
Dark Web Profile: Mallox Ransomware
Mallox, a strain of ransomware and a group with the same name, encrypts its victims’ data and subsequently demands a ransom, typically in cryptocurrency, in return for providing the decryption key, just as a usual ransomware operator. However, this ransomware exhibited more destructiveness than many other ransomware variants in some cases. The Mallox ransomware strain and the group behind it, has been operational since around mid-2021 and is still active as of 2024.
Who is Mallox Ransomware?
Mallox is also called “TargetCompany,” “Tohnichi,” or “Fargo” ransomware and has been active since 2021. The group behind Mallox specializes in multi-extortion tactics, encrypting victim data and issuing threats to publish it on their public TOR-based websites.

Threat actor card of Mallox Ransomware
According to SuspectFile’s interview blog with this ransomware group, Mallox stands out as one of the longest-running ransomware groups that remain active today (The interview was in the first month of 2023 and they are still active). The first encounter with its file samples dates back to June 2021, during which industry analysts initially labeled it as “TargetCompany ransomware.”
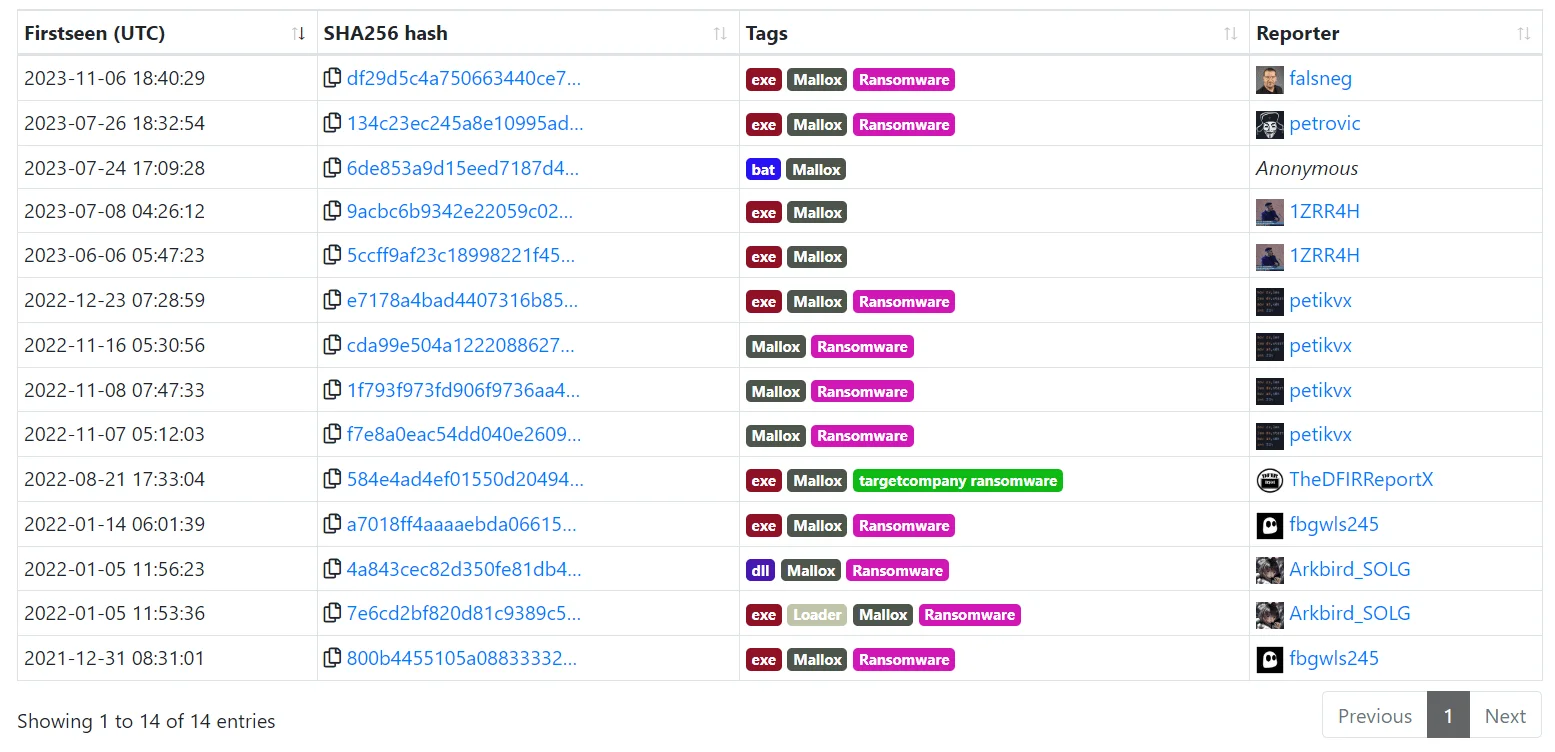
Uploaded samples of Mallox to Malwarebazaar over the years
A year later, around mid to late 2022, the group gained the name Fargo due to an extension added to encrypted files. Presently, it is identified as Mallox ransomware. During 2022, researchers recorded a surge in Mallox samples.
