
CVE-2020-17519 in Apache Flink Enters CISA’s KEV Catalog & GitLab Patches XSS Flaw, CVE-2024-4835
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has recently updated its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog to include another CVE, warning against exploitation. The CVE highlighted by the agency is CVE-2020-17519, a high-severity vulnerability affecting Apache Flink.
Apache Flink is widely used for continuous streaming and batch analytics, making this a significant concern for entities relying on the framework for real-time data processing.

What is Apache Flink used for? (flink.apache.org)
Concurrently, GitLab has addressed a Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability in both its Community Edition (CE) and Enterprise Edition (EE) – details on this patch will follow later in this blog post, so stay tuned.
What is CVE-2020-17519 in Apache Flink?
This vulnerability, identified as CVE-2020-17519 and scoring a 7.5 on the CVSS scale, stems from improper access control mechanisms within Apache Flink’s JobManager component, particularly through its REST interface.
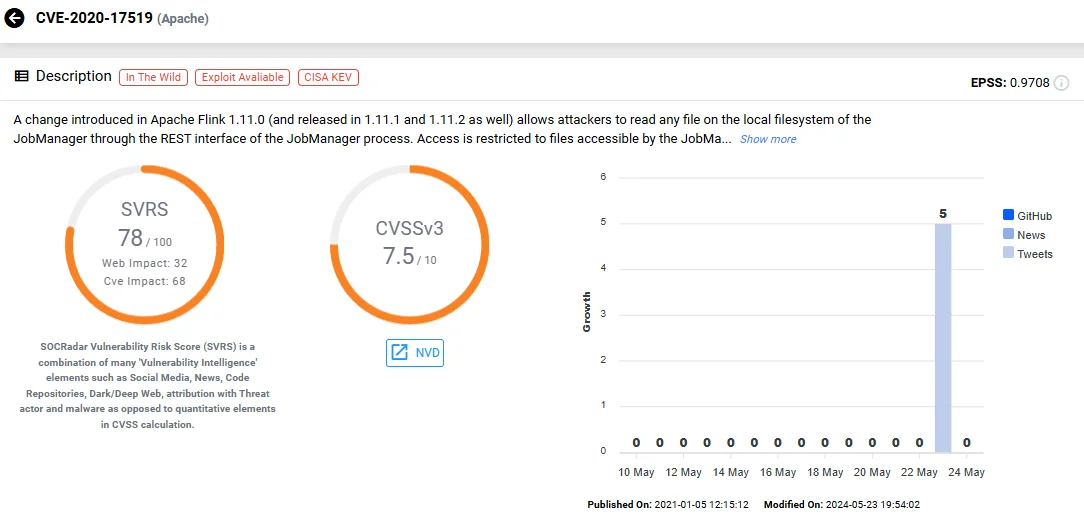
Vulnerability card of CVE-2020-17519 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
CVE-2020-17519 allows unauthorized attackers to exploit a directory traversal weakness to read any file accessible to the JobManager process. This includes potentially sensitive files that should not be exposed externally.
The impacted versions of Apache Flink are 1.11.0 to 1.11.2.
A Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit for the vulnerability illustrates the ease with which this vulnerability can be exploited: by sending a specially crafted HTTP GET request to the /jobmanager/logs/ endpoint. Attackers could, for instance, navigate to critical system files such as /etc/passwd, which contains essential user account details on Unix-based systems, thereby gaining information that could facilitate further malicious activities.
New in the KEV Catalog: CISA Flags CVE-2020-17519 as Exploited
CISA has issued an alert stating that the CVE-2020-17519 vulnerability is now included in the KEV Catalog due to evidence of active exploitation.
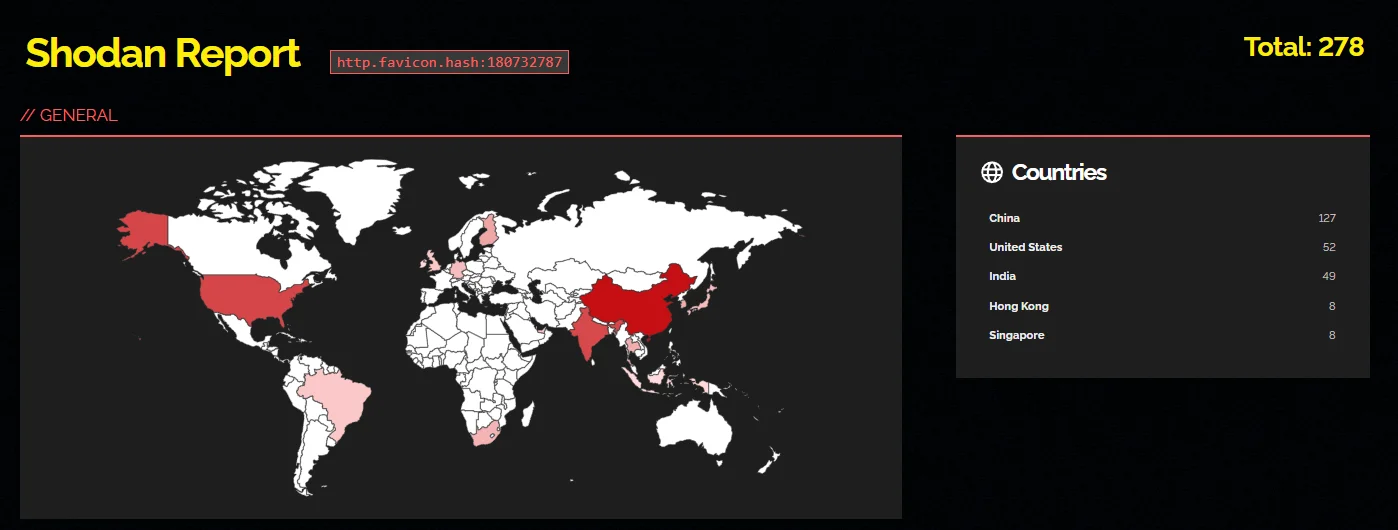
Shodan search results for the Apache Flink instances that are exposed online and potentially targetable.
