
New High-Severity Vulnerability in Apache ActiveMQ Poses Risk of Unauthorized Access: CVE-2024-32114
A high-severity vulnerability, CVE-2024-32114, has been discovered in Apache ActiveMQ, potentially granting unauthorized access to the API layers without authentication.
Apache ActiveMQ, a widely adopted open-source Java-based message broker, serves as a vital communication conduit between various components across diverse servers and programming languages, including Python, C++, JavaScript, and others.
What is CVE-2024-32114? Which Apache ActiveMQ versions are affected?
CVE-2024-32114 impacts users of Apache ActiveMQ versions 6.x (prior to 6.1.2).
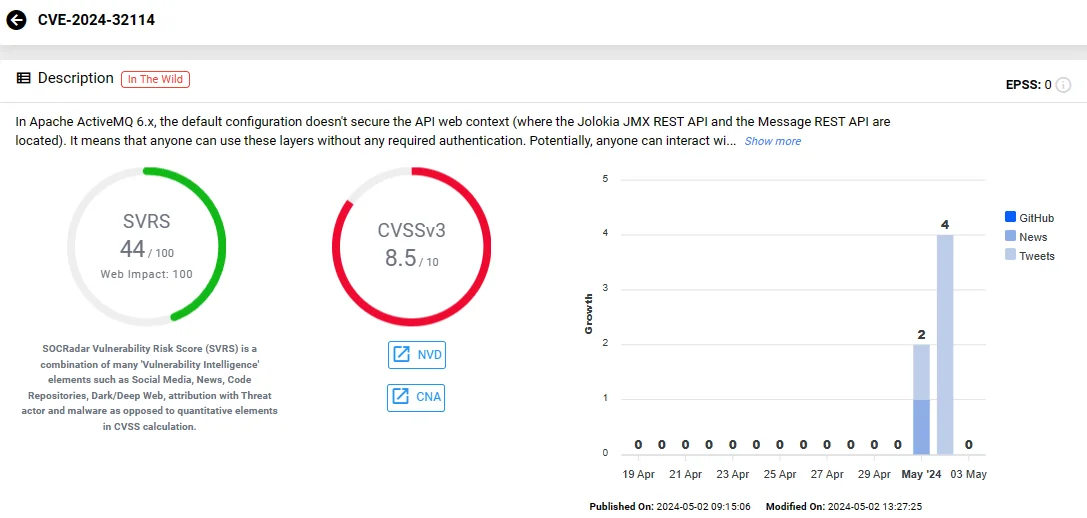
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-32114 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
The issue arises from an insecure default configuration concerning the Jolokia JMX REST API and the Message REST API. These APIs are both accessible through the API web context without authentication because they are not secure in ActiveMQ’s default configuration (in versions 6.x before 6.1.2).
For real-time monitoring of CVEs and exploitation trends, leverage SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence feature. Stay updated, identify exploits, and gain insights for proactive vulnerability management effortlessly.
Trending CVEs on SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence
How critical is CVE-2024-32114?
CVE-2024-32114 carries a severity score of 8.5 on the CVSS scale, signifying a high risk level. Tagged as a major priority issue on Jira, exploitation of this vulnerability could result in major loss of function.
How could attackers exploit CVE-2024-32114? How does it affect Apache ActiveMQ?
CVE-2024-32114 could be exploited by potential attackers who utilize the Jolokia JMX REST API or manipulate messaging functions, such as producing/consuming messages and purging/deleting destinations via the Message REST API.
Such exploitation may lead to unauthorized data access, data loss, or service disruption, severely compromising the application’s integrity and availability.
Ultimately, the absence of authentication grants attackers unauthorized access, posing significant risks to the users of ActiveMQ.
Has CVE-2024-32114 been exploited to compromise Apache ActiveMQ instances?
Currently, there are no reports of exploitation associated with CVE-2024-32114, and no known threat actors have targeted it. However, a search on Shodan reveals over 3,000 Apache ActiveMQ instances exposed on the internet, which could attract malicious actors.
