
October 2024 Patch Tuesday Update – Microsoft Fixes 117 Vulnerabilities, 2 Actively Exploited Zero-Days
[Update] October 22, 2024: “PoC Exploit Released for Critical WinReg Vulnerability (CVE-2024-43532)”
Microsoft has released its October 2024 Patch Tuesday updates, addressing a total of 117 security vulnerabilities across various products and services. Among these, three vulnerabilities were deemed critical in max severity, with four zero-day vulnerabilities also receiving patches. Notably, two of these zero-days are under active exploitation.
The breakdown of the vulnerabilities patched in the October 2024 Patch Tuesday update includes:
- 42 Remote Code Execution (RCE) Vulnerabilities
- 28 Elevation of Privilege (EoP) Vulnerabilities
- 26 Denial of Service (DoS) Vulnerabilities
- 7 Security Feature Bypass Vulnerabilities
- 7 Spoofing Vulnerabilities
- 6 Information Disclosure Vulnerabilities
- 1 Tampering Vulnerability
In this blog, we’ll explore the most critical vulnerabilities addressed in this month’s updates, their potential impacts, and the steps you can take to secure your systems.
Microsoft Addresses 4 Zero-Day Vulnerabilities in October 2024 Patch Tuesday
This month’s Patch Tuesday resolves four zero-day vulnerabilities, including two that were actively exploited in the wild. Notably, all four vulnerabilities were publicly disclosed before patches were available.
The two actively exploited zero-day vulnerabilities, CVE-2024-43572 and CVE-2024-43573, allow remote attackers to perform arbitrary code execution and spoofing attacks, respectively. CISA has included these two vulnerabilities in its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog with no delay, urging federal agencies to patch it by the due date of October 29, 2024.
