
Microsoft’s September 2024 Patch Tuesday Addresses 79 CVEs, 4 Zero-Days; Critical Ivanti EPM Updates
[Update] September 17, 2024: “PoC Exploit Released for Critical Ivanti EPM Vulnerability (CVE-2024-29847)”
[Update] September 16, 2024: “CVE-2024-43461 Now Marked as Zero-Day Following Exploitation Reveal”
Microsoft has released the September 2024 Patch Tuesday updates, addressing a total of 79 CVEs, including seven that are categorized as critical. These updates also include four zero-day vulnerabilities currently under active exploitation, making immediate patching essential for safeguarding systems.
The vulnerabilities addressed in the September 2024 Patch Tuesday updates span a variety of types:
- 30 Elevation of Privilege (EoP) Vulnerabilities
- 23 Remote Code Execution (RCE) Vulnerabilities
- 11 Information Disclosure Vulnerabilities
- 8 Denial of Service (DoS) Vulnerabilities
- 4 Security Feature Bypass Vulnerabilities
- 2 Spoofing Vulnerabilities
- 1 Cross-site Scripting (XSS) Vulnerability
In other security news, the Ivanti Endpoint Management (EPM) software has also received critical security patches. The most significant vulnerability in Ivanti’s update, CVE-2024-29847, has a CVSS score of 10/10, and demands urgent attention due to its potential to allow attackers to execute arbitrary code.
Microsoft Patches 4 Actively Exploited Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
In the September 2024 Patch Tuesday, Microsoft addressed four zero-day vulnerabilities that have been actively exploited. Reportedly, one of these vulnerabilities may have been in use for several years.
Here’s a breakdown of the four zero-day vulnerabilities:
CVE-2024-43491 (CVSS: 9.8)
This critical Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability affects Microsoft Windows Update on Windows 10, version 1507 (Windows 10 Enterprise 2015 LTSB and IoT Enterprise 2015 LTSB).
The issue stems from a code defect that caused certain ‘Optional Components’ to revert to their previous versions, leaving them exposed to previously fixed vulnerabilities.
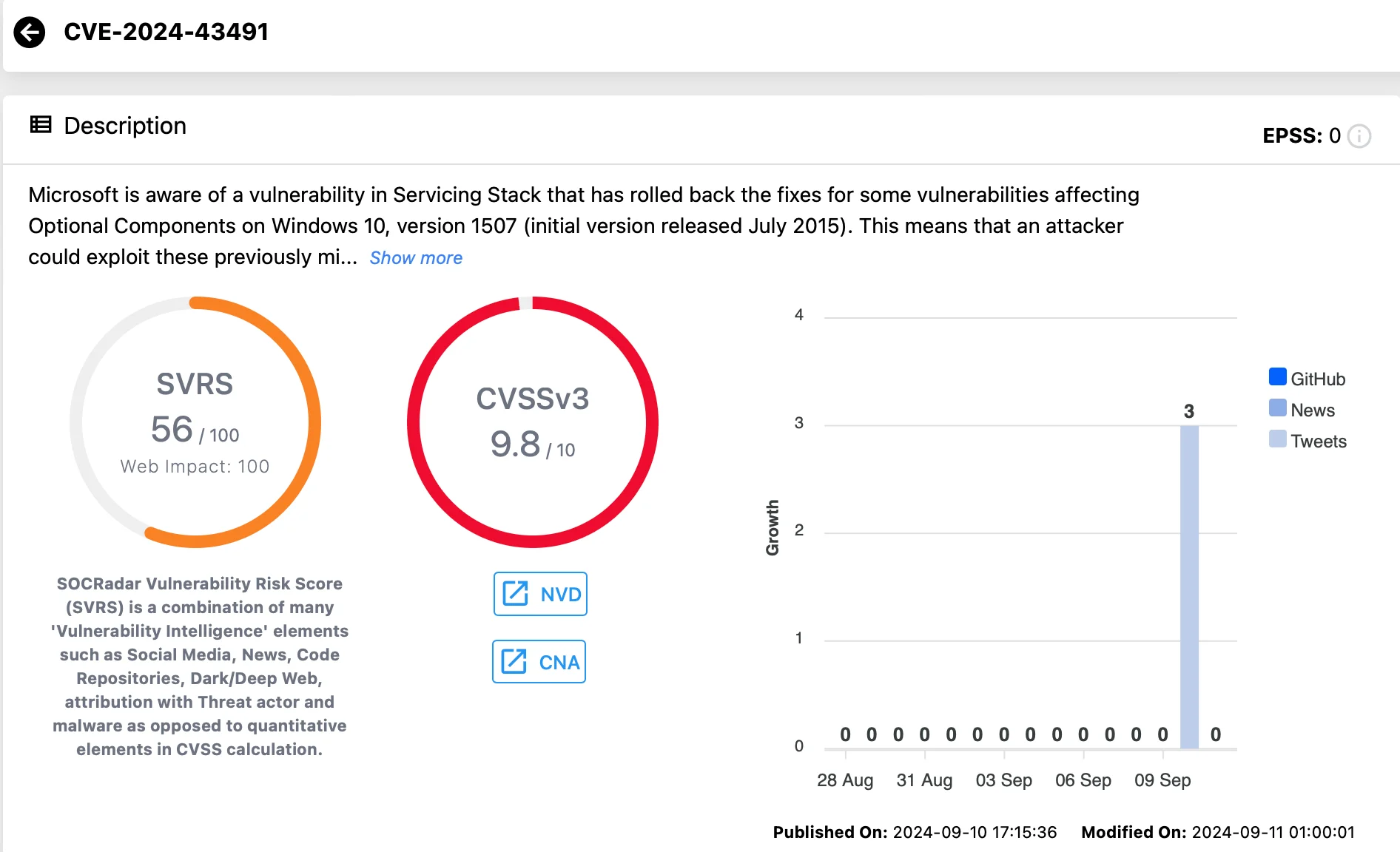
Vulnerability card for CVE-2024-43491 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Systems with security updates from March 2024 (KB5035858) to August 2024 are at risk. The issue is resolved by installing the September 2024 Servicing Stack update (SSU KB5043936) and the Windows security update (KB5043083), in order.
