
July 2024 Patch Tuesday Fixes 139 CVEs, Actively Exploited Zero-Days; CISA Highlights Citrix Updates
[Update] September 17, 2024: “PoC Exploit Available for CVE-2024-38080 in Windows Hyper-V”
[Update] August 23, 2024: “PoC Released for CVE-2024-38054, Elevated Risk of Exploitation”
[Update] July 11, 2024: “Proof-of-Concept Exploit Available for SharePoint RCE Vulnerabilities”
Microsoft has issued the July 2024 Patch Tuesday updates, working to strengthen its products against numerous security threats through fixes and enhancements. The latest release addresses 139 CVEs, five of which are critical, and three are zero-day vulnerabilities.
Here’s a categorization of vulnerabilities addressed in the July 2024 Patch Tuesday updates:
- 59 Remote Code Execution (RCE) Vulnerabilities
- 24 Elevation of Privilege (EoP) Vulnerabilities
- 24 Security Feature Bypass
- 17 Denial of Service (DoS) Vulnerabilities
- 8 Information Disclosure Vulnerabilities
- 6 Spoofing
This month’s focus is mostly on RCE vulnerabilities, with a considerable number of EoP and Security Feature Bypass vulnerabilities, the latter of which are unusually high in comparison to previous months.
In addition, one advisory, CVE-2024-38075, is temporarily inaccessible, thus its vulnerability category is not listed above.
In this overview of the latest Patch Tuesday updates, we will look at the specifics of these vulnerabilities, their potential impact, and the essential patches that have been implemented.
The Zero-Day Vulnerabilities of July 2024 Patch Tuesday Update: CVE-2024-35264, CVE-2024-38080, and CVE-2024-38112
The July 2024 Patch Tuesday addressed three zero-day vulnerabilities; one of these flaws was publicly disclosed before the patch was available, and two are actively exploited in real-world attacks. Here are the details of the zero-day vulnerabilities in July 2024 Patch Tuesday:
CVE-2024-35264 (CVSS: 8.1) is a significant vulnerability affecting .NET and Visual Studio, disclosed before a patch was released. The vulnerability allows RCE but requires an attacker to win a race condition.
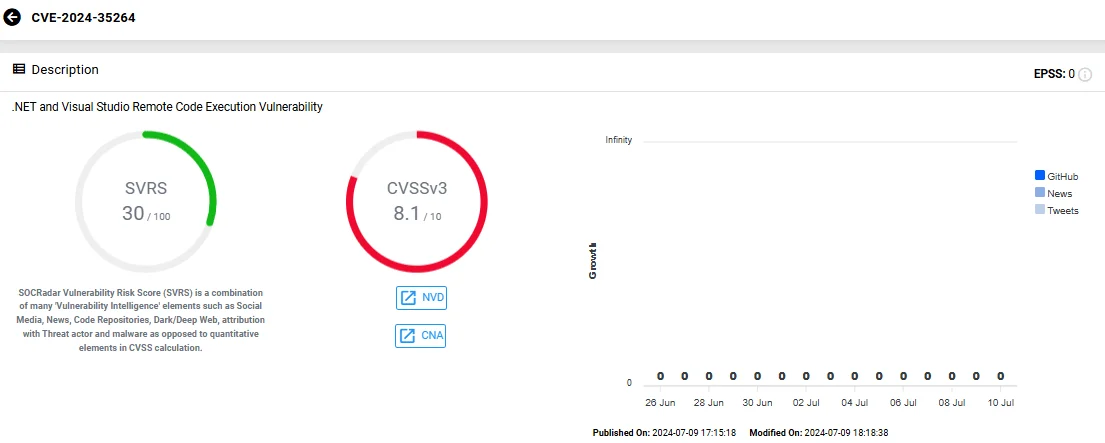
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-35264 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
The two zero-day vulnerabilities that have seen active exploitation are CVE-2024-38080 and CVE-2024-38112, posing risks of privilege escalation and spoofing, respectively.
CVE-2024-38080 (CVSS: 7.8) targets Windows Hyper-V and its exploitation allows attackers to gain SYSTEM privileges; as reported, it has been actively exploited, yet further details are currently unavailable.