CVE-2024-43572 (CVSS: 7.8), RCE in Microsoft Management Console (MMC)
CVE-2024-43572 is a Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability in Microsoft Management Console (MMC). An attacker could exploit this flaw by convincing the target to open a specially crafted Microsoft Saved Console (MSC) file, resulting in code execution.
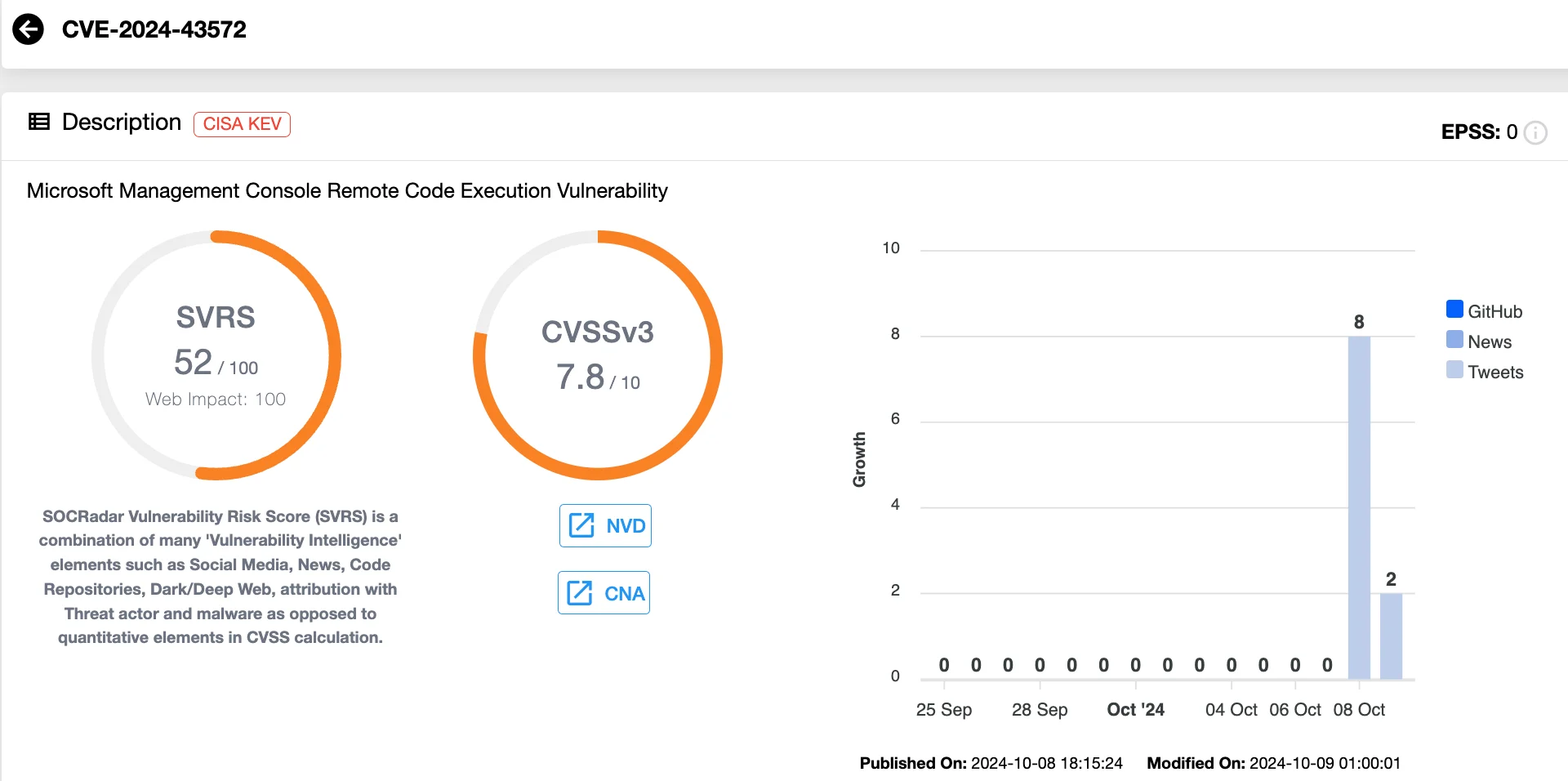
Microsoft MMC RCE Vulnerability, CVE-2024-43572 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
This vulnerability was exploited in the wild as a zero-day, and Microsoft addressed it in this month’s Patch Tuesday by preventing untrusted MSC files from being opened.
CVE-2024-43573 (CVSS: 6.5), Spoofing Flaw in the MSHTML Platform
CVE-2024-43573 is a spoofing vulnerability in the Windows MSHTML platform. An unauthenticated attacker could exploit this flaw by tricking a target into opening a malicious file.
Although details of exploitation are not available, Microsoft notes that the MSHTML platform remains critical for Internet Explorer mode in Edge and other applications that rely on WebBrowser control.
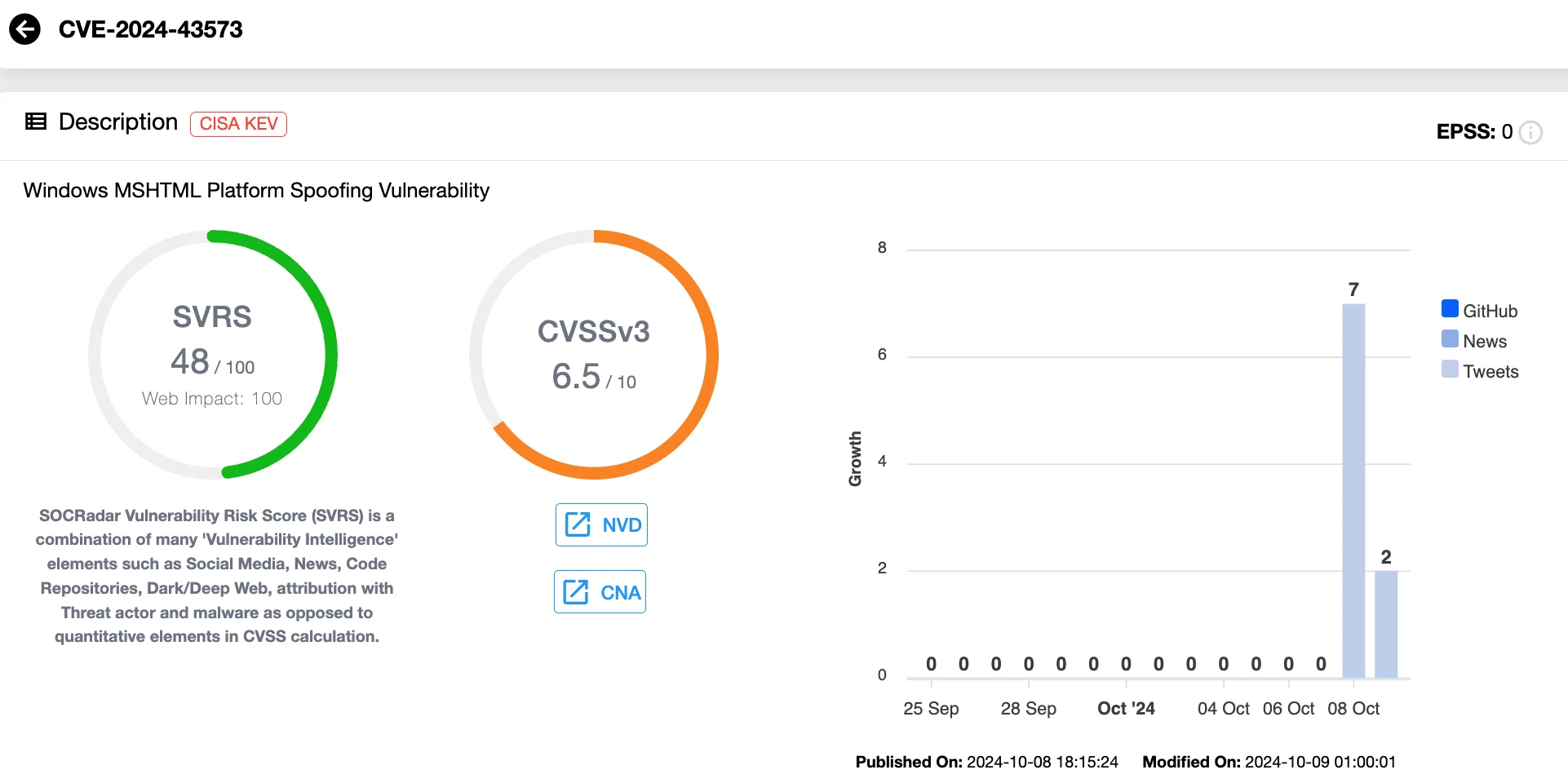
Windows MSHTML Platform Spoofing Vulnerability, CVE-2024-43573 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