CVE-2024-38014 (CVSS: 7.8)
This Elevation of Privilege vulnerability in Windows Installer has also been exploited in the wild. Upon its exploitation, attackers can gain SYSTEM level privileges, making it a significant risk.
Microsoft has not shared specific exploitation details but stresses the importance of patching CVE-2024-38014.
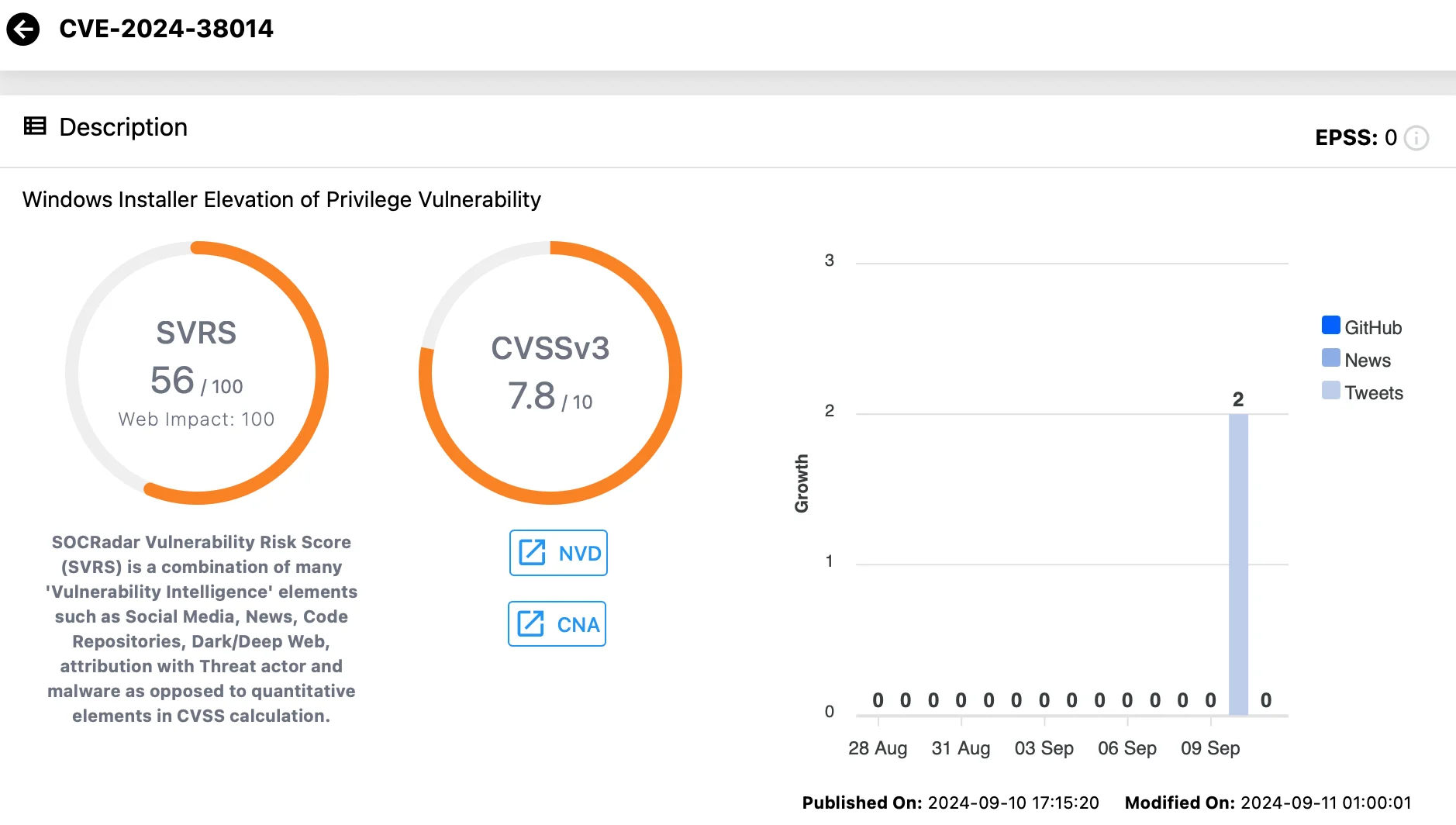
Vulnerability card for CVE-2024-38014 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
CVE-2024-38226 (CVSS: 7.3)
This Security Feature Bypass vulnerability impacts Microsoft Publisher and has been exploited as a zero-day.
Due to CVE-2024-38226, attackers can bypass Office macro policies by tricking users into downloading a crafted file, allowing them to execute malicious code. Notably, the Preview Pane is not an attack vector for this flaw.
