OpenVPN Fixed Multiple Vulnerabilities on Windows Version: Risk of Privilege Escalation, Remote Access
OpenVPN, with the release of a new version, addressed severe security vulnerabilities, specifically impacting the Windows platform. These vulnerabilities could cause system crashes and privilege escalation, and allow remote attackers to access the service pipe.
OpenVPN is a widely used VPN (Virtual Private Network) tool for establishing secure connections between networks, ensuring privacy and data security.
Threat actors can exploit these vulnerabilities to compromise the data transmitted via the VPN tunnels, making patching critical for ensuring the integrity and security of your network connections.
What Vulnerabilities Did OpenVPN Fix?
OpenVPN has disclosed and subsequently patched four vulnerabilities in version 2.6.10. Below, we outline the descriptions of these vulnerabilities and the fixes implemented to address them.
CVE-2024-27459:
This vulnerability affects the interactive service component, potentially leading to local privilege escalation when triggered by an oversized message.
To mitigate this risk, the VPN solution now terminates connections upon detecting excessively large messages, preventing stack overflow exploits.
CVE-2024-24974:
Previously, the VPN tool’s Windows implementation allowed remote access to its service pipe, posing a security risk. Using compromised credentials, a threat actor could communicate with OpenVPN to orchestrate attacks.
OpenVPN has patched CVE-2024-24974 by blocking remote access to the service pipe.
CVE-2024-27903:
