Critical Security Updates for Cisco Smart Licensing Utility & Veeam Products
[Update] March 21, 2025: “Confirmed Exploitation Activity Surfaces: CVE-2024-20439 and CVE-2024-20440”
[Update] October 17, 2024: CISA adds actively exploited Veeam vulnerability (CVE-2024-40711) to KEV Catalog*
[Update] October 11, 2024: “Veeam Backup RCE Vulnerability (CVE-2024-40711) Exploited in Akira and Fog Ransomware Attacks”
[Update] September 18, 2024: “PoC Exploit Released for CVE-2024-40711 in Veeam Backup & Replication”
Cisco and Veeam have recently issued critical security updates for major products, including Cisco Smart Licensing Utility and Veeam Backup & Replication. These vulnerabilities, bearing high severity, pose serious risks to enterprise systems, potentially enabling unauthorized access and remote code execution.
Cisco Addresses Critical Vulnerabilities in Smart Licensing Utility (CVE-2024-20439 and CVE-2024-20440)
On September 4, 2024, Cisco released advisories detailing six security vulnerabilities, two of which are rated critical and one high severity.
The critical vulnerabilities, identified as CVE-2024-20439 and CVE-2024-20440, stand out for their potential impact on Cisco Smart Licensing Utility, with the possibility of allowing unauthenticated remote attackers to access sensitive information or gain control over licensing services.
While both vulnerabilities are serious, Cisco has clarified that they are independent of one another, meaning that exploiting one does not necessitate the exploitation of the other.
Here’s a breakdown of these critical vulnerabilities:
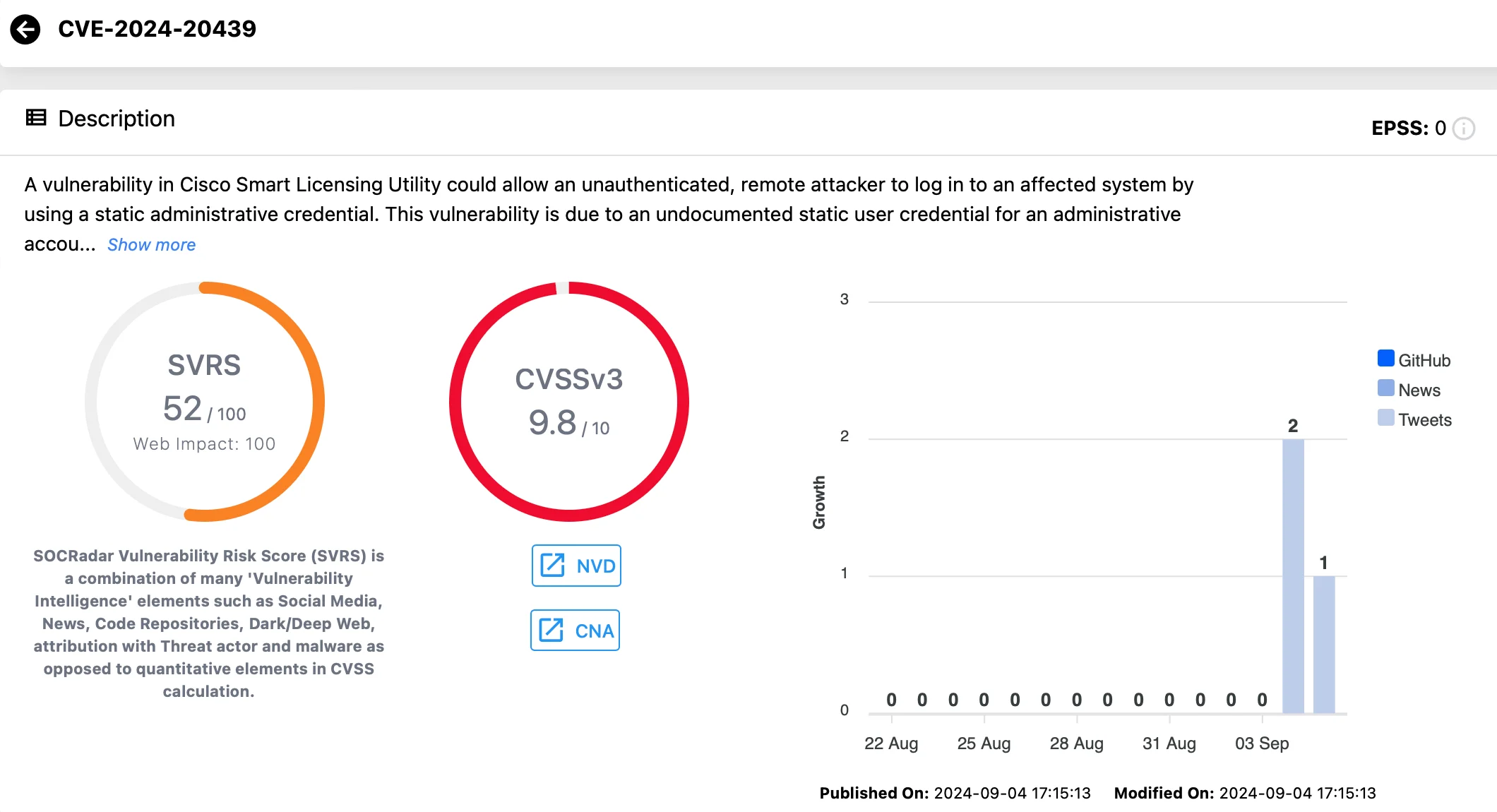
CVE-2024-20439 (CVSS: 9.8):
This vulnerability allows an unauthenticated, remote attacker to gain administrative access to the affected system by using a static credential.