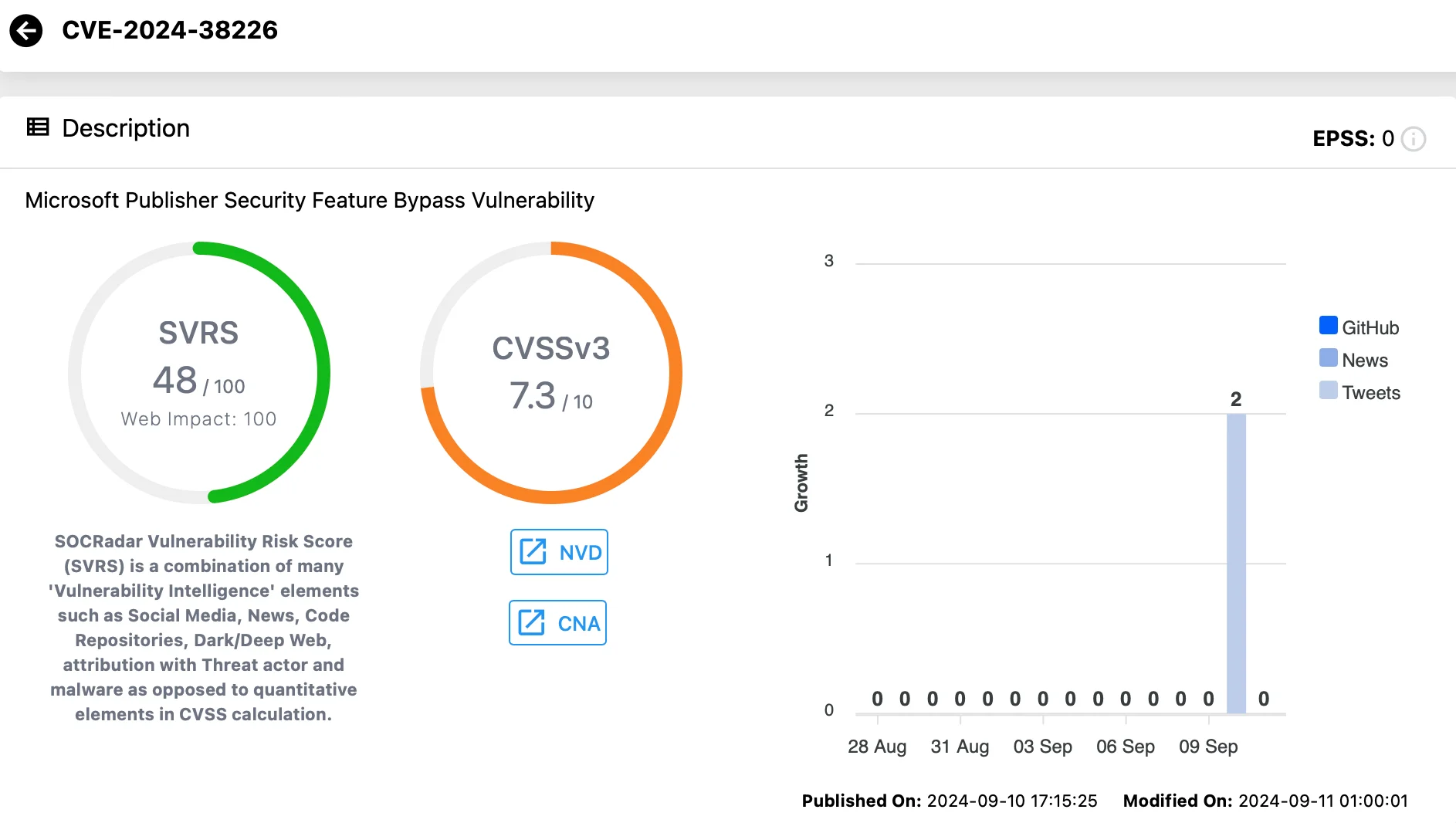
Vulnerability card for CVE-2024-38226 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
CVE-2024-38217 (CVSS: 5.4)
CVE-2024-38217 is a vulnerability in Mark of the Web (MOTW), used by Windows to identify files downloaded from the internet.
This flaw has been exploited in the wild and was disclosed prior to the patch. Attackers can convince users to open specially crafted files that bypass MOTW defenses to exploit this vulnerability.
Research suggests this vulnerability may have been exploited since 2018, with older samples found in VirusTotal.