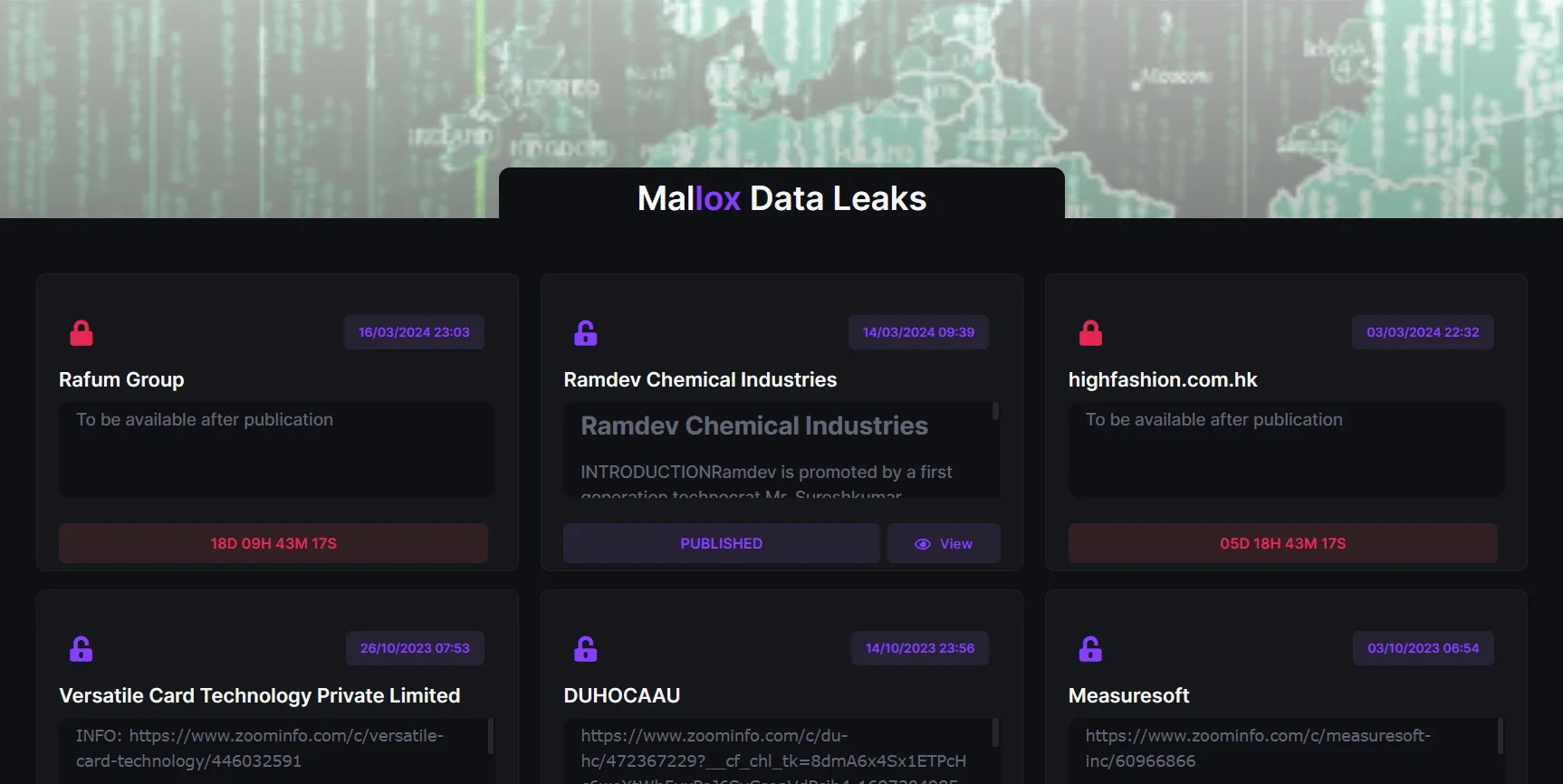
Mallox website is named as Mallox Data Leaks
While the successful operations of law enforcement agencies and counter ransomware initiatives continued to crack down on ransomware groups, many groups focused only on data leak and extortion. Mallox named their website as Mallox Data Leak on its home page. One question that comes to mind is, do they only do extortion anymore?
