
CISA’s Weekly Summary – CVSS 10 Vulnerabilities in Progress’ LoadMaster and OpenEdge, Myriad Critical Flaws
[Update] March 29, 2024: “Threat Actors Exploit LoadMaster Vulnerability (CVE-2024-1212)”
[Update] March 20, 2024: “PoC Exploit Publicly Available for the Critical LoadMaster Vulnerability, CVE-2024-1212”
[Update] March 11, 2024: “PoC Exploit for the OpenEdge Authentication Gateway Vulnerability, CVE-2024-1403, Is Available”
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has released a summary of the vulnerabilities that came to light for the week of February 19, 2024. This latest CISA weekly vulnerability summary includes CVEs issued between February 16 and February 24, 2024.
In this blog post, we will outline some of the most noteworthy vulnerabilities highlighted in CISA’s summary. These vulnerabilities, if exploited, could have profound implications for the digital resilience of organizations across various industries.
Among the vulnerabilities outlined in this blog post are those affecting ScreenConnect, Fortinet products, GitLab, ProgressSoftware’s LoadMaster, Mastodon, the Fiber web framework, and Kubernetes Charts’ package manager Helm. Additionally, we discuss significant flaws found in IBM, PostgreSQL, and VMware products.
As we navigate through this weekly roundup, we aim to underscore the urgency of addressing these vulnerabilities and enhancing organizational security measures.
Max Severity Flaws in Progress Software’s LoadMaster and OpenEdge
Progress has recently patched two critical vulnerabilities with CVSS scores of 10. One of these vulnerabilities, CVE-2024-1212, was highlighted in CISA’s weekly vulnerability summary, while the other, tracked as CVE-2024-1403, was announced by the vendor on February 27, 2024.
CVE-2024-1212 affects LoadMaster, a load balancing and application delivery solution utilized across various IT environments. All releases of LoadMaster after 7.2.48.1, as well as the LoadMaster Multi-Tenant (MT) VFNs, are susceptible to this issue.
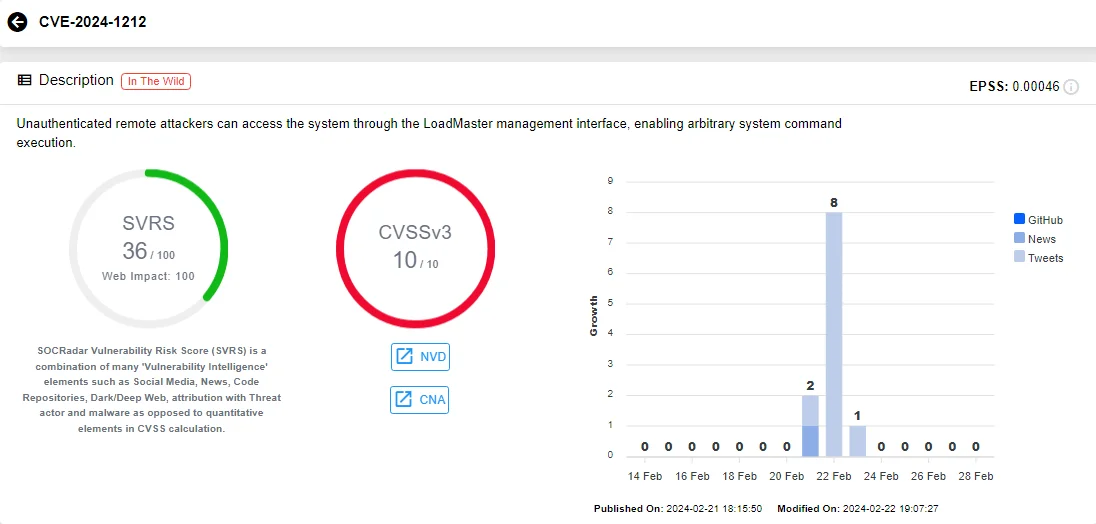
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-1212 (SOCRadar)
This critical vulnerability enables unauthenticated remote attackers to gain access to the system via the LoadMaster management interface, allowing them to execute arbitrary system commands.
The latest vulnerability, CVE-2024-1403, impacts OpenEdge Authentication Gateway and AdminServer versions prior to 11.7.19, 12.2.14, 12.8.1, on all platforms supported by the OpenEdge product.
CVE-2024-1403 constitutes a bypass to authentication, stemming from a failure to properly handle usernames and passwords. Unexpected content passed into the credentials can lead to unauthorized access without proper authentication.
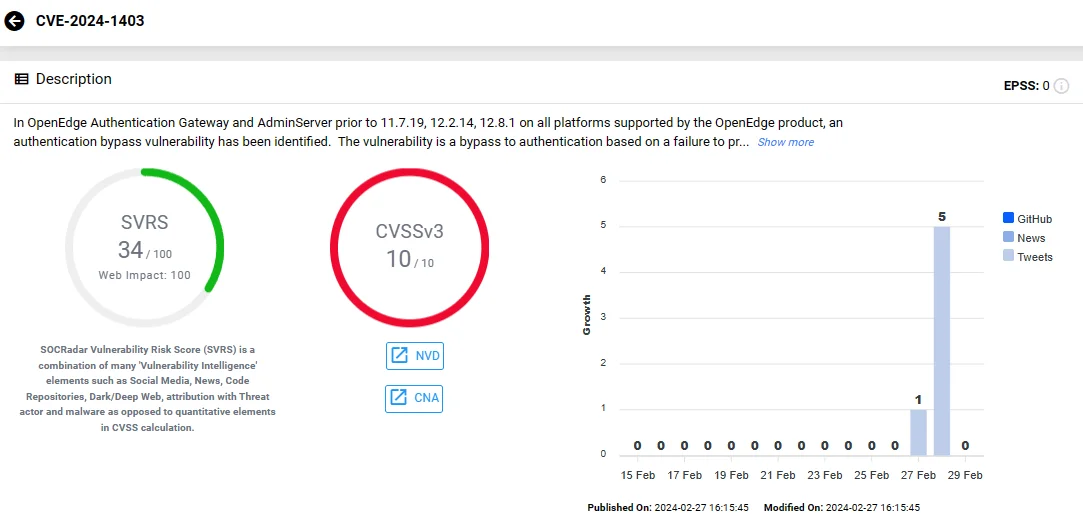
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-1403 (SOCRadar)
Exploitation of this vulnerability could grant attackers access to various OpenEdge components, including sensitive databases.