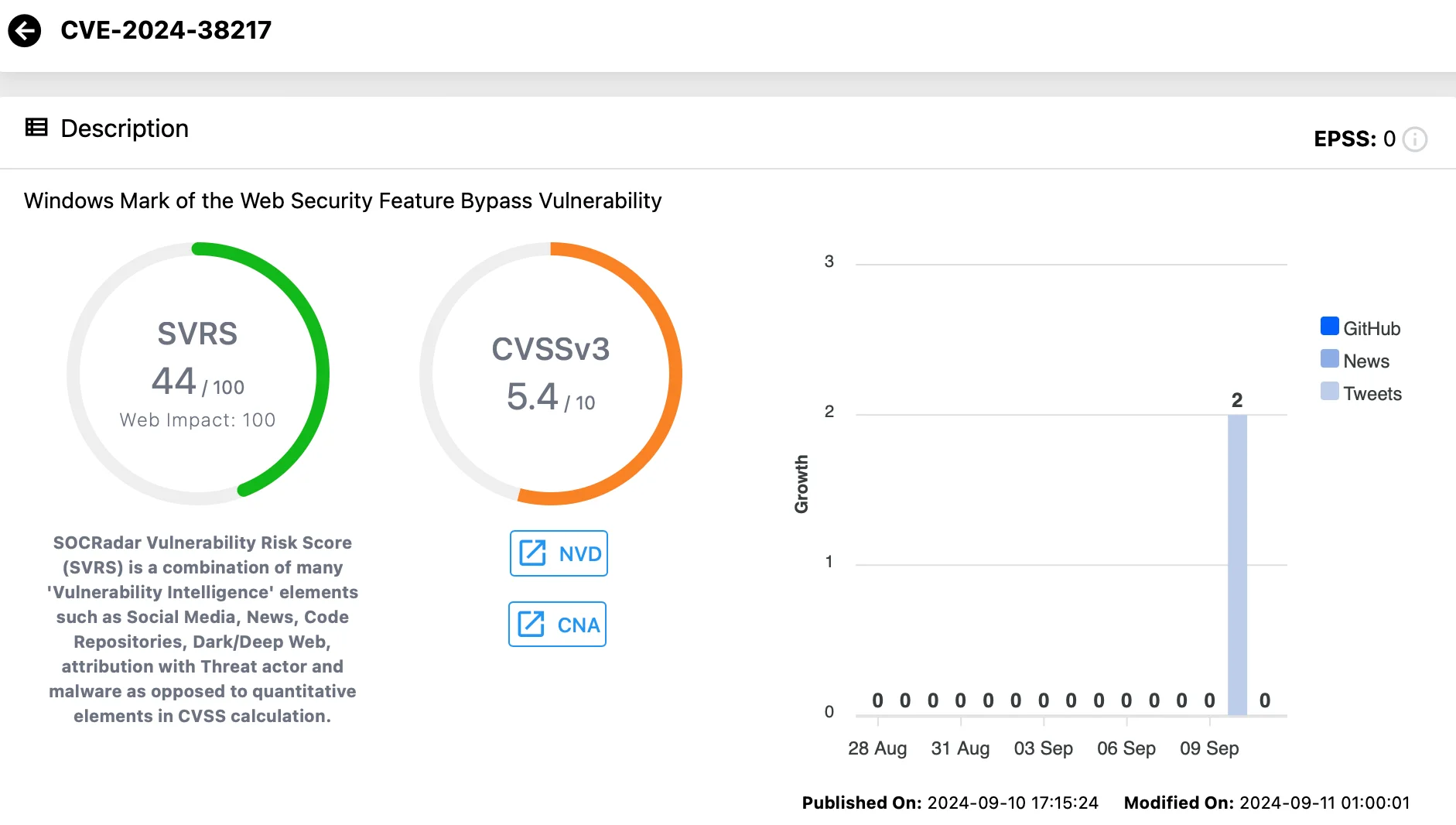
Vulnerability card for CVE-2024-38217 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
To access more details on CVE-2024-38217 and see how attackers may exploit it, visit Elastic Security’s blog post here.
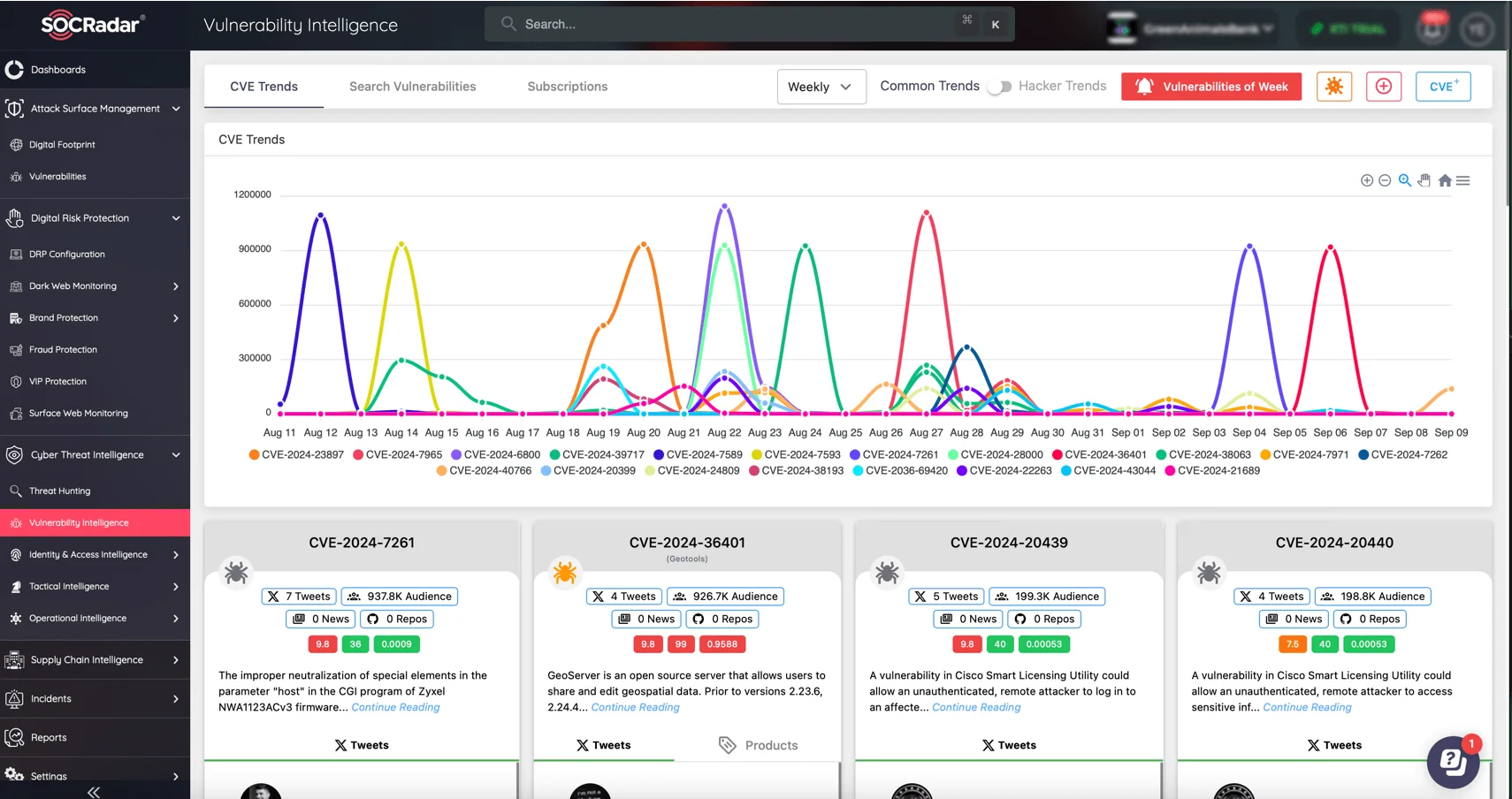
SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence module
To stay ahead of potential breaches, it’s necessary to monitor emerging exploits and developments across various platforms. In this pursuit, SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence module provides you with in-depth analysis of identified vulnerabilities, offering essential insights into new threats.