This vulnerability follows a pattern of MSHTML platform exploitation, as seen in previous Patch Tuesday updates with vulnerabilities like CVE-2024-43461 and CVE-2024-38112. These flaws were exploited by the Void Banshee APT group in campaigns deploying the Atlantida infostealer, targeting sensitive information such as passwords, tokens, and cryptocurrency wallets. See the September 2024 Patch Tuesday update and July 2024 Patch Tuesday update for more information.
The other two zero-day vulnerabilities, while not exploited so far, were publicly disclosed and are detailed as follows.
CVE-2024-20659 (CVSS: 7.1), Security Feature Bypass in Hyper-V
This is a security feature bypass vulnerability in Windows Hyper-V. While exploitation is considered ‘less likely,’ due to specific conditions such as user-required actions, successful exploitation could allow an attacker to bypass a virtual machine’s UEFI protections, potentially compromising the hypervisor and host system kernel.
CVE-2024-43583 (CVSS: 7.8), Privilege Escalation Flaw in Winlogon
CVE-2024-43583 is an Elevation of Privilege (EoP) vulnerability affecting Winlogon, allowing local, authenticated attackers to achieve SYSTEM privileges on Windows systems.
The vulnerability was publicly disclosed before a patch was available, thereby marked as a zero-day. Microsoft recommends administrators ensure a first-party IME is enabled to protect against vulnerabilities associated with third-party input method editors (IMEs) during sign-in.
Visit Microsoft’s Knowledge Base article KB5046254 for more information on IME vulnerability.
Critical RCE Vulnerabilities Addressed by Microsoft: CVE-2024-43468, CVE-2024-43488, CVE-2024-43582
This month, Microsoft advisories identified three vulnerabilities as critical, all of which pose a significant risk of Remote Code Execution (RCE).