It is crucial for organizations using LoadMaster and OpenEdge products to apply the necessary patches promptly to mitigate the risk of exploitation. Additionally, implementing stringent access controls and monitoring solutions can help detect and prevent unauthorized access attempts.
PoC Exploit for the OpenEdge Authentication Gateway Vulnerability, CVE-2024-1403, Is Available
Details and a Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit for the OpenEdge Authentication Gateway and AdminServer vulnerability, CVE-2024-1403 (CVSS: 10), have been released.
The vulnerability resides within the authentication procedures of the OpenEdge Authentication Gateway (OEAG) when set up with an OpenEdge Domain utilizing the OS local authentication provider. Researchers explain that this vulnerability also impacts the connections established by OpenEdge Explorer (OEE) and OpenEdge Management (OEM) to the AdminServer, as they similarly use the OS local authentication provider for user-id and password logins.
Horizon3.ai has examined the vulnerable AdminServer service to devise the PoC exploit, identifying the problem to be in the connect() function. The function activates when a remote connection is established; it triggers authorizeUser(), which validates credentials and initiates direct user authentication if the username aligns with “NT AUTHORITYSYSTEM.”
See the full PoC exploit on GitHub.
Critical Vulnerability in ScreenConnect Is Actively Exploited in Ransomware Attacks
ConnectWise also recently addressed a critical vulnerability with a CVSS score of 10, affecting its ScreenConnect product, a desktop and mobile remote access support software.
Tracked as CVE-2024-1709, the vulnerability arises from an authentication bypass weakness. Attackers can exploit it to gain administrative access, access confidential data, or execute Remote Code Execution (RCE) without necessitating user interaction. Furthermore, by exploiting CVE-2024-1709, an attacker could create a new admin account and seize control of the ScreenConnect instance.
Reports indicate that the critical CVE-2024-1709 vulnerability has been leveraged to breach the networks of multiple organizations and deploy malware associated with LockBit’s operations. Following its exploitation to deploy LockBit ransomware, ScreenConnect servers have most recently become targets for the Black Basta and Bl00dy ransomware groups due to the vulnerability.
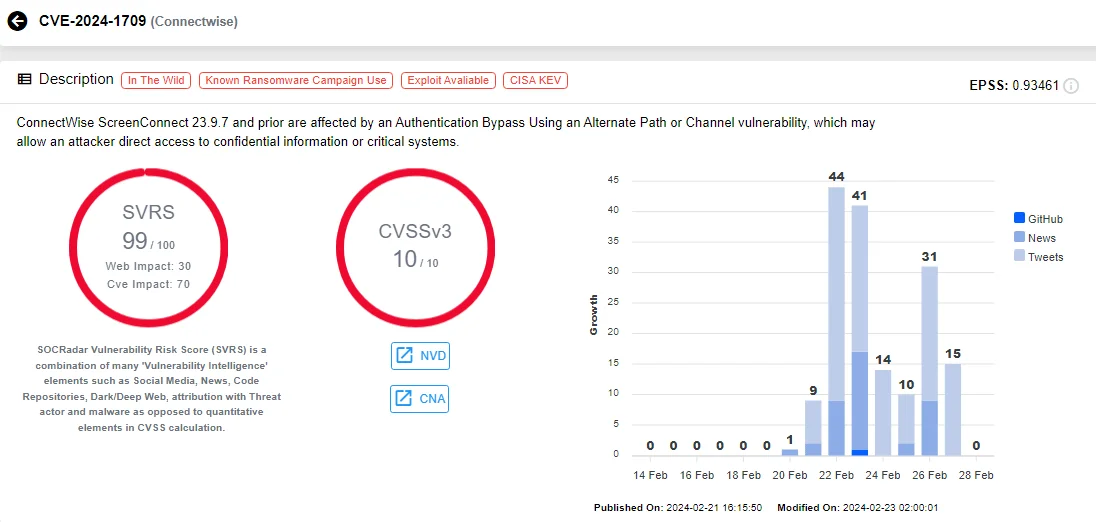
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-1709 (SOCRadar)
For further insights into the critical CVE-2024-1709 vulnerability, refer to the SOCRadar blog post: Vulnerabilities in ConnectWise ScreenConnect.
PoC Exploit Publicly Available for the Critical LoadMaster Vulnerability, CVE-2024-1212
Researchers have publicly released a Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit for the critical vulnerability in Progress Kemp LoadMaster, CVE-2024-1212. Technical details of the vulnerability are also available.
The vulnerability resides in the LoadMaster’s administrator Web User Interface (WUI), enabling attackers to inject malicious commands without authentication.