However, Mallox strains continue to appear around, and some companies have already been attacked with Mallox strains in 2024. Therefore for Mallox its not possible to say that they are now just an extortion group.
Modus Operandi of Mallox Ransomware
Initial Access Strategies:
Mallox Ransomware employs various techniques to gain initial access to target systems. This includes:
- Exploiting vulnerabilities in publicly exposed services such as MS-SQL and ODBC interfaces. Mallox specifically targets unpatched instances of old Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerabilities like CVE-2019-1068 in Microsoft SQL Server and CVE-2020-0618 in Microsoft SQL Server Reporting Services.
- Conducting brute-force attacks against weakly configured services and applications accessible over the internet.
- Utilizing phishing emails with malicious attachments or links to deliver attack frameworks like Cobalt Strike and Sliver helps establish initial access.
Persistence Mechanisms:
Once initial access is gained, Mallox ensures persistence on the compromised systems through various methods:
- Installing legitimate remote desktop software like AnyDesk to maintain access without relying solely on malware, ensuring continued control over the system.
- Creating backdoor accounts and scripts for persistent access allows the threat actors to re-enter the system even if discovered and removed initially.
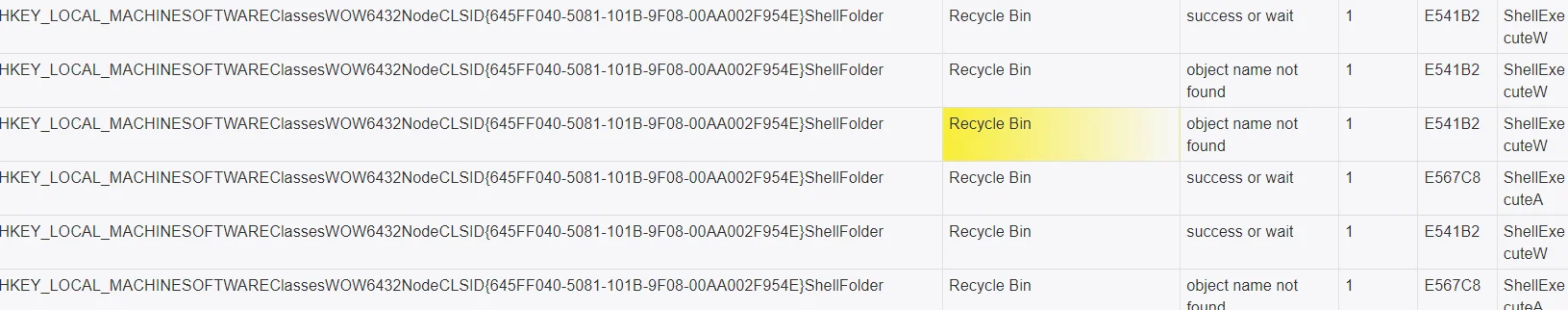
With PowerShell Mallox creates files in the recycle bin to hide itself (JoeSandbox)
Privilege Escalation Techniques:
Mallox employs privilege escalation tactics to elevate its access privileges within the compromised network:
- Using tools like Mimikatz to dump credentials and extract plaintext passwords from memory, enabling them to escalate privileges and gain access as domain administrators or other high-privileged accounts.
