
Critical Vulnerabilities in Palo Alto Networks Expedition Could Expose Firewall Credentials, Patch Available
[Updated] November 15, 2024: “CISA Alerts of Active Exploitation: CVE-2024-9463 and CVE-2024-9465”
[Updated] November 8, 2024: “Palo Alto Expedition Vulnerability (CVE-2024-5910) Enters CISA KEV Catalog”
Palo Alto Networks has released patches addressing a set of critical vulnerabilities in its Expedition tool, which, if left unpatched, could lead to severe security risks. These flaws allow attackers to execute commands and access sensitive data, including user credentials that could potentially lead to the compromise of firewall admin accounts.
Expedition, an advanced version of the Palo Alto Networks Migration Tool, is designed to help the process of migrating configurations from various vendors to Palo Alto Networks’ PAN-OS. By simplifying these migrations, the tool saves administrators significant time while optimizing configurations.
In this blog post, we’ll look into the details of the vulnerabilities, the potential impact, and how to secure your systems.
Details of the Palo Alto Networks Expedition Vulnerabilities
Palo Alto Networks has disclosed a total of five new vulnerabilities affecting the tool, which could allow attackers to access sensitive information like usernames, cleartext passwords, device configurations, and API keys for PAN-OS firewalls. These flaws, including OS command injections, SQL injection, cleartext storage of credentials, and Cross-site Scripting (XSS), present significant risks.
The most critical vulnerabilities include:
- CVE-2024-9463 (CVSS 9.9): An unauthenticated attacker can execute OS commands as root and access sensitive data like usernames, cleartext passwords, and PAN-OS firewall API keys.
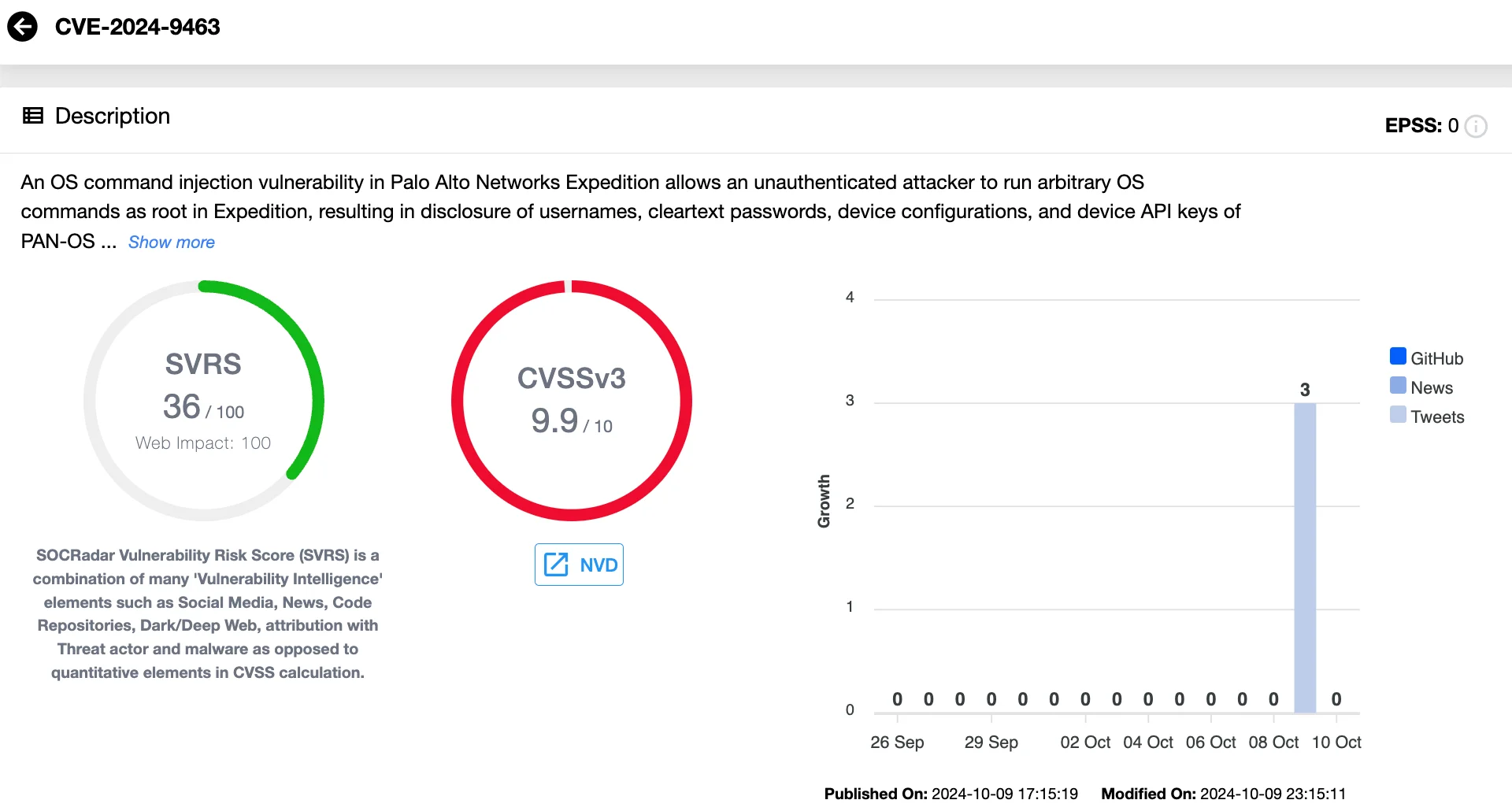
Details of CVE-2024-9463 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
- CVE-2024-9464 (CVSS 9.3): Exploitable by an authenticated user, this command injection flaw lets attackers run OS commands as root, leading to similar data exposure as CVE-2024-9463.