Despite the REST API for administration being disabled, attackers can bypass restrictions by crafting requests, reactivating the interface. The vulnerable LoadMaster accepts basic authentication headers without validation, allowing attackers to supply malicious data as legitimate commands.
By manipulating basic authentication headers to access the “/access” REST API endpoint, attackers can execute system commands on the LoadMaster, leading to unrestricted control.
The PoC exploit, available on GitHub, also includes a Metasploit module for security researchers.
Threat Actors Exploit LoadMaster Vulnerability (CVE-2024-1212)
Recent reports indicate that cybercriminals are actively exploiting the critical LoadMaster vulnerability, CVE-2024-1212. This revelation does not come as a shock, considering that exploits for this vulnerability have been circulating for over a week.
SonicWall initially detailed the vulnerability in a blog post dated March 27. However, the post is currently unavailable. In their statement, SonicWall had disclosed that their monitoring systems already flagged a noticeable uptick in exploitation attempts.
Accompanying their statement was a graph illustrating the frequency of exploitation attempts targeting CVE-2024-1212:
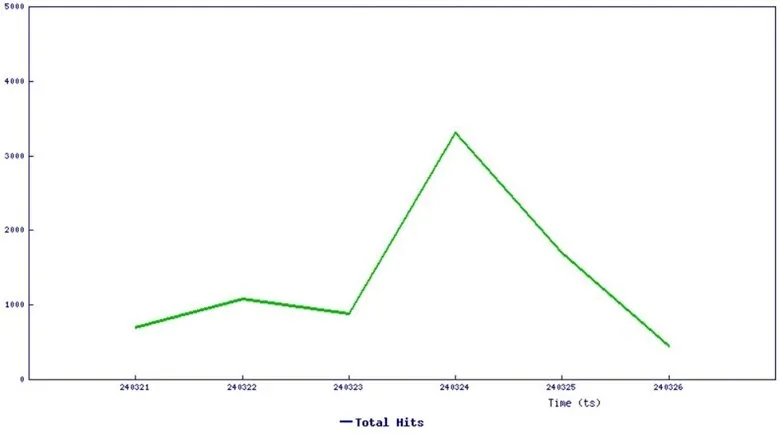
Threat graph (SonicWall)
High-Severity Flaws in Fortinet’s FortiManager, FortiOS, FortiProxy, and FortiPAM Could Lead to Code Execution
Two high-severity vulnerabilities have emerged in Fortinet products, labeled as CVE-2023-42791 and CVE-2023-29181, both carrying CVSS scores of 8.8.
These vulnerabilities pose the risk of enabling an attacker to execute unauthorized code or commands.
The first vulnerability, CVE-2023-42791, involves a path traversal flaw in Fortinet FortiManager, which attackers can exploit through crafted HTTP requests. Meanwhile, the second vulnerability, CVE-2023-29181, originates from the utilization of externally-controlled format strings in Fortinet FortiOS, FortiProxy, and FortiPAM. Exploitation of CVE-2023-29181 occurs through specially crafted commands.
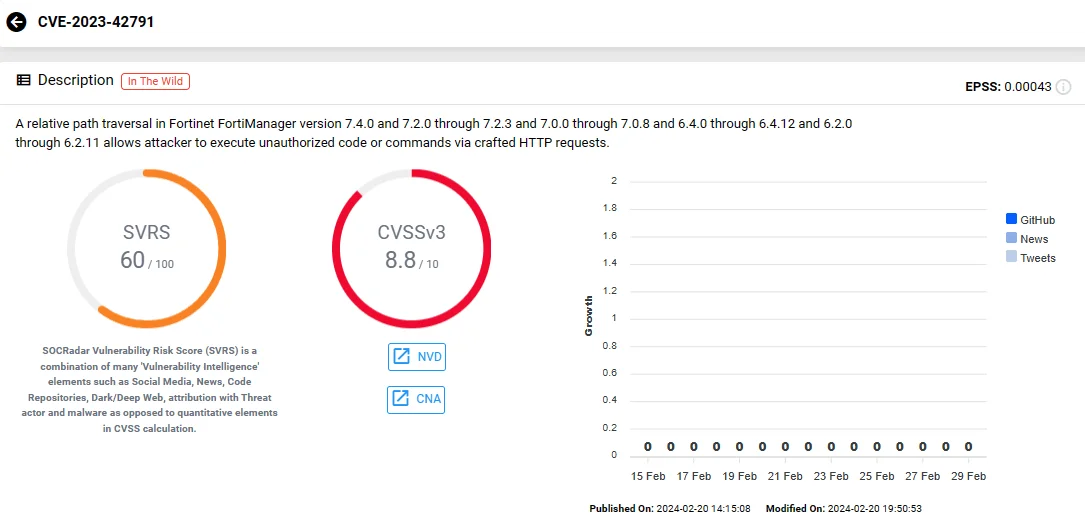
Vulnerability card of CVE-2023-42791 (SOCRadar)
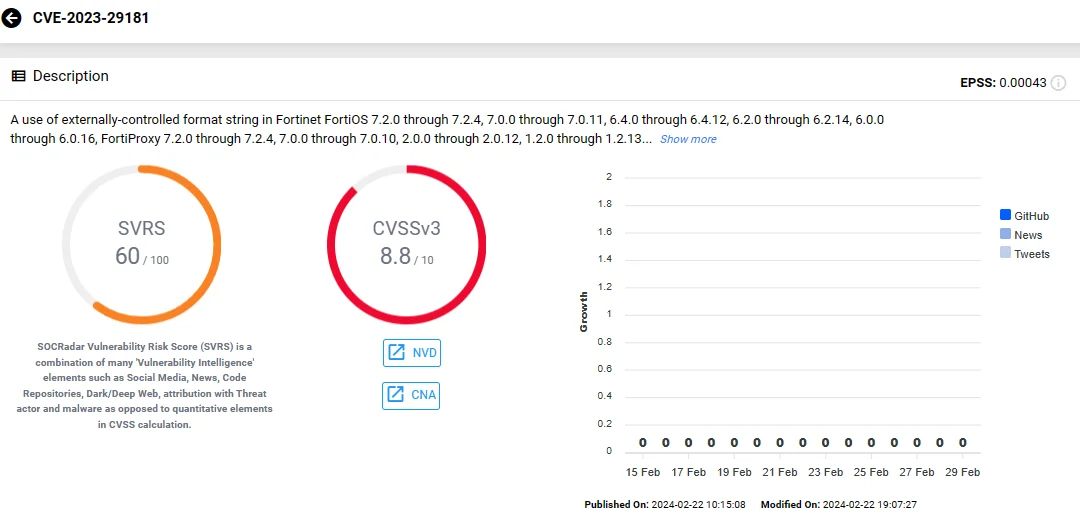
Vulnerability card of CVE-2023-29181 (SOCRadar)
Vulnerability in GitLab CE/EE Allows XSS Attacks
A vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-1451 (CVSS: 8.7), has been identified in GitLab CE/EE, affecting all versions from 16.9 prior to 16.9.1.