- Exploiting misconfigurations or vulnerabilities in the target system to escalate privileges and gain deeper access into critical areas of the network.
Network Enumeration and Reconnaissance:
Before moving laterally within the network, Mallox conducts thorough network enumeration and reconnaissance:
- Utilizing legitimate network scanning tools like netscan.exe to map out the network topology, identify active hosts, and gather information about network services and configurations.
- Enumerating user accounts, group memberships, and access permissions to identify high-value targets and potential avenues for lateral movement.
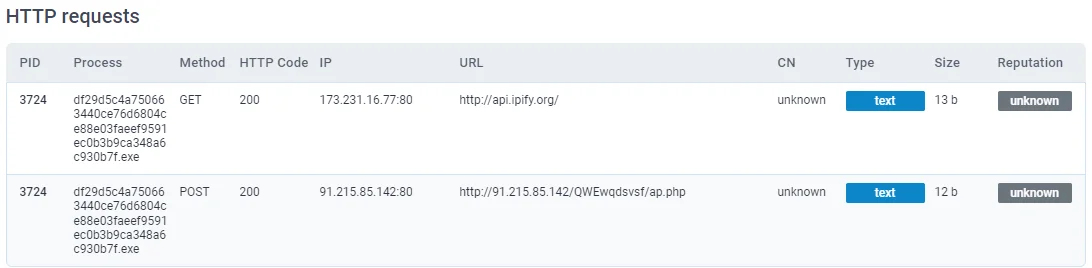
Whenever possible, it communicates with the C2 server to transfer commands and files. (Any.run report)
Lateral Movement Strategies:
Once familiar with the network, Mallox initiates lateral movement to expand its reach and compromise additional systems:
- Creating and using custom scripts or tools to move laterally across the network, exploiting vulnerabilities or weak security controls in interconnected systems.
- Leveraging compromised credentials or stolen tokens to move laterally between systems and escalate privileges further within the network hierarchy.
Data Exfiltration Techniques:
Mallox Ransomware often includes data exfiltration as part of its operation to maximize the impact of the attack:
- Using command-line utilities like Robocopy or PowerShell scripts to copy sensitive data from compromised systems to external servers controlled by the threat actors.
- Employing file compression tools or encryption algorithms to compress and encrypt exfiltrated data makes it harder for defenders to detect or recover.
Preparation for Encryption:
Before initiating the encryption process, Mallox takes specific preparatory steps to ensure a successful and widespread impact:
- Disabling or bypassing security controls such as firewalls, antivirus software, and endpoint detection systems to prevent early detection of ransomware activity.
- Suspending or terminating processes that may interfere with the encryption process, such as backup services or file synchronization utilities, to maximize the number of encrypted files.

By deleting critical services related to SQL Server and forcefully terminating processes, the ransomware aims to disrupt the normal functioning of the victim’s system (Any.run report)
File Encryption Procedures:
Mallox Ransomware employs advanced encryption techniques to render files inaccessible and demand ransom for decryption:
- Strong encryption algorithms like AES-256 or RSA-2048 can be used to encrypt files and append them with a unique file extension, making it clear which files have been encrypted.
- Encrypting files across a wide range of formats, including documents, spreadsheets, images, videos, databases, and archives, to maximize the impact on the victim’s operations.