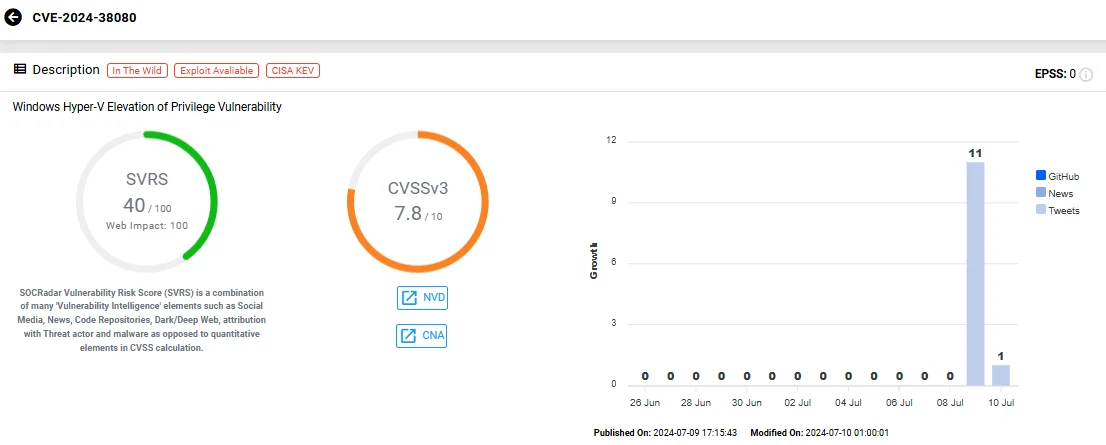
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-38080 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
The third zero-day vulnerability, CVE-2024-38112 (CVSS: 7.5), affects the Windows MSHTML platform, enabling spoofing attacks. This vulnerability can be exploited with malicious files, but requires the victim to execute them. Additionally, attackers need to take preparatory steps to set up the target environment for exploitation.
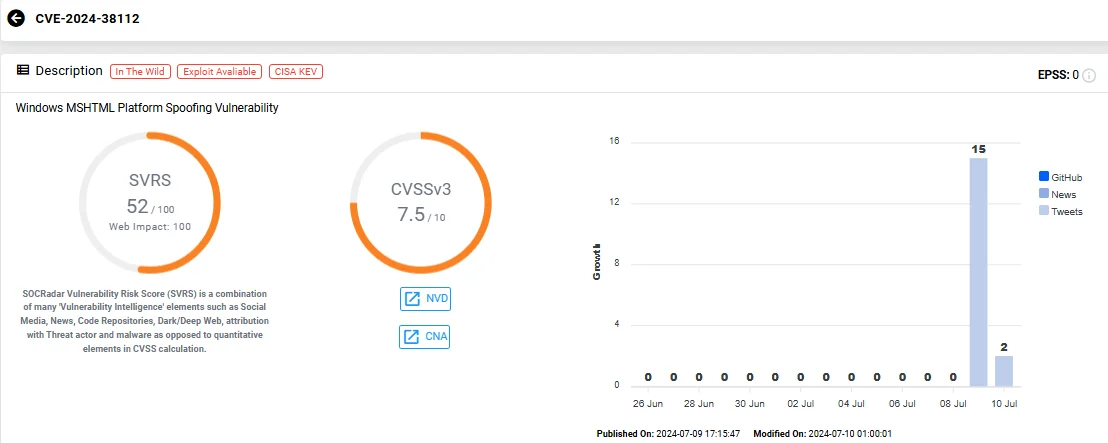
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-38112 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has promptly added CVE-2024-38080 and CVE-2024-38112 to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog, with a deadline for federal agencies to patch by July 30, 2024.
Exploitation Details of CVE-2024-38112
Threat actors have potentially exploited the zero-day vulnerability CVE-2024-38112 for over 18 months before its disclosure in Patch Tuesday.
This vulnerability affects the MSHTML (Trident) engine of the retired Internet Explorer (IE) browser, but also impacts Windows 10 and 11 systems with Edge as the default browser.
Researcher Haifei Li, who reported the flaw to Microsoft in May, explained that CVE-2024-38112 enables attackers to send victims specially crafted .URL files. When clicked, these files use IE to open an attacker-controlled URL, regardless of the default browser.
Attackers also use an IE trick to disguise dangerous HTML application (.hta) files as PDF documents.
At least two threat actors are believed to be exploiting CVE-2024-38112, targeting individuals in Vietnam and Turkey. One campaign involves deploying the Atlantida information stealer via compromised WordPress platforms using HTA and PowerShell files.
