Critical Auth Bypass in GoAnywhere MFT: Is It a New Ransomware Gateway? (CVE-2024-0204)
Fortra has disclosed a critical vulnerability in its GoAnywhere MFT (Managed File Transfer) software – an authentication bypass that poses a severe security risk. Upon its successful exploitation, attackers could establish a new admin user, potentially paving the way for additional malicious actions.
GoAnywhere MFT stands as a globally utilized secure managed file transfer solution, facilitating the seamless exchange of data among systems, employees, customers, and trading partners.
Details of the New GoAnywhere MFT Vulnerability, CVE-2024-0204
The vulnerability, identified as CVE-2024-0204 with a CVSS score of 9.8, potentially grants a remote unauthorized attacker the ability to create users with admin-level privileges through the product’s administration portal. This can lead to severe consequences, including unauthorized access to sensitive data, malware infections, and even the possibility of a complete device takeover.
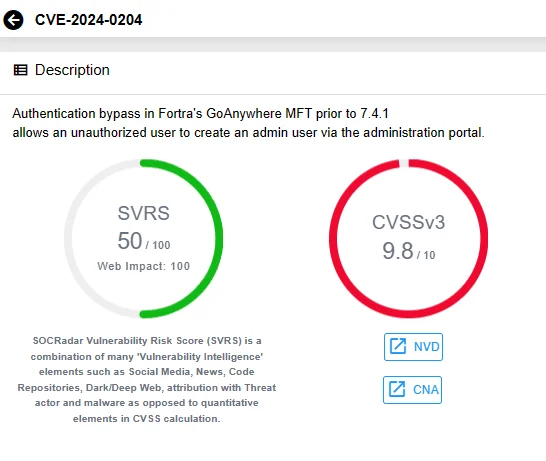
Details of CVE-2024-0204 on SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence
Discovered on December 1, 2023, Fortra promptly addressed the issue on December 7 by releasing GoAnywhere MFT version 7.4.1. While private advisories were swiftly dispatched to customers few days after the vulnerability’s detection, a public security advisory, albeit limited in information, has just recently been issued.
Versions affected by this vulnerability include:
- Fortra GoAnywhere MFT 6.x from 6.0.1
- Fortra GoAnywhere MFT 7.4.0 and earlier
As of now, there are no reported instances of active exploitation of CVE-2024-0204 in the wild.
Take advantage of SOCRadar’s continuous monitoring capabilities to ensure the safety of your digital assets; the platform proactively identifies and reports security vulnerabilities and incidents in real time, allowing for prompt action and providing actionable insights to improve the remediation process.
The Attack Surface Management module allows you to view vulnerabilities that impact your assets.
Can CVE-2024-0204 Become a Successor to CVE-2023-0669? The Ransomware Menace Looming Over GoAnywhere MFT
Fortra’s GoAnywhere MFT, a globally-utilized file transfer product for businesses, inherently attracts threat actors. The software was previously hit by a significant vulnerability, CVE-2023-0669, which served as a gateway for ransomware attacks by the infamous Cl0p Ransomware.
The successful exploitation of CVE-2023-0669 granted malicious actors with Remote Code Execution (RCE) capabilities, although it could only be exploited by gaining access to the application’s administrative console.
Beyond Cl0p, the GoAnywhere MFT RCE vulnerability was exploited by ransomware groups like LockBit and BlackCat (ALPHV), and the vulnerability contributed to a 91% increase in ransomware attacks in a single month.
GoAnywhere MFT is not alone in facing such threats, as we witnessed similar aggressions targeting Progress Software’s MOVEit Transfer, another file transfer software, by Cl0p ransomware group. Throughout 2023, the ransomware actor paralyzed thousands of organizations by leveraging MOVEit exploits, threatening them with data leaks.
The current concern centers around CVE-2024-0204, a critical authentication bypass vulnerability, and its potential to become the successor to CVE-2023-0669. While no active exploitation has been reported thus far, considering the history with its predecessor and past instances where file transfer products were exploited, there is a looming threat that organizations should proactively defend against.
Stay ahead of vulnerability and exploitation trends through SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence module. Gain access to detailed information on identified vulnerabilities and fortify your defenses against potential cyber attacks.