- CVE-2024-43468 (CVSS: 9.8) – This vulnerability affects Microsoft Configuration Manager. An unauthenticated attacker could exploit it by sending specially crafted requests, which are processed unsafely, allowing them to execute commands on the server or manipulate the underlying database.
- CVE-2024-43488 (CVSS: 8.8) – This RCE flaw involves the deprecated Visual Studio Code extension for Arduino. Microsoft will not be issuing a fix for this vulnerability and instead recommends users switch to the official Arduino IDE software for safer development.
- CVE-2024-43582 (CVSS: 8.1) – This vulnerability in Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) servers could allow attackers to gain remote code execution by sending malformed packets to the RPC host, which could lead to unauthorized control of the server. The Microsoft advisory notes that exploiting this issue requires winning a race condition.
With new vulnerabilities being discovered almost daily, businesses face increasing exposure to cyberattacks like Remote Code Execution (RCE). In the case of zero-days, exploitation can occur before a patch is even available. These vulnerabilities give attackers direct access to compromise systems, leading to data breaches, financial losses, and operational disruptions.
Exploit trends and cybercriminal activity around these vulnerabilities can escalate quickly. Knowing when an exploit is actively being used is essential for prioritizing patches. Helping organizations in this pursuit, SOCRadar provides real-time alerts and detailed insights into the latest threats by continuously monitoring vulnerability disclosures and exploit activity through its Vulnerability Intelligence module.
