
The WarmCookie Malware Campaign: A Sneaky Threat Posed by Fake Browser Updates
The WarmCookie malware campaign poses a significant threat by deceiving users into downloading malicious software under the guise of legitimate browser updates. Disguised as critical updates for popular browsers like Chrome and Firefox, these fake notifications infect systems, steal sensitive data, and spread rapidly.

DALL-E illustration of WarmCookie Malware campaign
How WarmCookie Malware Spreads
The WarmCookie malware campaign uses fake browser update alerts to lure users into downloading malicious software. Upon installation, WarmCookie infiltrates systems, enabling data theft, device profiling, arbitrary command execution, and file exfiltration. The campaign affects various sectors, including finance, healthcare, retail, and national security, with threat actors leveraging compromised websites to deliver malware through misleading updates.
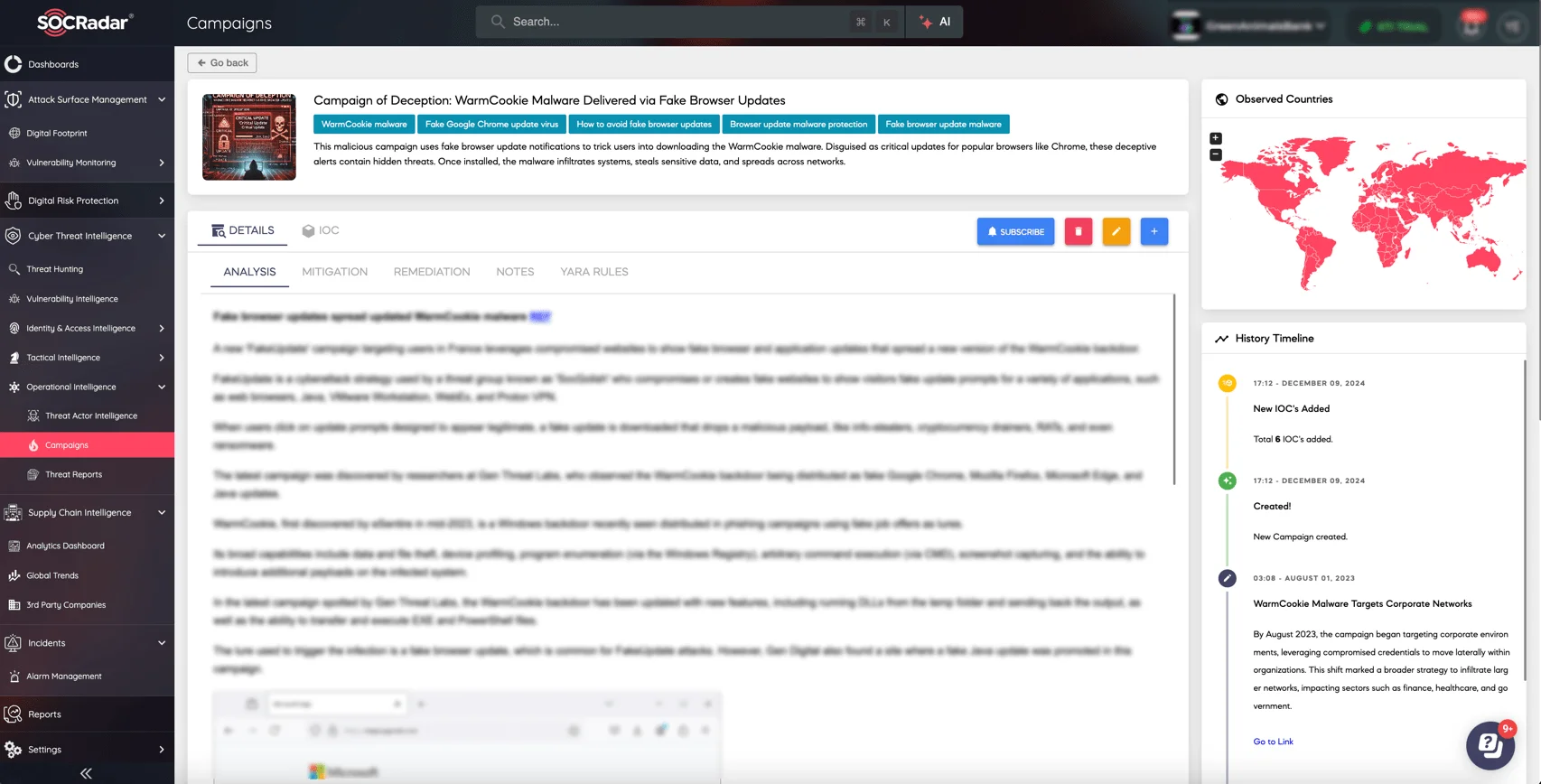
The campaign page for WarmCookie Malware on SOCRadar XTI platform
Find out more about the WarmCookie malware campaign by visiting SOCRadar’s LABS Campaigns.
Breaking Down the Fake Update Attack
The latest WarmCookie campaign, discovered by Gen Threat Labs, uses fake browser and application update prompts to lure victims into downloading malicious software. Known as a ‘FakeUpdate’ attack, the campaign utilizes compromised websites that display alerts for supposed updates to Chrome, Firefox, and other applications. Once the user interacts with the update prompt, the malware installs and performs actions such as anti-virtual machine checks, device fingerprinting, and command execution. The malware has evolved to bypass detection and deliver varied payloads, including info-stealers, remote access tools, and ransomware, targeting both individual users and corporations alike.
A key development in this campaign is the use of JavaScript and HTML to mask the malicious software, making it more difficult for traditional security tools to detect. The attackers use social engineering techniques, exploiting users’ trust in the legitimacy of browser update notifications. The malware is capable of harvesting credentials, capturing screenshots, recording keystrokes, and even exfiltrating sensitive documents, making it a highly versatile and dangerous threat.
TTPS
| Technique ID | Mitigation | Description |
| T1566 | Antivirus/Antimalware | Enable antivirus to automatically quarantine suspicious files. |
| T1566 | Network Intrusion Prevention | Implement network systems to block malicious links or attachments. |
| T1566 | User Training | Train users to recognize social engineering tactics in phishing emails. |
| T1204 | Behavior Prevention on Endpoint | Enable ASR rules on Windows to restrict executable files from untrusted sources. |
| T1059.001 | Execution Prevention | Limit PowerShell execution to only signed scripts and apply Constrained Language mode. |
| T1082 | System Information Discovery | Proactive monitoring of API calls and command-line executions that attempt to gather system details. |
| T1053 | Privileged Account Management | Limit the creation of scheduled tasks to authorized users only, configuring permissions via GPO. |
Conclusion
The WarmCookie malware campaign demonstrates the increasing sophistication of cyber threats exploiting common user behaviors, such as trusting browser update notifications. This tactic underscores the importance of caution when interacting with update prompts, even when they appear to come from trusted sources. As cybercriminals continue to refine their methods, organizations must stay vigilant and continuously update their security measures.
To learn more about this and other active campaigns, SOCRadar’s Campaigns page offers a comprehensive view of emerging cyber threats, helping you stay prepared against a wide array of potential security risks.



































