
Atlassian and Ivanti Address Critical Vulnerabilities in May Updates: CVE-2024-21683, CVE-2023-4759, CVE-2024-29822, and More
[Update] October 3, 2024: “CISA Added Ivanti EPM Vulnerability (CVE-2024-29824) to KEV Catalog”
[Update] May 24, 2024: “PoC Exploit for Confluence RCE Vulnerability (CVE-2024-21683) Circulates Hacker Channels”
In their latest security updates, Atlassian and Ivanti have addressed numerous vulnerabilities.
Atlassian’s update fixes 35 high-severity vulnerabilities and 2 critical-severity vulnerabilities across its Bamboo, Confluence, and Jira Data Center and Server products, including dangerous Remote Code Execution (RCE) and SQL injection flaws.
Simultaneously, Ivanti’s May 2024 security update patches several critical and high-severity vulnerabilities in Ivanti EPM (Endpoint Manager), which are primarily associated with risks of code execution.
Given their role in management, collaboration, and continuous delivery, Atlassian and Ivanti products are widely used by businesses. Unaddressed, these vulnerabilities could disrupt workflows and lead to substantial data breaches, inflicting severe financial and reputational damage on organizations.
Critical SQL Injection and RCE Vulnerabilities in Atlassian’s Jira and Confluence Data Center and Server
In its latest security bulletin for May 2024, Atlassian has announced the remediation of many vulnerabilities, including a critical SQL injection vulnerability and severe Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerabilities.
The critical SQL injection flaw, identified as CVE-2024-1597, originates from an external dependency used in Jira and Confluence. The vulnerability resides in the PostgreSQL JDBC driver, which has been previously discussed in one of our blog posts.
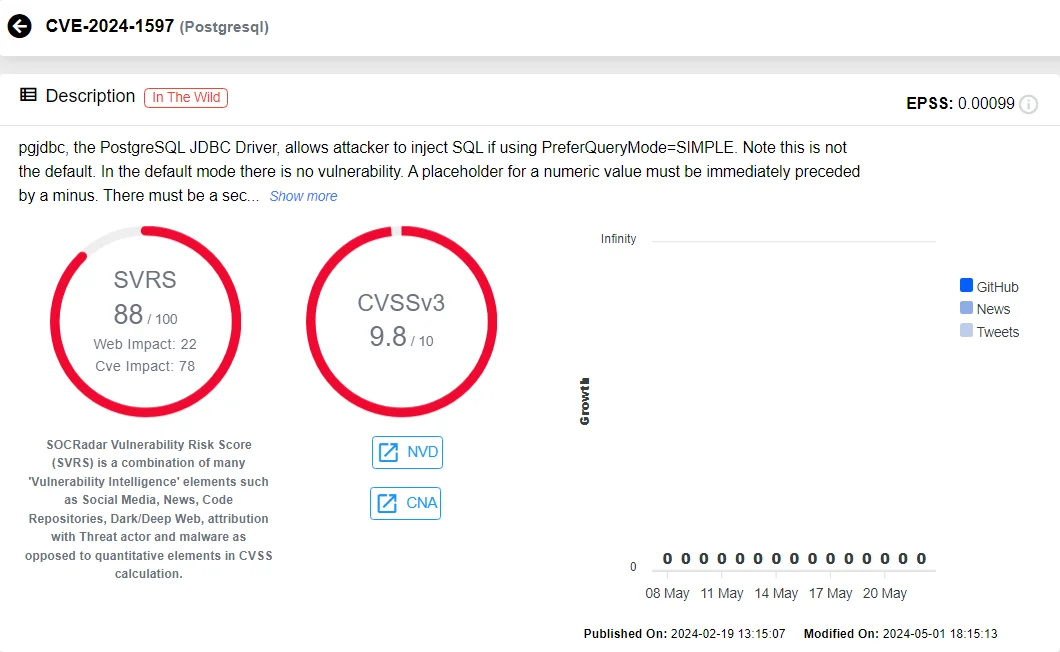
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-1597 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Despite the severity of the underlying issue in the PostgreSQL JDBC driver, Atlassian has assessed the risk to its applications as comparatively lower.
