence, another agent analyzes patterns, and a third agent creates a risk report — all without human intervention.
Why the hype?
- They promise exponential productivity gains.
- Complex tasks can be broken into smaller, specialized agent tasks.
What will the real difference be? Instead of one intelligent assistant, businesses will have entire digital teams of agents working together.
Real-life scenario: In an investment firm, multiple agents could scan market news, analyze risk, create summaries, and feed insights into trading systems.
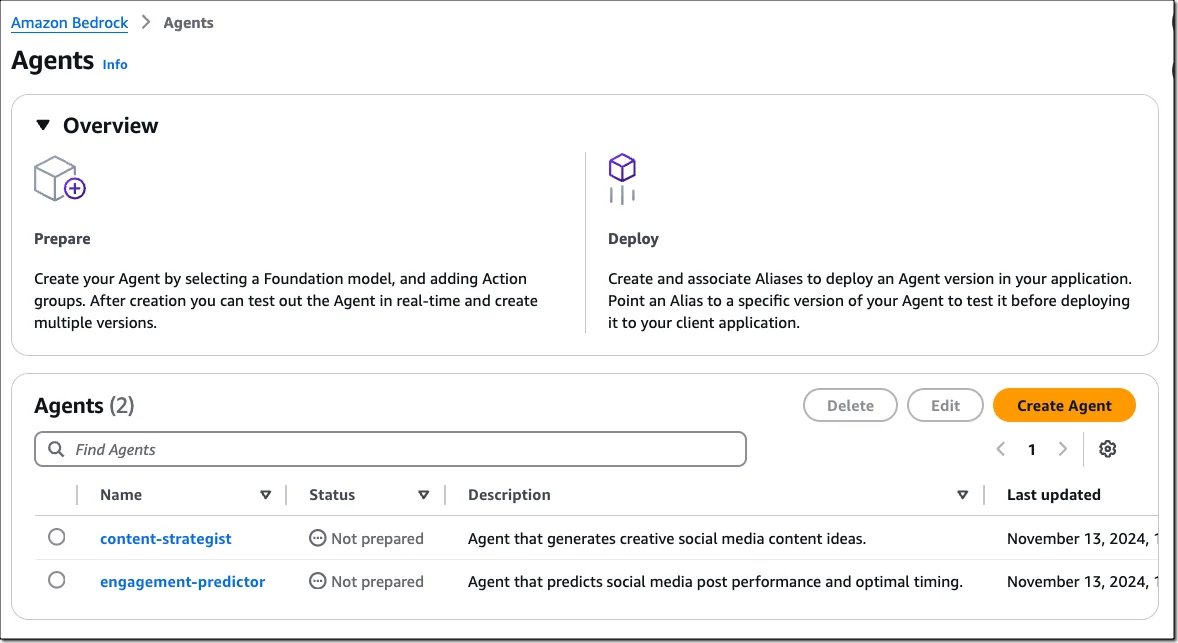
Multi-Agent Collaboration functionality on Amazon Bedrock
Q13: What are examples of well-known open-source and commercial workflow and AI agent platforms?
- Open-source platforms:
- n8n: Visual workflow automation tool allowing users to create complex integrations without code.
- Hugging Face Transformers Agents: Open-source AI agents that interact with models and APIs.
- Auto-GPT (open-source): Early-stage autonomous GPT-based agent.
Auto-GPT claims: Businesses, marketers, educators, and even small business owners can now leverage the power of AI without the need for extensive technical expertise.
- Commercial products:
- Zapier: Leading no-code automation platform.
- Make (formerly Integromat): Commercial workflow automation tool with advanced scenarios.
- Cognosys: Commercial multi-agent platform for task execution.
- CrewAI: A commercial agentic AI tool enabling multiple agents to collaborate on goals.
Example: A company using n8n to connect Slack, Google Sheets, and Jira, while also leveraging Auto-GPT for decision support and CrewAI for automatically generating project documentation.
Conclusion
The hype around AI agents is partly real and partly inflated. The potential is enormous, but practical use cases are still emerging. MCPs are likely to push this evolution forward, enabling AI ecosystems to perform tasks that today require large teams of human specialists.
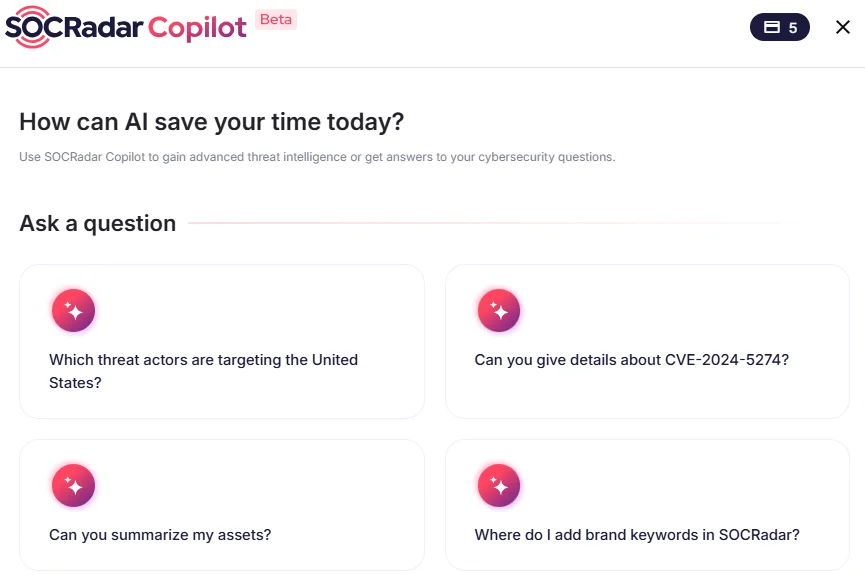
If you’re a business leader or cybersecurity professional, now is the time to start experimenting with AI agents — but keep your expectations grounded and start small. SOCRadar’s Platform already showcases AI’s role in strengthening threat intelligence and automating security processes, offering a glimpse into its growing impact.