The flaw stems from an undocumented administrative account in the system, giving attackers a direct route to log in and manage Cisco Smart Licensing Utility services through its API.
Vulnerability card for CVE-2024-20439 (Vulnerability Intelligence)
Successful exploitation grants attackers administrative privileges, putting the system’s core services at risk of unauthorized control.
On March 31, 2025, CISA included the Cisco Smart Licensing Utility vulnerability (CVE-2024-20439) in its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog. Federal organizations have until April 21, 2025, to patch this flaw, which enables unauthenticated attackers to access systems remotely using static credentials, potentially gaining full administrative control. Prompt action is recommended to mitigate active exploitation risks.
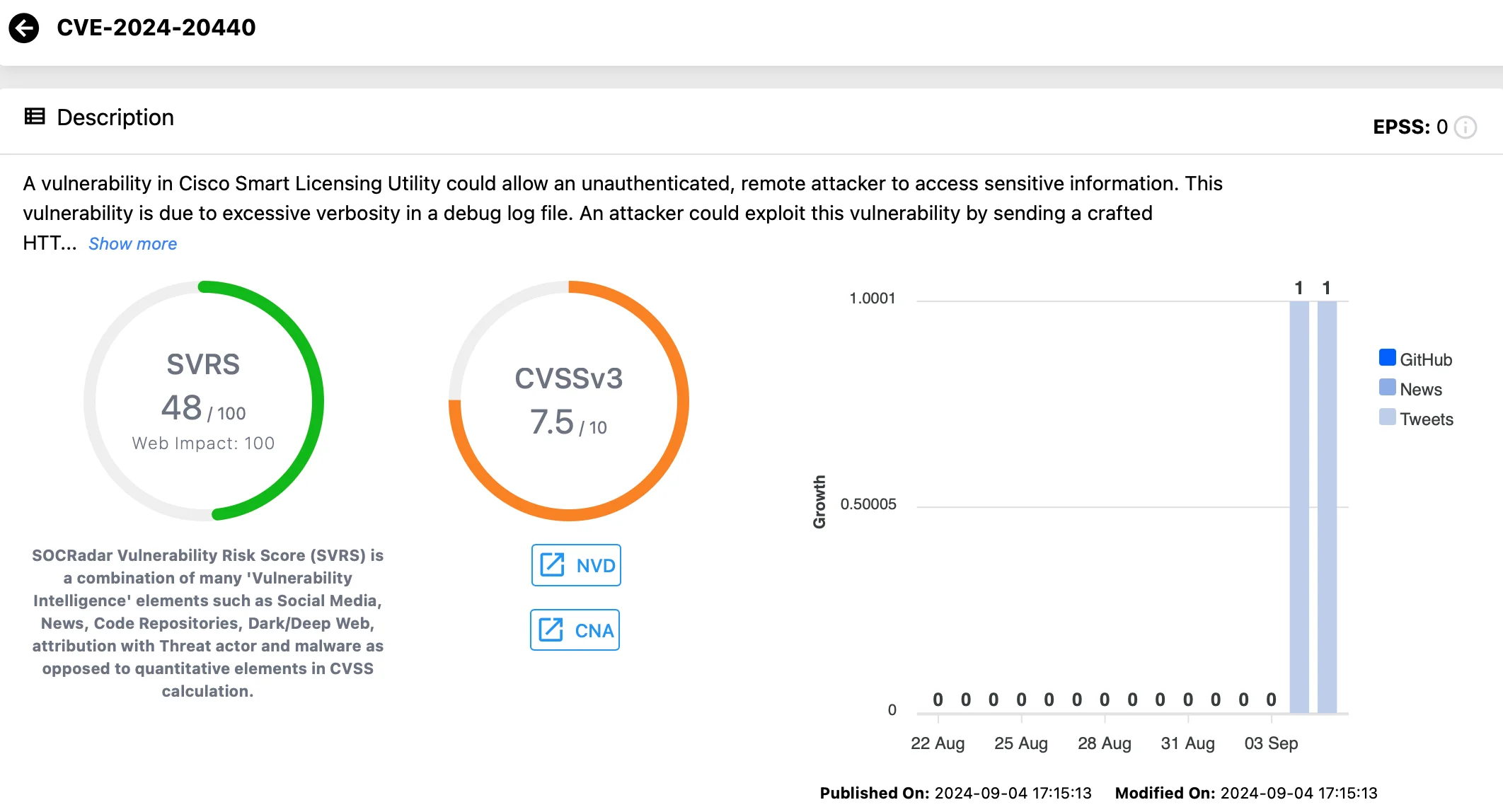
CVE-2024-20440 (CVSS: 9.8):
The second critical flaw is an information disclosure vulnerability caused by overly verbose logging in a debug log file. Attackers could exploit this by sending a specially crafted HTTP request, retrieving sensitive log files containing credentials that can be used to further access the API and the system.
According to the Cisco advisory, the vulnerability has a CVSS base score of 9.8, although NVD lists it as 7.5 at the time of writing.
Vulnerability card for CVE-2024-20440 (Vulnerability Intelligence)
Both vulnerabilities pose serious risks to organizations using affected versions of Cisco Smart Licensing Utility, underlining the importance of implementing security patches immediately.
Which Versions of Cisco Smart Licensing Utility Are Affected?
The identified vulnerabilities affect Cisco Smart Licensing Utility (SLU) versions 2.0.0, 2.1.0, and 2.2.0.
Moreover, the flaws only pose a risk when Cisco SLU is active on the system, as stated in Cisco’s official advisory, and systems running version 2.3.0 are unaffected.
Since there are no available workarounds, Cisco strongly advises organizations using older versions to promptly upgrade to the fixed release.