The CVE-2024-1597 vulnerability, with a critical severity rating of 9.8 on the CVSS scale, impacts several versions of both Jira Data Center and Server, as well as Confluence Data Center and Server.
New RCEs in Atlassian Confluence and Bamboo: CVE-2024-21683 and CVE-2023-4759
A high-severity Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability, identified as CVE-2024-21683 (CVSS: 8.3), has been discovered in multiple versions of Confluence Data Center and Server. Its exploitation allows an authenticated attacker to execute arbitrary code with no user interaction required.
First appearing in version 5.2, this vulnerability poses a significant risk to confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
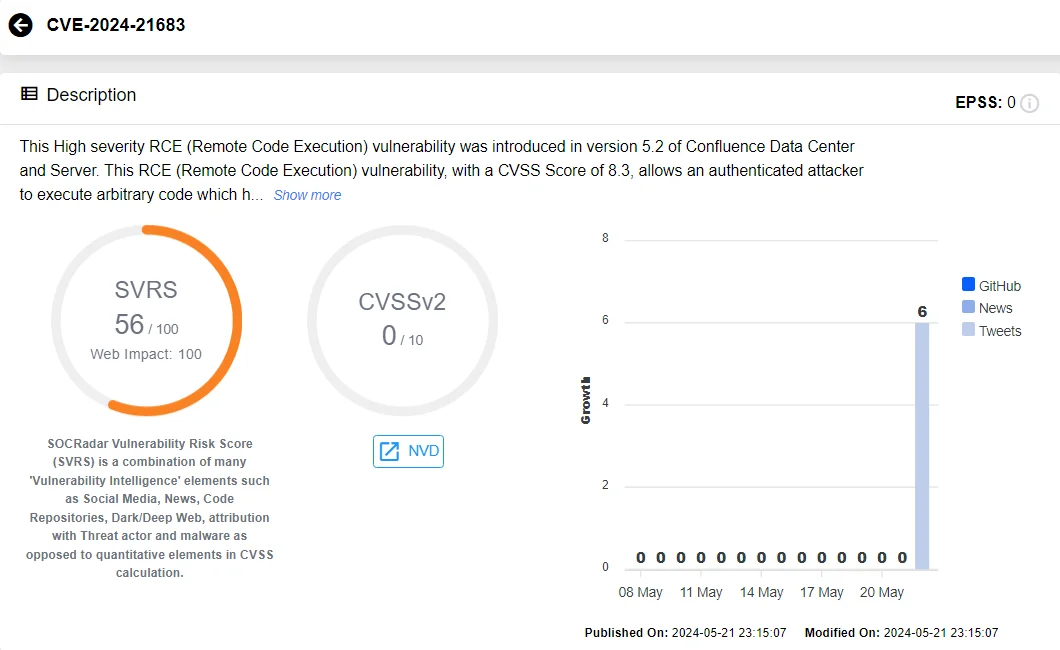
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-21683 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Additionally, Bamboo Data Center and Server is impacted by another RCE flaw, tracked as CVE-2023-4759 with a CVSS score of 8.8. It is described as an Arbitrary File Overwrite issue in Eclipse JGit versions up to and including 6.6.0.