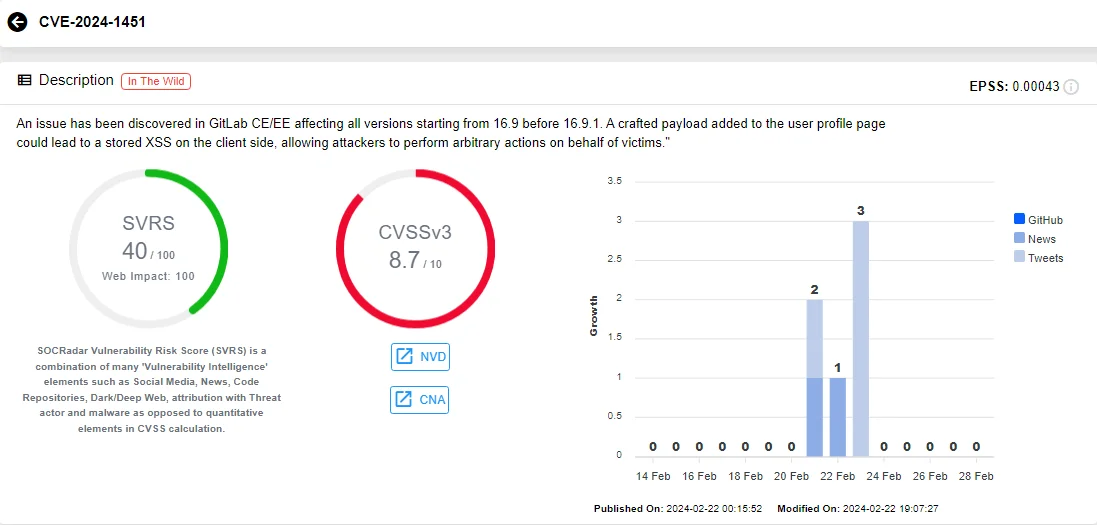
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-1451 (SOCRadar)
This vulnerability permits the addition of a crafted payload to the user profile page, resulting in a Stored Cross-site Scripting (XSS) on the client side. As a consequence, attackers gain the ability to execute arbitrary actions on behalf of victims.
Insecure CORS Configurations Awake a Critical Vulnerability in Fiber
Fiber, a web framework written in Go, is affected by a critical vulnerability prior to version 2.52.1.
Tracked as CVE-2024-25124 (CVSS: 9.4), the vulnerability stems from insecure configurations within the CORS middleware, potentially exposing the application to multiple CORS-related vulnerabilities.
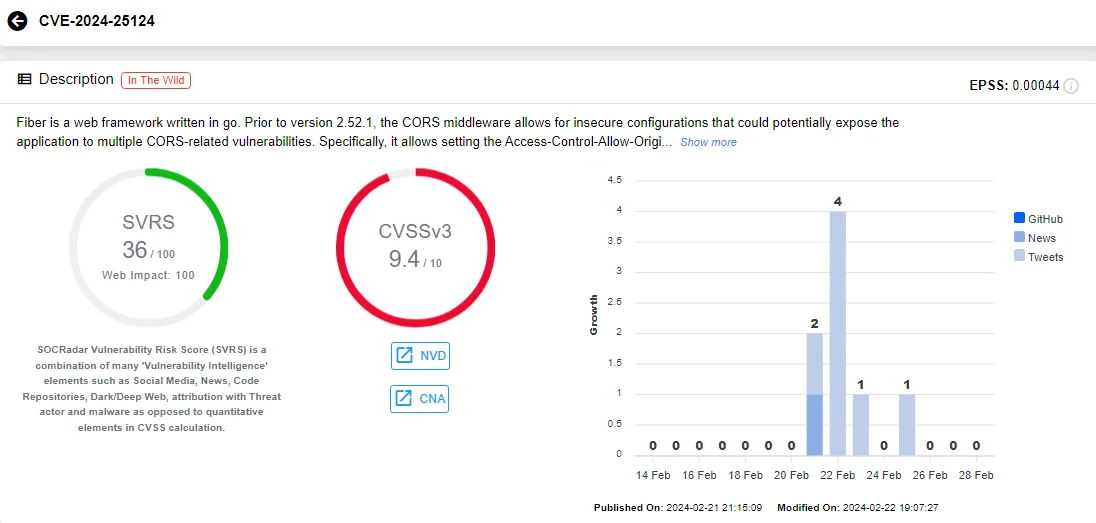
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-25124 (SOCRadar)
Specifically, the middleware permits setting the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header to a wildcard (*) while also enabling Access-Control-Allow-Credentials, a practice contradicting recommended security standards.