For more details, you can visit Cisco’s official security advisory here.
Confirmed Exploitation Activity Surfaces: CVE-2024-20439 and CVE-2024-20440
As of March 2025, security analysts have confirmed that the vulnerabilities CVE-2024-20439 and CVE-2024-20440 are being actively targeted by threat actors in the wild. Researchers from the SANS Technology Institute report a noticeable uptick in exploitation attempts against exposed Cisco Smart Licensing Utility (CSLU) instances, particularly those still running vulnerable software versions. Attackers are leveraging the hardcoded credential to gain initial access, then exploiting the log file vulnerability to harvest sensitive data – forming a potent exploitation chain.
This development follows the public disclosure of technical details and even the decoded static password shortly after Cisco’s advisory went live in September 2024. While Cisco’s PSIRT has not confirmed any successful breaches linked directly to these flaws, the increased activity emphasizes the urgency for organizations to patch without delay. Threat actors appear to be opportunistically scanning for CSLU instances, especially those exposed to the internet, making timely upgrades more critical than ever.
High-Severity Vulnerability in Cisco Meraki Systems Manager Agent (CVE-2024-20430)
Cisco has also addressed a high-severity vulnerability (CVE-2024-20430, CVSS: 7.3) in the Cisco Meraki Systems Manager (SM) Agent for Windows. While not as critical as the previously mentioned vulnerabilities, it poses a serious risk as it could allow attackers to escalate privileges on affected systems.
The vulnerability is caused by the improper handling of directory search paths during runtime, and could allow an authenticated, low-privileged attacker to install malicious configuration and DLL files on the system.
Once the Cisco Meraki SM Agent is launched, the malicious files will be read and executed, allowing the attacker to run arbitrary code with SYSTEM-level access.
Cisco notes that this vulnerability does not affect Cisco Meraki SM Agent for Mac. For more information, visit the official advisory.