This module also allows you to filter vulnerabilities by vendor, product, severity, and other parameters, helping you pinpoint and prioritize the most critical risks to your digital assets. With SOCRadar’s targeted approach, you can ensure a more efficient and effective response to vulnerabilities.
Critical Vulnerabilities in the September 2024 Patch Tuesday Update
The September 2024 Patch Tuesday release addresses seven critical vulnerabilities, including the actively exploited CVE-2024-43491. Below are the details of the other critical flaws fixed in this update:
- CVE-2024-38220 (CVSS: 9.0) – An Elevation of Privilege (EoP) vulnerability in Azure Stack Hub that could allow attackers to gain unauthorized access to system resources and interact with other tenants’ applications and data.
- CVE-2024-38018 (CVSS: 8.8) – A Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability in Microsoft SharePoint Server. With minimal permissions (Site Member), an authenticated attacker could exploit this flaw to execute code remotely on the SharePoint Server.
- CVE-2024-38194 (CVSS: 8.4) – An EoP vulnerability in Azure Web Apps. An attacker can use improper authorization within the app to elevate their privileges over the network.
- CVE-2024-38216 (CVSS: 8.2) – Another EoP flaw in Azure Stack Hub, allowing attackers to access system resources with elevated privileges. To exploit this, the attacker must wait for a victim to initiate a connection.
- CVE-2024-38119 (CVSS: 7.5) – An RCE vulnerability in Windows Network Address Translation (NAT), where the attacker must first gain network access and win a race condition to exploit the flaw.
- CVE-2024-43464 (CVSS: 7.2) – Another RCE vulnerability in Microsoft SharePoint Server. An authenticated attacker with Site Owner permissions can upload a malicious file and use crafted API requests to trigger remote code execution on the server.
Microsoft’s High-Risk Vulnerabilities, Likely to Be Exploited (September 2024)
Several vulnerabilities in the September 2024 Patch Tuesday release are flagged as “more likely to be exploited,” making them also high-priority for patching, alongside zero-day and critical CVEs.
Two vulnerabilities previously mentioned in this article, CVE-2024-43464 and CVE-2024-38018, are among these, highlighting their critical nature. Additionally, the following vulnerabilities require immediate attention due to their high exploitability:
- CVE-2024-43461 (CVSS: 8.8) – Windows MSHTML Platform
- CVE-2024-38237 (CVSS: 7.8) – Microsoft Streaming Service
- CVE-2024-38238 (CVSS: 7.8) – Microsoft Streaming Service
- CVE-2024-38241 (CVSS: 7.8) – Microsoft Streaming Service
- CVE-2024-38242 (CVSS: 7.8) – Microsoft Streaming Service
- CVE-2024-38243 (CVSS: 7.8) – Microsoft Streaming Service
- CVE-2024-38244 (CVSS: 7.8) – Microsoft Streaming Service
- CVE-2024-38245 (CVSS: 7.8) – Microsoft Streaming Service
- CVE-2024-38247 (CVSS: 7.8) – Microsoft Graphics Component
- CVE-2024-38249 (CVSS: 7.8) – Microsoft Graphics Component
- CVE-2024-38252 (CVSS: 7.8) – Windows Win32K – ICOMP
- CVE-2024-38253 (CVSS: 7.8) – Windows Win32K – ICOMP
- CVE-2024-43457 (CVSS: 7.8) – Windows Setup and Deployment
- CVE-2024-38227 (CVSS: 7.2) – Microsoft Office SharePoint
- CVE-2024-38228 (CVSS: 7.2) – Microsoft Office SharePoint
- CVE-2024-38246 (CVSS: 7.0) – Windows Win32K – GRFX
- CVE-2024-43487 (CVSS: 6.5) – Windows Mark of the Web (MOTW)
Given the higher likelihood of exploitation, it’s essential to prioritize patches for these vulnerabilities to ensure your systems are secure.
For further details, refer to Microsoft’s official Release Note on the September 2024 Patch Tuesday update.
CVE-2024-43461 Now Marked as Zero-Day Following Exploitation Reveal
The Windows MSHTML spoofing vulnerability (CVE-2024-43461), patched during the September 2024 Patch Tuesday, has been classified as a zero-day. Microsoft recently updated its advisory to confirm that the vulnerability had been actively exploited by the Void Banshee APT group before it was patched.
