
Apache Tomcat RCE Vulnerability (CVE-2025-24813) Under Active Exploitation: Patch Now
A serious vulnerability in Apache Tomcat, CVE-2025-24813, is being actively exploited in the wild. This flaw allows attackers to take advantage of Tomcat’s request-handling mechanism, potentially leading to full server compromise.
With real-world attacks already observed, organizations using affected Tomcat versions must act immediately to mitigate the risk. In this blog, we break down how the vulnerability works, its real-world impact, and what steps you should take to secure your systems.
What is CVE-2025-24813? How the Exploit Works
At its core, CVE-2025-24813 (CVSS 5.5) is an unauthenticated Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability that abuses Tomcat’s handling of PUT and GET requests.
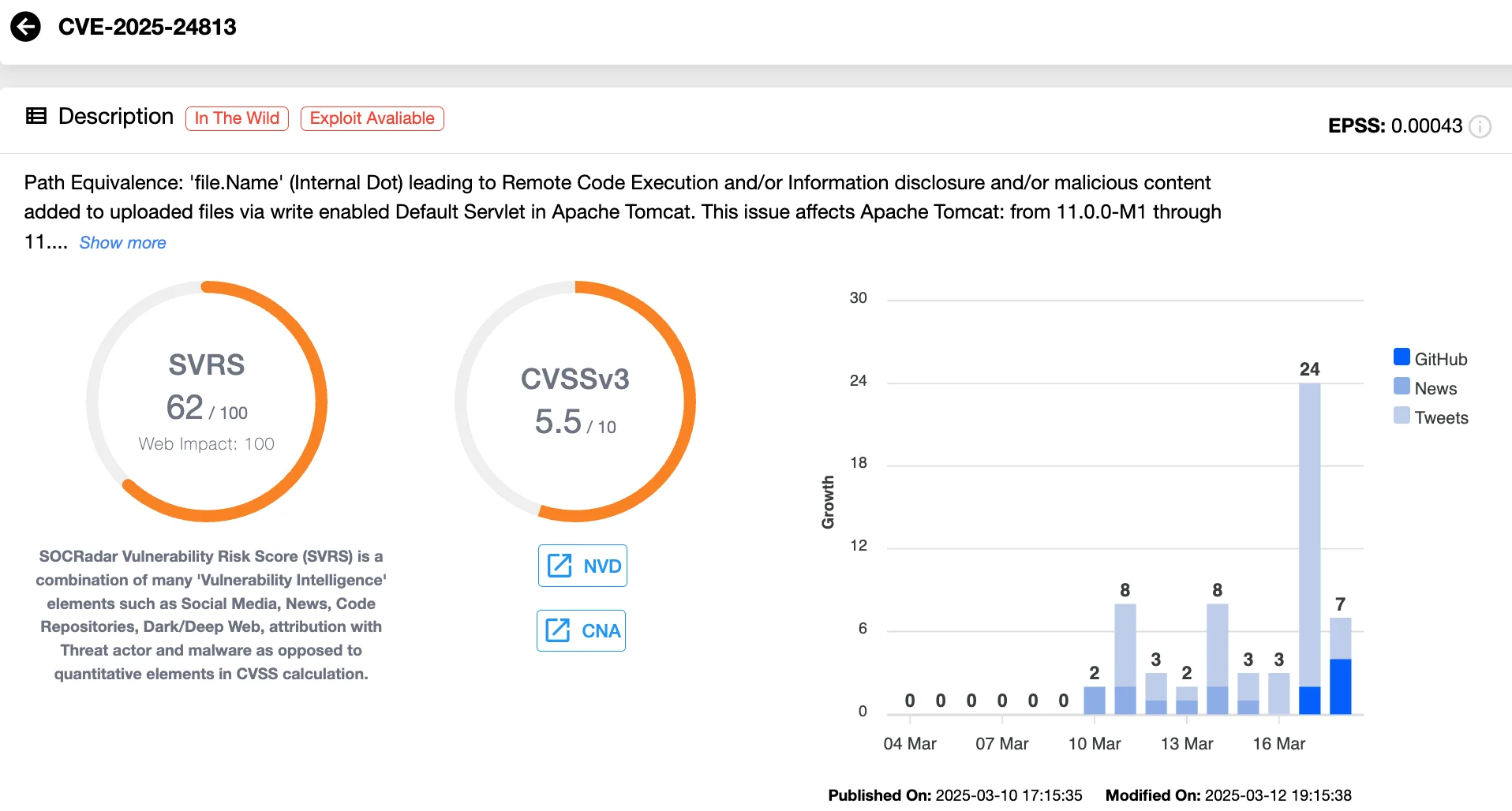
Vulnerability card of CVE-2025-24813 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
The attack follows a two-step process, according to Wallarm researchers:
- Uploading a malicious session file – The attacker sends a PUT request containing a base64-encoded serialized Java payload, which is stored in Tomcat’s session storage.