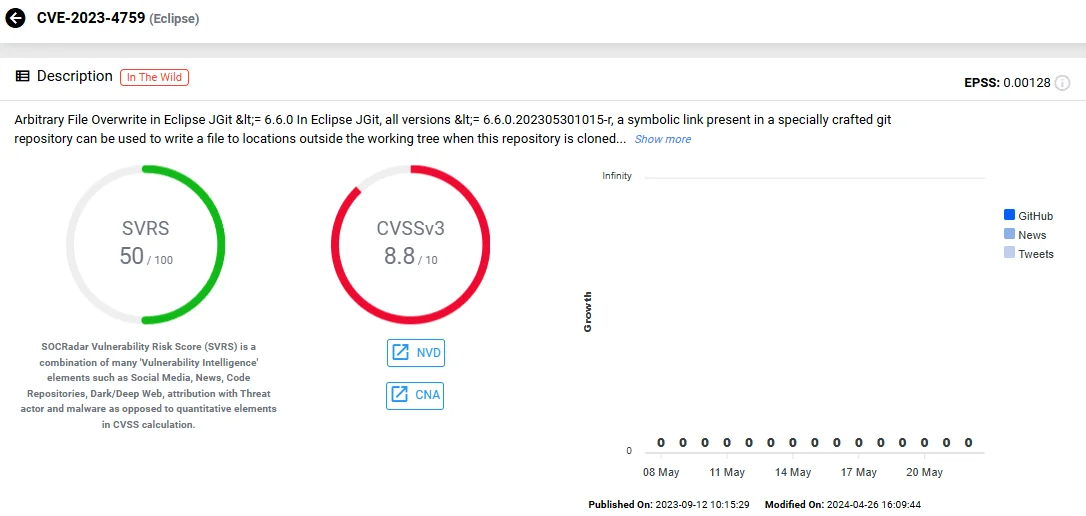
Vulnerability card of CVE-2023-4759 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
PoC Exploit for Confluence RCE Vulnerability (CVE-2024-21683) Circulates Hacker Channels
A Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit for the recent CVE-2024-21683 vulnerability affecting Atlassian Confluence is already available on GitHub.
More concerning is that threat actors have started discussing the exploit on hacker channels without delay. SOCRadar observed that the exploit has been shared on a Telegram hacker channel with nearly 24,000 members.
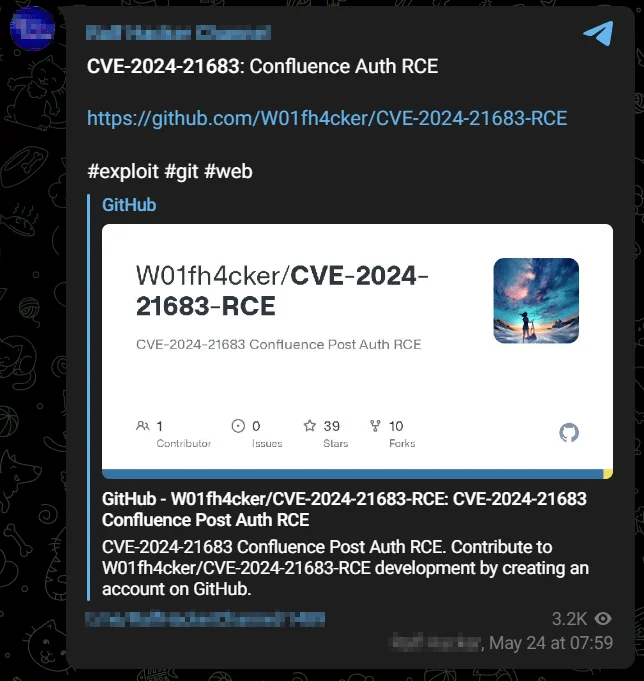
An exploit post for the Confluence RCE (CVE-2024-21683)
was discovered on a Telegram hacker channel.
It is well known that once technical details or a PoC exploit for a vulnerability is made public, potential threat actors begin their act. They may soon weaponize the exploit in real-world attacks, targeting organizations that have yet to implement the necessary patches or mitigations.
Which Atlassian Products and Versions Are Affected?
The critical SQL injection (CVE-2024-1597) could allow database takeovers, whereas the RCEs (CVE-2024-21683 and CVE-2023-4759) could allow authenticated attackers to gain control of affected systems, potentially resulting in data breaches and operational disruptions. As a result, it is critical that organizations using Atlassian Confluence, Bamboo, and Jira Data Center and Server products review the security advisory and apply the necessary security updates. The following are the affected versions of these products.