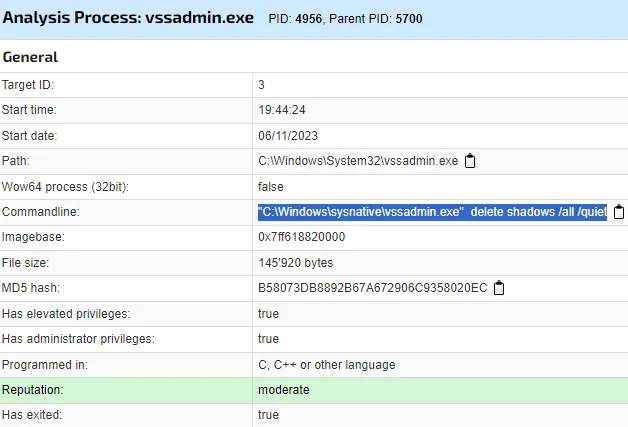
Shadow copies are backups created by Windows to allow users to restore previous versions of files. By deleting these shadow copies, Mallox tries to prevent users from using built-in recovery options to restore their encrypted files. (JoeSandbox)
Ransom Note Delivery:
After encrypting files, Mallox delivers ransom notes to inform victims of the encryption and provide instructions for ransom payment:
- Ransom notes are typically placed in each encrypted folder or on the desktop, typically in the form of text files or pop-up messages containing details about the ransom amount, payment deadlines, and contact information.
- Threatening victims with permanent data loss or exposure of sensitive information if the ransom is not paid within the specified timeframe creates a sense of urgency and pressure.
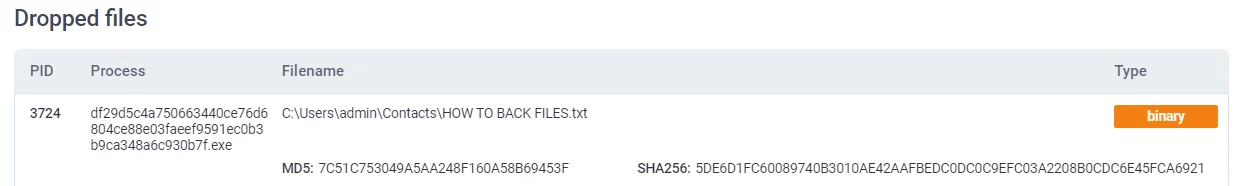
Mallox drops countless HOW TO BACK FILES.txt (Any.run report)
Ransom Payment Infrastructure:
Mallox establishes a ransom payment infrastructure to facilitate communication and payment processing with victims:
- Providing victims with unique Bitcoin wallet addresses or cryptocurrency payment portals to send ransom payments securely and anonymously.
- Setting up TOR-based communication channels or encrypted email addresses for direct communication with victims, ensuring anonymity and confidentiality during negotiations.
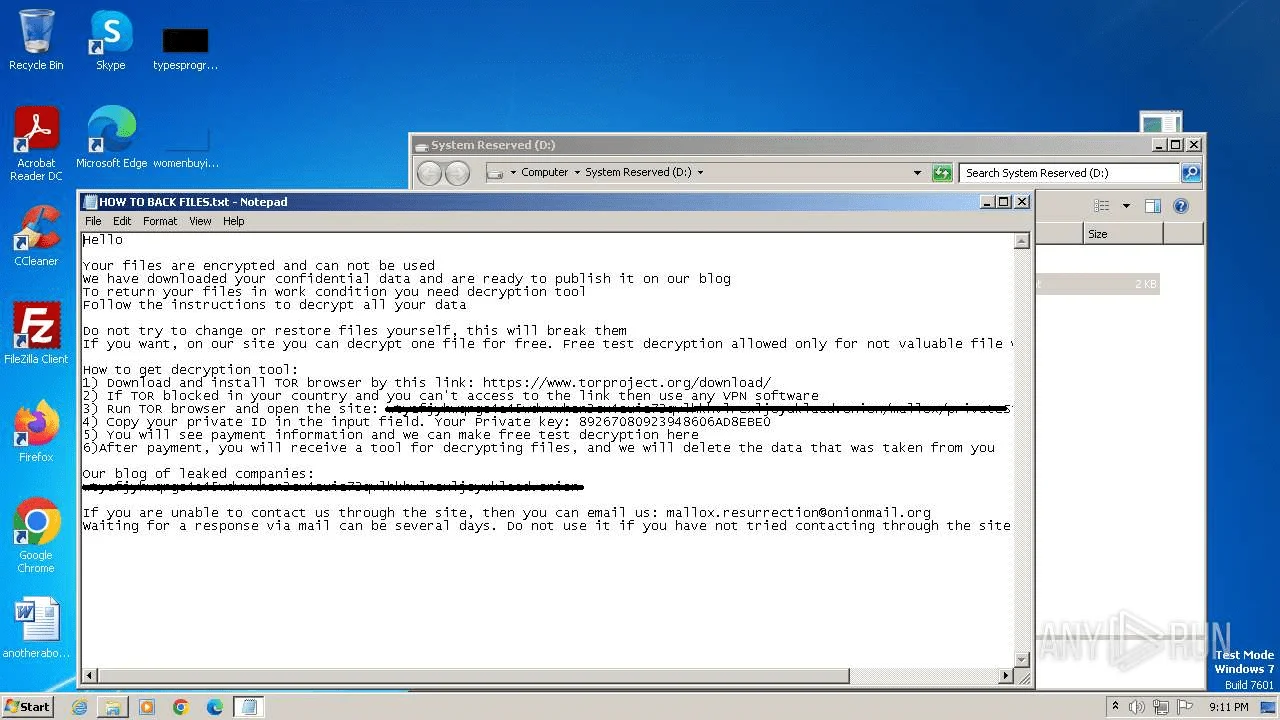
Ransom note delivery, victims are also instructed to install TOR to access their data leak site (Any.run report)