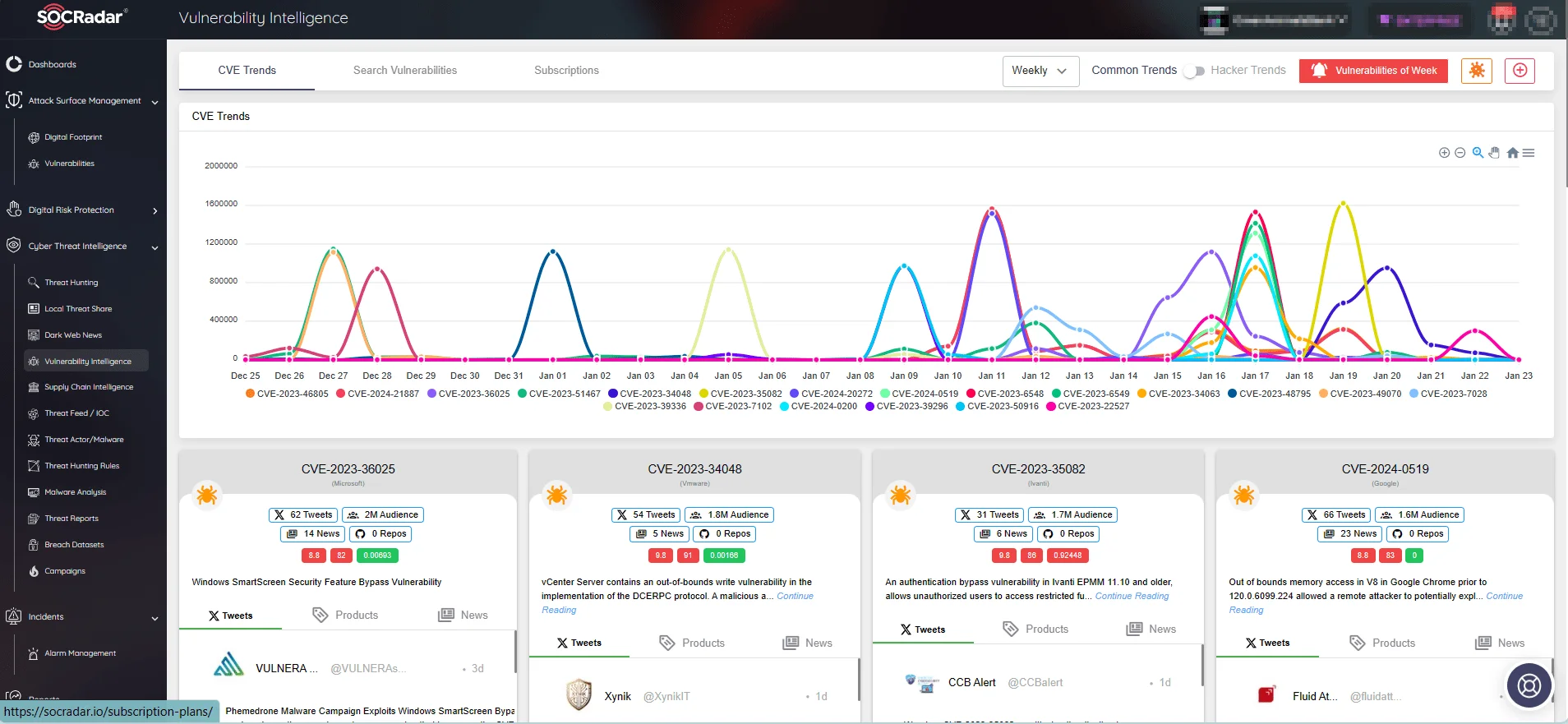
CVE trends on SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence
How to Fix the CVE-2024-0204 Vulnerability? Is There a Way Other Than Patching the GoAnywhere MFT Software?
Fortra strongly recommends users to safeguard their systems from potential exploitation of the CVE-2024-0204 vulnerability by upgrading GoAnywhere MFT installations to version 7.4.1 or higher. Additionally, the advisory outlines alternative, manual methods to eliminate the vulnerability.
For non-container deployments, Fortra suggests deleting the InitialAccountSetup.xhtml file in the install directory and restarting the services to mitigate the vulnerability. In instances where GoAnywhere MFT is deployed in containers, Fortra advises replacing the file with an empty counterpart and subsequently restarting to effectively address the issue.
Is There a Public Proof-of-Concept (PoC) Exploit for the CVE-2024-0204 Vulnerability?
Researchers at Horizon3 published a technical analysis of the vulnerability and provided a Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit on their GitHub.
The PoC exploit capitalizes on the path traversal issue behind CVE-2024-0204, granting access to the /InitialAccountSetup.xhtml endpoint and thereon facilitating the creation of new admin users.
To stay informed of public exploits or repositories related to a vulnerability, you can leverage SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence.
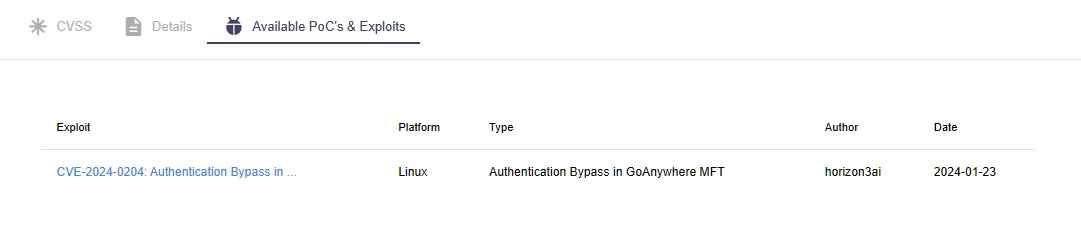
Available PoCs and exploits of CVE-2024-0204 on SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence
Given the availability of the PoC exploit, there is a potential risk of threat actors scanning for the vulnerability in exposed GoAnywhere MFT instances.
Researchers recommend monitoring any new additions to the ‘Admin users’ group in the GoAnywhere administrator portal Users -> Admin Users section. This can help determine if a compromise has occurred, and if the attacker has left a user in this group, observing its last logon activity may offer insights into the approximate date of compromise.



