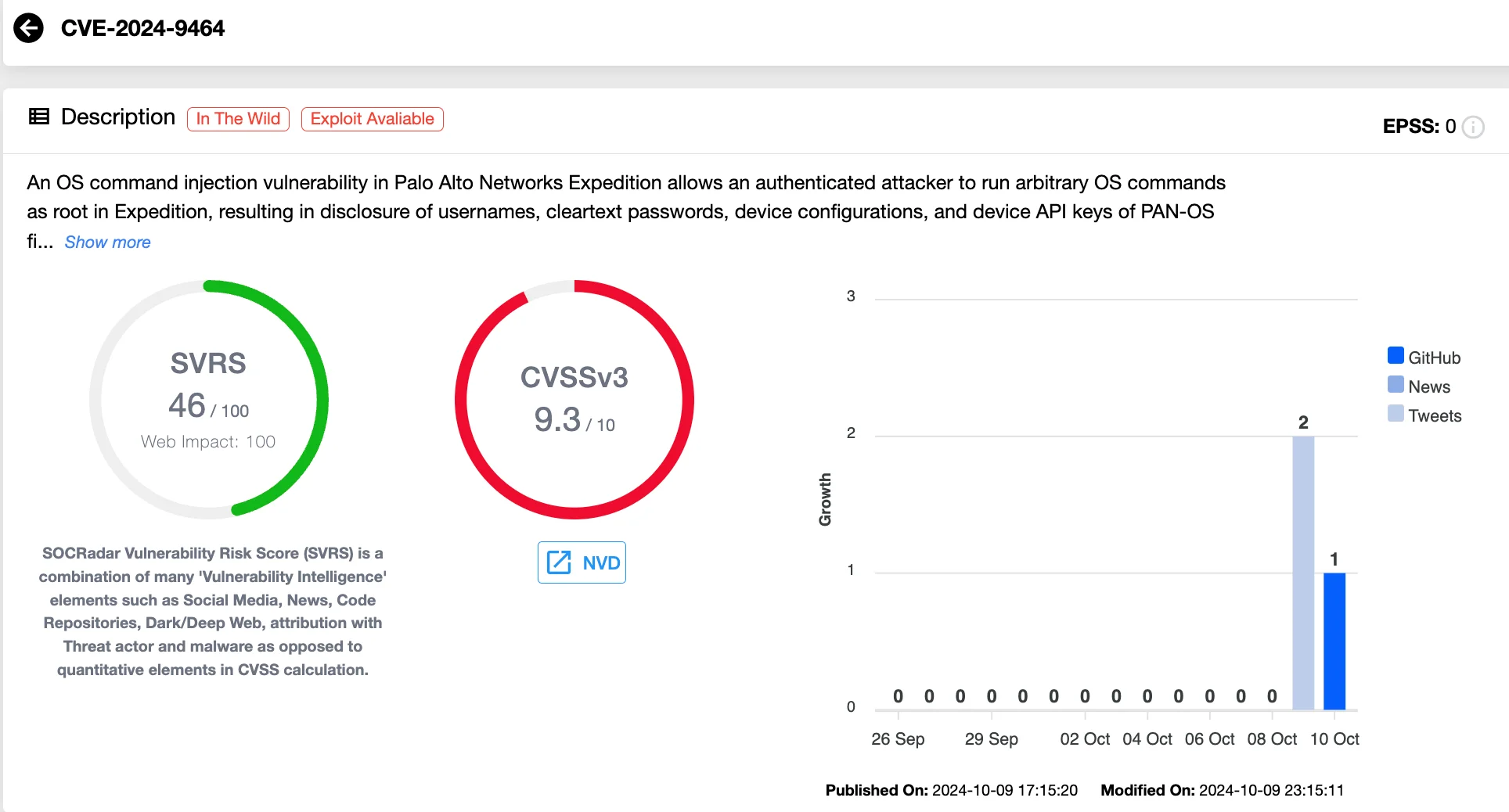
Details of CVE-2024-9464 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
- CVE-2024-9465 (CVSS 9.2): An unauthenticated SQL injection vulnerability that provides access to the Expedition database, exposing usernames and password hashes, and allowing attackers to create and read files.
