
Examples of AI-Assisted Cyber Attacks
AI-assisted cyberattacks, driven by the rapid advancements in generative AI, have become a significant concern in the cybersecurity landscape. Cybercriminals are increasingly leveraging these technologies to craft sophisticated and convincing attacks that traditional security measures often struggle to counter.

An illustration for “AI-powered cyber attacks” by DALL-E
From generating realistic phishing emails to creating advanced malware, generative AI is transforming the way threats are executed, making them more dangerous and difficult to detect.
This article explores how cybercriminals are using generative AI in their attacks and what this means for the future of cybersecurity.
How Is Generative AI Used for Cyber Attacks?
Generative AI has rapidly emerged as a powerful tool for both cybersecurity professionals and cybercriminals. Its ability to generate realistic and sophisticated content has opened new avenues for malicious activities, creating significant challenges in the cybersecurity landscape.
Here are three common ways generative AI could be utilized by attackers:
1. AI-Generated Phishing and Social Engineering
One of the most common uses of generative AI in cyber attacks is crafting highly convincing phishing emails and social engineering campaigns.
AI models like GPT can generate emails that mimic the tone, style, and language of legitimate communications from trusted organizations. These AI-generated emails are often devoid of the common errors that make traditional phishing attempts detectable, making them significantly harder to identify as fraudulent.
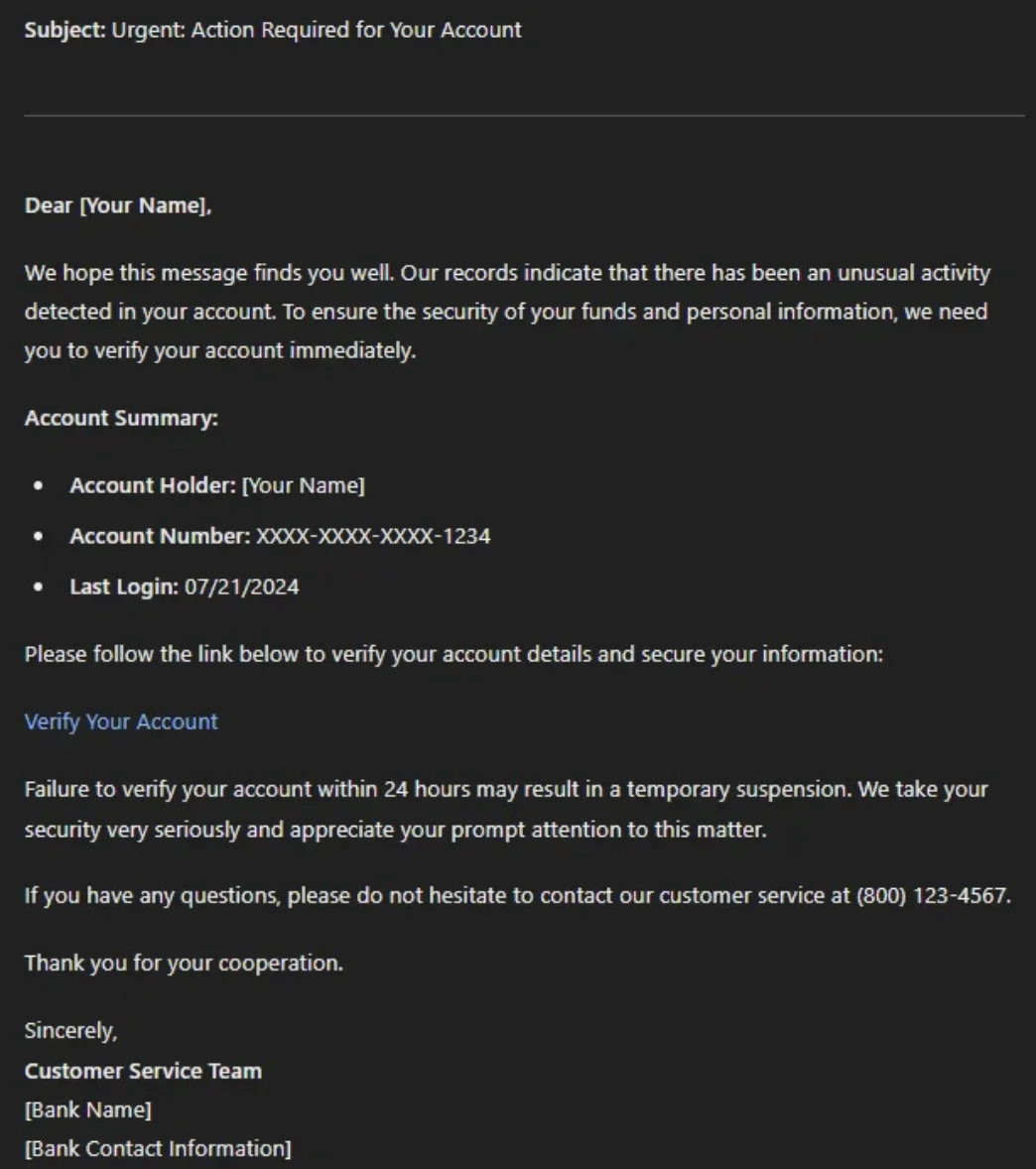
A bank phishing scam, generated by AI
An example case is HackerGPT, a generative AI model designed for ethical hacking; it is a test case, used to generate phishing emails that are virtually indistinguishable from legitimate communications. For instance, when prompted to create a phishing email targeting hospital employees, HackerGPT produced a highly convincing message that bypasses traditional security filters, making the “typos in phishing emails” point obsolete.
