
GitLab Security Update: Critical Authentication & RCE Flaws Demand Immediate Action
Cybersecurity threats continue to evolve, and organizations relying on GitLab for code hosting, collaboration, and CI/CD must remain vigilant. The latest GitLab security patch – versions 17.9.2, 17.8.5, and 17.7.7 – addresses multiple vulnerabilities, including authentication bypass risks and a Remote Code Execution (RCE) threat, which could be exploited by attackers to compromise user accounts, leak sensitive data, or disrupt operations.
This blog will outline the latest GitLab updates, highlighting the most severe security issues and recommended mitigation steps.
The Biggest Security Concerns in GitLab’s Latest Patch
The latest patch fixes a range of vulnerabilities, some of which are deemed critical in severity. Understanding these risks is essential to maintaining the security of your GitLab environment.
Authentication Bypass via SAML (CVE-2025-25291 & CVE-2025-25292)
GitLab has addressed two critical vulnerabilities (CVSS 9.8) in the ruby-saml library, which is used when SAML SSO authentication is enabled.
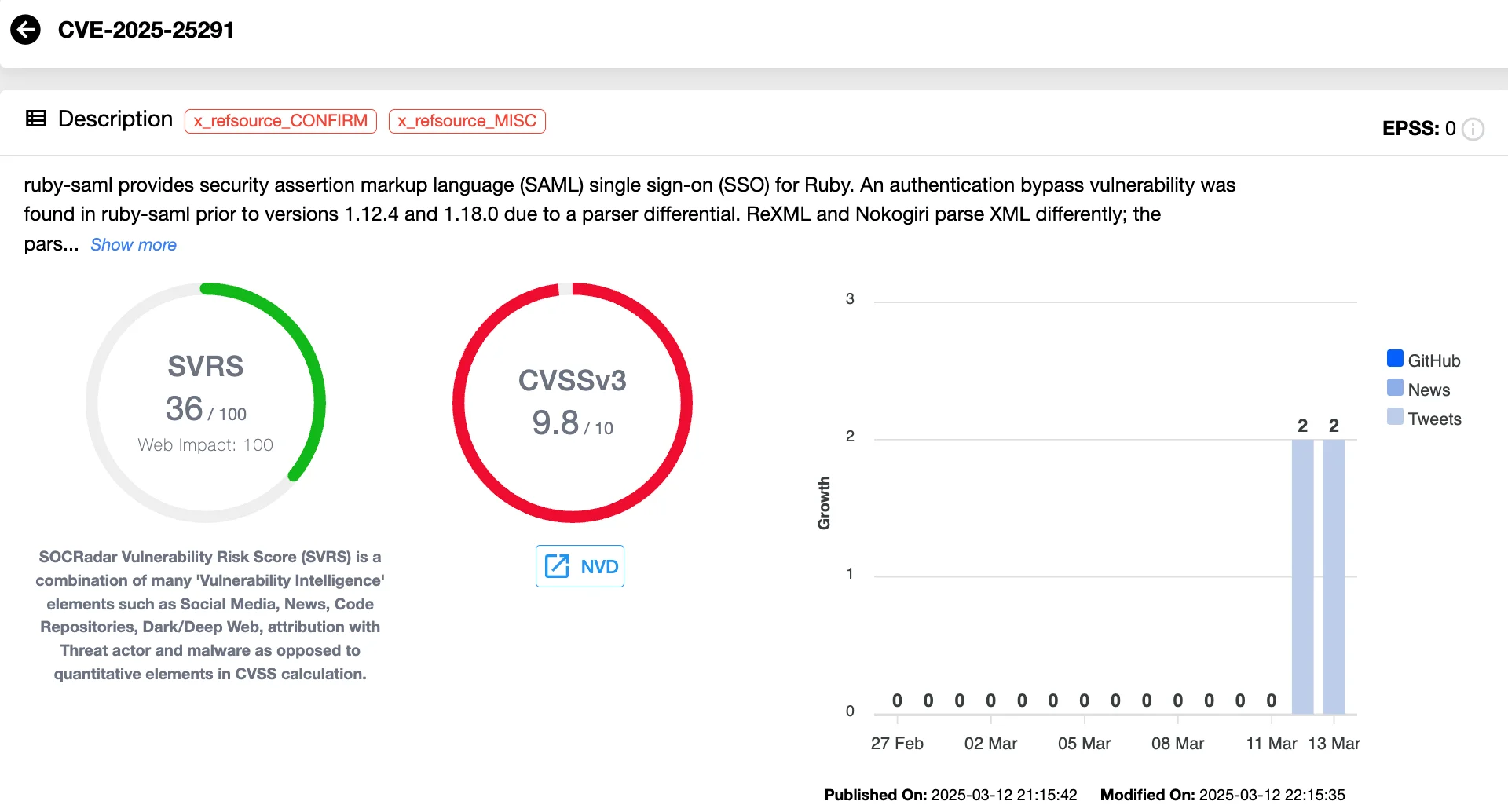
Vulnerability card of CVE-2025-25291 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Exploiting these flaws, an attacker with access to a legitimate signed SAML document from an identity provider (IdP) could bypass authentication and assume the identity of another valid user, potentially leading to unauthorized access to sensitive repositories and data.