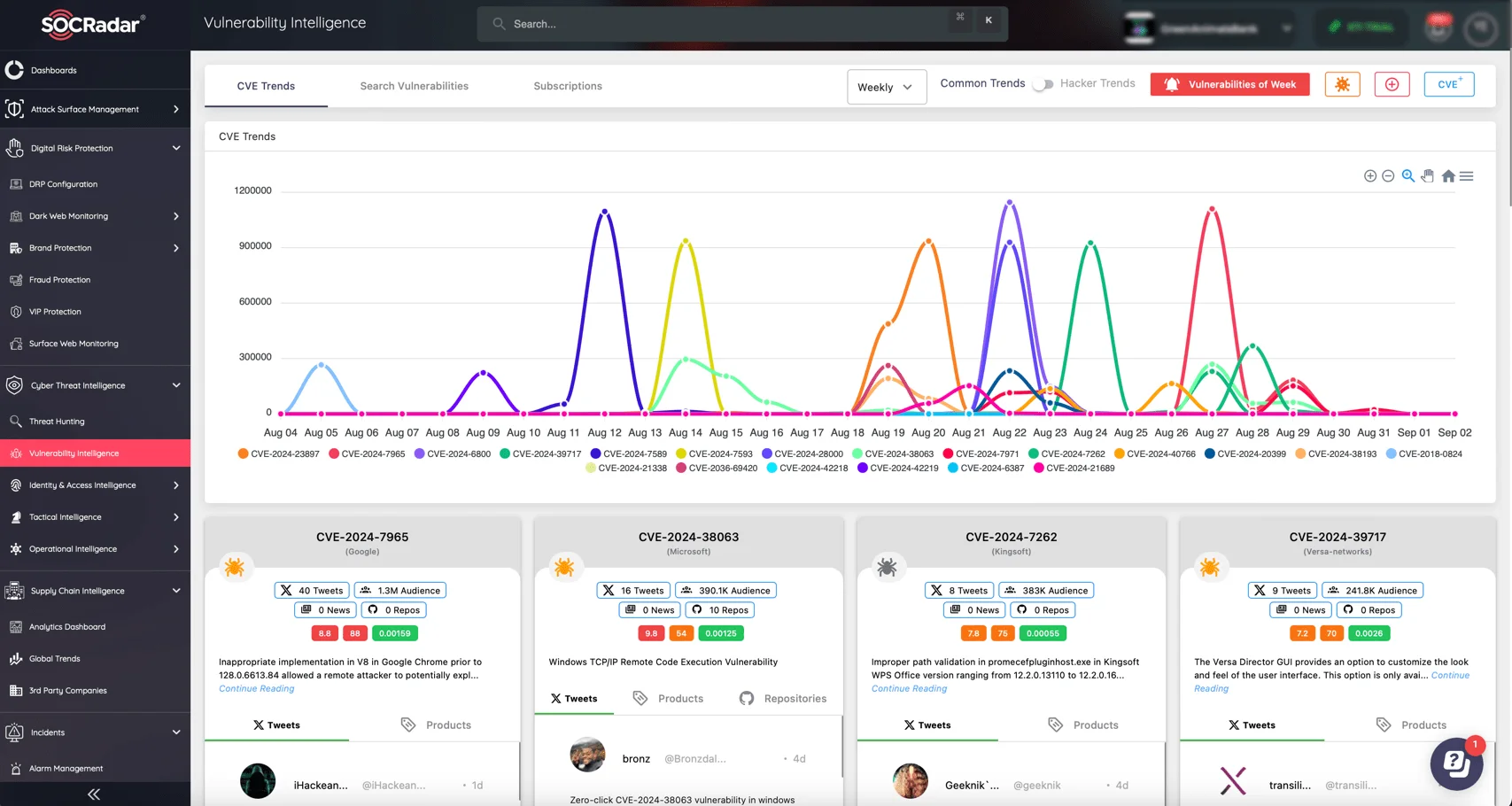
Stay informed on the latest vulnerabilities with SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence module, which allows you to monitor CVEs, understand exploitation trends, and act swiftly to protect your systems from emerging threats.
SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence
Critical Vulnerabilities Addressed in Veeam’s September 2024 Security Bulletin
Veeam, a leading provider of backup and cloud solutions, has released its September 2024 Security Bulletin, addressing several critical vulnerabilities across its product line.