2. Creation of Malware and Ransomware with AI
Generative AI can also be employed to develop polymorphic malware – malicious software that continuously changes its code to evade detection.
AI-generated malware can be designed to modify itself in real-time, making it nearly impossible for traditional security measures to identify and neutralize it. This capability has been demonstrated in proof-of-concept attacks, such as those involving AI-generated malware like BlackMamba, which uses generative AI to create polymorphic code designed to bypass endpoint detection and response (EDR) systems.
3. AI-Automated Scam and Fraud Operations
Cybercriminals use AI to automate and scale their fraudulent activities. For instance, AI-generated websites and fake reviews can deceive consumers into trusting and transacting with fraudulent entities. Custom GPT models tailored for specific malicious purposes, such as generating scam websites or automating social engineering attacks, have further escalated the scale of these operations.
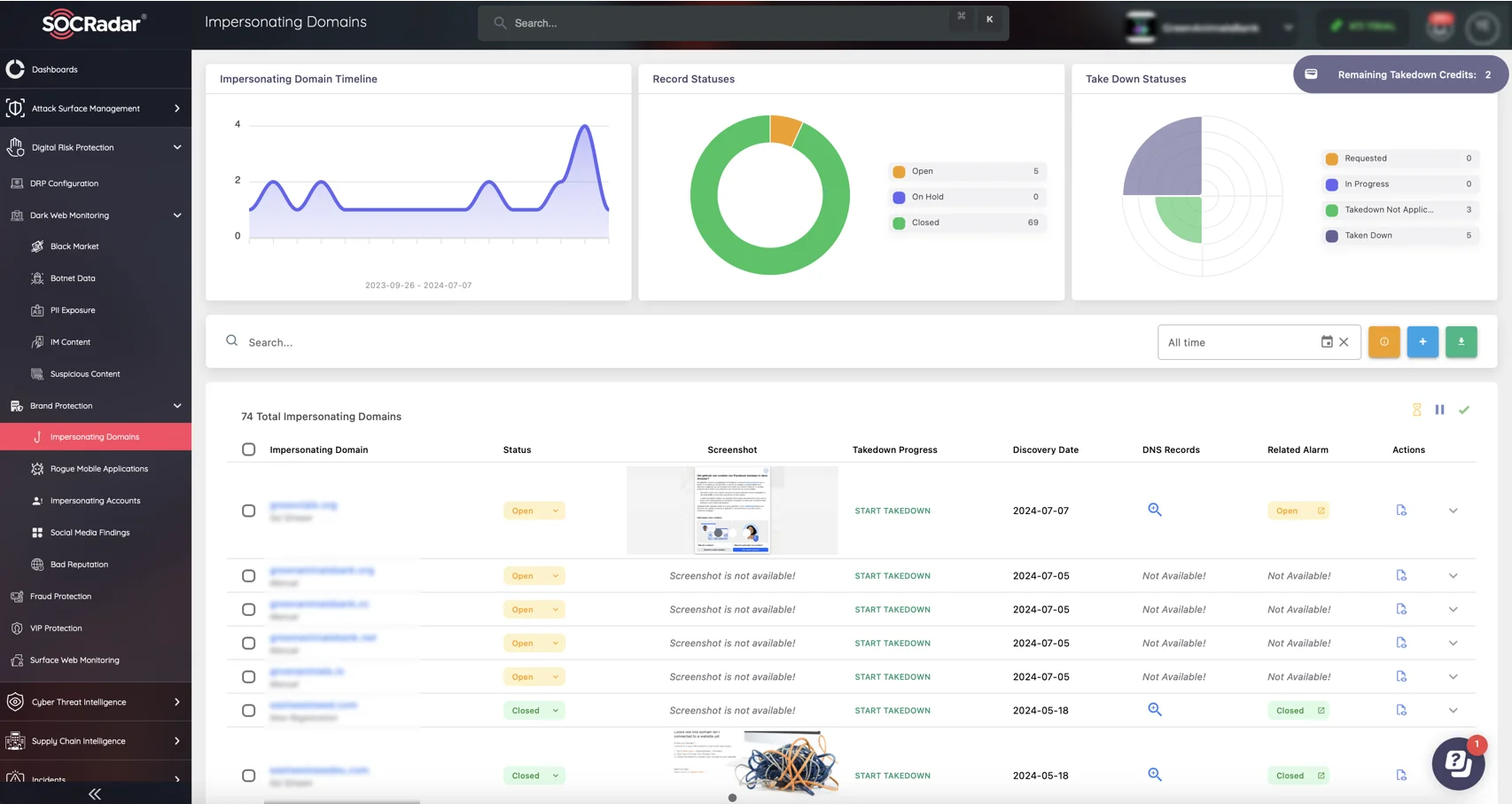
Monitor the web for impersonating domains and initiate a takedown (SOCRadar Brand Protection)
By understanding how generative AI is utilized in cyber attacks, organizations can better prepare and implement robust defense mechanisms to counteract these sophisticated threats. Integrating AI-driven threat detection tools into cybersecurity protocols is essential to staying ahead in this evolving battle between attackers and defenders.
In a previous post, we have thoroughly discussed how AI, or Custom GPT models, could be weaponized by threat actors to commit fraud. Read it on SOCRadar blog for further context: How Custom GPT Models Facilitate Fraud in the Digital Age.
What is AI Generated Malware?
AI-generated malware represents a new frontier in cybersecurity threats, leveraging the power of artificial intelligence to create more sophisticated and adaptable malicious software.
Unlike traditional malware, which is typically static and relies on predefined code, AI-generated malware can be designed to dynamically modify its behavior (to be ‘polymorphic’), making it harder to detect and counteract.
