
New in CISA KEV: Check Point VPN Zero-Day CVE-2024-24919 & Linux Kernel Flaw CVE-2024-1086
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Agency (CISA) updated its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog to include two CVEs, calling for organizations to address them as soon as possible to avoid compromise.
These CVEs, identified as CVE-2024-24919 and CVE-2024-1086, represent significant security vulnerabilities in Check Point Quantum Security Gateways and the Linux kernel.
What is CVE-2024-24919?
The vulnerability tracked as CVE-2024-24919 poses a high-severity risk with a CVSS score of 8.6, leading to unauthorized information disclosure. It affects Check Point Quantum Security Gateways, specifically within their VPN functionalities – including IPSec VPN, Remote Access VPN, and Mobile Access.
Notably, it was exploited as a zero-day vulnerability before patches became available. Check Point quickly responded to the emergence of this vulnerability by releasing necessary hotfixes; however, this action was preceded by their observations of attacks on VPN devices.
Exploits of CVE-2024-24919 have been documented since April 30, with attackers primarily stealing Active Directory credentials to facilitate lateral movement across networks. These incidents primarily exploited scenarios where old local accounts utilized password-only authentication, which is not recommended due to its susceptibility to such attacks.
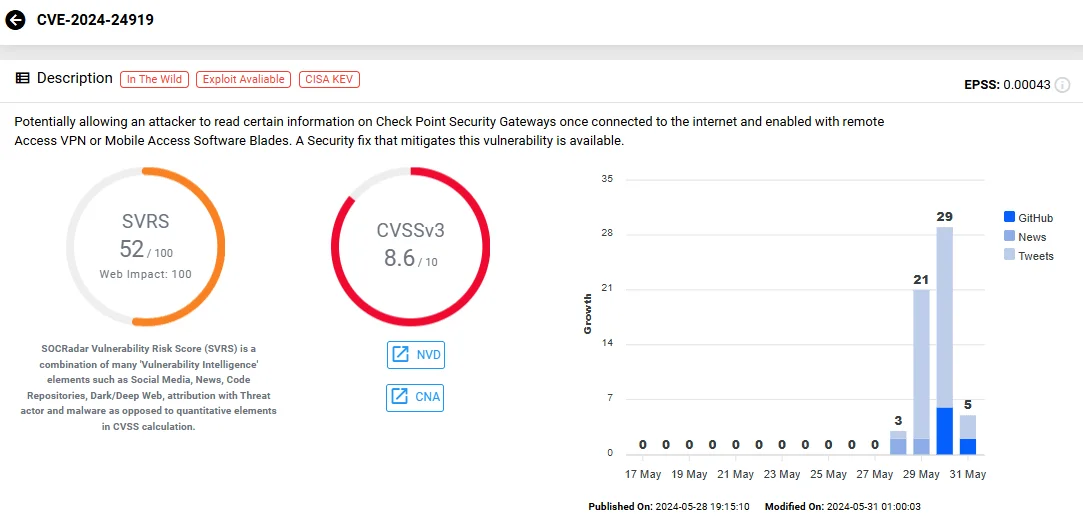
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-24919 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
To stay ahead of threats like CVE-2024-24919, SOCRadar offers its Vulnerability Intelligence feature. This service provides detailed insights into emerging CVEs, including exploits, mentions across different platforms, affected systems, observed attacks in the wild, and inclusion in the CISA KEV Catalog.
By integrating SOCRadar’s tools, organizations can enhance their cybersecurity posture through timely and actionable intelligence, ensuring they are well-prepared to address such vulnerabilities.