These steps illustrate the systematic and sophisticated approach employed by Mallox Ransomware throughout its attack lifecycle, from initial access to ransom payment facilitation.
Victimology
There are only 42 victims on the currently live leak site of Mallox, which has victims from almost all over the world over the years. These countries in the graph below are portrayed in parallel with their targeting intensity but only according to Mallox’s latest leak site’s index.
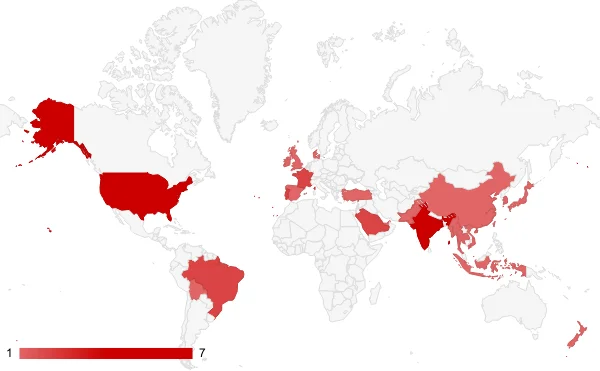
Targeted countries by Mallox as indexed by their data leak site
Mallox, whose hundreds of attacks have been reported over the years, continues to be a detected strain, although it is not as active as before. However, it seems to be one of the candidate groups to fill the gap in the ransomware landscape, especially after the operations carried out against large ransomware operators.
Even though it is certain that there are Russian hackers among the members of the group, we are not sure about calling the group completely Russia-based. Although former USSR countries are not targeted, unlike typical Russian-based ransomware, there is an attack targeting China.
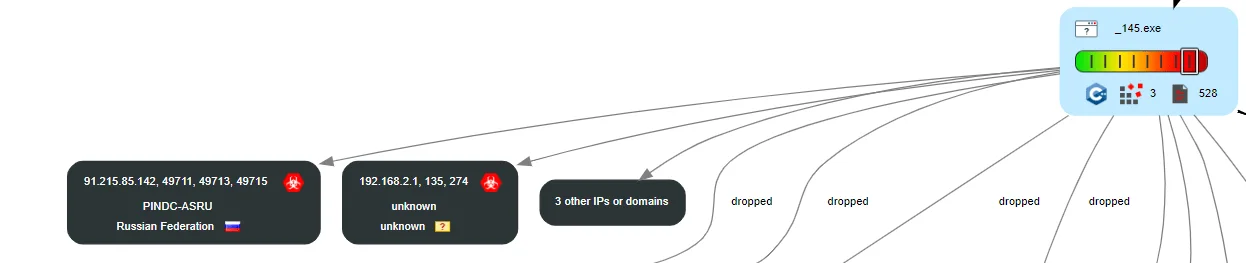
Latest uploaded sample make contact with a Russia-based IP address (JoeSandbox)
Iran is not among the targets, although the group has intensive operations in the Middle East. Therefore, we can say that they are probably a Russia-based ransomware, but there are minor doubts.
