
Inside the Dark Web Economy: Key Insights from SOCRadar’s Annual Dark Web Report 2024
With cyber threats evolving and growing more sophisticated every year, the dark web remains a key hotspot for distribution and trade. SOCRadar’s 2024 Annual Dark Web Report offers valuable insights for cybersecurity professionals, shedding light on the most significant developments and emerging threats in this hidden corner of the internet.
In this blog post, we delve into key statistics from the report, offering an overview of the most critical areas shaping the dark web landscape.
1. Malware, Exploits, Tools, and Services
One of the most prevalent and effective threats in the cybercrime ecosystem is malware, along with the exploits that facilitate its use.
Malicious Software and Tools
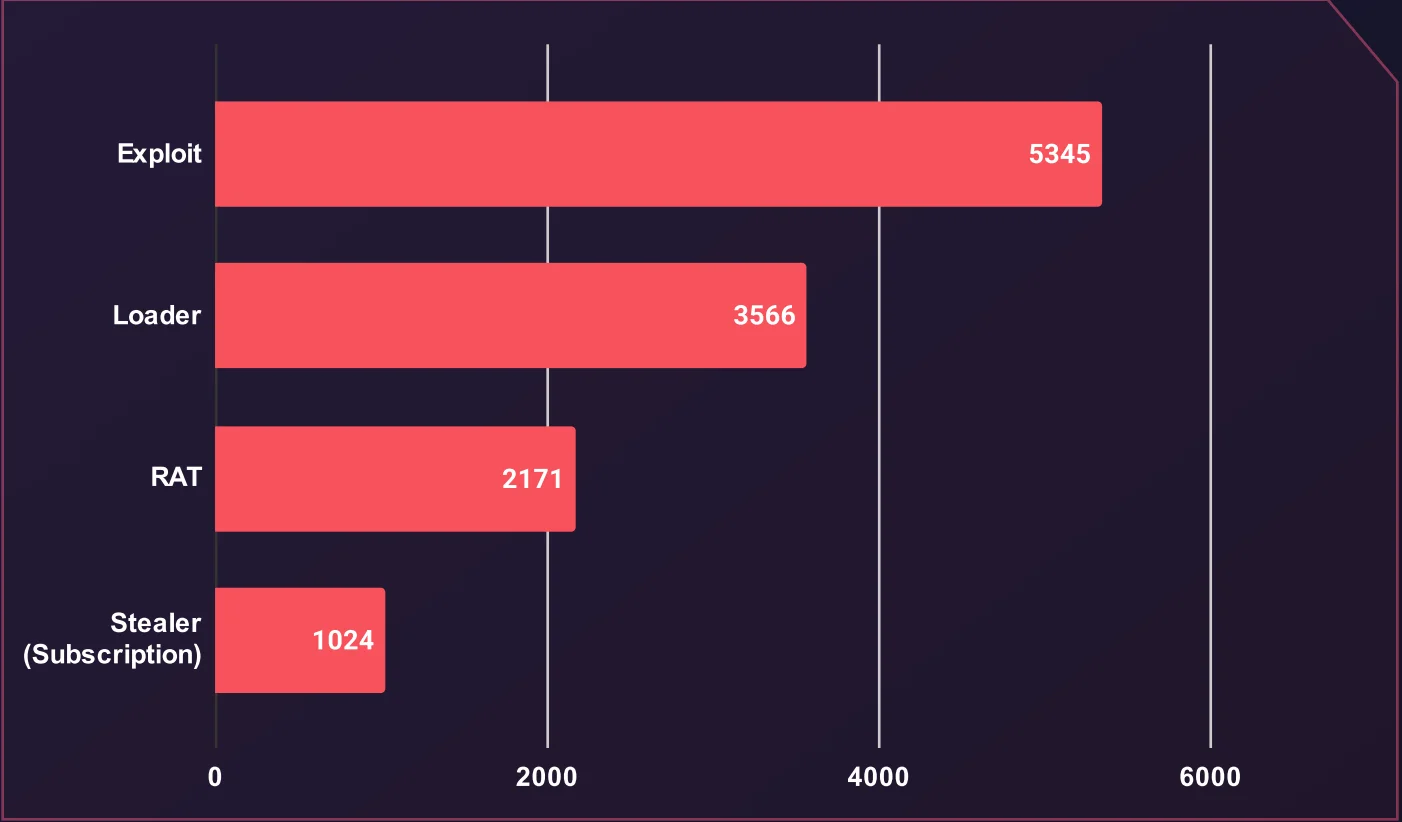
Average Price of Various Software and Tools (USD)
Exploits command the highest average price at $5,345, reflecting their impact and potential for accessing victim systems. Loaders follow at an average of $3,566.