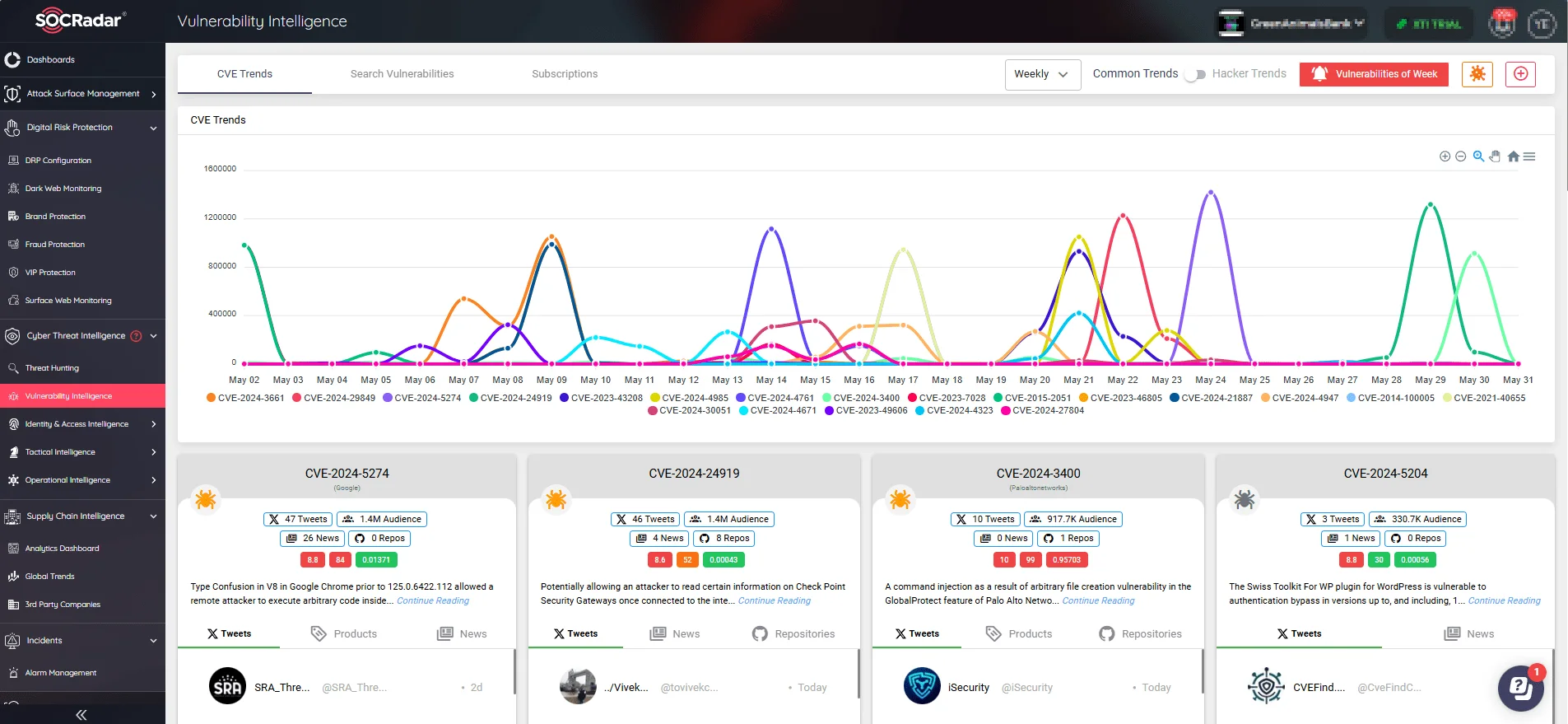
New CVEs, mentions, and exploitation trends (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Which products and versions are affected by CVE-2024-24919?
The vulnerability has a broad impact across several Check Point product lines. This includes:
- CloudGuard Network
- Quantum Scalable Chassis
- Quantum Security Gateways
- Quantum Maestro,
- Quantum Spark
The affected product versions are also extensive, comprising R80.20.x, R80.20SP (EOL), R80.40 (EOL), R81, R81.10, R81.10.x, and R81.20.
According to a Shodan search, approximately 32,000 instances of these products are currently exposed over the internet, potentially placing them at risk of exploitation through CVE-2024-24919. On the other hand, LeakIX has identified around 8,500 gateways vulnerable to this security vulnerability.