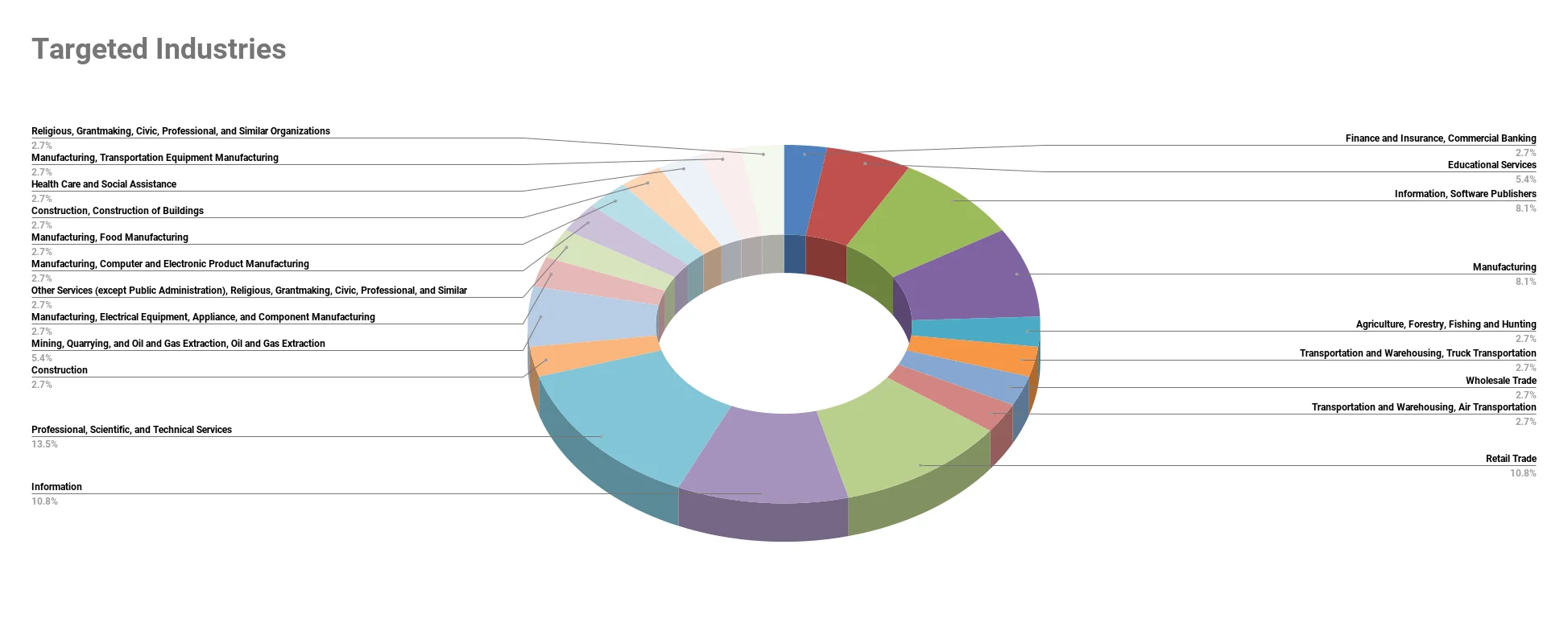
Indexed victim’s associated industries
There is no definitive target for Mallox ransomware, which has victims in almost every sector, but Professional, Scientific and Technical Services, Information, and Retail Trade appear to be the main targeted sectors.

A recent victim listing by Mallox
When you enter an indexed victim’s page on their data leak site, a text introducing the company, revenue, and the size of the leak is written. They upload data leaks to file sharing sites accessible on the clear web. In this example, pixeldrain[.]com is used and the password to access the file is given.
![]()
Uploaded file on pixeldrain[.]com
The uploaded file was viewed only 29 times and downloaded 6 times. While this number rises to thousands even in ransomware groups whose impact is thought to be much smaller, Mallox’s leak had very little impact. While the uploaded file is claimed to be 3+ GB, the .rar version takes up 2 GB and the file was uploaded to the file sharing website 2 hours before it was uploaded to data leak sites.