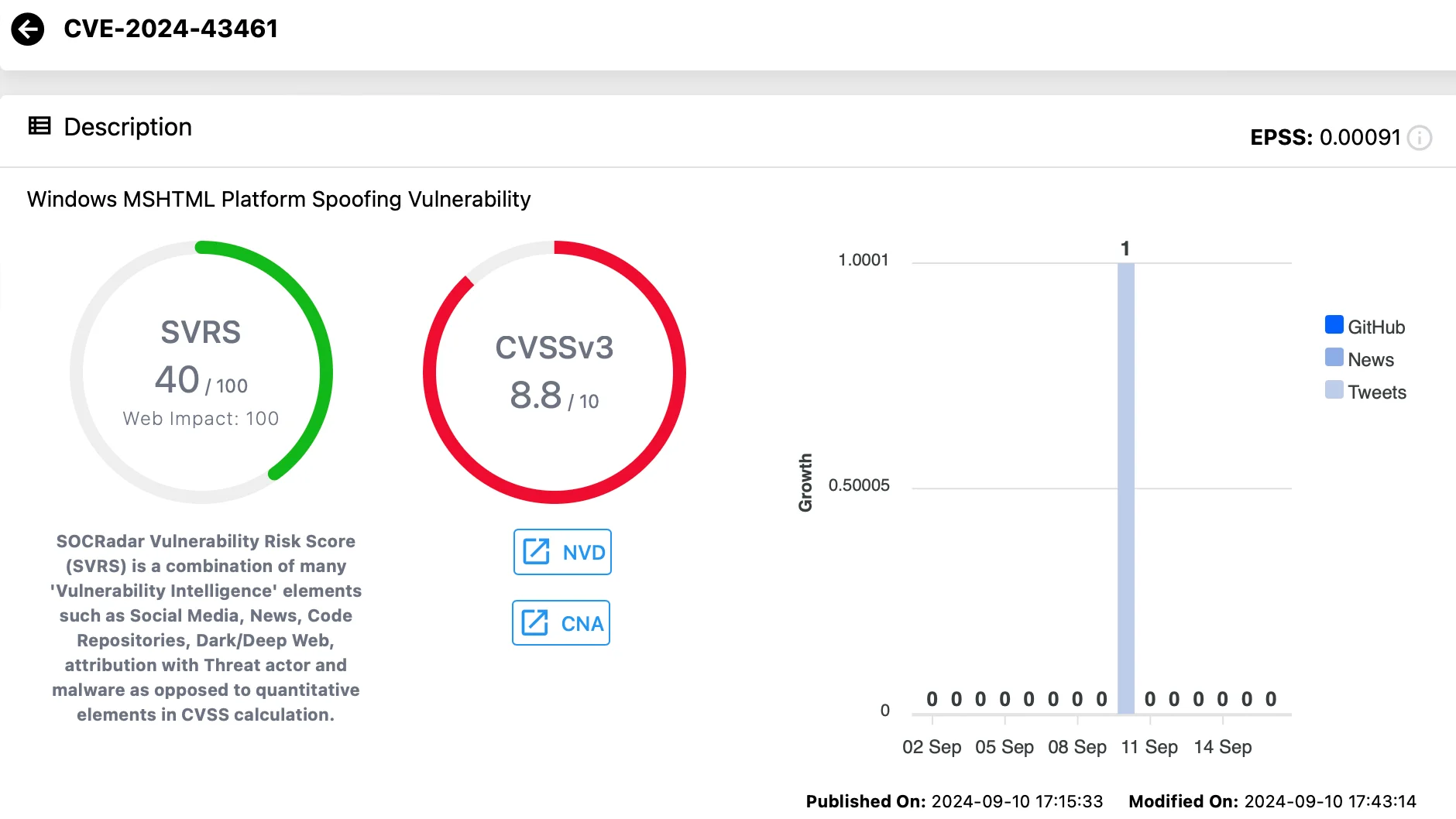
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-43461 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Void Banshee used CVE-2024-43461 alongside CVE-2024-38112 in a campaign to install the Atlantida infostealer, which targets passwords, tokens, and cryptocurrency wallets. The attackers tricked victims into opening malicious HTA files by disguising them as PDFs, using encoded characters to hide the true file extension.
Although the latest patch ensures Windows shows the correct .hta extension in prompts, the use of encoded whitespace characters may still cause confusion, making the file appear as a PDF.
*After its classification as a zero-day, CISA has included the critical Microsoft Windows MSHTML Platform Spoofing vulnerability, CVE-2024-43461, to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog as of September 16. CISA warns that vulnerabilities like CVE-2024-43461 are frequently targeted and pose substantial risks to federal systems. As a result, CISA has mandated that federal agencies apply the necessary patches by the due date of October 7, 2024.
Ivanti Patches Critical Vulnerabilities in Endpoint Manager, Including RCE Flaw CVE-2024-29847 (CVSS: 10)
While Microsoft rolled out its September patches, Ivanti also released critical updates for its Ivanti Endpoint Manager (EPM), addressing several high-risk vulnerabilities that demand immediate attention. The most severe of these, CVE-2024-29847, could lead to Remote Code Execution (RCE) if left unpatched, and requires no authentication.
Details of the Latest Ivanti Vulnerabilities
The latest vulnerabilities in Ivanti Endpoint Manager (EPM) affect EPM 2024 and EPM 2022 (versions prior to SU6) and have been addressed in the recent updates. Below are the key vulnerabilities fixed:
CVE-2024-29847 (CVSS: 10.0)
This critical deserialization vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code without requiring authentication. Exploiting this flaw gives attackers full control over vulnerable endpoints, enabling them to deploy ransomware or steal sensitive data.