Confluence Data Center and Server:
- 8.9.0
- 8.8.0 to 8.8.1
- 8.7.1 to 8.7.2
- 8.6.0 to 8.6.2
- 8.5.0 to 8.5.8 (LTS)
- 8.4.0 to 8.4.5
- 8.3.0 to 8.3.4
- 8.2.0 to 8.2.3
- 8.1.0 to 8.1.4
- 8.0.0 to 8.0.4
- 7.20.0 to 7.20.3
- 7.19.0 to 7.19.21 (LTS)
Jira Data Center and Server:
- 9.14.0 to 9.14.1
- 9.13.0 to 9.13.1
- 9.12.0 to 9.12.6 (LTS)
- 9.11.0 to 9.11.3
- 9.10.0 to 9.10.2
- 9.9.0 to 9.9.2
- 9.8.0 to 9.8.2
- 9.7.0 to 9.7.2
- 9.6.0
- 9.5.0 to 9.5.1
- 9.4.0 to 9.4.19 (LTS)
- 9.3.0 to 9.3.3
- 9.2.0 to 9.2.1
- 9.1.0 to 9.1.1
- 9.0.0
Bamboo Data Center and Server:
- 9.5.0 to 9.5.1
- 9.4.0 to 9.4.4
- 9.3.0 to 9.3.6
- 9.2.1 to 9.2.13 (LTS)
- 9.1.0 to 9.1.3
- 9.0.0 to 9.0.4
Refer to Atlassian’s official security bulletin for more information.
Ivanti’s May 2024 Security Update Fixes 6 Critical SQL Injection Flaws Leading to Code Execution
Ivanti has addressed six critical vulnerabilities within its Ivanti EPM (Endpoint Manager) product, which could potentially allow unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary code on network endpoints.
These vulnerabilities, with CVSS scores of 9.6, are identified as CVE-2024-29822, CVE-2024-29823, CVE-2024-29824, CVE-2024-29825, CVE-2024-29826, and CVE-2024-29827.
They allow attackers within the same network to manipulate database queries and execute unauthorized commands, leading to potential Remote Code Execution (RCE) and full system control. These vulnerabilities stem from an unspecified SQL Injection flaw in the Core server of Ivanti EPM for versions up to 2022 Service Update 5 (SU5).
CISA Added Ivanti EPM Vulnerability (CVE-2024-29824) to KEV Catalog
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has updated its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog to include one of the critical Ivanti EPM vulnerabilities, CVE-2024-29824.