In versions prior to 2.6.10, OpenVPN could load plugins from unreliable directories, opening the door to potential compromise.
OpenVPN has mitigated the risk by restricting plugin load. Plugins can now only be loaded from the software’s install directory, the Windows system directory, and the plugin_dir directory under the software’s installation.
CVE-2024-1305:
OpenVPN lastly addressed an integer overflow vulnerability.
Tracked as CVE-2024-1305, the vulnerability stemmed from the ‘TapSharedSendPacket’ function of the Windows TAP driver used by the VPN software. Its exploitation could lead to system crashes through memory corruption.
For further details and the software updates, you can read the official release note here.
How Can You Secure Your OpenVPN Installation from Vulnerabilities?
For Windows users of OpenVPN, installing the update to version 2.6.10 is critical to mitigating potential security risks. By promptly applying these security fixes, you can protect your system from exploitation by threat actors.
To further enhance vulnerability monitoring and patch management, use SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) module. Receive real-time notifications for new vulnerabilities and gain insights to optimize patch prioritization.
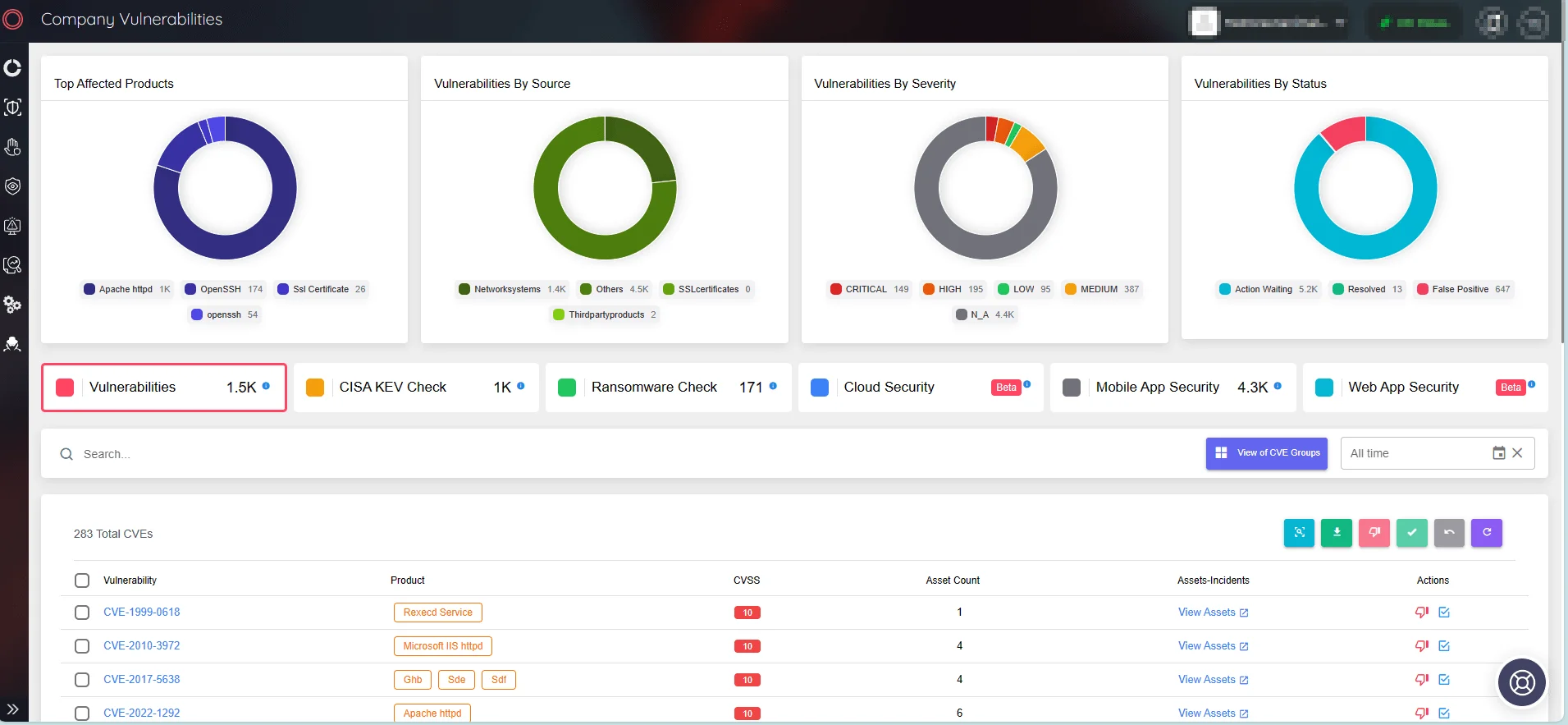
Monitor company vulnerabilities and take quick action (SOCRadar ASM)
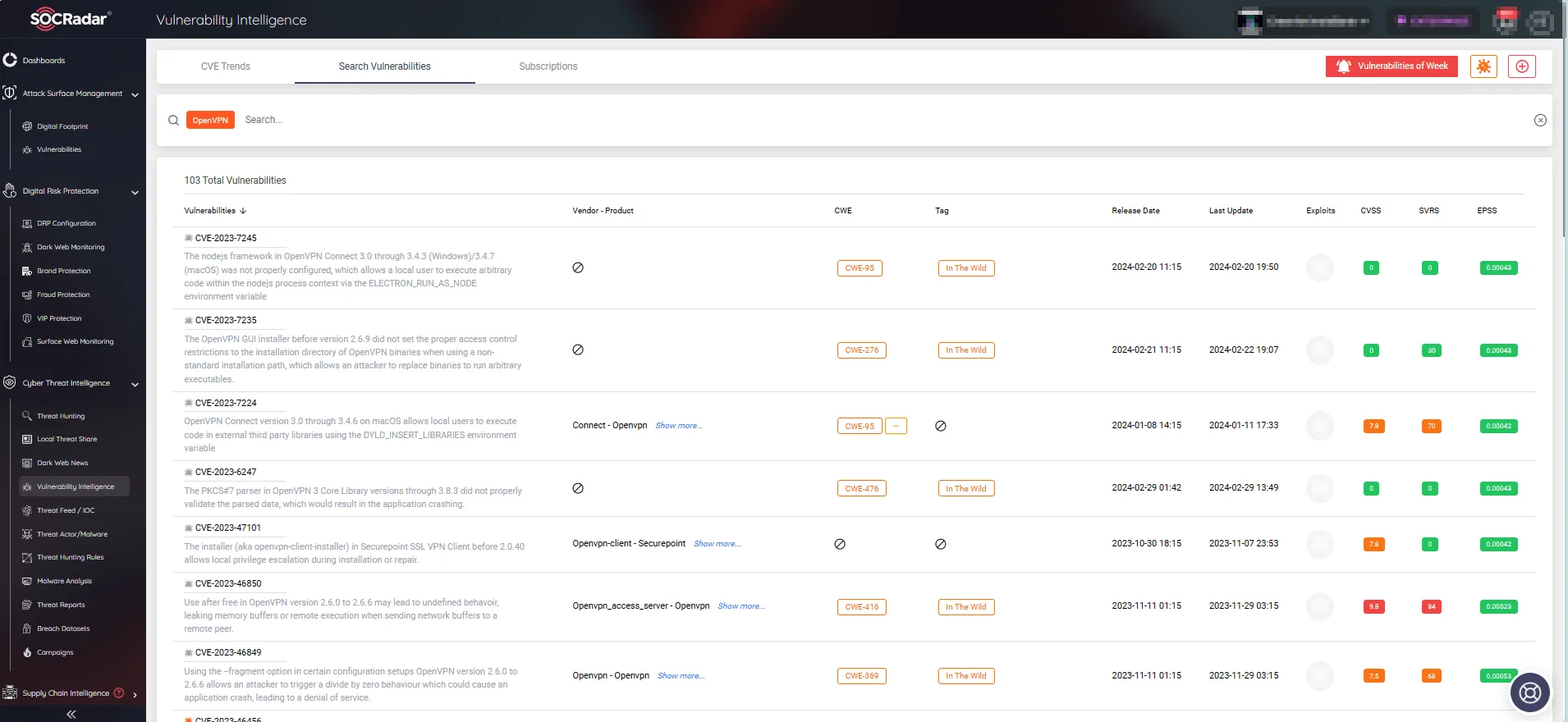
Additionally, with SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence feature, you can search for vendor or product-specific vulnerabilities and access comprehensive details, including the latest updates and exploits.