Such misconfiguration poses a significant risk, allowing unauthorized access to sensitive user data and leaving the system vulnerable to various attacks.
Version 2.52.1 includes a patch for this vulnerability, and as a temporary solution, users are advised to manually validate their CORS configurations, ensuring that wildcard origins are not permitted when credentials are enabled.
IBM Aspera Console Vulnerable to SQL Injection
IBM Aspera Console versions 3.4.0 through 3.4.2 are susceptible to SQL injection attacks due to a high-severity vulnerability, identified as CVE-2022-43842 (CVSS: 8.6).
Exploiting this vulnerability, a remote attacker could inject specially crafted SQL statements, potentially granting unauthorized access to view, add, modify, or delete information stored in the backend database.
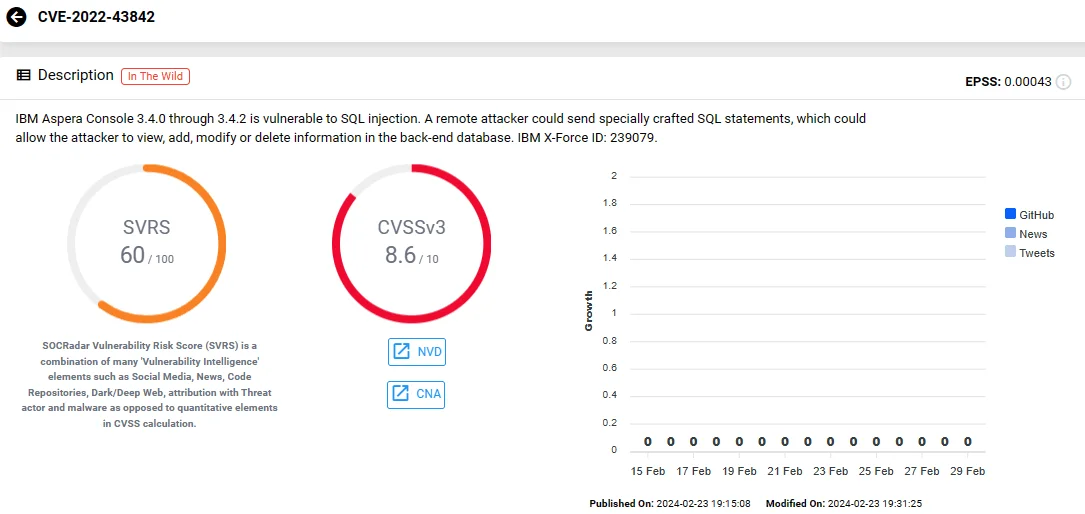
Vulnerability card of CVE-2022-43842 (SOCRadar)
Severe Uninitialized Variable Vulnerability in Helm Package Manager
Helm, a package manager for Charts for Kubernetes, contains a vulnerability related to uninitialized variables in versions preceding 3.14.2.
The vulnerability, CVE-2024-26147 (CVSS: 7.5), arises when Helm attempts to parse index and plugin YAML files that lack the expected content. In cases where either the ‘index.yaml’ file or a plugin’s ‘plugin.yaml’ file lacks all metadata, Helm experiences a panic.
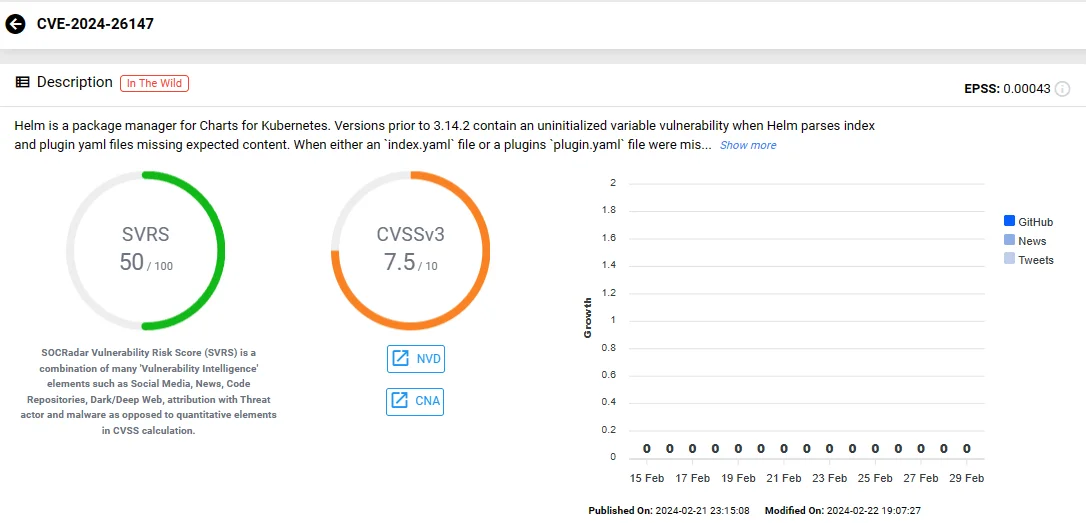
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-26147 (SOCRadar)
This vulnerability affects functions within the Helm SDK, notably the LoadIndexFile and DownloadIndexFile functions in the repo package, as well as the LoadDir function in the plugin package. For Helm client users, the issue impacts functions related to adding a repository, as well as all Helm functions if a malicious plugin is introduced, given that Helm inspects all known plugins with each invocation.