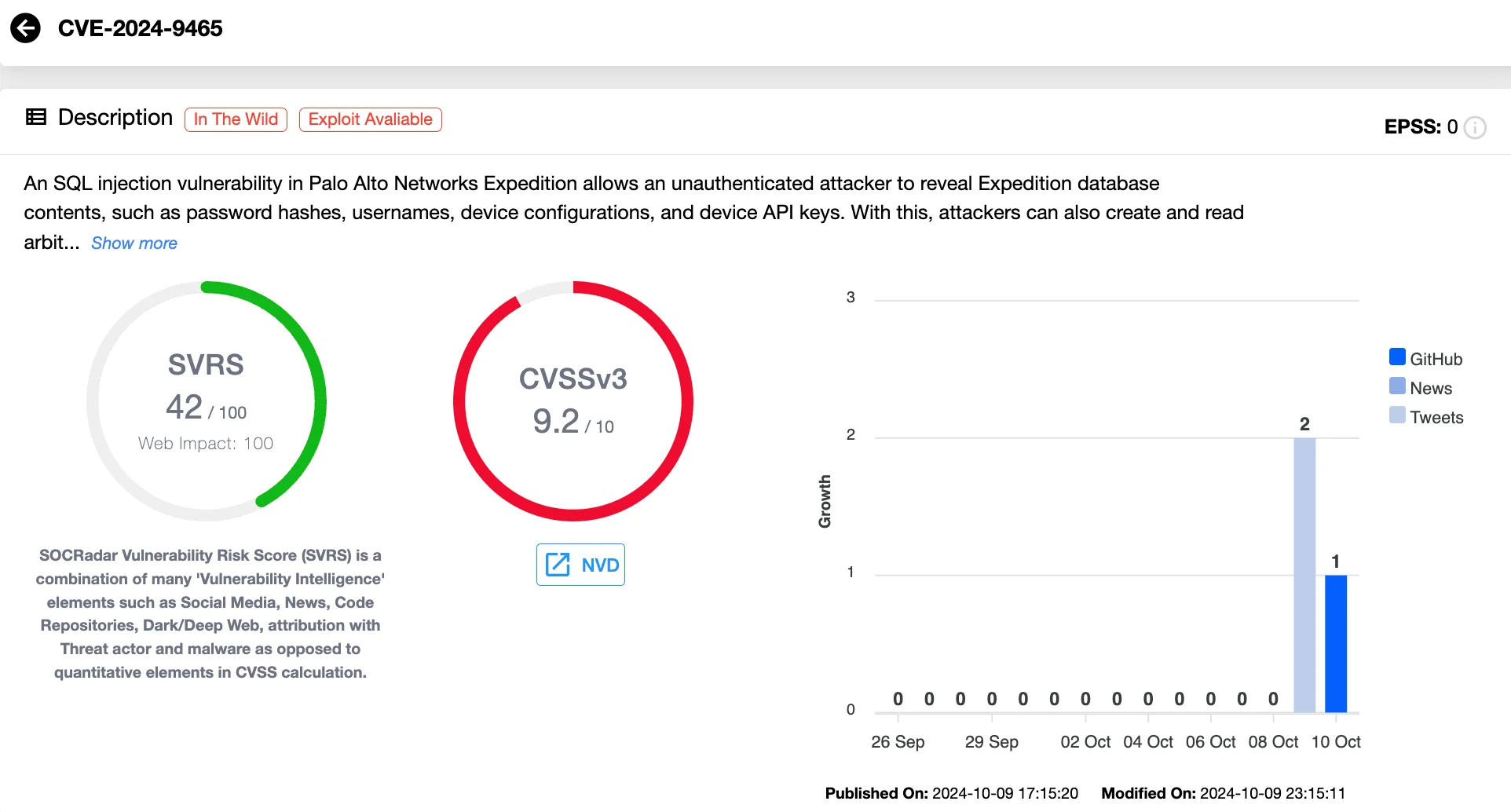
Details of CVE-2024-9465 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Additionally, two high-severity vulnerabilities are noted:
- CVE-2024-9466 (CVSS 8.2): Cleartext storage of sensitive data enables attackers to reveal usernames, passwords, and API keys.