Loaders, which facilitate the delivery of malicious payloads, have an average price of $3,566, indicating demand for their utility in deploying other types of malware. Subscription-based Stealers are priced considerably lower, averaging $1,024, which aligns with their widespread usage and the competitive market for such services.
0-Day Market
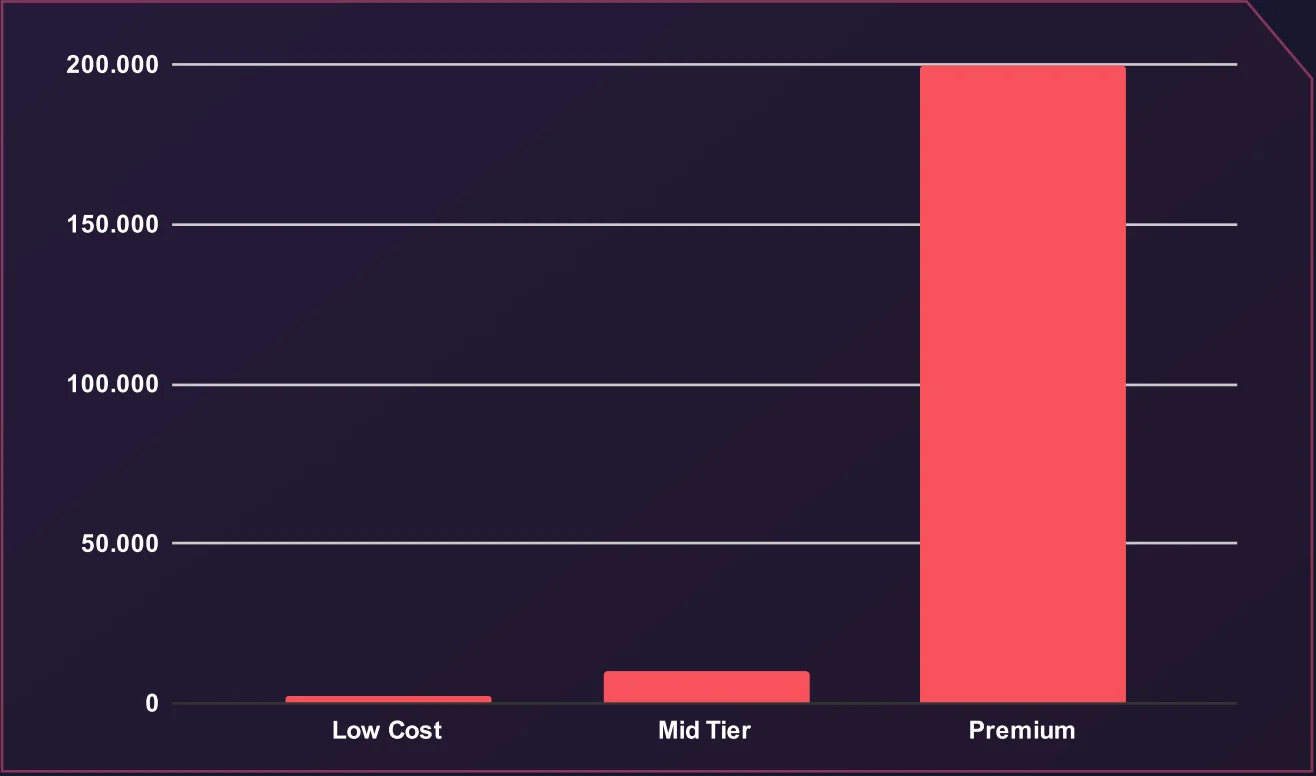
Average 0-Day Price
The Dark Web marketplace for zero-day vulnerabilities reveals a diverse pricing spectrum, ranging from $100 to $200,000, reflecting the exploit’s target, exclusivity, and potential impact. Low-cost listings ($100–$1,000) often include less critical or commoditized vulnerabilities, while premium 0-Days target high-value systems such as Windows OS and enterprise VPNs.