In scenarios where a vulnerable plugin triggers panics in all Helm client commands, users can manually remove the offending plugin from the filesystem. Additionally, for users of Helm SDK versions predating 3.14.2, calls to affected functions can utilize recover to capture the panic.
Threat Actors Can Impersonate Mastodon Accounts Due to Severe Vulnerability
A high-severity vulnerability, designated as CVE-2024-25623 (CVSS: 8.5), has been identified in the open-source social network server Mastodon.
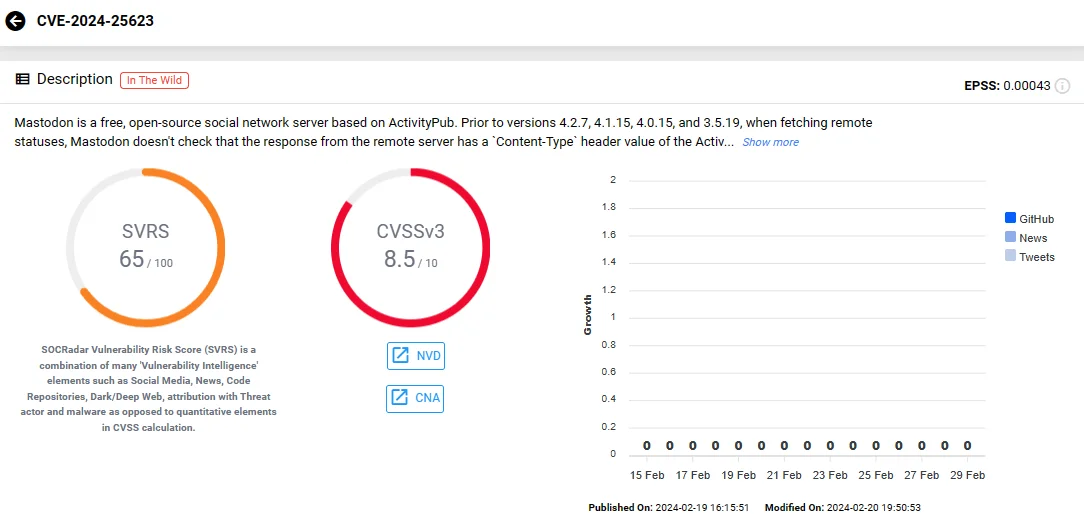
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-25623 (SOCRadar)
Versions preceding 4.2.7, 4.1.15, 4.0.15, and 3.5.19 are susceptible to this vulnerability, where Mastodon fails to validate the Content-Type header value of the response from remote servers when fetching statuses. Consequently, threat actors can upload a specially crafted Activity Streams document to a remote server, prompting a Mastodon server to retrieve it if the remote server permits arbitrary user uploads.
Exploiting this vulnerability enables threat actors to impersonate an account on a remote server that meets specific criteria, such as allowing the attacker to register an account, accepting arbitrary user-uploaded documents, and hosting them on the same domain as the ActivityPub actors.
Critical SQLi Vulnerability in PostgreSQL JDBC Driver
The PostgreSQL JDBC Driver, also known as PgJDBC, has recently been found to harbor a critical vulnerability rated with a maximum severity score of 10.
The identified vulnerability, CVE-2024-1597, emerges in the PostgreSQL JDBC Driver when it operates under PreferQueryMode=SIMPLE, a non-default configuration known to be susceptible to SQL injection attacks in certain versions. It represents a significant risk to database security, as it could result in the exposure and manipulation of sensitive data, including customer and corporate information.
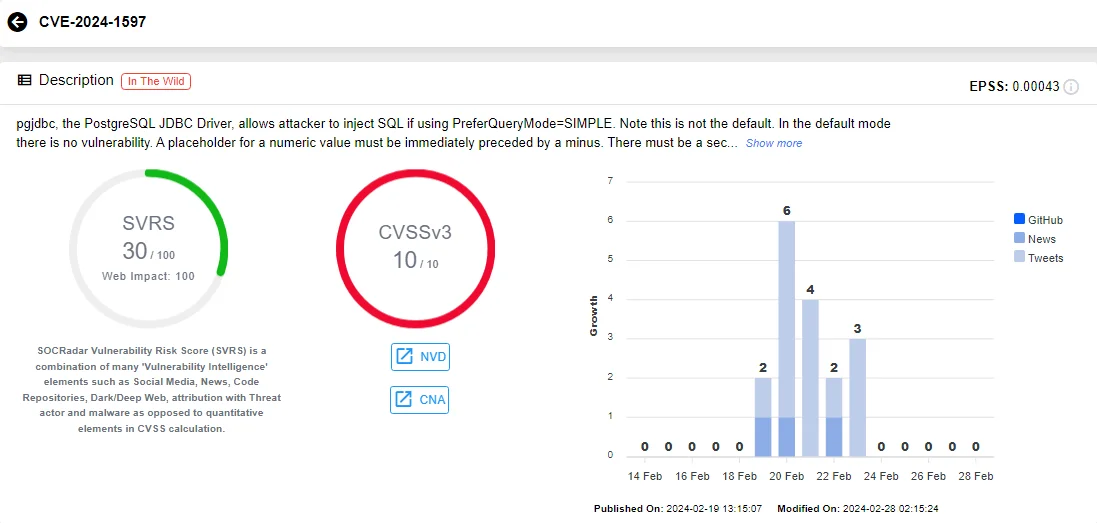
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-1597 (SOCRadar)
Further details regarding the intricacies of this vulnerability can be found in an additional SOCRadar blog post.