This month’s critical security patches were delivered to Veeam Backup & Replication, Veeam Agent for Linux, Veeam ONE, Veeam Service Provider Console, Veeam Backup for Nutanix AHV, and Oracle Linux Virtualization Manager.
Critical RCE in Veeam Backup & Replication: CVE-2024-40711
One of the most critical vulnerabilities is CVE-2024-40711, an unauthenticated Remote Code Execution (RCE) flaw in Veeam Backup & Replication, carrying a CVSS score of 9.8. The vulnerability affects Veeam Backup & Replication 12.1.2.172 and all previous version 12 builds.
Unpatched versions of the Veeam Backup & Replication software are also affected by several other high-risk vulnerabilities, including MFA bypass and credential interception issues, making it vital for organizations to update their systems immediately.
*On October 17, 2024, CISA added the Veeam Backup and Replication vulnerability, CVE-2024-40711, to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog. This deserialization vulnerability has been actively exploited, and CISA has set a compliance deadline of November 7, 2024, for federal agencies to patch this issue.
Other critical vulnerabilities in Veeam’s September 2024 updates are outlined below.
Veeam Service Provider Console
Versions Affected: 8.1.0.21377 and all earlier version 8 builds
- CVE-2024-38650 (CVSS: 9.9): This critical vulnerability allows low-privileged attackers to access the NTLM hash of the service account on the VSPC server.
- CVE-2024-39714 (CVSS: 9.9): A vulnerability that permits arbitrary file uploads on VSPC servers, leading to Remote Code Execution (RCE).
Veeam ONE
Versions Affected: 12.1.0.3208 and all earlier version 12 builds
- CVE-2024-42024 (CVSS: 9.1): This vulnerability enables Remote Code Execution (RCE) for attackers in possession of Veeam ONE Agent service account credentials.
- CVE-2024-42019 (CVSS: 9.0): A flaw allowing attackers to access the NTLM hash of the Veeam Reporter Service service account, requiring user interaction and data collected from Veeam Backup & Replication.
How to Address Veeam Vulnerabilities
These vulnerabilities present a serious threat to the security of critical data. Organizations utilizing Veeam products should take immediate action by updating to the following secure builds:
- Veeam Backup & Replication: Version 12.2 build 12.2.0.334
- Veeam ONE: Version 12.2 build 12.2.0.4093
- Veeam Service Provider Console: Version 8.1 build 8.1.0.21377
For a full list of vulnerabilities and further updates, refer to Veeam’s September 2024 Security Bulletin here.
PoC Exploit Released for CVE-2024-40711 in Veeam Backup & Replication
A Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit for CVE-2024-40711 has been publicly released.
The critical vulnerability stems from a deserialization flaw in the Veeam Backup & Replication software, allowing attackers to bypass security controls and execute remote code on the server. Specifically, the flaw enables malicious actors to exploit the ObjRef class, which bypasses Veeam’s whitelist and blacklist functionalities.
With the PoC now publicly available on GitHub, organizations using Veeam Backup & Replication must urgently update their software to prevent potential exploitation.
For more details on the vulnerability, read the analysis here.
Veeam Backup RCE Vulnerability (CVE-2024-40711) Exploited in Akira and Fog Ransomware Attacks
The critical RCE vulnerability in Veeam Backup & Replication servers, CVE-2024-40711, has been actively exploited in recent ransomware attacks, according to findings of Sophos X-Ops.
Researchers reported incidents involving the Akira and Fog ransomware families, where attackers used previously compromised credentials to create a local account, “point,” granting it administrative privileges and access to Remote Desktop Users.
Attackers initially breached targets through compromised VPN gateways without Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), with some VPNs running outdated software. They exploited Veeam’s /trigger URI on port 8000, leveraging Veeam.Backup.MountService[.]exe to execute the attack.
In one case, Fog ransomware was deployed on an unprotected Hyper-V server, followed by data exfiltration using the rclone tool.
Organizations using Veeam Backup & Replication should immediately apply security patches to mitigate this vulnerability and prevent potential ransomware exploitation. Ensuring VPNs are up-to-date and MFA is enabled is also important in strengthening defenses.
Ensure rapid response to newly discovered vulnerabilities with SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) module.
Use SOCRadar’s ASM module to monitor digital assets and identify company vulnerabilities
ASM helps safeguard your digital assets by delivering real-time threat alerts, enabling you to take preemptive action and strengthen your cybersecurity defenses.