This significant number underscores the extensive attack surface and the potential for exploitation by adversaries.
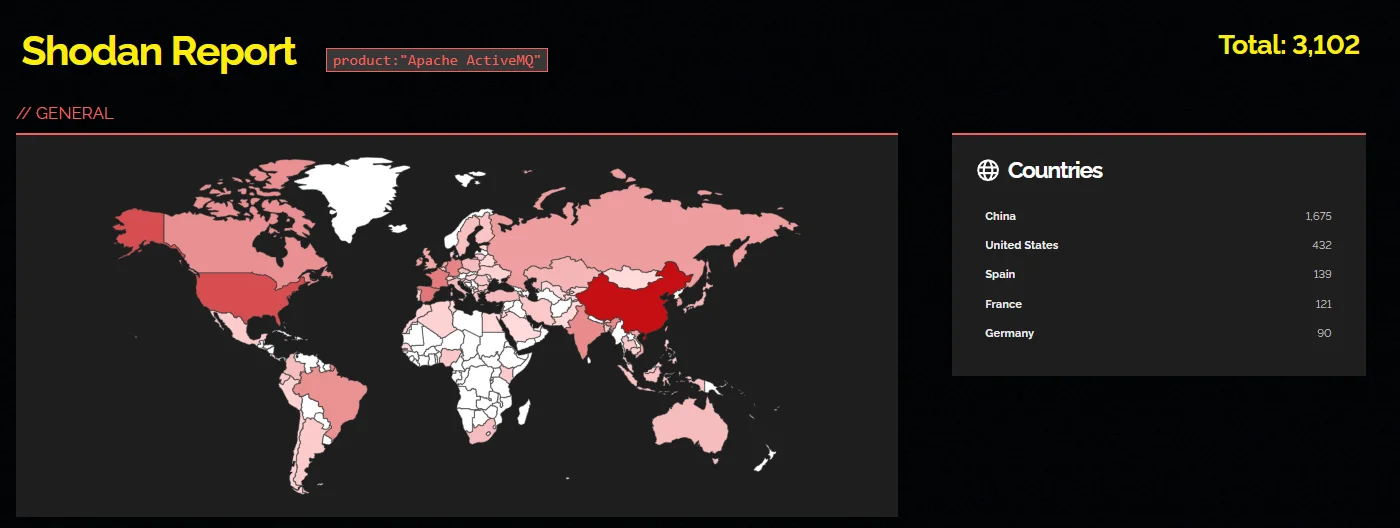
Shodan results for Apache ActiveMQ
Previously, a different vulnerability in Apache ActiveMQ (CVE-2023-46604) was exploited by a ransomware threat group known as “HelloKitty Ransomware.” These initial attacks spurred other threat actors to exploit the issue, deploying diverse malware in subsequent attacks.
Is there a workaround available?
A mitigation method mentioned in the advisory involves modifying the default configuration in the conf/jetty.xml file to enforce authentication.
To implement the mitigation, you can add the constraint mapping below to the configuration, ensuring that authentication is required for access to the API web context
<bean id=”securityConstraintMapping” class=”org.eclipse.jetty.security.ConstraintMapping”>
<property name=”constraint” ref=”securityConstraint” />
<property name=”pathSpec” value=”/” />
</bean>
How to fix CVE-2024-32114?
Although a mitigation method exists, it is strongly advised to update to ActiveMQ version 6.1.2 to permanently fix the issue, as it features an enhanced default configuration that automatically secures the Jolokia and REST APIs.
See the release note for ActiveMQ version 6.1.2 here.
Stay Updated on Emerging Vulnerabilities with SOCRadar
Stay ahead of cyber threats with SOCRadar’s security solutions, bolstering your organization’s vulnerability management tactics.
Harnessing SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) in tandem with Vulnerability Intelligence keeps you abreast of the latest security risks, ensuring robust protection for your products and software with actionable insights and security alerts.
Protect your digital assets through ongoing monitoring with SOCRadar ASM



