The CVE-2024-29824 vulnerability, rated a critical 9.6 on the CVSS scale, highlights a severe SQL injection vulnerability found in the Core Server of Ivanti EPM, versions 2022 SU5 and earlier. This flaw could permit an unauthenticated attacker, if they’re on the same network, to execute arbitrary code. This underscores a significant security risk, necessitating immediate attention and remediation.
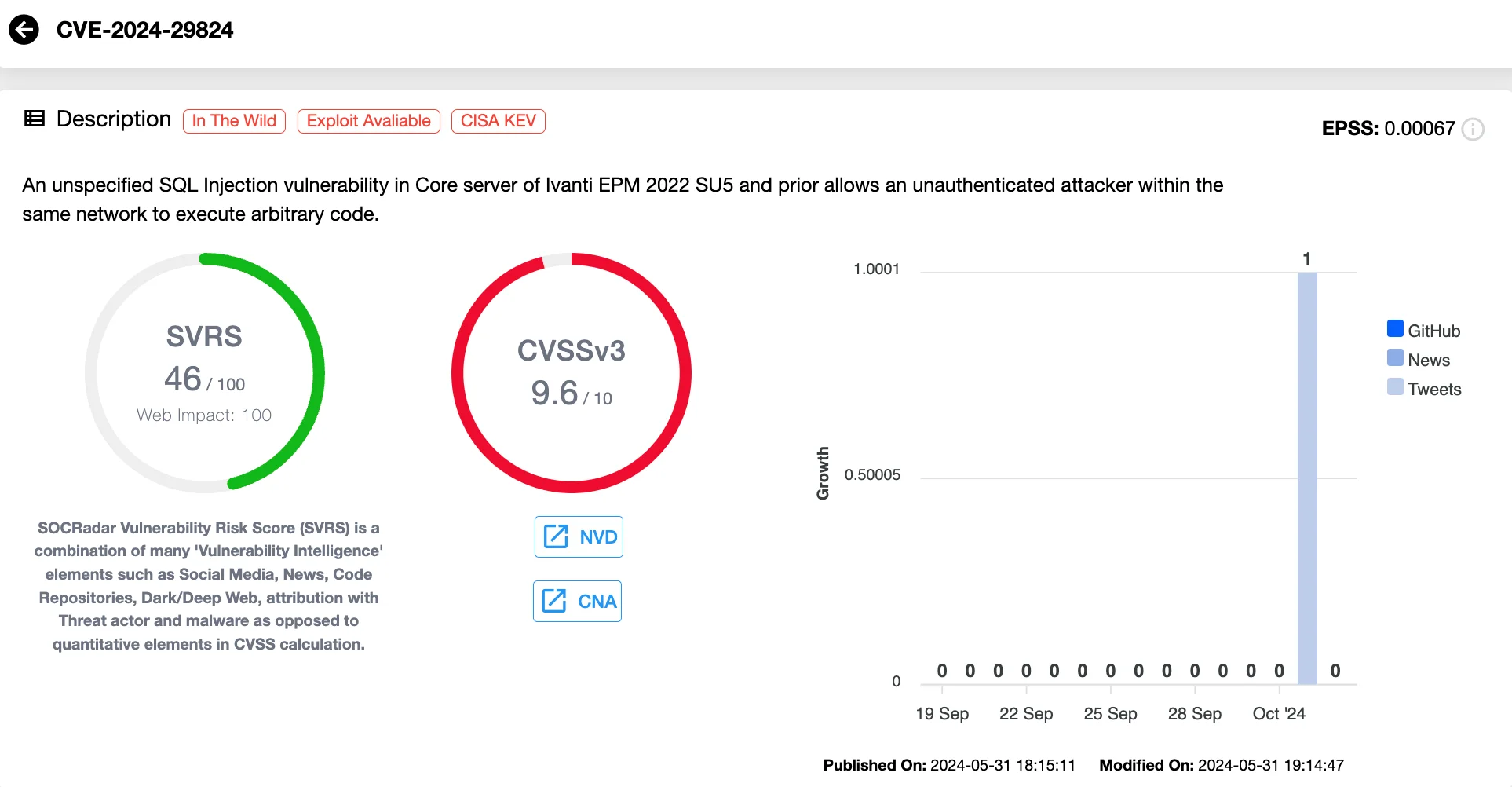
Details of CVE-2024-29824 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Horizon3 previously disclosed the technical details of the Ivanti EPM vulnerability and released a Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit in June. Evidence of exploitation can be seen in SQL logs that record the xp_cmdshell command, commonly used by attackers to execute system-level commands.
CISA urges federal agencies to patch this vulnerability promptly, setting a compliance deadline of October 23, 2024. For more information on this vulnerability and access to the PoC, visit the research here.
High-Severity Vulnerabilities in Ivanti EPM, Neurons for ITSM, and Connect Secure
A number of less serious vulnerabilities were also addressed in Ivanti EPM. These flaws, identified as CVE-2024-29828, CVE-2024-29829, CVE-2024-29830, and CVE-2024-29846, with CVSS scores of 8.4, are SQL injection issues that require authentication to exploit.
Additional high-severity vulnerabilities were also discovered and fixed in Ivanti Neurons for ITSM and Ivanti Connect Secure, which could lead to SQL injection, unrestricted file upload, and CRLF injection. The SQL injection vulnerability in Neurons for ITSM could cause Denial-of-Service (DoS), while Ivanti Connect Secure’s CRLF injection flaw could allow Cross-site Scripting (XSS) attacks.
How Can Organizations Address the Latest Ivanti Vulnerabilities?
Although there have been no reports of active exploitation, the severity and potential impact of these vulnerabilities necessitate urgent action.
Ivanti strongly recommends that all organizations using Ivanti EPM 2022 prior to Service Update 5 (SU5) and other impacted products update to the latest patched versions immediately to mitigate these risks.
