
Using Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity (Ultimate Guide)
Welcome to the first of our ultimate guides on cybersecurity topics, starting with artificial intelligence in cybersecurity. In these compilations, we aim to address common questions about pressing issues. We wish these contents to be short, readable, and understandable handbooks for managers, CISOs, and cybersecurity experts.
With the cyberattack surface in modern enterprise environments rapidly expanding, cybersecurity and intelligence organizations are continuously battling with new threats to businesses. Therefore, analyzing and improving an organization’s cybersecurity posture requires much more than human intervention.
How Artificial Intelligence Changed Cybersecurity?
When it comes to the benefits of AI in cybersecurity, analyzing vast amounts of data quickly might be the most useful use case. This capability of AI models allows organizations to detect threats more efficiently. Machine learning algorithms can identify patterns indicating a security breach, which allows organizations to respond faster.
Many tasks in cybersecurity are repetitive tasks where human intervention is not necessary in particular. Since AI models are great at automating things, the usage of AI in cybersecurity can speed up many processes such as threat detection and incident response related tasks. This automation will also help to reduce human error, which is responsible for a significant percentage of data breaches, and allows cybersecurity teams to focus on more strategic initiatives.
In addition to the tasks in the cybersecurity field, many other tasks organizations need to satisfy are also routine and repetitive. Human error is also a factor in those areas. Applying AI solutions to various departments in an organization can lighten the workload of cybersecurity experts.
AI also equips cybercriminals with sophisticated tools. For instance, generative AI can be used to create malware, conduct phishing attacks, and discover vulnerabilities in systems, making attacks more targeted and damaging.
In addition to that, the ease of use of AI tools has lowered the barrier to entry for cybercriminals, enabling individuals with average technical skills to launch attacks and therefore broadened the threat landscape.
AI in the Hands of Hackers and Defenders
AI is a powerful tool that can be used by both hackers (offensive) and defenders (defensive) in the cybersecurity landscape. Here’s a breakdown of how AI can be employed by both sides:
AI in the Hands of Hackers (Offensive Use)
Threat actors can leverage AI models to generate malware. Since these models require training on existing data, the resulting malware designed can only evade traditional detection systems or harm unpatched systems.
Another capability of AI models that threat actors can exploit is text generation. They can create more convincing phishing messages by generating tailored texts for organizations or individuals after identifying patterns and relationships from open sources. Additionally, these models enable attackers to produce error-free content.
AI-Powered Deepfake Technology is another way for threat actors to utilize AI. Hackers can use AI to create deepfake videos, audio, or images that impersonate key individuals (e.g., company executives or politicians), which can be used for fraudulent activities like wire transfers, social engineering, or damaging reputations.
For more detailed information, here is SOCRadar’s CISO Guide to Deepfake Scams.
AI in the Hands of Defenders (Defensive Use)
One of the most significant advancements in cybersecurity is the use of AI for threat detection. Traditional methods often struggle to keep pace with the sheer volume and complexity of potential threats. However, AI in cybersecurity empowers defenders to detect and analyze threats at a scale and speed that humans simply cannot match. Through behavioural analysis, AI can identify anomalies in network traffic or user activity that may indicate a security breach.

SOCRadar Threat Hunting Module
Another use of AI in cybersecurity is in automating incident response. Critical aspects of incident management can be streamlined through AI-driven systems, which can perform real-time attack mitigation. For instance, these systems can automatically isolate compromised devices, block suspicious IP addresses, or shut down affected applications. AI can reduce response times significantly.
AI also enhances the threat hunting capabilities of cybersecurity analysts. By identifying patterns across vast amounts of data, AI can surface relevant Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) more efficiently than traditional methods. Moreover, AI can reduce false positives and improve the accuracy of threat intelligence. This allows defenders to focus their efforts on real threats, rather than wasting time on false positives.
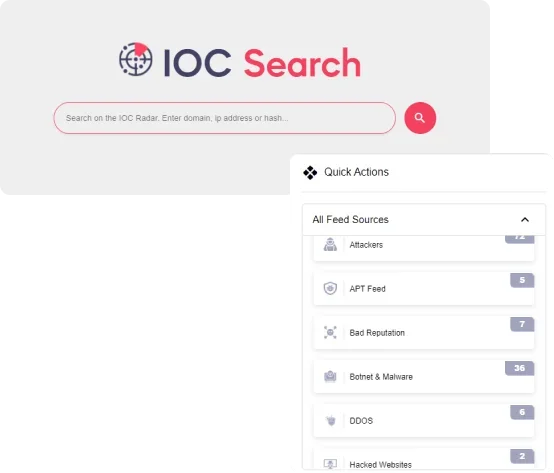
SOCRadar Threat Feed & IOC Management Module
Staying ahead of attackers is essential in the cybersecurity landscape, and the usage of AI in cybersecurity enables experts to do just that through predictive threat intelligence. By analyzing historical attack data, AI can help predict future attack methods or targets, giving organizations a strategic advantage. Additionally, we will see the development of AI solutions in cybersecurity that can anticipate zero-day vulnerabilities by identifying patterns in code or system architecture. This will allow defenders to proactively address potential weaknesses before they can be exploited.