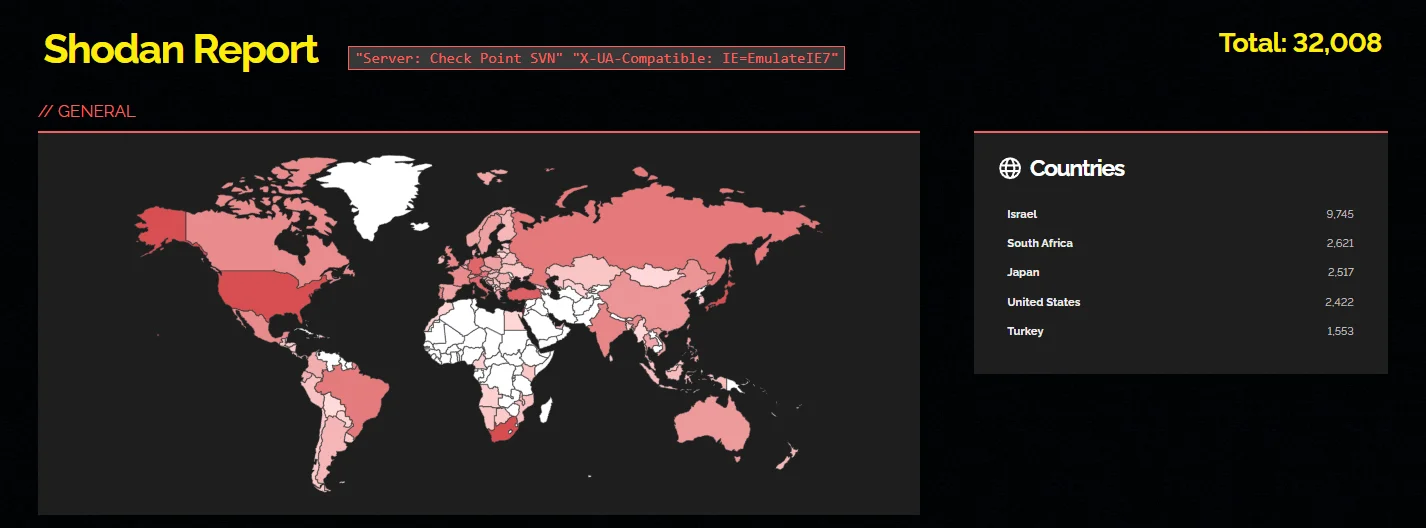
Search report from Shodan
PoC Exploit and Detection Template for CVE-2024-24919
For organizations seeking to identify potential exposure, a Nuclei template is available on GitHub. The template is designed to detect the CVE-2024-24919 vulnerability in Check Point Quantum Security Gateways.
The Nuclei template involves a Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit that was initially shared on the social platform X:
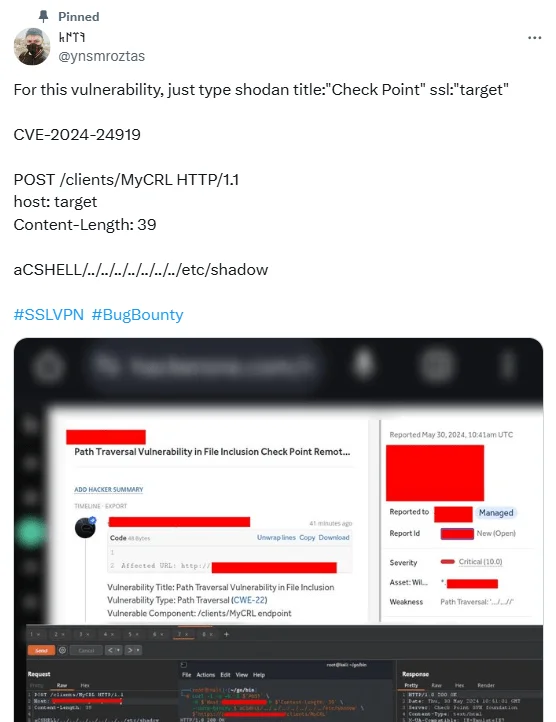
PoC exploit code for CVE-2024-24919 (@ynsmroztas on X)
This PoC exploit demonstrates how attackers could abuse a directory traversal flaw through an HTTP POST request and access sensitive files like /etc/shadow.
The researcher who created the detection template reported finding several instances, including financial institutions in Latin America (LATAM) and IT providers, vulnerable to CVE-2024-24919.
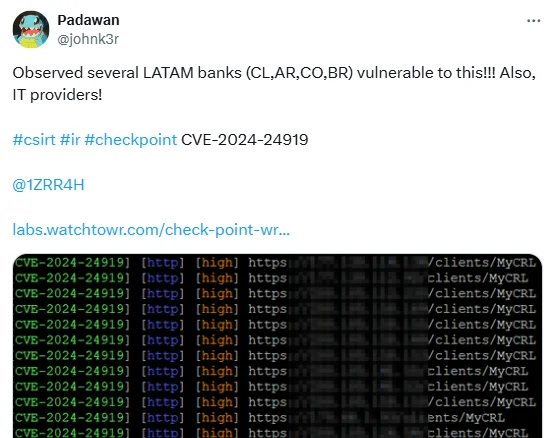
The researcher tweeted about observing vulnerable instances (@johnk3r on X)
How to address the Quantum Security Gateway vulnerability?