What is Polymorphic Malware?
One of the most significant examples of AI-generated malware is polymorphic malware. This type of malware can change its code structure every time it infects a new system, effectively evading traditional signature-based detection methods used by antivirus software.
The AI engine behind this malware continuously rewrites its code, ensuring that each iteration is unique. For example, BlackMamba, also as mentioned in an earlier section, is a polymorphic AI-generated malware that uses generative AI to create and execute different versions of itself, making it extremely difficult for security solutions to identify and eliminate.
Explore more on the context and how to prevent AI malware attacks on our blog, “AI vs. AI: Future of the Cybersecurity Battles.”
Key Features of an AI-Assisted Malware: Evasion Techniques & Autonomous Attack Strategies
AI-generated malware often employs advanced evasion techniques, such as code obfuscation, where the malware’s code is deliberately made more complex and difficult to analyze. Additionally, these malware types can use AI to mimic legitimate software behavior, blending into normal system operations, which allows them to operate undetected. This adaptability makes AI-generated malware particularly dangerous, as it can continuously evolve to bypass even the most advanced security measures.
Another characteristic of AI-generated malware is its ability to autonomously strategize attacks. AI can analyze the target environment, choose the most effective attack vectors, and deploy payloads at optimal times. This level of sophistication means that AI-generated malware is not just a tool for initial infiltration but can also manage and execute complex attack chains, from exfiltration of data to launching ransomware attacks.
Mitigating the Risks of AI-Powered Cyber Attacks
To effectively mitigate the risks of AI-assisted cyber threats, organizations can implement several key strategies:
- Continuous Monitoring: Employ continuous monitoring of networks and systems to detect and respond to threats in real time. SOCRadar’s platform enhances this process by providing up-to-the-minute threat intelligence and actionable alerts.