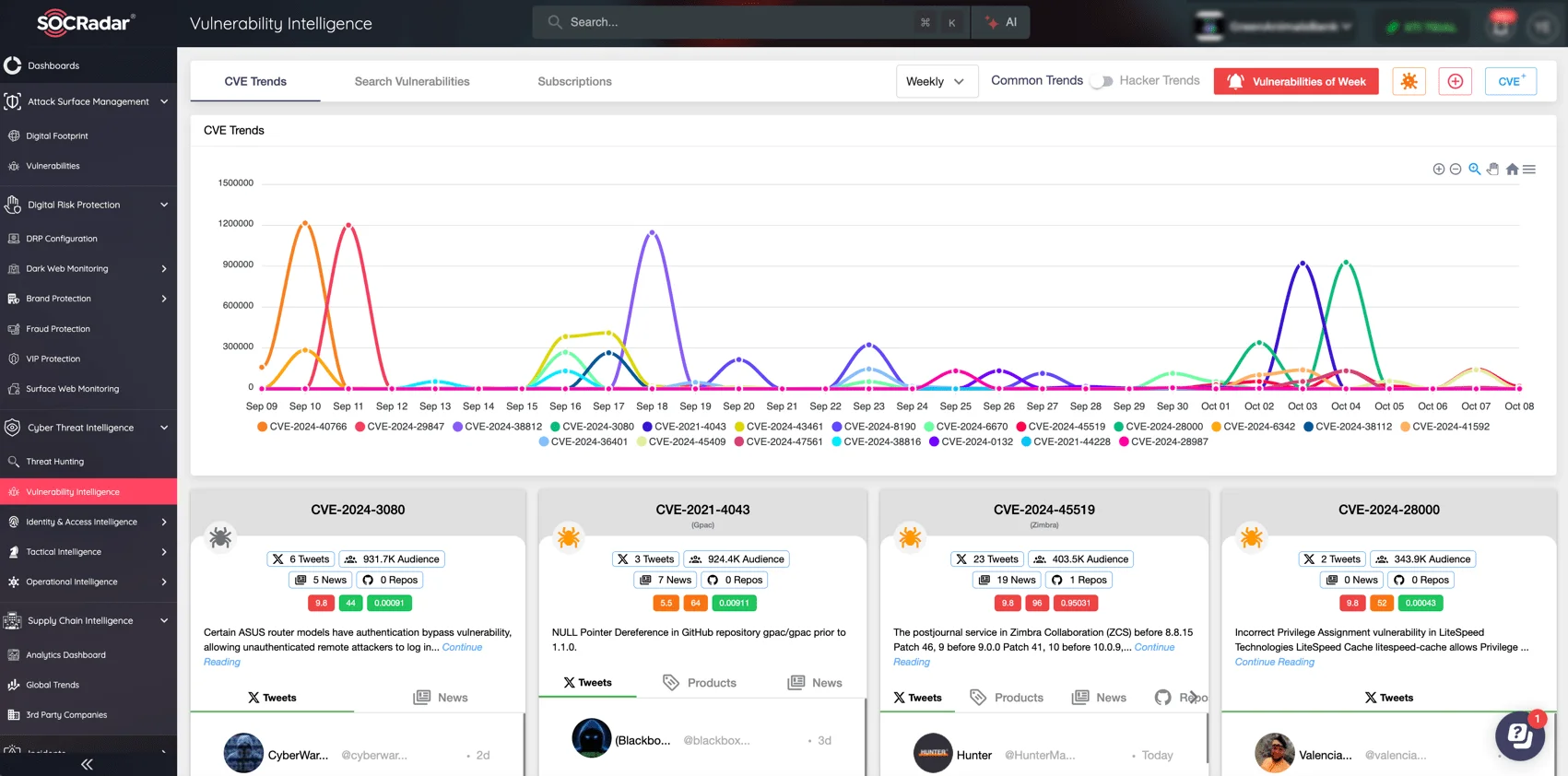
SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence module; search for CVEs, track hacker trends and latest updates
This module enables organizations to track exploit trends, identify high-priority risks, and receive timely updates on identified vulnerabilities, helping security teams act swiftly to mitigate potential attacks before they escalate.
Exploitation is More Likely for These Microsoft Vulnerabilities
Among the notable vulnerabilities in Microsoft’s October 2024 Patch Tuesday update are several tagged by Microsoft as ‘More Likely’ to be exploited. This designation highlights the potential for attackers to target these flaws. Additionally, there are no available workarounds for these vulnerabilities, making patching the only option for mitigation:
- CVE-2024-43583 (CVSS: 7.8) – Winlogon
- CVE-2024-43509 (CVSS: 7.8) – Microsoft Graphics Component
- CVE-2024-43556 (CVSS: 7.8) – Microsoft Graphics Component
- CVE-2024-43560 (CVSS: 7.8) – Windows Storage Port Driver
- CVE-2024-43581 (CVSS: 7.1) – OpenSSH for Windows
- CVE-2024-43502 (CVSS: 7.1) – Windows Kernel
- CVE-2024-43615 (CVSS: 7.1) – OpenSSH for Windows
- CVE-2024-43609 (CVSS: 6.5) – Microsoft Office
PoC Exploit Released for Critical WinReg Vulnerability (CVE-2024-43532)
A Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit is now available for CVE-2024-43532 (CVSS 8.8), a critical elevation of privilege vulnerability affecting Microsoft’s Remote Registry client.
This flaw, patched in the October updates, arises from a fallback mechanism in the WinReg client that insecurely defaults to obsolete transport protocols when SMB is unavailable – attackers can exploit this to relay NTLM authentication details.