Low-cost listings generally feature vague descriptions and claim to work across a wide range of products, including both software and hardware.
Mid-tier listings typically target widely used tools. While these tools are popular, they are not necessarily critical regarding the data they collect or their role within a larger workflow.
The most expensive 0-days, or premium-tier exploits, usually focus on operating systems and enterprise-level VPN services.
Spamming and DDoS Services
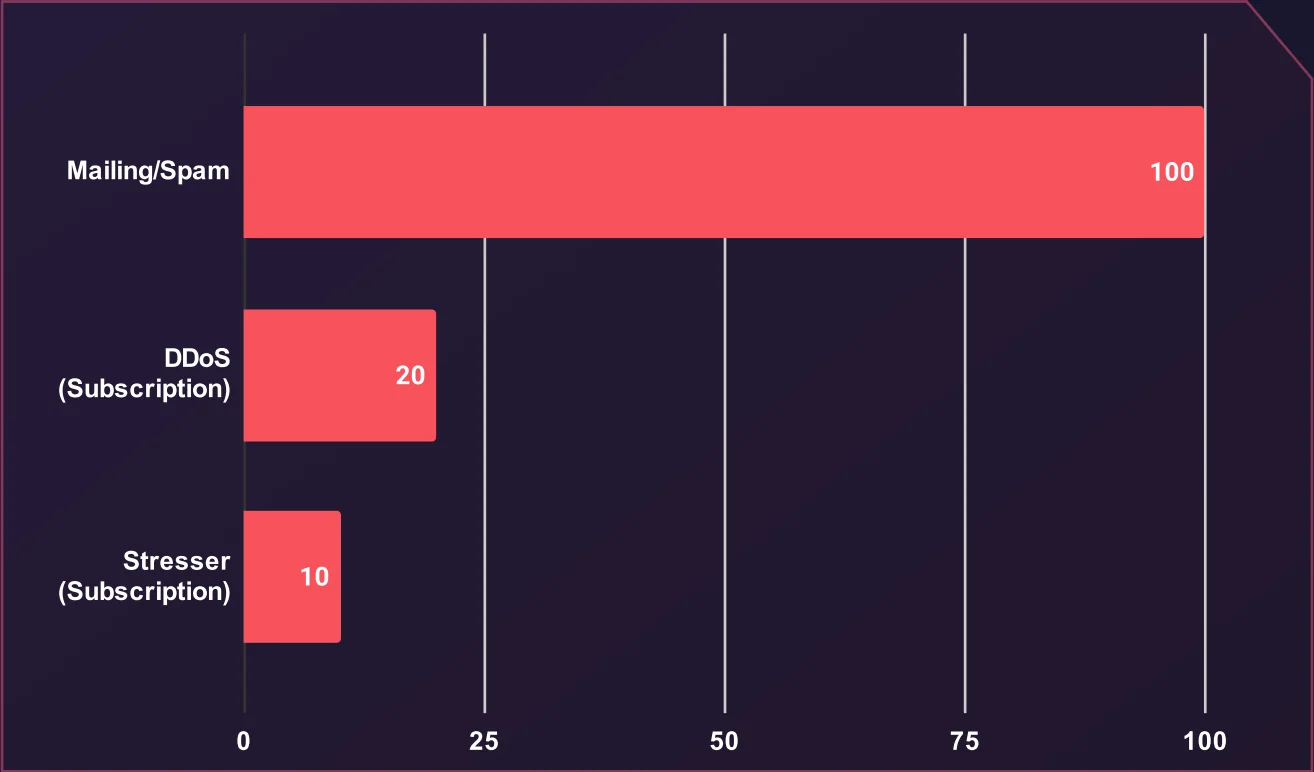
Average Price of Various Spamming and DDoS Services (USD)
Mailing and spam services command the highest price in this category, averaging $100. This higher cost likely reflects the infrastructure required to conduct large-scale email campaigns, including access to compromised email lists, automated tools, and specialized configurations to bypass spam filters effectively. Such services are often used for phishing campaigns, malware distribution, or fraud.
DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks offered on a subscription basis average $20, providing attackers with affordable and sustained means to disrupt online services. Stressers, often marketed as legitimate tools for network testing but widely misused for DDoS attacks, are even cheaper, with subscription prices averaging $10.
Hacking Services
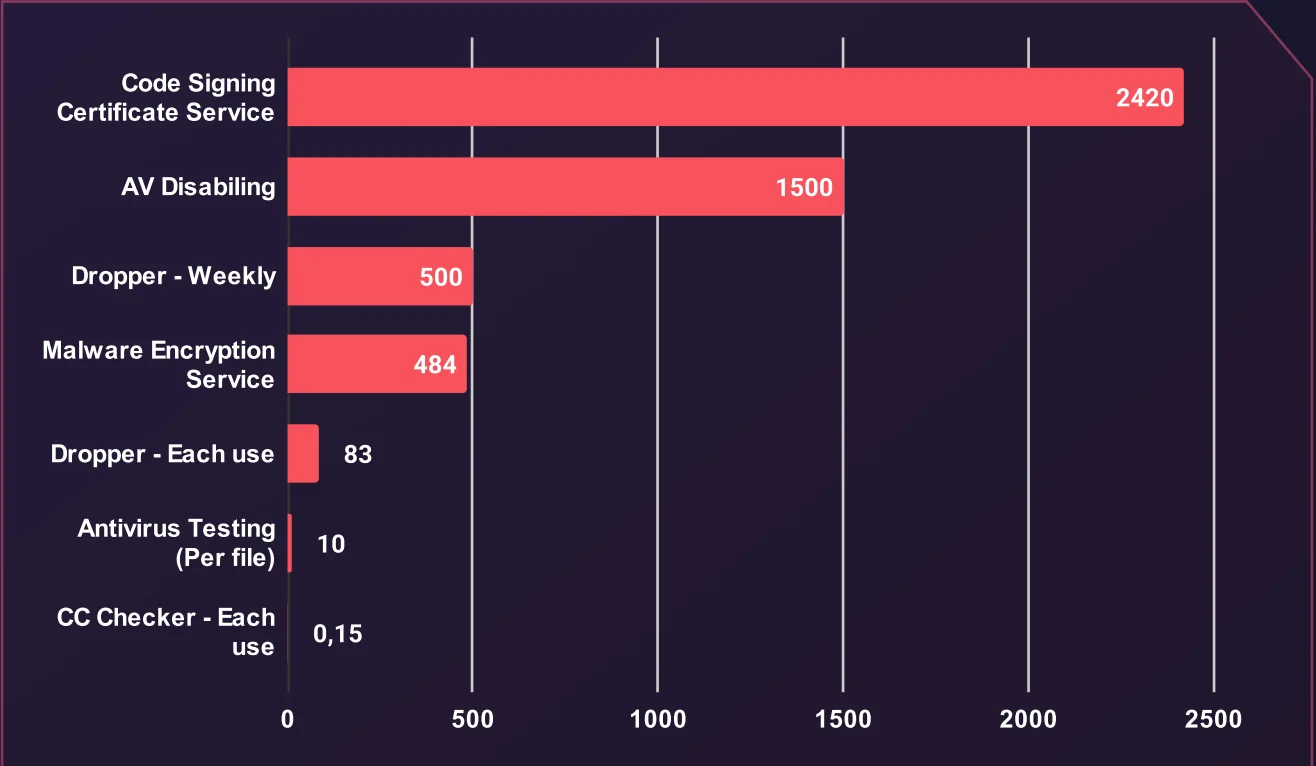
Average Price of Various Hacking Services (USD)
Code signing certificate services top the list at an average of $2,420, highlighting their value in making malware appear legitimate. Antivirus-disabling services follow at $1,500, prized for helping malware slip past detection.