For details on the vulnerabilities, refer to Ivanti’s official security advisory.
How Can SOCRadar Help Organizations Address These Vulnerabilities?
Use SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) and Vulnerability Intelligence to stay up to date on the latest security vulnerabilities and improve the protection of your products and software.
SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence feature provides real-time monitoring of CVE and exploitation trends.
With access to a large database and advanced analytics, you can monitor updates, detect exploits, and gain actionable information. This proactive approach to vulnerability management keeps you ahead of potential security threats.
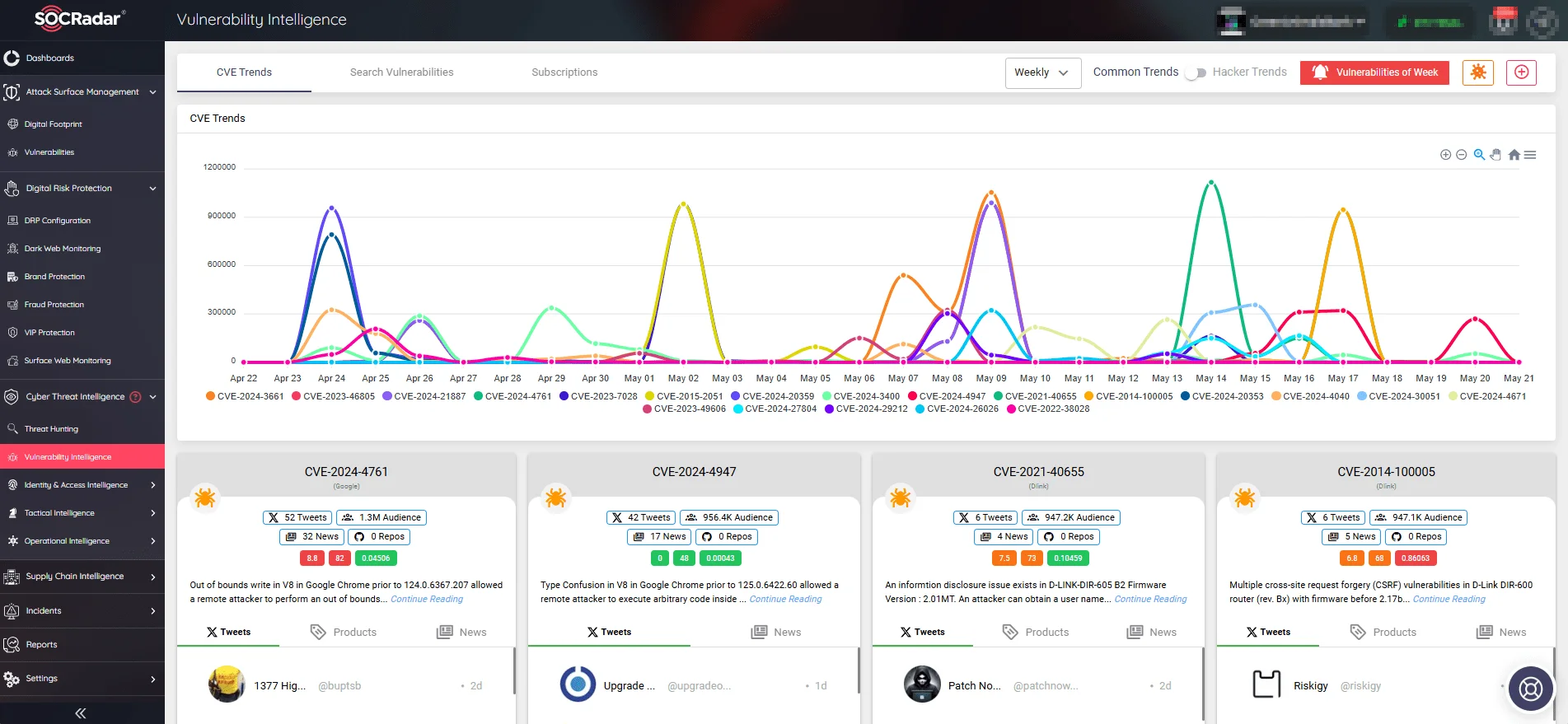
CVE trends, mentions, and exploit events (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Additionally, the platform’s customization options allow you to tailor your vulnerability search using various filters such as vendor, product, and SVRS score. This targeted search capability allows you to identify and prioritize the most critical vulnerabilities specific to your products, resulting in more effective and focused cybersecurity measures.