- Triggering execution – A GET request is sent with a JSESSIONID cookie referencing the uploaded session file. This forces Tomcat to deserialize and execute the malicious Java code, granting the attacker full control over the server.
Wallarm further noted that most Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) struggle to identify CVE-2025-24813 exploitation. There are several reasons for this:
- Legitimate-looking PUT requests – Since PUT requests are commonly used for file uploads, security solutions often fail to flag them.
- Obfuscated payloads – The exploit uses base64 encoding, making it harder to detect malicious intent.
- Multi-step execution – The harmful code is not executed in the initial request, making traditional pattern-based detection ineffective.
Because partial PUT support is enabled by default in Tomcat, and file-based session storage is common in deployments, many servers remain vulnerable unless specifically hardened.
Identify and secure your digital assets with SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM). ASM continuously monitors your external-facing assets, detects vulnerabilities, and also highlights shadow IT risks and third-party exposures, helping your organization minimize attack vectors and proactively reduce your digital risk profile.
- Continuous discovery of exposed assets
- Real-time vulnerability identification
- Visibility into third-party risks and shadow IT
SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management Module (ASM) module
Real-World Exploitation Details
The first known attack leveraging CVE-2025-24813 was detected on March 12 in Poland, even before the first public Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit was available. Shortly after disclosure, PoC exploits surfaced on GitHub, making it easier for attackers to weaponize the vulnerability.
Red Hat has rated this vulnerability 8.6, categorizing it to be high severity. The exploit’s simplicity and effectiveness make it a serious concern, as attackers can use it to:
- Deploy malicious JSP files for persistent access.
- Modify Tomcat configurations to escalate privileges.
- Plant backdoors outside session storage for long-term control.
Researchers warn that this may be just the first wave of attacks, with future exploits likely focusing on uploading rogue JSP files, altering configurations, and establishing persistent access beyond session storage.
Affected Versions & Security Patches for Apache Tomcat
CVE-2025-24813 affects multiple versions of Apache Tomcat:
- 11.0.0-M1 to 11.0.2
- 10.1.0-M1 to 10.1.34
- 9.0.0.M1 to 9.0.98
To address this vulnerability, Apache advises that users upgrade to one of the following versions as soon as possible:
- 11.0.3 or later
- 10.1.35 or later
- 9.0.99 or later
Organizations using affected versions must upgrade immediately to protect their systems from potential compromise.
For more information, refer to Apache’s security note.
Another Emerging Threat: Apache Camel Vulnerability (CVE-2025-29891)
Alongside CVE-2025-24813, a PoC exploit has also surfaced for CVE-2025-29891 (CVSS 4.2), a vulnerability in Apache Camel that allows malicious header injection in HTTP requests. Attackers could manipulate application behavior by exploiting Camel’s default header filtering.