AI is also making significant progress in fraud detection and identity management. By monitoring and analyzing user behavior such as login attempts and transaction patterns, AI can detect fraudulent activities in real time.
Finally, AI in cybersecurity assists defenders in vulnerability management and patch prioritization. By analyzing large datasets on vulnerabilities and exploits, AI can help organizations identify and address the most critical vulnerabilities effectively. This capability is also reducing the time spent on manual assessments significantly just like it does with automating incident response.
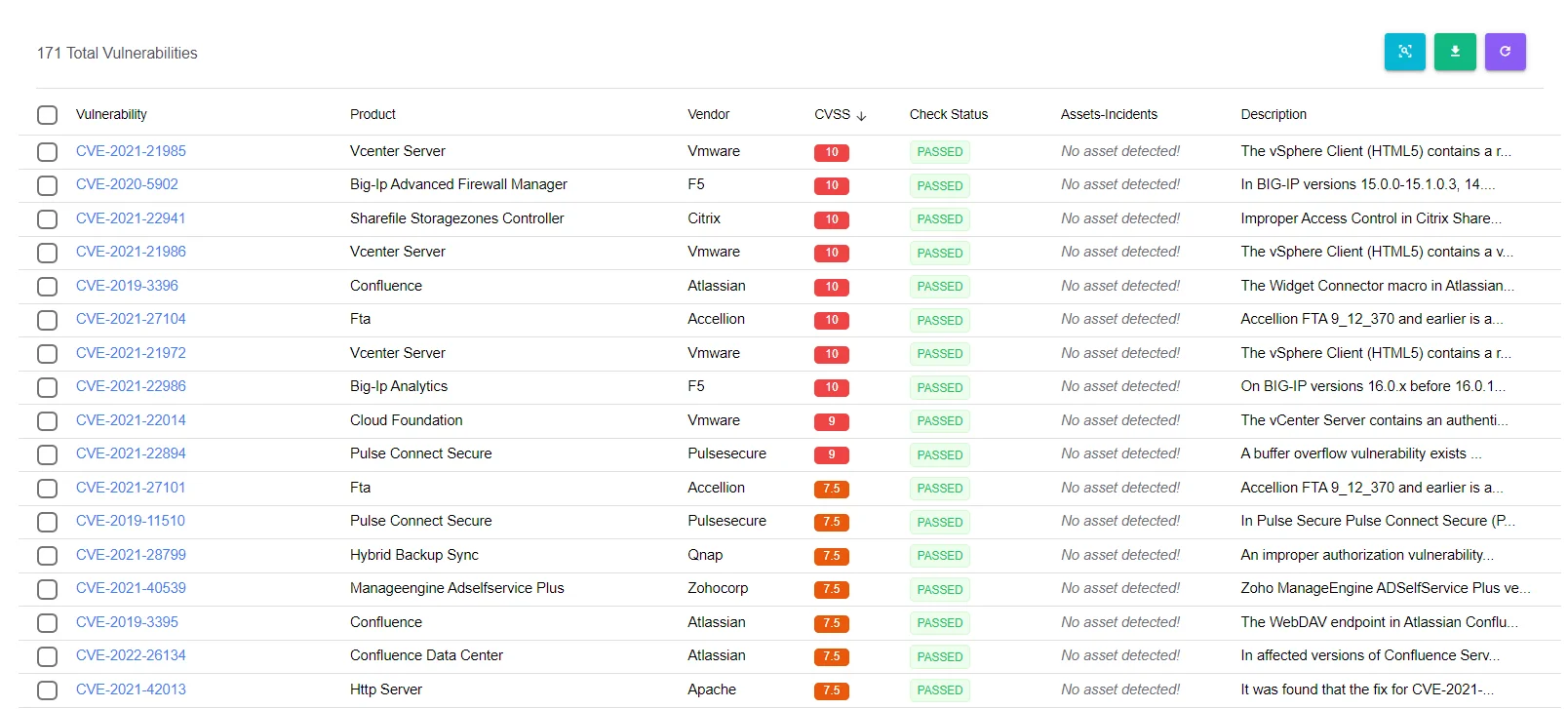
SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence Module
Conclusion
In summary, the last few years have seen AI become a pivotal element in cybersecurity, enhancing threat detection and response capabilities while simultaneously presenting new challenges.
When evaluating both perspectives, individuals leveraging AI in cybersecurity hold a distinct advantage because the use of AI models requires large datasets for effective training. While malicious applications of AI—such as generating phishing emails, correcting errors, and creating rudimentary malware—remain a concern, AI’s primary benefit lies in enhancing defensive capabilities.



