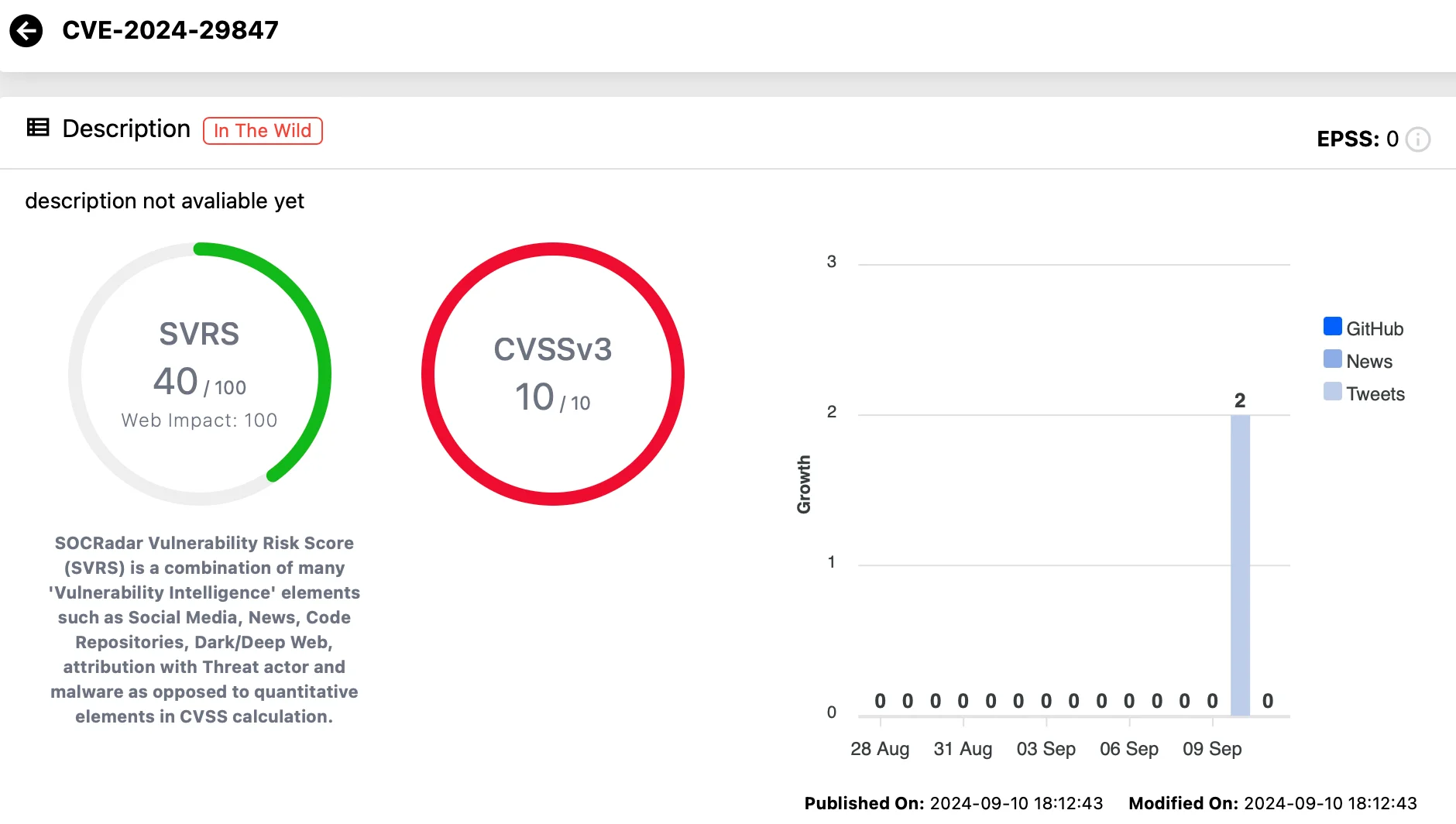
Vulnerability card for CVE-2024-29847 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
The severity and ease of exploitation make this vulnerability particularly dangerous for enterprise environments.
CVE-2024-32840 to CVE-2024-34785 (CVSS: 9.1)
These SQL injection vulnerabilities allow attackers with administrative access to execute arbitrary code by manipulating SQL queries within the EPM management console.
By exploiting these flaws, attackers can bypass input validation, gaining unauthorized access to data or escalating privileges within the system.
Other less critical vulnerabilities in Ivanti’s updates include:
- CVE-2024-8320 (CVSS: 5.3) and CVE-2024-8321 (CVSS: 5.8): Affecting the Network Isolation feature, these missing authentication flaws allow attackers to manipulate the isolation status of critical devices, potentially disrupting network segmentation strategies.
- CVE-2024-8441 (CVSS: 6.7): An uncontrolled search path vulnerability, which enables local attackers with administrative privileges to escalate to SYSTEM level and take full control of the machine.
Ivanti urges all users to apply the July and September 2024 security patches for Ivanti Endpoint Manager 2024 or update to 2022 SU6 or later for EPM 2022 to mitigate these risks.
PoC Exploit Released for Critical Ivanti EPM Vulnerability (CVE-2024-29847)
A Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit for the critical CVE-2024-29847 vulnerability in Ivanti EPM is now publicly available, accompanied by detailed technical information. Researcher Sina Kheirkhah (@SinSinology on X) discovered the flaw, which originates from insecure deserialization in the AgentPortal[.]exe executable. The issue lies in the OnStart method of the service, which uses the outdated Microsoft .NET Remoting framework to enable communication between remote objects.