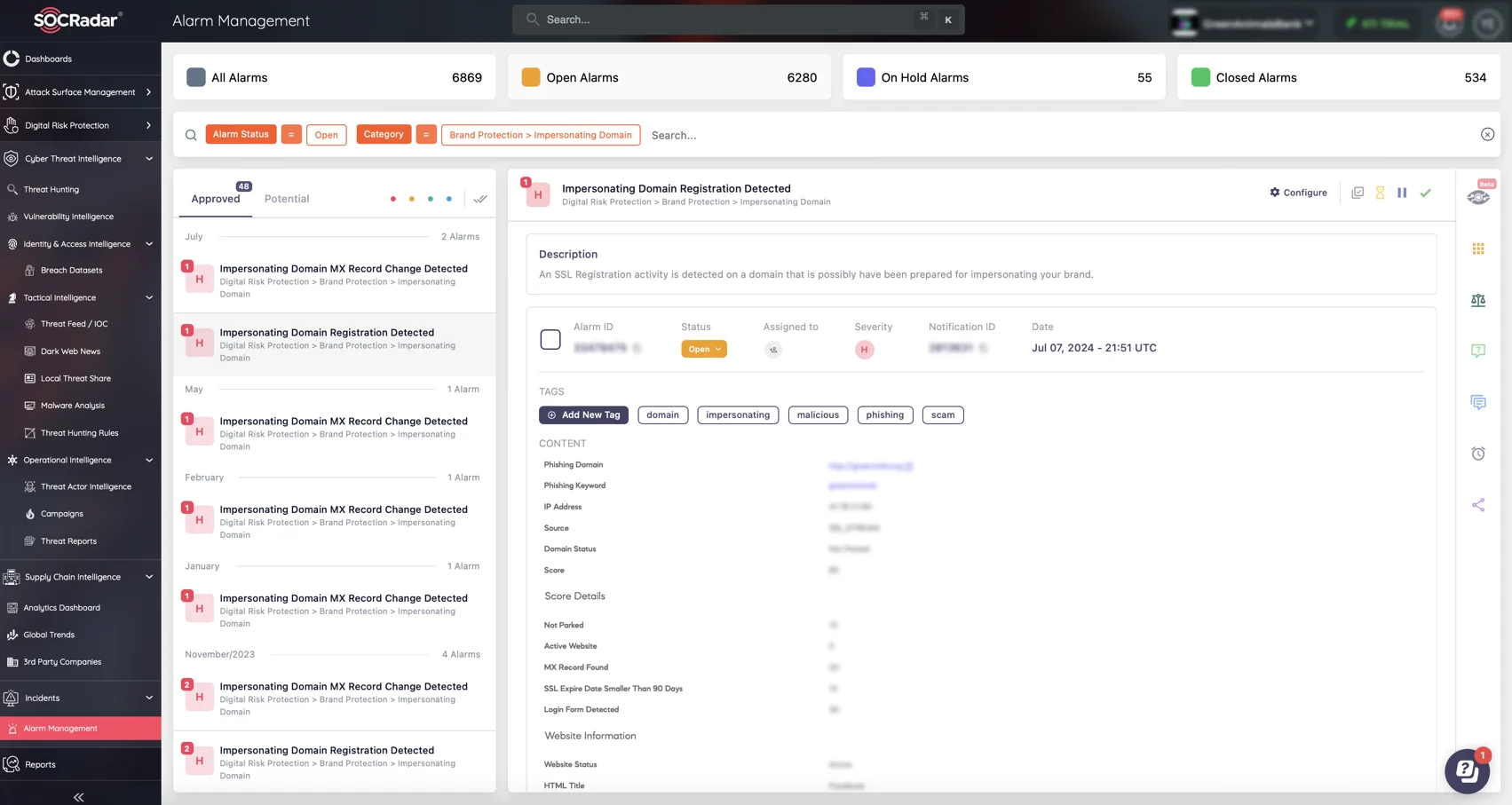
A SOCRadar alarm for an Impersonating Domain
- Threat Detection: Implement advanced threat detection systems that analyze behavioral patterns and identify suspicious activities early. SOCRadar’s platform integrates with existing tools, improving detection capabilities.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits and patch vulnerabilities promptly. Use SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence feature to stay informed about emerging threats and ensure timely remediation.