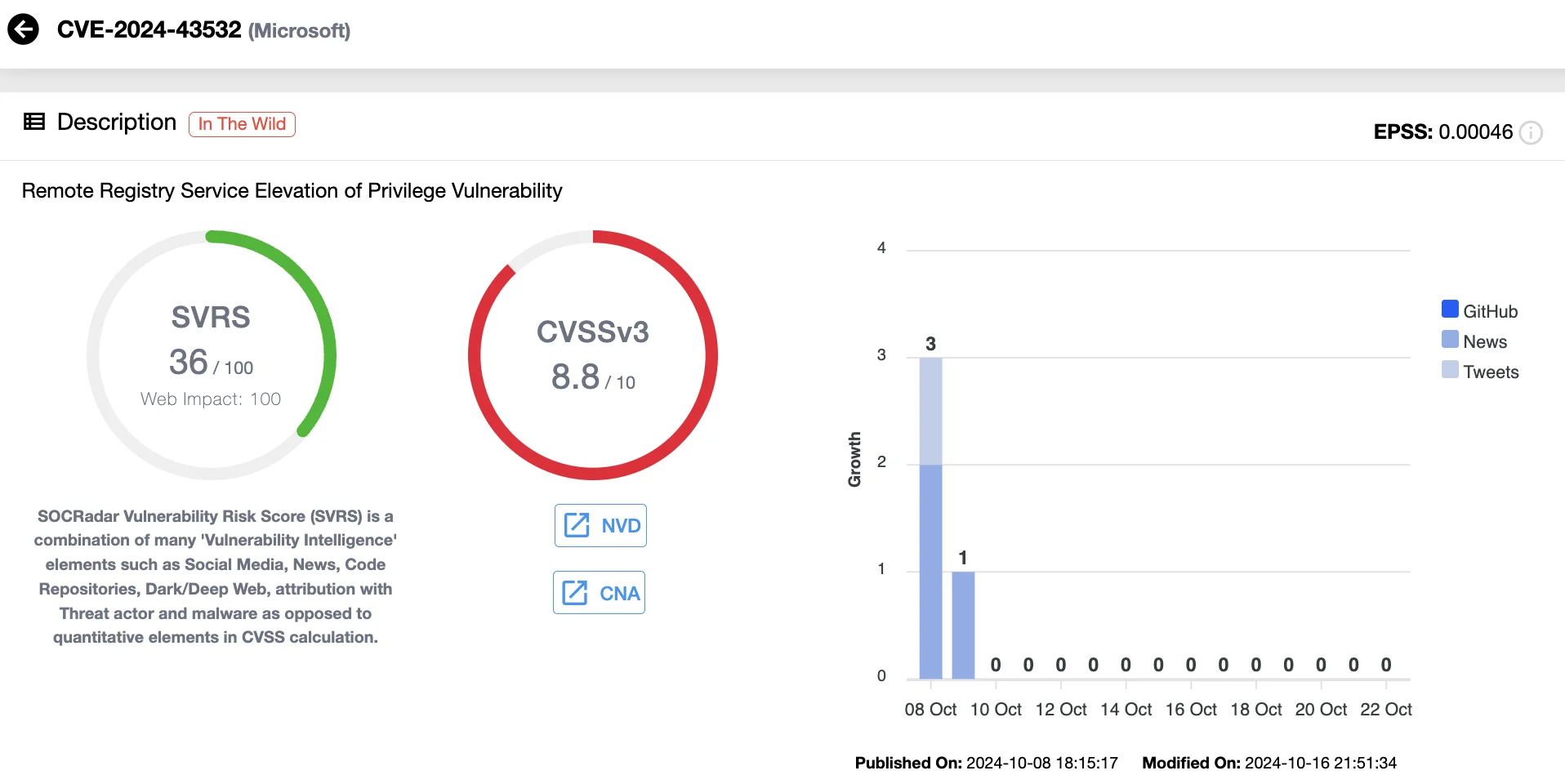
Details of CVE-2024-43532 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Security researcher Stiv Kupchik has demonstrated how attackers can relay the NTLM credentials to Active Directory Certificate Services (ADCS) and request a user certificate, enabling further authentication within the domain.
The researcher observed that insecure authentication levels in many Remote Procedure Call (RPC) interactions enable attackers to relay credentials across networks using a Machine-in-the-Middle attack without the client’s knowledge.
For technical details, refer to the researcher’s blog. The PoC exploit is available on GitHub.
Unpatched vulnerabilities leave systems exposed to potential exploitation, increasing the risk of data breaches, system compromises, and operational disruptions. In this case, where no workarounds are available, applying patches immediately is essential to reduce these risks.
To achieve complete visibility into your organization’s security posture, SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) module provides real-time monitoring and in-depth insights into exposed assets and potential vulnerabilities. With ASM, you can proactively assess, prioritize, and patch security gaps before they become a threat, helping you minimize your digital footprint and reduce exposure to attacks.