Check Point rolled out hotfixes to enhance the security of various Quantum Security Gateway and CloudGuard Network products. The hotfix ensures that suspicious login attempts that use weak credentials/authentication methods are blocked and a log is created.
- Quantum Security Gateway and CloudGuard Network Security: Versions R81.20, R81.10, R81, R80.40.
- Quantum Maestro and Quantum Scalable Chassis: Versions R81.20, R81.10, R80.40, R80.30SP, R80.20SP.
- Quantum Spark Gateways: Versions R81.10.x, R80.20.x, R77.20.x.
Check Point has also made updates available for versions that have reached End-of-Life (EOL), although these must be downloaded and applied manually. This step is vital to ensure that even systems no longer in the mainstream support pipeline remain protected against potential exploits.
For detailed guidance and to download the necessary updates, visit Check Point’s support downloads page.
Recommended Extra Security Measures to Mitigate CVE-2024-24919
In addition to applying the latest security updates, the company recommends implementing several additional security measures to address the vulnerability’s impact:
- Password Security Enhancements:
- Change the password of the LDAP Account Unit.
- Reset passwords for local accounts that connect to the VPN using password-only authentication.
- Prevent local accounts from connecting to VPNs with password-only authentication. Check Point provides a script to aid in this process, enhancing the security configuration.
- Certificate and SSH Key Management:
- Renew server certificates for both inbound and outbound HTTPS Inspection on the Security Gateway to prevent any interception or spoofing.
- Regenerate SSH local user certificates and renew certificates for SSH Inspection to secure communication channels and administrative access.
- Operating System Security:
- Reset Gaia OS passwords for all local users to ensure that no unauthorized access is possible through default or compromised credentials.
What is CVE-2024-1086?
The second new entry in the CISA KEV Catalog is CVE-2024-1086 (CVSS: 7.8), which is a Use-After-Free vulnerability in the Linux kernel. Although less severe than CVE-2024-24919 in Quantum Security Gateways, this vulnerability still poses significant risks.
The vulnerability resides in the netfilter subsystem, which manages packet filtering along with network address translation (NAT) and other packet manipulations, affecting the nftables (netfilter: nf_tables) component.
It occurs due to improper memory management in the nft_verdict_init() function, which allows for positive values as drop errors in the hook verdict, subsequently leading to a double free error and allowing an attacker with local access to escalate privileges on the system.
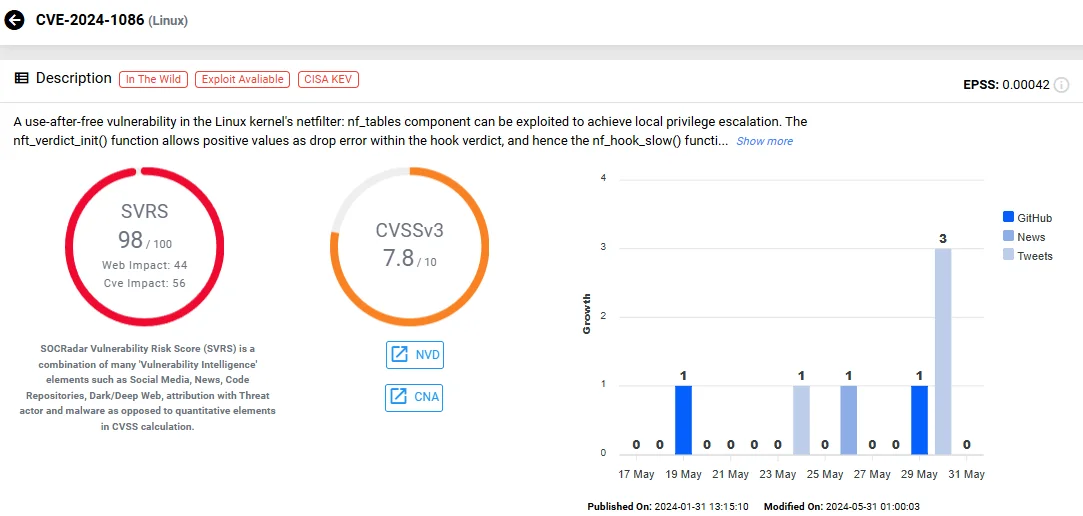
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-1086 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
CVE-2024-1086 impacts a wide array of Linux kernel versions, from v5.14.21 to v6.6.14. This extensive range includes many popular Linux distributions that are widely used in various computing environments, from personal computers to enterprise servers.