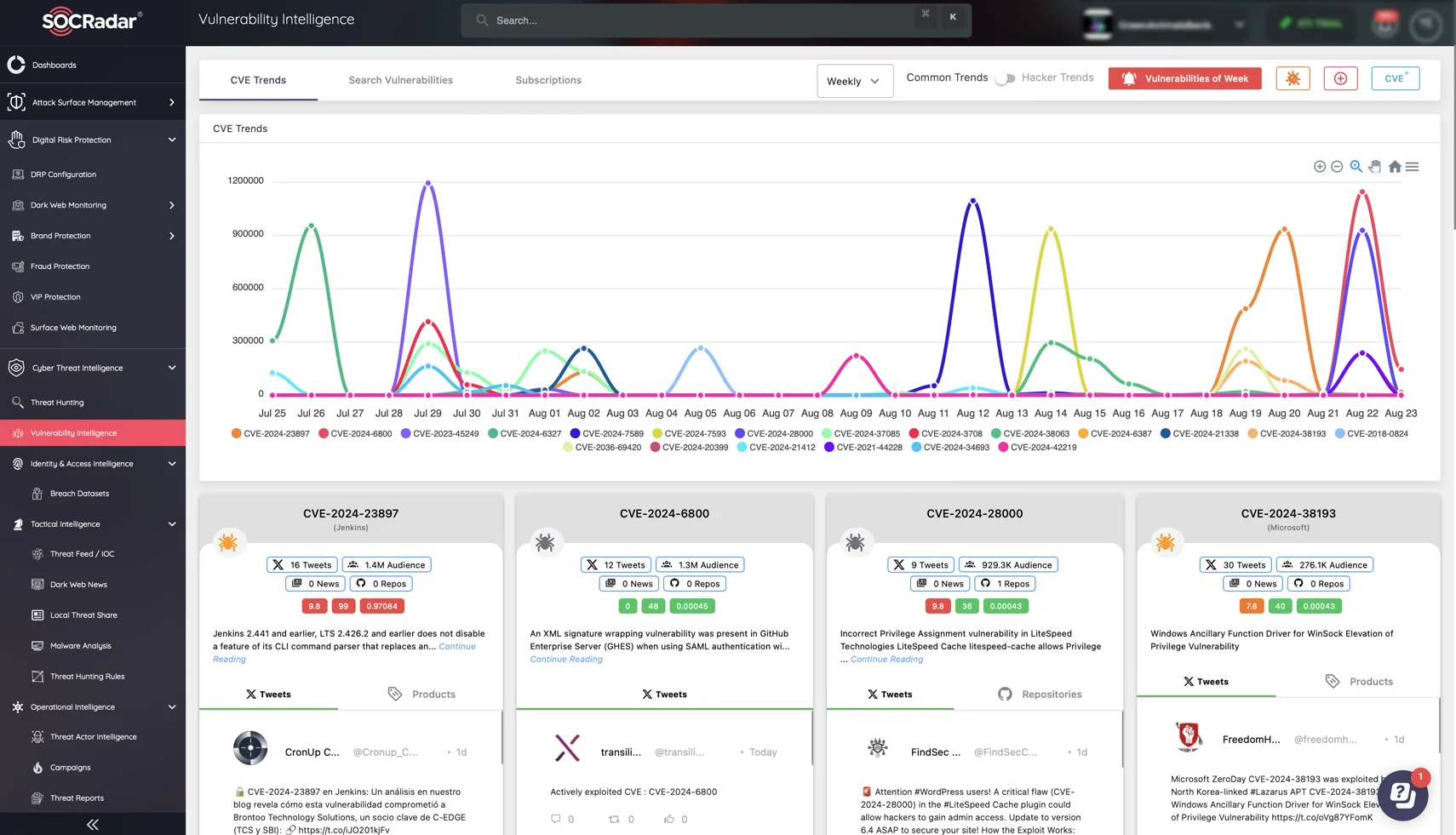
Vulnerability Intelligence module of SOCRadar
- Advanced Email and Content Filtering: Use sophisticated filtering solutions to block phishing attempts and other malicious content. SOCRadar’s Digital Risk Protection module helps monitor and protect against such threats, helping you detect fraud attempts and exposed information.
In addition, you can use SOCRadar LABS’s free Email Analyzer feature to scan EML files for malicious content and protect yourself from phishing attacks.

Email Threat Analyzer on SOCRadar LABS
- Employee Training: Regularly train employees to recognize and respond to AI-powered cyber threats, particularly those involving phishing and social engineering.
These strategies, when combined with SOCRadar’s comprehensive cybersecurity solutions, create a robust defense against AI-driven threats. Additionally, AI can be utilized to automate many of these defense procedures, enhancing efficiency and response times.
Conclusion – The Future of AI in Cybersecurity: Defense vs Offense
As AI technology advances, its role in cybersecurity will continue to evolve, with both cybercriminals and defenders leveraging its capabilities.
On the offense, AI is being utilized to create sophisticated malware, automate phishing campaigns, and conduct large-scale fraud, posing significant challenges to traditional security measures. However, on the defense side, AI-driven tools are helping organizations stay ahead of these threats by enhancing detection, response, and monitoring capabilities.
The future of cybersecurity will likely see a continued arms race between these two sides, with AI playing a central role. By adopting advanced strategies and integrating solutions like those offered by SOCRadar, organizations can improve their defenses and stay resilient against the growing threat landscape. The balance between AI’s offensive and defensive applications will shape the future of cybersecurity.





