The agency stressed that such vulnerabilities are common attack vectors and issued a warning to federal enterprises, emphasizing the importance of patching this vulnerability to prevent potential security breaches.
The agency has set a compliance deadline of June 13, 2024, to ensure that all affected systems are secured in a timely manner.

CISA KEV entry for CVE-2020-17519
For a detailed discussion on how vulnerabilities are prioritized and added to the KEV Catalog, refer to our blog post: CISA KEV Timeframe Problems While Prioritizing Vulnerabilities.
How to Address Apache Flink’s CVE-2020-17519?
To secure systems against the CVE-2020-17519 vulnerability, users of Apache Flink should urgently upgrade to version 1.11.3 or later, where the flaw has been fully remediated.
See the downloads for Apache Flink.
Visit the Vulnerability Intelligence page to see any updates to the vulnerability’s lifecycle, including new exploits and mentions.

Latest lifecycle updates on the Apache Flink flaw, CVE-2020-17519 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Moreover, for continuous monitoring and management of vulnerabilities, SOCRadar offers an advanced Vulnerability Intelligence feature.
Users can leverage SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence to obtain detailed information on emerging CVEs, including new exploits, mentions across different platforms, relevant repositories, affected software and systems, all references, observations of the vulnerability in the wild, exploitability scores, and its inclusion in the CISA KEV Catalog.
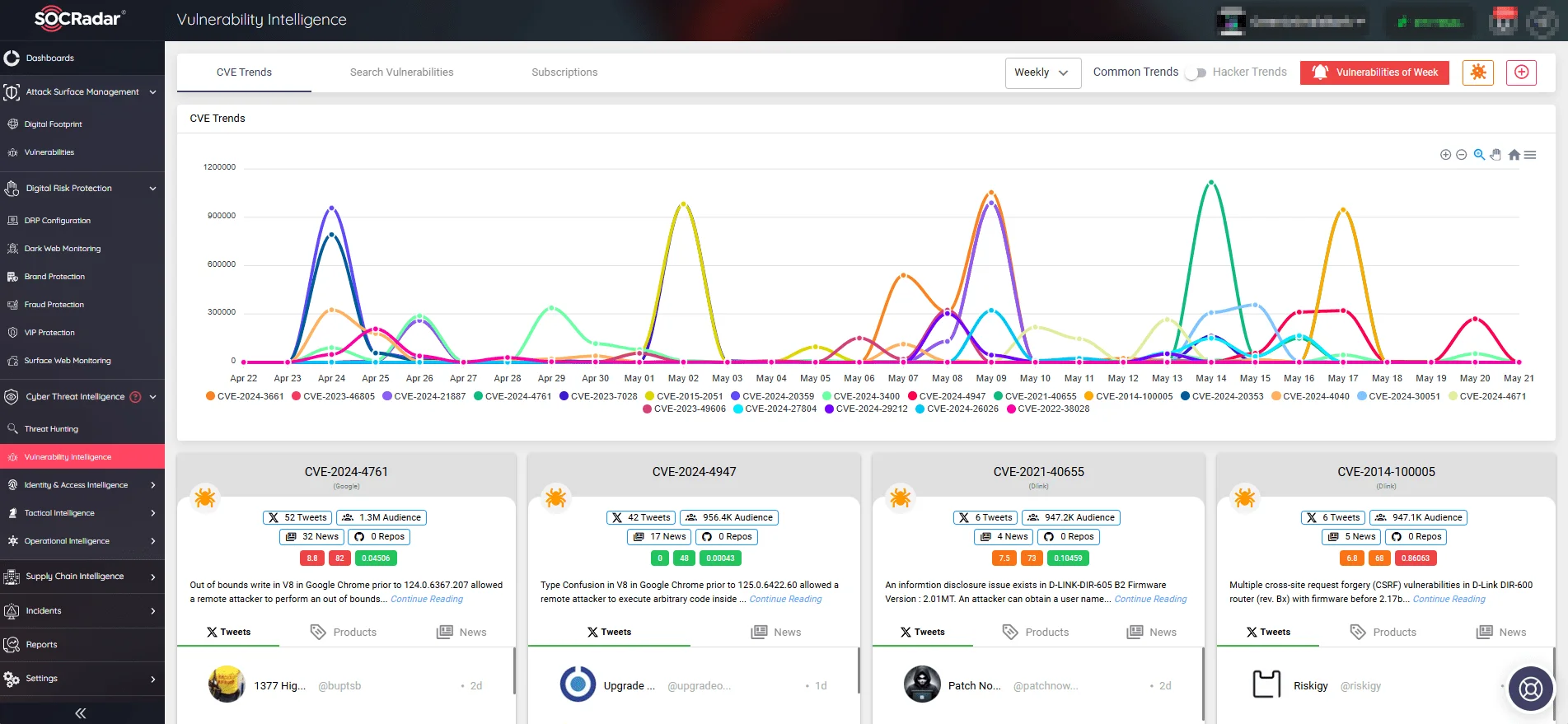
SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence
XSS Vulnerability in GitLab (CVE-2024-4835) Received a Patch
Another recent and significant development in the vulnerability landscape is GitLab’s patching of a severe vulnerability, CVE-2024-4835, which could lead to Cross-site Scripting (XSS) attacks.