Droppers, used to deliver malware, vary in price $500 for weekly access and $83 per use offering flexibility for different attack strategies. Malware encryption services average $484, reflecting their importance in hiding malicious code from security tools.
Phishing Kits and Templates
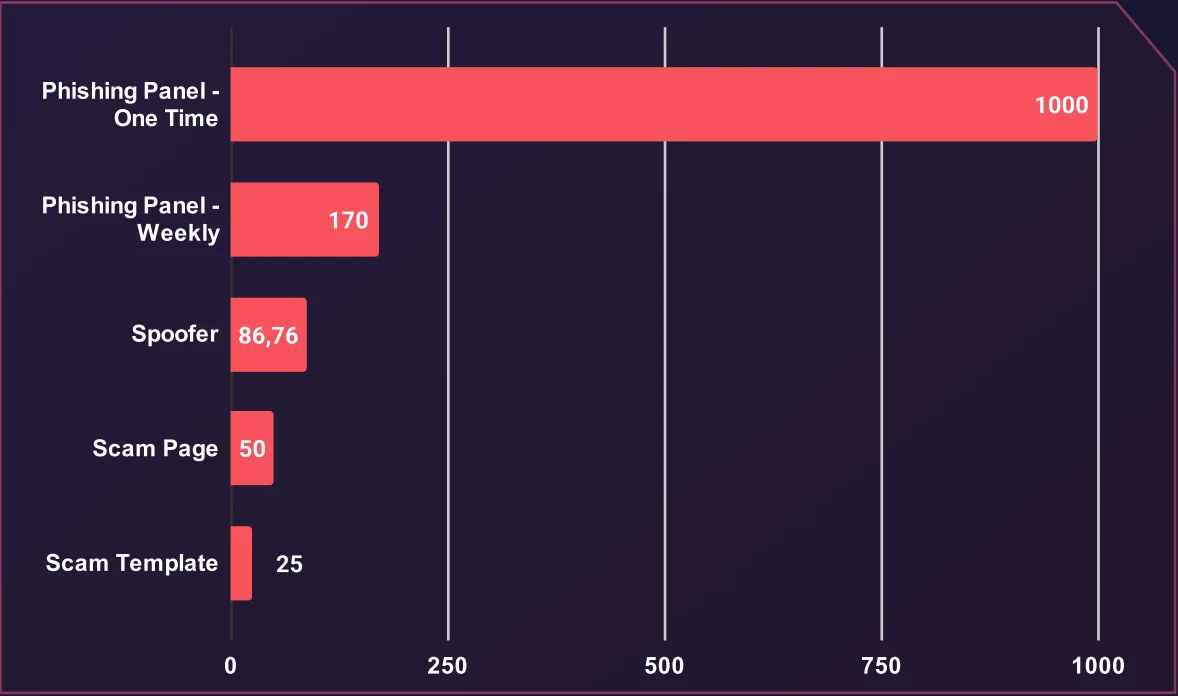
Average Price of Phishing Material (USD)
Phishing panels, a centralized platform for managing phishing campaigns, are the most expensive in this category. A one-time purchase costs $1,000 on average, while a weekly subscription averages $170, reflecting demand for long-term and short-term use cases.
Spoofers, designed to manipulate communications or impersonate entities, have an average price of $86.76, making them a relatively affordable but versatile tool in phishing campaigns. Scam pages, typically used to deceive victims into providing sensitive information, average $50 per instance, while scam templates, offering pre-designed content for fraudulent activities, are the most inexpensive at $25.