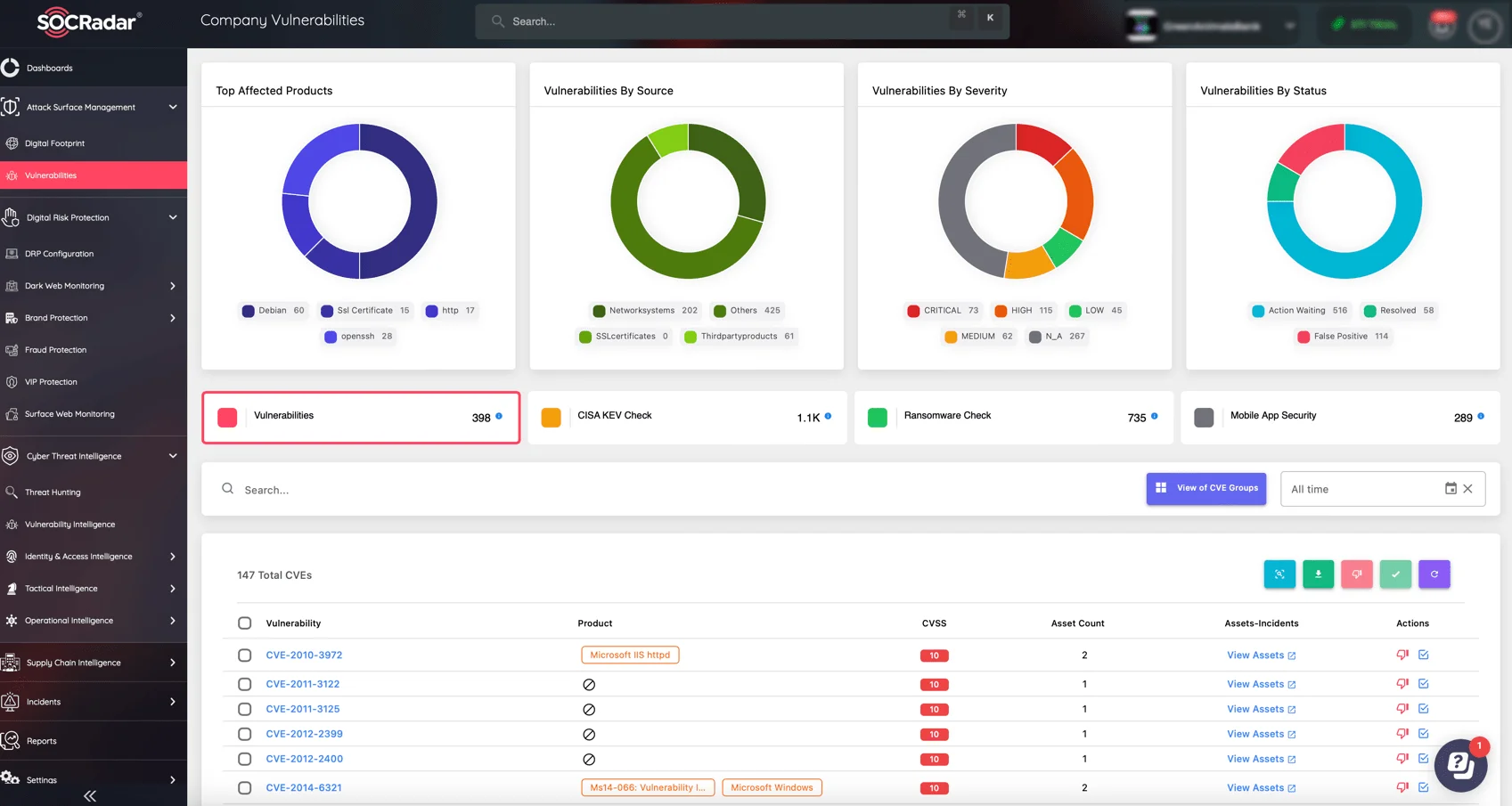
SOCRadar Attack Surface Management (ASM), Company Vulnerabilities
SOCRadar also offers an Advanced Dark Web Monitoring solution, providing alerts when your critical assets are mentioned in underground forums or when vulnerabilities related to your environment are being exploited. This approach strengthens your ability to defend against emerging threats, while keeping you informed of the latest exploit activity and trends.
For more details about Microsoft’s October 2024 Patch Tuesday updates, view the official Release Note.


