VMware Warns of Critical Flaw in Enhanced Authentication Plugin (EAP)
VMware issued a warning, urging administrators to remove the Enhanced Authentication Plugin (EAP), which was deprecated in 2021, from their systems. This decision comes in response to the discovery of two unpatched vulnerabilities: CVE-2024-22245 (CVSS: 9.6) and CVE-2024-22250 (CVSS: 7.8).
The primary concern lies with CVE-2024-22245, categorized as critical. This vulnerability opens the door for attackers to manipulate domain users with EAP installed in their web browsers. By exploiting this flaw, attackers can coerce unsuspecting users into requesting and relaying Kerberos service tickets for arbitrary Active Directory Service Principal Names (SPNs). Consequently, they can gain control over privileged EAP sessions, posing a significant security risk to affected systems.
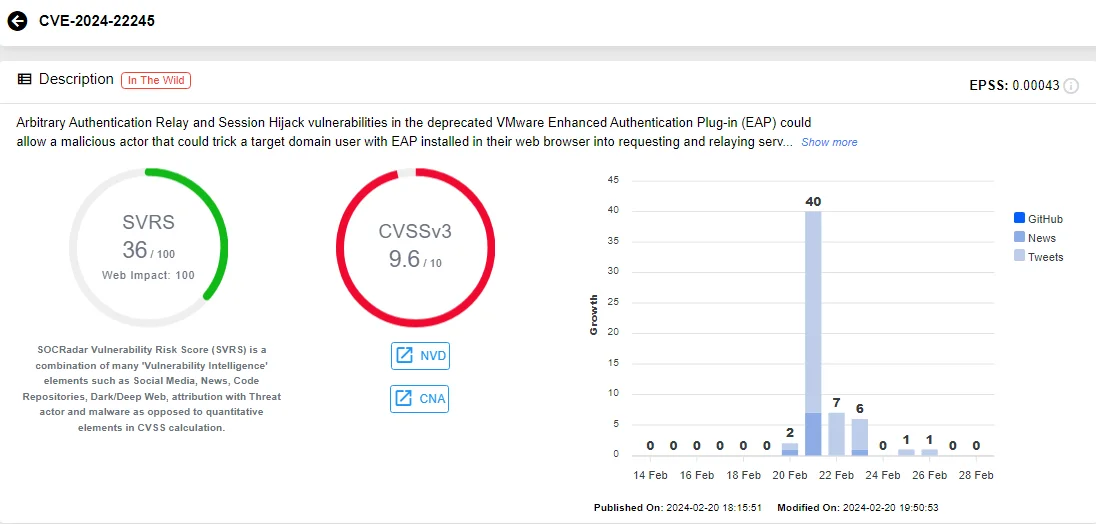
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-22245 (SOCRadar)
Administrators are advised to take prompt action to safeguard their systems and prevent potential exploitation.