2. Financial Services and Fraud
Credit Cards
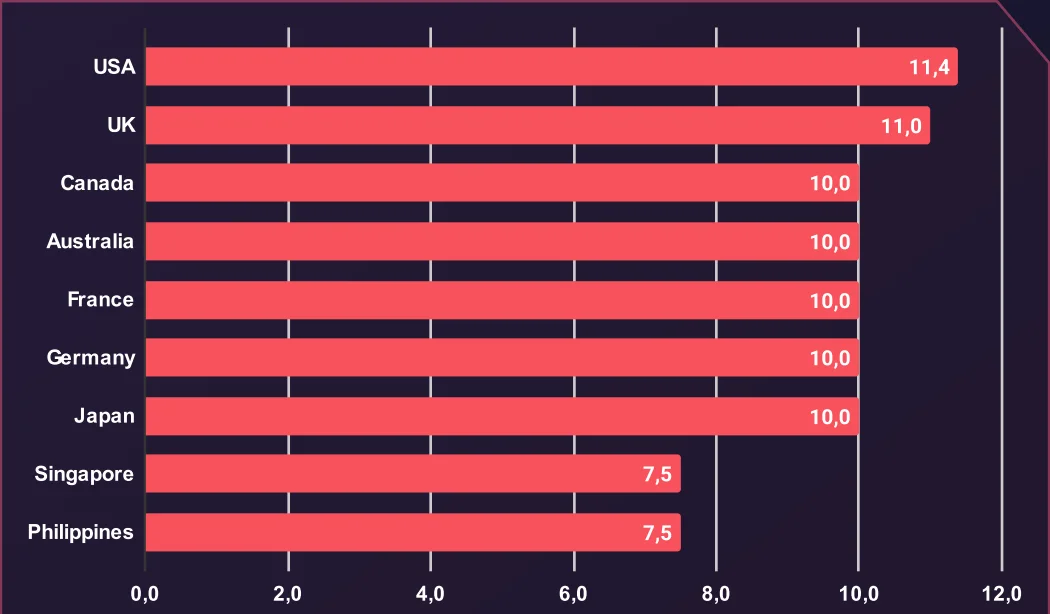
Average Credit Card Prices by Country (USD)
U.S. credit cards are the most expensive, averaging $11.40, followed closely by the U.K. at $11.00. These higher prices may reflect greater spending limits, higher credit availability, or perceived profitability of fraudulent transactions in these regions.
These pricing patterns reflect the demand for and profitability of compromised credit card data across different regions. The higher prices associated with U.S. and U.K. cards indicate these markets are particularly lucrative for threat actors.
Personal Information and Documents
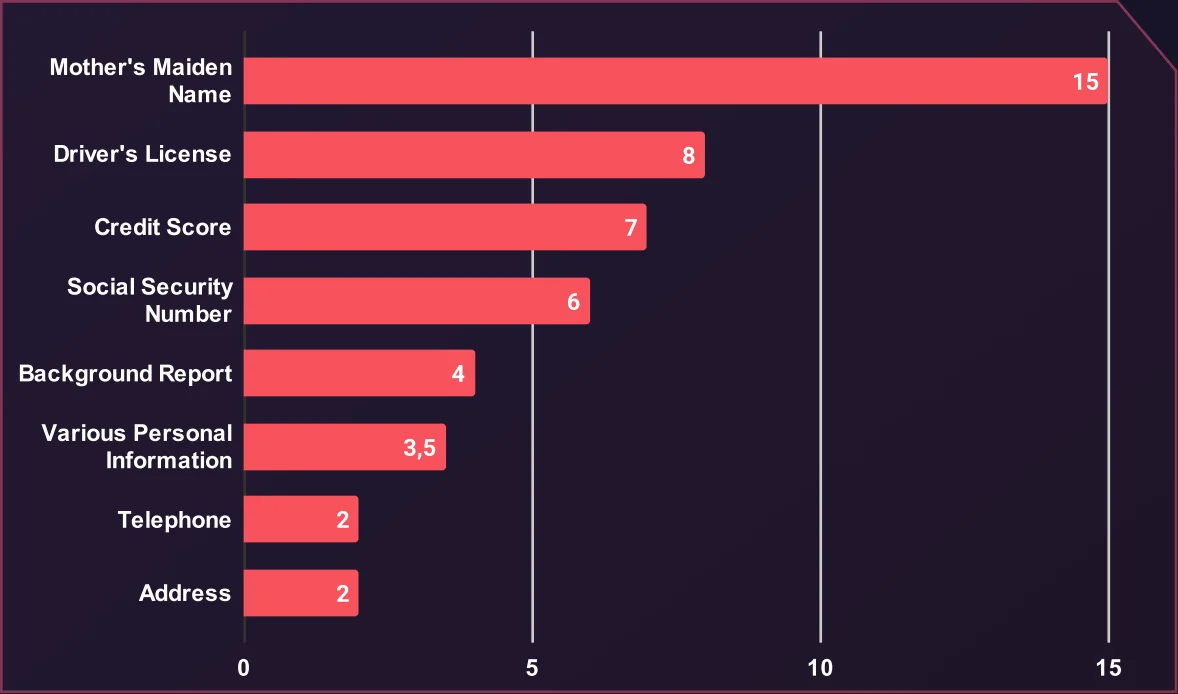
Average Price for Personal Information (USD)
Mother’s maiden name holds the highest average price at $15 due to its use in account recovery security questions, making it a valuable target for attackers. Driver’s licenses and credit scores follow at $8 and $7, often exploited for identity theft and financial fraud.