To minimize the risk of exploitation, administrators should take the following steps:
- Require all user accounts to enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) for an added layer of security.
- Ensure the SAML two-factor bypass option is disabled to prevent authentication bypass.
- Set admin approval as mandatory for automatically created new users to prevent unauthorized access.
Remote Code Execution via GraphQL (CVE-2025-27407)
Another critical vulnerability (CVSS 9.0) addressed was in the Ruby graphql library – it could enable Remote Code Execution (RCE) under certain conditions. If an attacker-controlled authenticated user account attempted to transfer a maliciously crafted project via GitLab’s Direct Transfer feature, they could potentially execute arbitrary code on the system.
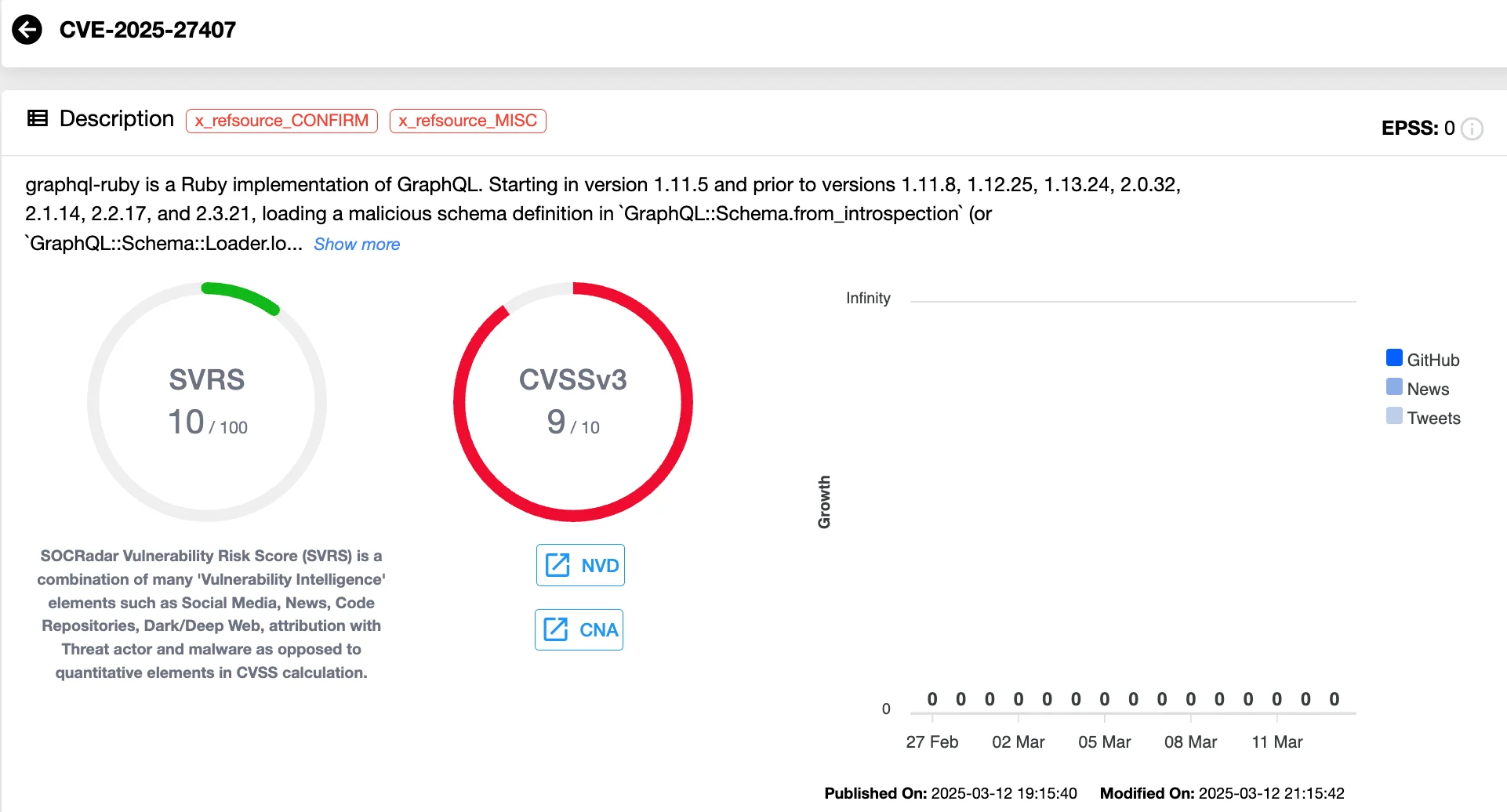
Vulnerability card of CVE-2025-27407 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
GitLab notes that since Direct Transfer is still in beta and disabled by default for all self-managed instances, it presents a lower immediate risk. However, if enabled, this vulnerability could be exploited to gain unauthorized control over a system, making it a serious concern.
To protect against potential exploitation, consider the following actions:
- If Direct Transfer is enabled, disable it to eliminate the risk.
- Upgrade to the latest patch version to ensure the vulnerability is fully mitigated.
Other Security Fixes
The patch release also includes fixes for several medium and low-severity vulnerabilities:
- CVE-2025-1257 (CVSS 6.5):Denial of Service (DoS) vulnerability in GitLab Approval Rules – Unbounded field manipulation could cause service disruption.
- CVE-2024-13054 (CVSS 5.7): Denial of Service (DoS) due to inefficient input processing – Could allow an attacker to force a system reboot.
- CVE-2024-12380 (CVSS 4.4): Credentials exposure in repository mirroring – Certain repository mirroring failures could leak sensitive authentication information.
- CVE-2025-0652 (CVSS 4.3): Internal Notes Leak in Merge Requests – Internal notes could be emailed to non-members.