- CVE-2024-9467 (CVSS 7.0): A reflected XSS flaw, which allows malicious JavaScript execution, potentially leading to phishing attacks or session theft.
How Were the Flaws Discovered?
While investigating CVE-2024-5910 (a previous admin credential reset flaw), Horizon3.ai researcher Zach Hanley uncovered three additional critical issues: CVE-2024-9464, CVE-2024-9465, and CVE-2024-9466.
CVE-2024-5910 originally allowed attackers to reset admin credentials remotely due to missing authentication checks. After gaining admin access, Hanley discovered that attackers could achieve remote code execution through files like “CronJobs.php.” Further investigation revealed the SQL injection flaw in “CHECKPOINT.php,” enabling unauthorized access to database data.
Hanley has released a Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit that combines the initial admin reset vulnerability with the newly discovered command injection flaw, CVE-2024-9464, allowing unauthenticated command execution on vulnerable Expedition servers.
A proof-of-concept (PoC) for the CVE-2024-9465 vulnerability is also available and can be accessed at GitHub.
Palo Alto Expedition Vulnerability (CVE-2024-5910) Enters CISA KEV Catalog
CISA added the CVE-2024-5910 Palo Alto Expedition Missing Authentication Vulnerability to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog, warning of risks due to lack of authentication controls in Palo Alto Networks’ Expedition tool. This vulnerability may allow unauthorized access, placing system configurations and data at risk. Federal agencies are required to patch this flaw by November 28, 2024 to ensure adherence to security protocols.
CISA Alerts of Active Exploitation: CVE-2024-9463 and CVE-2024-9465
CISA has added the vulnerabilities CVE-2024-9463 and CVE-2024-9465 in Palo Alto Networks’ Expedition tool to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog, confirming their active exploitation.
Both vulnerabilities pose significant risks, with CVE-2024-9465 already having a publicly available Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit increasing its potential for threat actor weaponization.
Palo Alto Networks has resolved these issues in Expedition version 1.2.96 and strongly urges users to update their systems. Federal agencies must apply these patches by December 5, 2024, per CISA’s directive.
Which Versions of Expedition Are Affected?
Palo Alto Networks confirmed that these vulnerabilities impact Expedition versions earlier than 1.2.96. Importantly, the company clarified that the issues do not affect Palo Alto’s firewalls, Panorama, Prisma Access, or Cloud NGFW solutions.
Users are urged to update to version 1.2.96 or later, where fixes for all identified vulnerabilities are included. During the upgrade, the cleartext file linked to CVE-2024-9466 will be automatically removed to mitigate risks.
Are There Any Reports of Exploitation?
Palo Alto Networks has confirmed that currently there is no evidence of these vulnerabilities being actively exploited in attacks.
According to a Shodan search, only 22 Expedition servers are exposed to the internet – something researcher Hanley points out makes sense, as the application typically doesn’t need to be internet-facing.