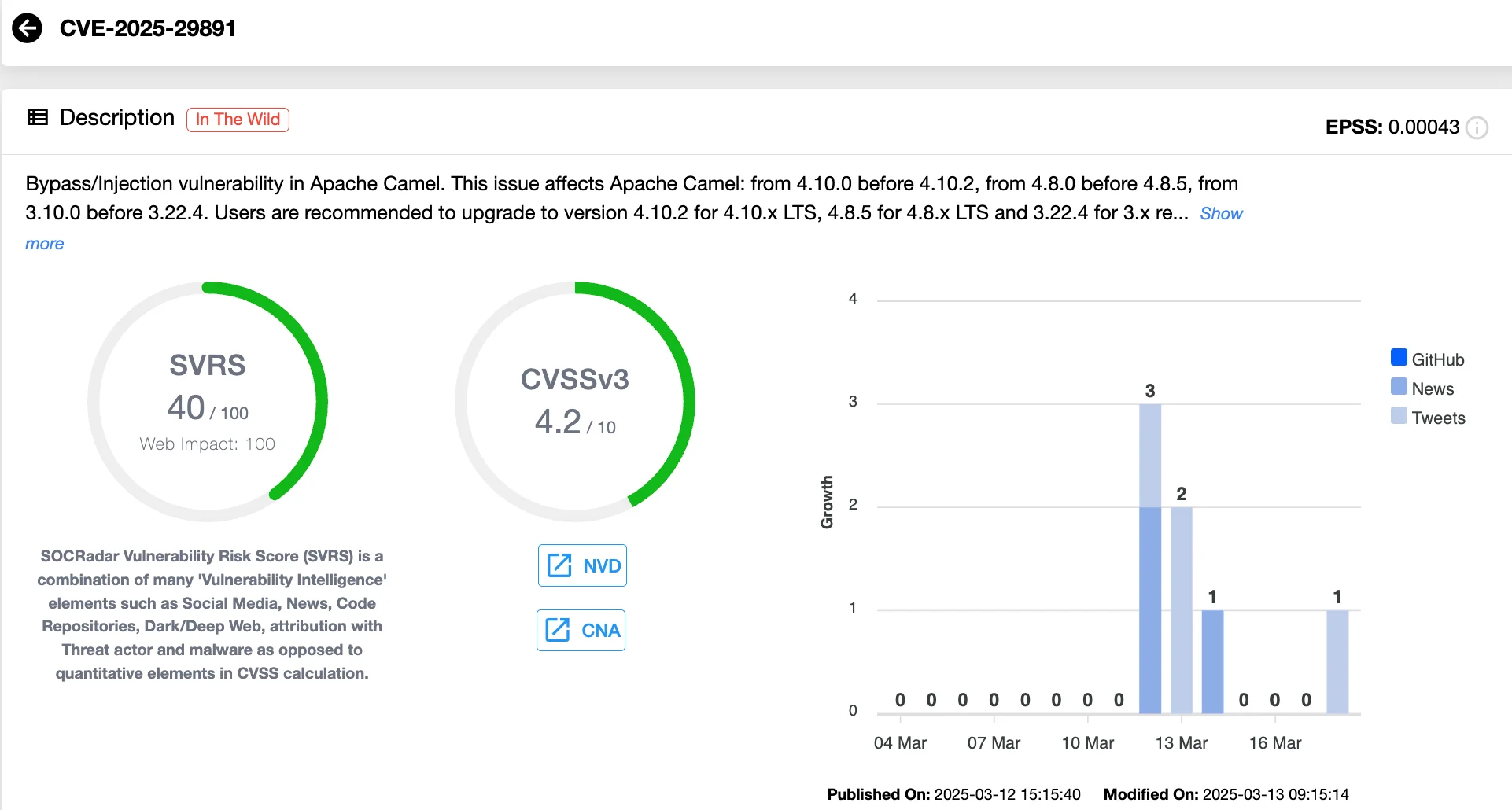
Vulnerability card of CVE-2025-29891 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
The flaw affects multiple versions of Camel’s HTTP components, including camel-servlet, camel-jetty, and camel-netty-http. Apache has patched the issue in Camel 3.22.4, 4.8.5, and 4.10.2, urging users to upgrade immediately.
For additional information, see researchers’ PoC on GitHub, which includes technical details, and the official Apache advisory.
SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence: Newest CVEs and hacker trends
To quickly identify vulnerabilities before attackers do, your organization needs continuous, real-time visibility into emerging threats.
SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence, part of the Cyber Threat Intelligence module, equips your security team to proactively identify critical threats. Track vulnerabilities, monitor real-time exploit activities, and prioritize remediation based on actual threat risks – not just severity scores. Move quickly from vulnerability discovery to mitigation, reducing potential impacts before attackers can exploit them.



