For detailed insights into these VMware Enhanced Authentication Plugin (EAP) vulnerabilities and comprehensive mitigation strategies, refer to the SOCRadar blog.
Stay Proactive with SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence
Keep up to date on the latest security vulnerabilities and ensure that your products and software are protected. SOCRadar remains vigilant, constantly monitoring your digital assets and sending out timely alerts whenever a vulnerability occurs within your organization’s digital ecosystem.
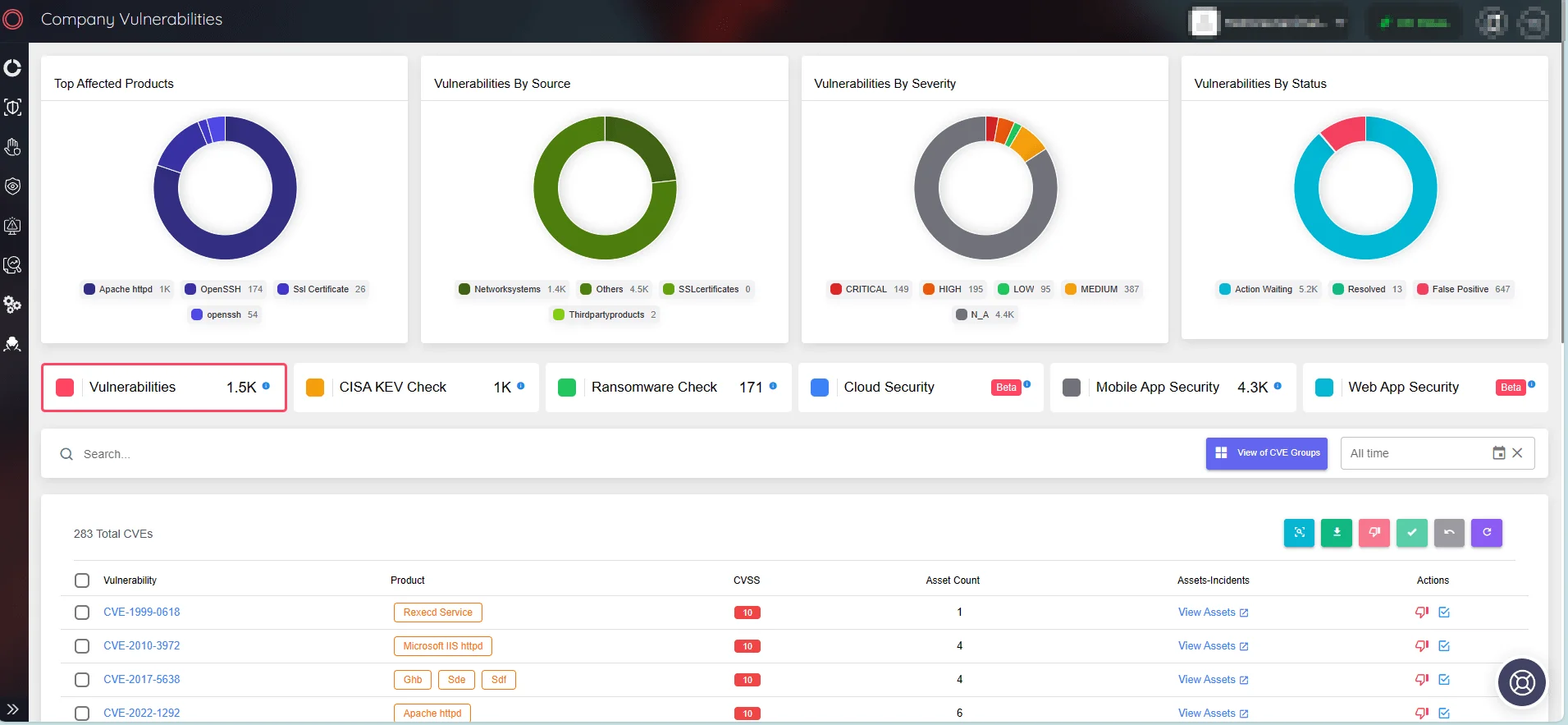
SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management/Company Vulnerabilities
Use SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence to efficiently address vulnerabilities and determine patch priorities. Within the platform, you can search for vulnerabilities and get detailed information about their lifecycle and potential exploits.
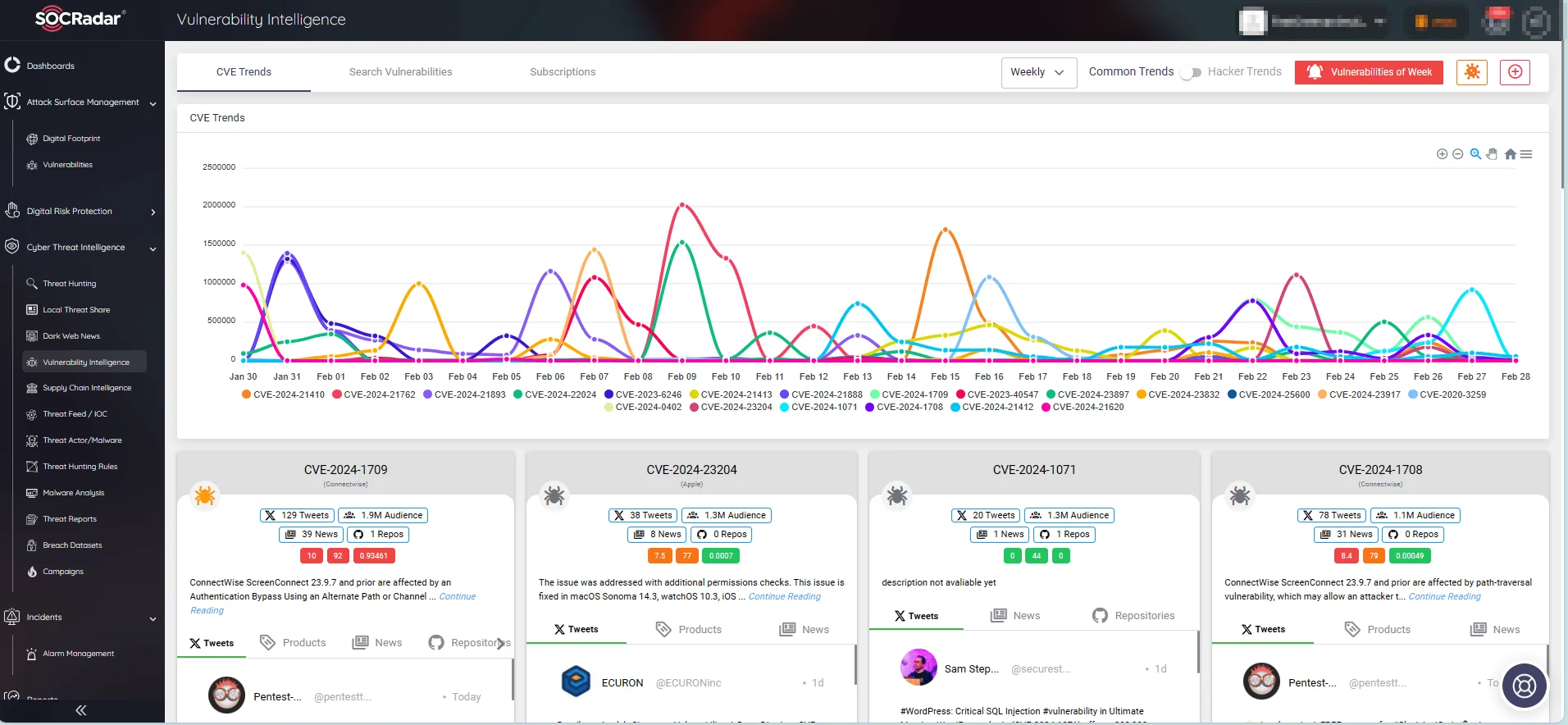
CVE trends on SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence


