PoC Exploit Available for CVE-2024-38080 in Windows Hyper-V
A detailed analysis and Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit code for the patched zero-day vulnerability in Windows Hyper-V, CVE-2024-38080, became available in early September.
This flaw allows attackers to manipulate system memory and execute code with SYSTEM-level privileges, granting full control of the compromised system. It originates from the VidExoBrokerIoctlReceive function, responsible for handling Ioctl requests in Hyper-V. Insufficient validation of data in I/O Request Packet (IRP) structures leads to an integer overflow, resulting in a buffer overflow and causing a Blue Screen of Death (BSOD).
Though Microsoft patched CVE-2024-38080 in July 2024 Patch Tuesday updates, the release of the PoC increases the risk of exploitation, particularly for organizations relying on Hyper-V for critical workloads. The PoC exploit code is publicly available on GitHub, while more information on the exploit can be found in the analysis here.
To stay ahead of potential breaches, it is essential to continuously monitor new exploits and developments across various platforms. In this pursuit, SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence module provides an in-depth view of identified security vulnerabilities, offering crucial insights into emerging threats.
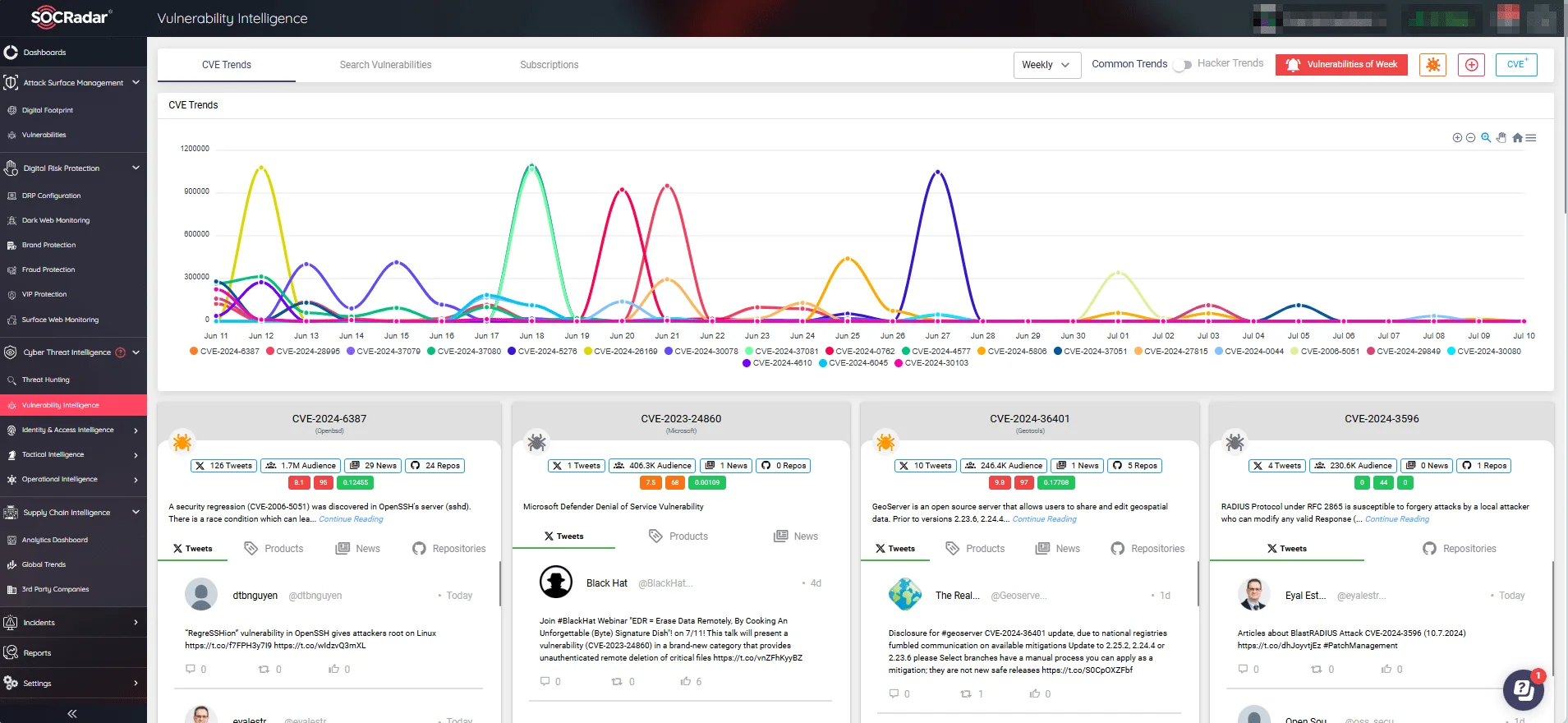
CVE trends, mentions, and exploit events (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence).