What is CVE-2024-4835?
CVE-2024-4835, marked with a CVSS score of 8.0, represents a high-severity vulnerability within GitLab’s VS Code editor (Web IDE).
It arises from improper input sanitization during the web page generation process, potentially enabling attackers to create pages that can execute unauthorized scripts in the context of a user’s session. This type of vulnerability, known as Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), can lead to the exfiltration of sensitive user information, and even supply chain attacks.
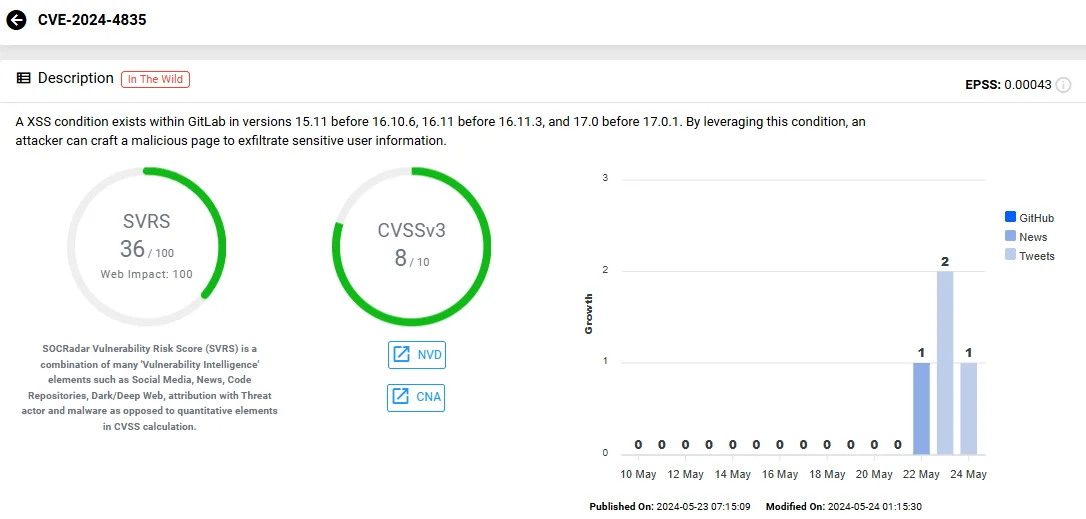
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-4835 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
The specific issue in GitLab’s Web IDE allows attackers, without needing authentication, to craft scenarios where unsuspecting users might trigger malicious scripts. Although this attack requires user interaction, the simplicity of inducing such interactions increases the practical risk of exploitation.
Given GitLab’s widespread use for managing extensive and sensitive data, such as API keys and source code, the repercussions of such an attack can be critical. An attacker gaining control of a GitLab account can lead to further adverse outcomes, such as the injection of malicious code into projects or the theft of sensitive data.
Update GitLab to Address CVE-2024-4835
To tackle CVE-2024-4835, GitLab promptly released updates for both the Community Edition (CE) and Enterprise Edition (EE). The patched versions, 17.0.1, 16.11.3, and 16.10.6, aim to secure affected systems against potential exploits.
Organizations and individual users are strongly advised to upgrade their GitLab installations without delay to safeguard their development environments from potential security breaches.
For detailed information on the updates, you can refer to the GitLab Patch Release.
In addition to applying these updates, leveraging tools like SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) module can further enhance your security posture. This module aids organizations by continuously monitoring digital assets, providing early warnings for vulnerabilities, and enabling swift proactive actions.
Company Vulnerabilities, Attack Surface Management module
By integrating SOCRadar’s ASM into your cybersecurity strategy, your team can respond to threats more rapidly.




