PoC Exploit and Technical Details Available for CVE-2024-1086
Security researcher ‘notselwyn’ released both technical details and a PoC exploit for the CVE-2024-1086 vulnerability, naming it ‘Flipping Pages’ on their blog.
The exploit associated with CVE-2024-1086 aims to escalate privileges on affected systems, targeting a wide range of Linux kernel versions from v5.14 to v6.6. It affects popular distributions such as Debian, Ubuntu, and KernelCTF.
According to the researcher, the exploit has an exceptionally high success rate of 99.4% when tested on KernelCTF images.
Despite its effectiveness, the exploit for CVE-2024-1086 does have limitations. It is not effective against Linux kernel versions v6.4 and newer if they are configured with CONFIG_INIT_ON_ALLOC_DEFAULT_ON=y, a setting found in Ubuntu v6.5. Furthermore, the exploit’s success relies on several specific conditions:
- Availability of user namespaces
- Unprivileged status of these namespaces
- Active nf_tables configuration
These prerequisites are fulfilled by default in the mentioned vulnerable distributions, which heightens the risk for those environments.
How to address the CVE-2024-1086 vulnerability?
Linux addressed this vulnerability in February, with a patch introduced past commit f342de4e2f33e0e39165d8639387aa6c19dff660. Organizations and users are urged to upgrade their systems to versions incorporating this fix to mitigate the risk posed by CVE-2024-1086.
Find the detailed lifecycle of identified vulnerabilities via SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence.
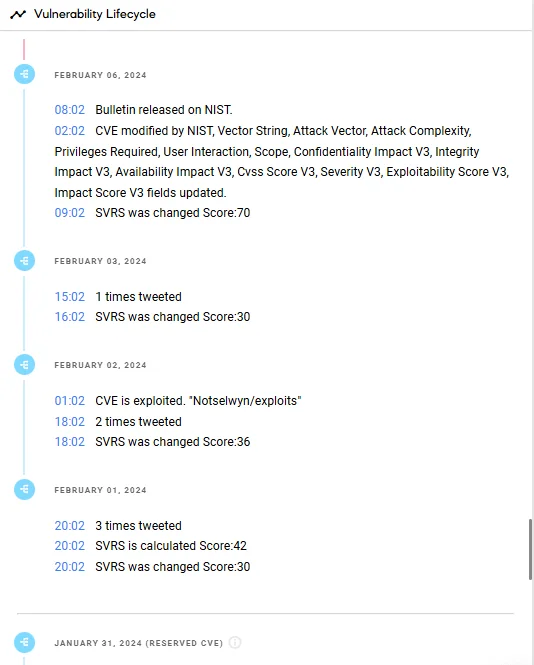
Lifecycle information on CVE-2024-1086 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
CISA Urges Organizations to Patch Check Point and Linux Vulnerabilities, CVE-2024-24919 and CVE-2024-1086
CISA has issued an alert addressing the serious risks associated with these vulnerabilities, CVE-2024-24919 and CVE-2024-1086, which have been confirmed as actively exploited threats, prompting their inclusion in CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog.
These vulnerabilities serve as critical attack vectors that could compromise the integrity and security of federal and non-federal systems alike.
Under the Binding Operational Directive (BOD) 22-01, CISA mandates Federal Civilian Executive Branch (FCEB) agencies to implement necessary patches by the compliance deadline of June 20, 2024.
For those looking to understand how vulnerabilities are evaluated and prioritized for inclusion in the KEV Catalog, our dedicated blog post, “CISA KEV Timeframe Problems While Prioritizing Vulnerabilities,” provides additional insights.
Ensure Security and Compliance with SOCRadar
SOCRadar’s suite of tools, including Vulnerability Intelligence and Attack Surface Management (ASM), provides essential capabilities to stay ahead of potential exploits.