The module additionally enables you to optimize vulnerability search using various parameters, including vendor, product, and severity scores. This allows identifying and prioritizing the most significant vulnerabilities targeting your products, leading to a more effective and focused response.
Critical RCE Vulnerabilities
The July 2024 Patch Tuesday addresses five security vulnerabilities classified as ‘critical’ in Microsoft’s advisories:
- CVE-2024-38074 (CVSS: 9.8): A Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability in the Windows Remote Desktop Licensing Service caused by an integer underflow.
- CVE-2024-38076 (CVSS: 9.8): An RCE vulnerability in the Windows Remote Desktop Licensing Service due to a heap-based buffer overflow.
- CVE-2024-38077 (CVSS: 9.8): Another RCE vulnerability in the Windows Remote Desktop Licensing Service due to a heap-based buffer overflow.
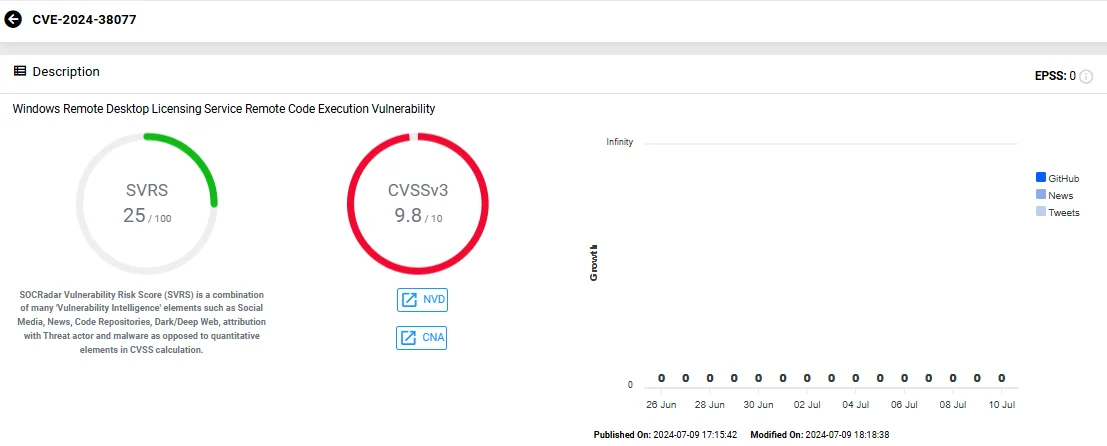
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-38077 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Microsoft strongly advises installing updates for these RCE vulnerabilities promptly. As an additional security measure, consider disabling the Remote Desktop Licensing Service if it is not required, as this can reduce exposure.
The remaining two vulnerabilities, although not possessing critical CVSS scores, are also tagged critical in maximum severity:
- CVE-2024-38060 (CVSS: 8.8): An RCE vulnerability in the Windows Imaging Component.
- CVE-2024-38023 (CVSS: 7.2): An RCE vulnerability in SharePoint Server.
Highly Exploitable Vulnerabilities in Microsoft’s July 2024 Patch Tuesday
The July 2024 Patch Tuesday release includes several vulnerabilities tagged as ‘more likely to be exploited,’ which demand immediate attention. There are no available workarounds for these vulnerabilities, making them also high priority for patching.