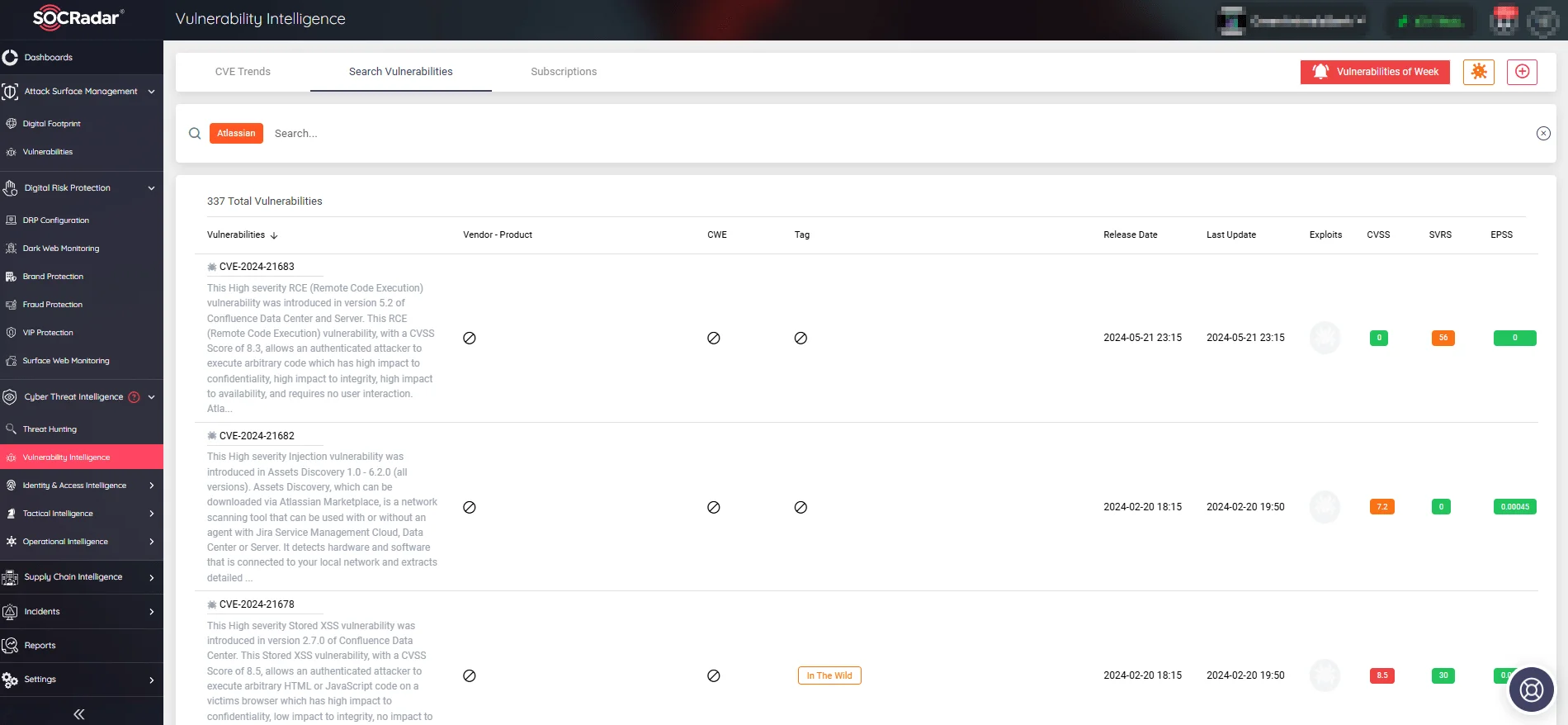
Atlassian security vulnerabilities shown on SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence search tab
Utilizing Attack Surface Management (ASM) in conjunction with Vulnerability Intelligence will help you stay notified of security issues affecting your digital assets and properly protect your software and products.