While the Vulnerability Intelligence feature keeps organizations updated on trends and provides extensive insights, the Attack Surface Management (ASM) module ensures continuous monitoring and assessment of their digital assets.
A standout feature of SOCRadar’s ASM is the integrated CISA KEV Check, which cross-references your system’s vulnerabilities against the vulnerabilities listed in the CISA KEV Catalog. This functionality ensures that your systems are not susceptible to any of the CVEs recognized by CISA as known exploited vulnerabilities, thereby aligning with compliance requirements.
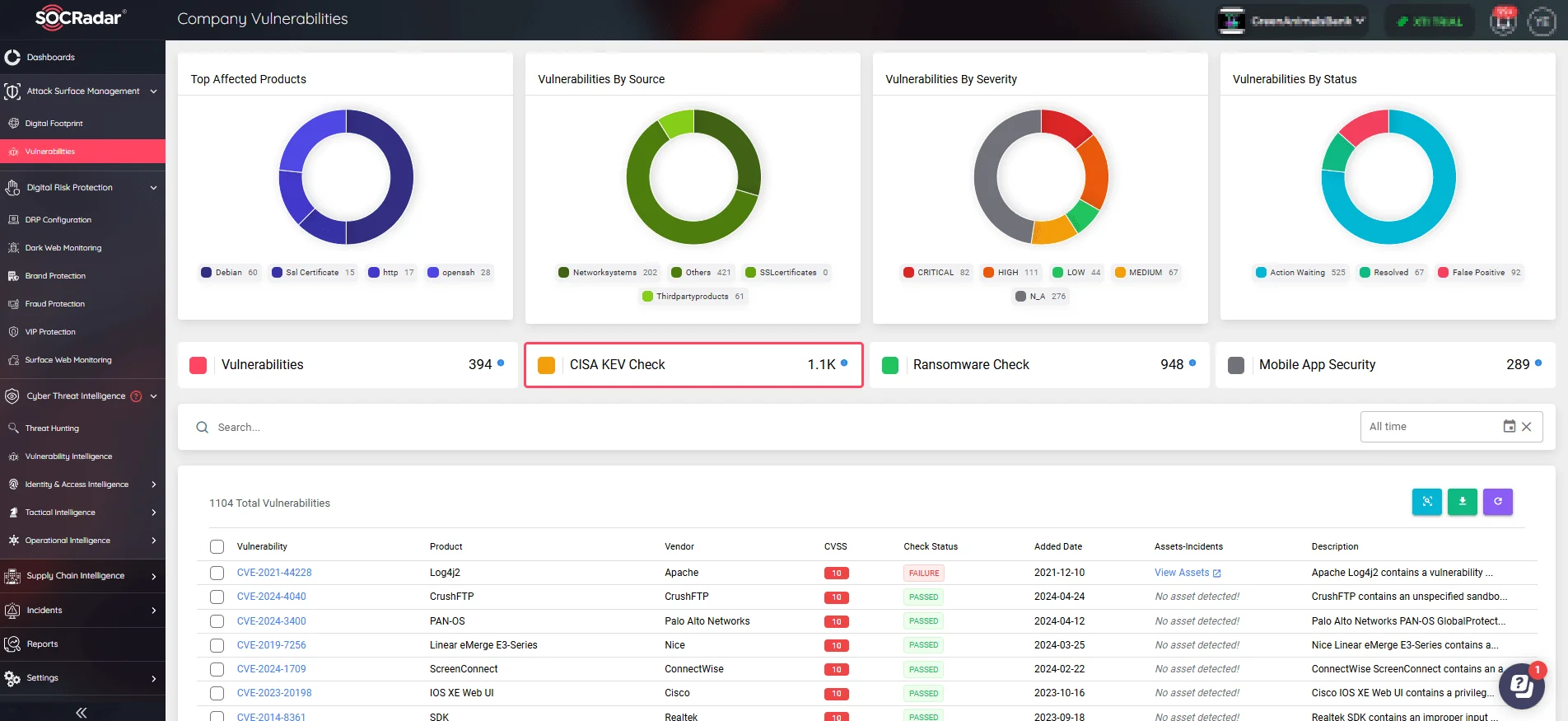
CISA KEV Check feature on SOCRadar’s ASM



