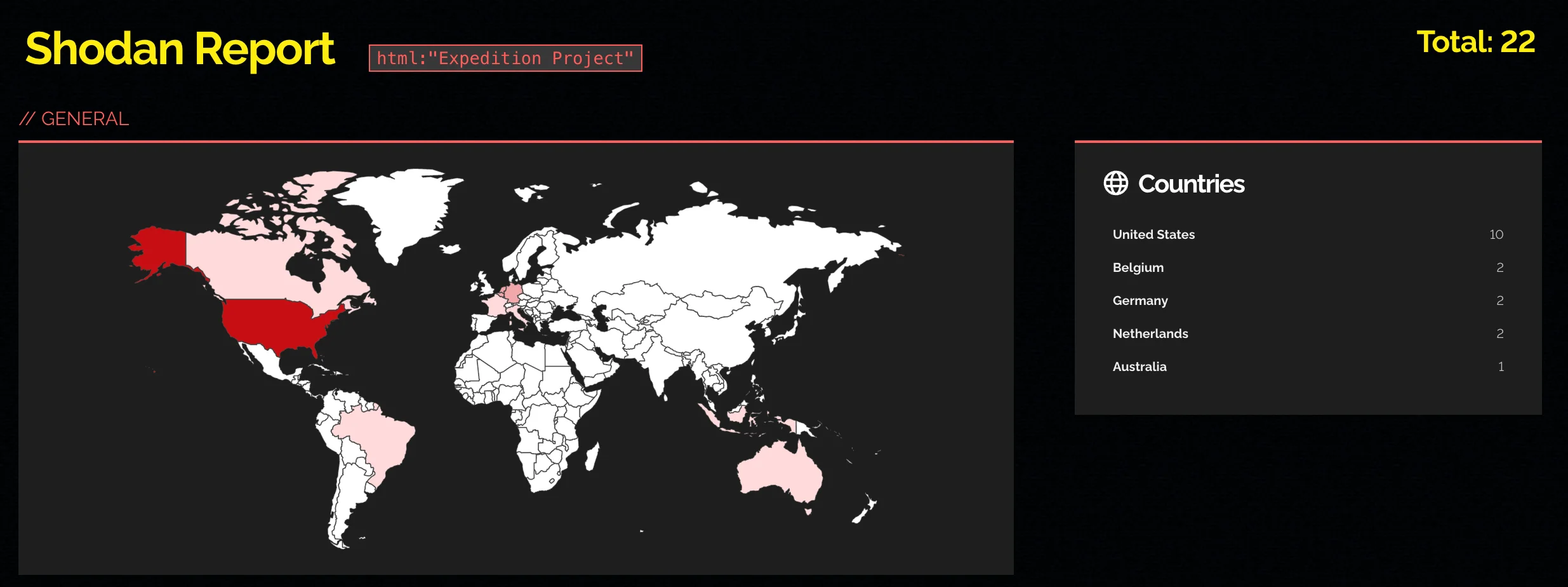
Shodan search results showing exposed Expedition instances
Nonetheless, since Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploits are publicly available, the risk of malicious use by threat actors is heightened, making timely patching essential to avoid exploitation.
In light of vulnerabilities like those recently patched by Palo Alto Networks, organizations need to act swiftly to avoid breaches and prevent sensitive data exposure. When such critical vulnerabilities go unpatched, they can lead to unauthorized access and exploitation, potentially resulting in catastrophic consequences for businesses relying on these tools.
SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence equips organizations with real-time monitoring and detailed analysis of emerging threats, helping your security team prioritize critical vulnerabilities and implement timely patches. Pairing it with the Attack Surface Management (ASM) module, you can also monitor organizational digital assets, ensuring that systems aren’t exposed to potential attacks.
Monitor new CVEs, exploit trends, and assess the vulnerability status of your assets with SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence and Attack Surface Management (ASM) modules.
Update and Secure Palo Alto Networks Expedition
Palo Alto Networks urges users to patch Expedition to version 1.2.96 or later to mitigate these critical vulnerabilities.
Along with applying the updates, it is recommended to rotate all usernames, passwords, and API keys, as well as firewall credentials. The company also advises restricting network access to authorized users, hosts, or networks, and ensuring the tool is shut down if not in active use.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
According to Horizon3.ai, to identify potential exploitation of these vulnerabilities, you can inspect the file /var/apache/log/access.log for suspicious HTTP requests targeting the following endpoints:
- /OS/startup/restore/restoreAdmin.php (Resets admin credentials)
- /bin/Auth.php (Authenticates with reset credentials)
- /bin/CronJobs.php (Inserts malicious SQL data for command injection)
- /bin/configurations/parsers/Checkpoint/CHECKPOINT.php (Unauthenticated SQL injection)
The Palo Alto Networks advisory also notes that for CVE-2024-9465, you can run the following command on an Expedition system to check for potential indicators of compromise. Replace “root” with your username if different:
mysql -uroot -p -D pandb -e “SELECT * FROM cronjobs;”
If records are returned, it could indicate a compromise. However, a lack of records does not necessarily confirm the system is secure.
For more details into the vulnerabilities and mitigation guidance, see the Palo Alto advisory and researchers’ technical write up.



