Some of the critical vulnerabilities previously highlighted in our article are also more likely to be exploited, including CVE-2024-38023, CVE-2024-38060, and CVE-2024-38080. Additionally, the following vulnerabilities are considered highly exploitable:
- CVE-2024-38021 (CVSS: 8.8) – Microsoft Office
- CVE-2024-38052 (CVSS: 7.8) – Microsoft Streaming Service
- CVE-2024-38054 (CVSS: 7.8) – Microsoft Streaming Service
- CVE-2024-38059 (CVSS: 7.8) – Windows Win32K – ICOMP
- CVE-2024-38066 (CVSS: 7.8) – Windows Win32K – GRFX
- CVE-2024-38079 (CVSS: 7.8) – Microsoft Graphics Component
- CVE-2024-38085 (CVSS: 7.8) – Windows Win32 Kernel Subsystem
- CVE-2024-38100 (CVSS: 7.8) – Windows COM Session
- CVE-2024-38094 (CVSS: 7.2) – Microsoft Office SharePoint
- CVE-2024-38024 (CVSS: 7.2) – Microsoft Office SharePoint
- CVE-2024-38099 (CVSS: 5.9) – Windows Remote Desktop Licensing Service
Given the high likelihood of exploitation, it is important to prioritize the patching of these vulnerabilities to protect your systems from potential attacks.
For detailed information on the vulnerabilities addressed in the July 2024 Patch Tuesday update, refer to Microsoft’s Release Note.
Proof-of-Concept Exploit Available for SharePoint RCE Vulnerabilities
A security researcher has devised a Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit for three recently patched Microsoft vulnerabilities affecting SharePoint Server, leading to Remote Code Execution (RCE): CVE-2024-38023, CVE-2024-38024, and CVE-2024-38094.
The PoC script, available on GitHub, automates authentication to a target SharePoint site using NTLM, creates a specific folder and file, and sends a crafted XML payload to trigger the vulnerability in the SharePoint client API.
Given the rapid emergence of this PoC, organizations must expedite their patching efforts. SOCRadar has observed that a threat actor has already mentioned this exploit on a Telegram hacker channel.
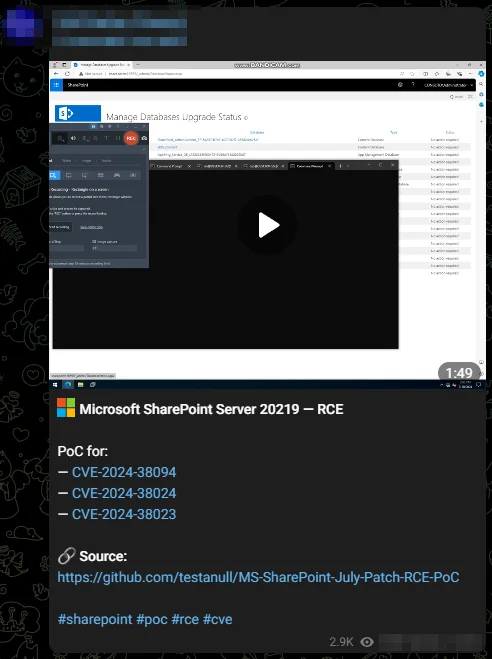
Exploit for the SharePoint RCE flaws was shared on a Telegram hacker channel
Severe Citrix Vulnerabilities Highlighted by CISA: Patch Now
Another recent series of patches for severe vulnerabilities came from Citrix, prompting the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) to issue an alert emphasizing the importance of these updates. The advisories issued for these patches pertain to various Citrix products, including NetScaler Console, Agent and SVM, NetScaler ADC, NetScaler Gateway, and the Workspace app.
The most critical vulnerability, CVE-2024-6235 (CVSS: 9.4), affects NetScaler Console 14.1 before 14.1-25.53 and poses a significant risk of sensitive information disclosure due to improper authentication. This vulnerability greatly impacts confidentiality, integrity, and availability, although exploitation requires access to the NetScaler Console IP.
Additionally, two other high-impact vulnerabilities, CVE-2024-6286 and CVE-2024-6151, each with CVSS scores of 8.5, were identified. Both are local privilege escalation issues, and their exploitation could allow a low-privileged user to gain SYSTEM privileges. However, exploitation requires local access to the target system.
PoC Released for CVE-2024-38054, Elevated Risk of Exploitation
A Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit code for the Windows Kernel Streaming WOW Thunk Service Driver vulnerability (CVE-2024-38054) is now publicly available. flaw allows local attackers to exploit a heap-based buffer overflow to escalate privileges to SYSTEM level.
While CVE-2024-38054 was initially labeled by Microsoft as likely to be exploited, the availability of a PoC significantly heightens the risk of exploitation by threat actors.