Social Security Numbers (SSNs), averaging $6, are frequently used for opening fraudulent accounts or committing tax fraud. Background reports at $4 help build detailed profiles for scams. Other personal data, like various information ($3.50), phone numbers ($2), and addresses ($2), are cheaper due to their wider availability.
3. Digital Goods
Social Media Accounts and Services
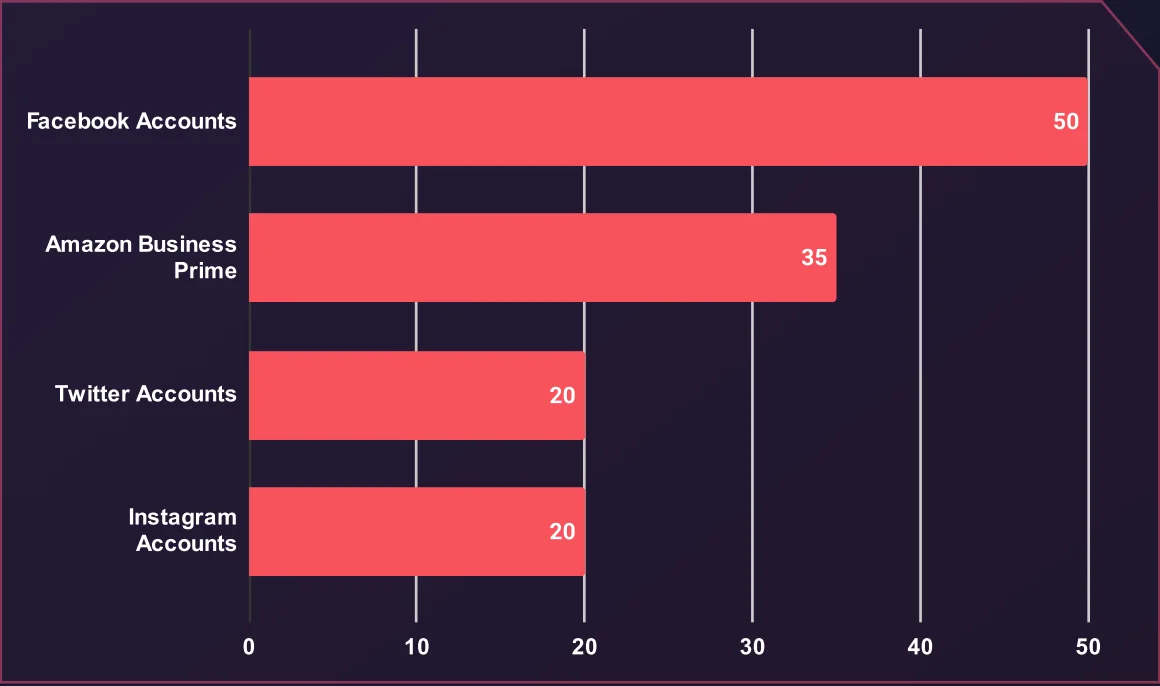
Average Price for Social Media and Other Types of Accounts (USD)
Facebook accounts top the list at an average of $50, reflecting their value for social engineering, phishing, and advertising fraud due to their personal and business use. Amazon Business Prime accounts follow at $35, appealing to fraudsters for exploiting business perks like bulk purchasing and discounted shipping.