The service registers a TCP channel with dynamically assigned ports but lacks proper security measures, allowing remote attackers to inject malicious objects. Attackers can exploit the vulnerability by crafting a Hashtable containing serialized objects and sending it to the vulnerable endpoint. Upon deserialization, these objects trigger arbitrary operations, such as reading or writing files, or deploying web shells for RCE.
Though the deserialization process includes a low-type filter meant to restrict objects, researcher James Forshaw demonstrated a bypass – by using a Hashtable as the top-level object, attackers can evade the restriction, allowing the remoting server code to execute malicious methods.
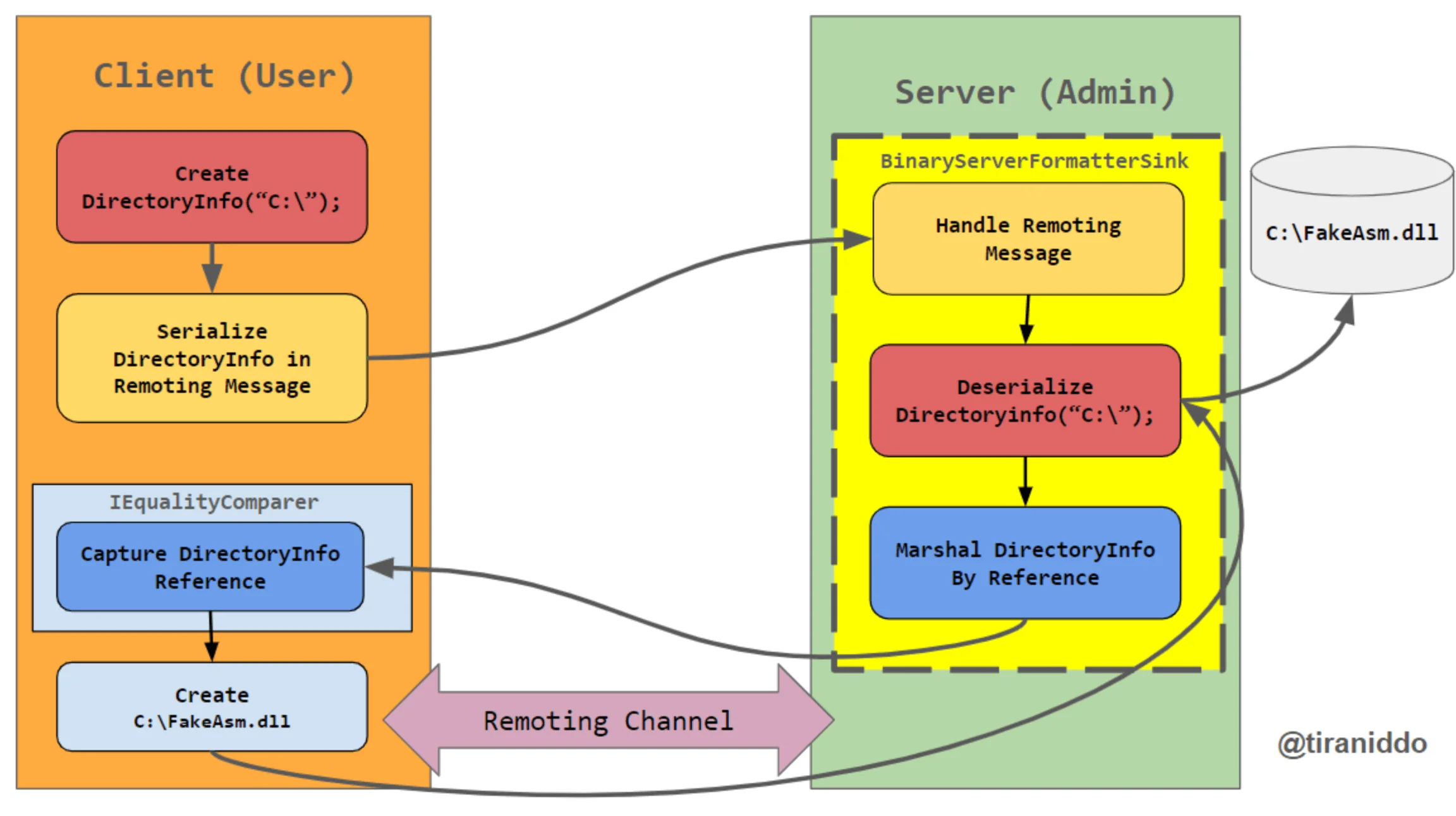
.NET Remoting exploitation flow by researcher James Forshaw (@tiraniddo on X)
For more details and the demonstration of the exploit, you can refer to the full analysis here. Make sure your Ivanti EPM software is updated to protect against potential attacks, as the public release of this PoC heightens the risk of exploitation.
Strengthen Vulnerability Management with SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Monitoring
In the face of constantly emerging threats, SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) module offers a comprehensive solution to protect your organization. ASM provides real-time monitoring of your digital assets, ensuring prompt alerts on potential vulnerabilities and security risks.
Monitor Digital Assets and Company Vulnerabilities via SOCRadar’s ASM module
By leveraging the actionable insights from SOCRadar, your organization can swiftly identify and address threats, helping you maintain a stronger and more proactive security posture.


