The researcher behind the PoC also intends to release a detailed vulnerability analysis, which could provide additional insights for defenders but could also be instrumental for exploitation. You can find the PoC on GitHub.
Organizations are urged to prioritize applying the July Patch Tuesday updates to mitigate this critical security risk.
To enhance your security monitoring against the numerous vulnerabilities that emerge daily, you can use SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) module. This tool allows for real-time monitoring of your digital assets, providing timely alerts on security issues.
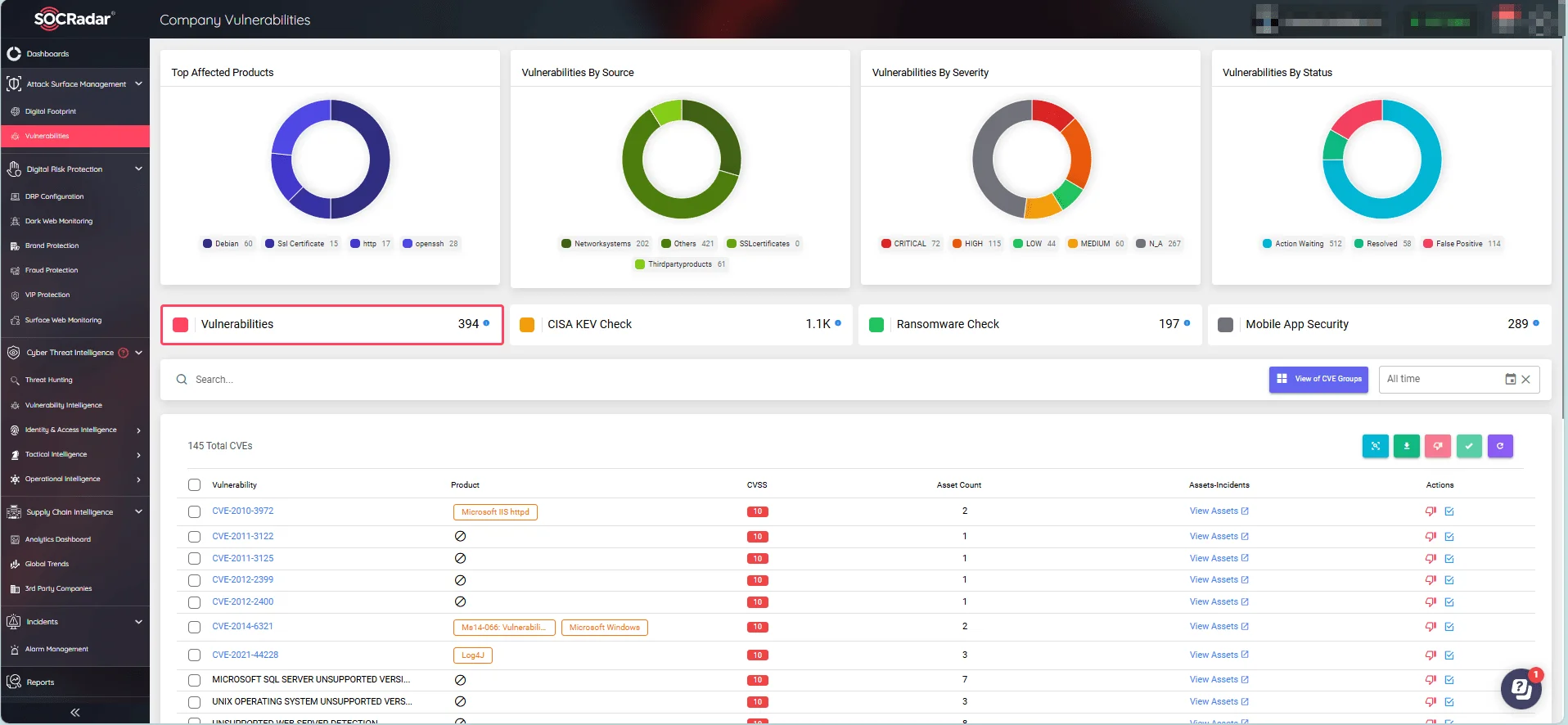
SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management module, Company Vulnerabilities
By leveraging actionable insights provided by the SOCRadar XTI platform, your organization can respond quickly to potential threats, effectively manage security concerns, and maintain system integrity.




