Twitter and Instagram accounts, both averaging $20, are often targeted for impersonation, spamming, and running scams or phishing campaigns.
BONUS: Average Prices for Malicious Content in Dark Web Forums
| Malicious Software and Tools | Avg. Price (USD)* |
| Exploit | 5345 |
| Loader | 3566 |
| RAT | 2171 |
| Stealer (Subscription) | 1024 |
| 0-Day Market | |
| Low Cost | 2.000 |
| Mid Tier | 10.000 |
| Premium | 200.000 |
| Spamming and DDoS Services | |
| Mailing/Spam | 100 |
| DDoS (Subscription) | 20 |
| Stresser (Subscription) | 10 |
| Hacking Services | |
| Code Signing Certificate Service | 2420 |
| AV Disabiling | 1500 |
| Dropper – Weekly | 500 |
| Malware Encryption Service | 484 |
| Dropper – Each use | 83 |
| Antivirus Testing (Per file) | 10 |
| CC Checker – Each use | 0,15 |
| Phishing Kits and Templates | |
| Phishing Panel – One Time | 1000 |
| Phishing Panel – Weekly | 170 |
| Spoofer | 86,76 |
| Scam Page | 50 |
| Scam Template | 25 |
| Credit Cards | |
| USA | 11,4 |
| UK | 11,0 |
| Canada | 10,0 |
| Australia | 10,0 |
| France | 10,0 |
| Germany | 10,0 |
| Japan | 10,0 |
| Singapore | 7,5 |
| Philippines | 7,5 |
| Online Payment Accounts | |
| Revolut Business | 100 |
| Revolut | 50 – 100 |
| PayPal | 50 – 100 |
| Wise | 50 – 100 |
| Bybit | 50 – 100 |
| Personal Information and Documents | |
| Mother’s Maiden Name | 15 |
| Driver License | 8 |
| Credit Score | 7 |
| Social Security Number | 6 |
| Background Report | 4 |
| Various Personal Information | 3,5 |
| Telephone | 2 |
| Address | 2 |
| Money Laundering Services* | |
| Per Operation | 750 |
| Social Media Accounts and Services | |
| Facebook Accounts | 50 |
| Amazon Business Prime | 35 |
| Twitter Accounts | 20 |
| Instagram Accounts | 20 |
| *Primarily operates on a commission-based structure. The share of cryptocurrency mixers tends to increase as the transaction amount grows. |
Conclusion
The findings from SOCRadar’s 2024 Annual Dark Web Report reveal the increasing sophistication and scale of cyber threats in today’s digital landscape. From high-value exploits and stolen credentials to fraudulent financial services and social media accounts, the dark web economy continues to evolve, creating new challenges for individuals and organizations alike.
Staying ahead of these threats requires proactive monitoring, robust security measures, and a deep understanding of emerging cyber risks. By leveraging insights from this report, cybersecurity professionals can better prepare, respond, and defend against the growing complexities of the underground cybercrime market.





