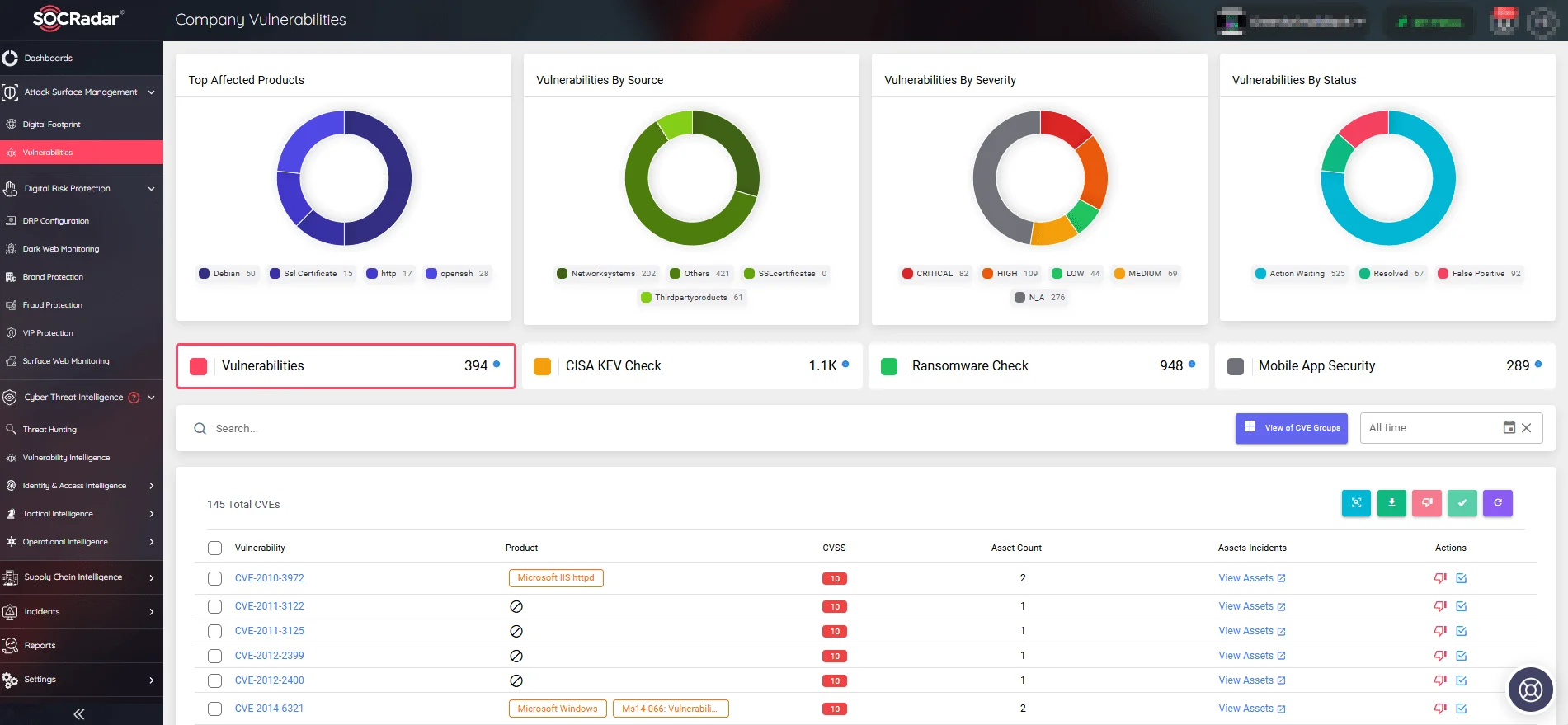
SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management module, Company Vulnerabilities

































