
New Malware “Statc Stealer” Targets Windows Devices to Steal Browser Data, Cryptowallets, and More
Researchers have identified a new information-stealing malware named “Statc Stealer.” This malware is designed to infect Windows devices by tricking victims into interacting with seemingly legitimate links or advertisements.
Statc Stealer is capable of stealing an extensive array of information, rendering it a concerning threat.
What Type of Data Is Targeted by the Statc Stealer?
The malware can steal sensitive data from a variety of popular web browsers, including Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Brave, Opera, Yandex, and Mozilla Firefox. It can also steal data from cryptocurrency wallets and messaging apps like Telegram.
The researchers used the Windows Process Monitor tool and discovered that Statc Stealer can successfully steal the following information:
- User cookies
- Web data
- Local state
- Data preferences
- Login data
- Cryptowallets’ information
- FileZilla
- AnyDesk
- ronin_edge
- MetaMask
- Telegram data
Autofill data, such as usernames and passwords, email addresses, personal addresses, credit card details, and other payment information, can also be stolen by the stealer malware.
Can Statc Stealer Evade Analysis?
Information stealer malware typically employ advanced techniques to evade execution in sandbox environments and analysis. Statc Stealer, according to researchers, also employs an anti-analysis method.
The stealer performs a filename check by comparing the file name to an encrypted string stored in its code, thereby verifying the correspondence between its filename and internal name. If the stealer malware detects any changes in its files, it promptly terminates its operations.
How Does a Statc Stealer Infection Work?
The infection begins when victims are lured into clicking on a seemingly genuine Google advertisement or a link.
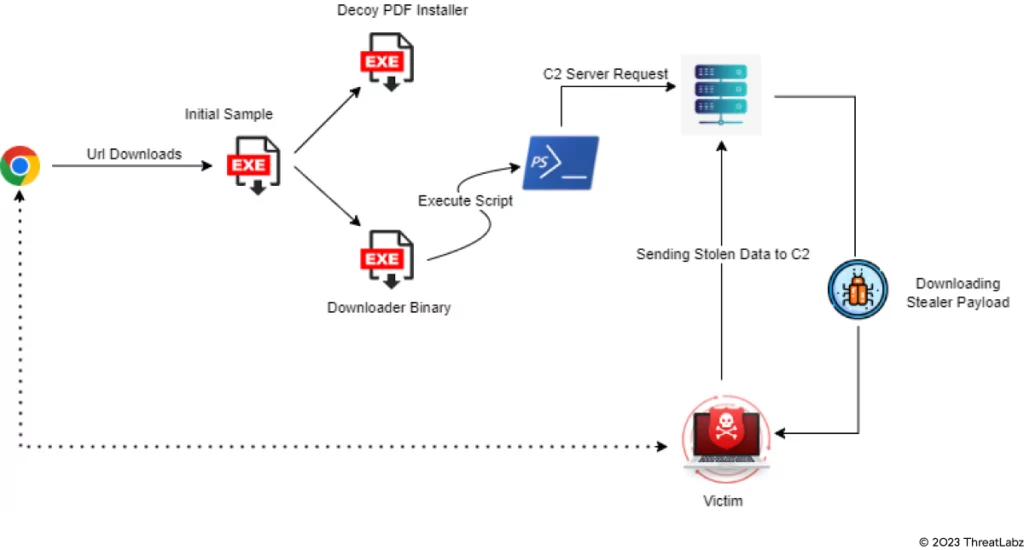
Unbeknownst to the user, clicking the malicious advertisement or link triggers the download of the Initial Sample file. Once the malicious file executes, it then proceeds to drop and run a Decoy PDF Installer, further advancing the compromise.
To retrieve the Statc Stealer payload via a PowerShell script, the Initial Sample file also drops and executes a Downloader Binary file. After Statc Stealer acquires the user’s data, it proceeds to encrypt the information, placing it within a text file. This encrypted data is then stored in the Temp folder.
From this point, Statc Stealer communicates with its command and control server (C2) to transfer the stolen and encrypted data. To hide its activities, the malware employs the HTTPS protocol while sending the data to the C2 server.
Indicators of Compromise (IoCs)
Filenames:
- Version2023-new[.]exe
- chtgpt_x64[.]exe
- SearchApplication[.]exe
- sound_adapter[.]exe
MD5 Hashes:
- f77dc89afbaab53e5f63626e122db61e (Dropper)
- 3834ec03aee0860dfd781805cac3e649 (Downloader)
- 65affc4e1d5242a9c3825ce51562d596 (Stealer malware)
- e002c90a035495631a0abf202720a79c (Stealer malware)
- f49348fa15d87e92896363b40267c9ae (Stealer malware)
URLs:
- 95[.]217[.]5[.]87[/]Setup64_new0[/]Version2023-new[.]exe
- check[.]topgearmemory[.]com/dw/9c890e1b2b4f2723a68fc905268ee010cae232be[.]txt
- https[:]//topgearmemory[.]com/kdsfedafa/stat?c=
SOCRadar’s Threat Actor & Malware Tracking
SOCRadar XTI employs automated data collection, classification, and AI-driven analysis across diverse sources on the surface, deep, and dark web. With this comprehensive approach, our Threat Actor & Malware panel is consistently updated, providing you with the most current details pertaining to threat actors and malware.
Armed with the insights on the SOCRadar platform, you can develop more effective use cases to detect and prevent malicious activities, and proactively protect your organization against potential threats.



