- CVE-2024-8402 (CVSS 3.7): Shell Code Injection in Google Integrations – A GitLab Maintainer could inject malicious shell code.
- CVE-2024-7296 (CVSS 2.7): Guest Permission Bypass – A guest user with custom admin permissions could approve user invitations beyond allowed limits.
Additionally, PostgreSQL versions 14.17 and 16.8 have been integrated as part of this update.
Act Now to Protect Your GitLab Instance from Critical Threats
If you operate a self-managed GitLab instance, updating immediately is strongly recommended to prevent potential breaches. GitLab.com has already been updated, and GitLab Dedicated customers will be notified once their instance has been patched.
If you’re using GitLab CE/EE, upgrade to one of the patched versions (17.9.2, 17.8.5, or 17.7.7) as soon as possible. Delaying this update could expose your GitLab instance to serious security risks.
For full details, mitigation instructions, and patching guidance, refer to the official update release note.
One Unified Solution for Cyber Risk Management: SOCRadar XTI
Patching vulnerabilities is just one piece of the cybersecurity puzzle. To truly secure your environment, your organization needs continuous threat visibility and proactive risk management. SOCRadar provides the tools to do just that.
Track the status of digital assets and company vulnerabilities with the ASM module
SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence and Attack Surface Management (ASM) work together to keep your organization secure. With real-time insights, automated alerts, and deep visibility into your digital assets, these tools help you:
- Identify and prioritize vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them.
- Monitor your external attack surface to detect exposed data, shadow IT, and infrastructure risks.
- Receive instant alerts on high-risk threats tied to your environment, ensuring swift mitigation.
By integrating these solutions, your organization can proactively detect, analyze, and respond to security threats before they escalate.


