Mitigation and Prevention Strategies Against Mallox Ransomware
- Employee Education and Awareness:
-
- Conduct regular training sessions to educate employees about the risks associated with ransomware attacks.
- Emphasize the importance of identifying and avoiding phishing emails, malicious attachments, and suspicious links.
- Encourage employees to report any suspicious activity immediately to the IT department.
- Password Security Measures:
-
- Implement a policy for strong and unique passwords for all user accounts.
- Enforce regular password updates and rotations.
- Ensure passwords are at least 8 characters long and include a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
-
- Enable MFA for all user accounts to add an extra layer of security.
- Utilize reliable authentication methods such as mobile apps (e.g., Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator), physical tokens, or smart cards.
- Regular System Updates and Patching:
-
- Establish a routine schedule for updating and patching all systems, including operating systems, applications, and firmware.
- Disable unnecessary or unused services and protocols to minimize vulnerabilities.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery (BDR) Plan:
-
- Implement a robust backup and disaster recovery plan.
- Conduct regular backups of all critical data and systems and store them securely in an offsite location.
- Test backups periodically to ensure they can be restored quickly and effectively in case of a ransomware attack.
- Incident Response Plan (IRP) and Incident Response Retainer (IRR):
-
- Develop a comprehensive IRP that outlines steps to be taken in the event of a ransomware attack.
- Consider having an IRR with a trusted team of professionals available 24/7/365 to handle immediate actions, prevent data loss, reduce ransom payments, and address legal liabilities.
- Immediate Actions During a Ransomware Attack:
-
- Isolate infected computers by disconnecting them from the internet and removing connected devices.
- Contact local authorities (e.g., FBI field office, Internet Crime Complaint Centre) and provide necessary information such as ransom note screenshots, communications with attackers, and encrypted file samples.
- Avoid restarting or shutting down systems to preserve evidence for digital forensics and investigation.
- Engage Ransomware Removal and Recovery Professionals:
-
- If an IRP or IRR is not available, contact reputable ransomware removal and recovery professionals immediately.
- Do not attempt to delete the ransomware or tamper with evidence, as it is crucial for investigation and identifying the attackers.
- Post-Attack Actions:
-
- Identify the ransomware infection and gather information about its type and IOCs for further analysis.
- Work with cybersecurity experts to remove the ransomware, eliminate exploit kits, and patch vulnerabilities to prevent future attacks.
- Restore data from backups and utilize data recovery services if necessary, avoiding ransom payments as they do not guarantee data retrieval.
- Preventive Measures:
-
- Install and regularly update antivirus/anti-malware software.
- Employ reliable cybersecurity solutions, including firewalls and intrusion detection systems.
- Maintain strong and secure passwords, and avoid using default credentials.
- Keep software, applications, and operating systems up to date with the latest patches and security updates.
- Conduct regular backups and test restoration processes.
- Educate employees continuously on cybersecurity best practices and threat awareness.
By implementing these strategies, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of Mallox ransomware attacks and enhance overall cybersecurity resilience.
How Can SOCRadar Help?
SOCRadar presents a formidable defense against the Mallox ransomware threat. Our proactive threat monitoring and intelligence solutions are tailored to enhance your organization’s security stance. With our platform, you can actively track and analyze specific threat actors, gaining deep insights into their tactics, targeted vulnerabilities, affiliations, and indicators of compromise. This proactive approach empowers you to anticipate and counter potential threats effectively, safeguarding your valuable assets.
SOCRadar, Attack Surface Management Module with Ransomware Check function
Furthermore, our Attack Surface Management module, equipped with the Ransomware Check function, offers continuous monitoring of all potential attack vectors. This ensures that you receive real-time alerts regarding any suspicious activities related to ransomware. By staying ahead of threats, you can swiftly respond and fortify your cybersecurity defenses, mitigating the risk posed by Mallox ransomware and other emerging threats.
MITRE ATT&CK Tactics and Techniques
| Tactics | Techniques |
| Initial Access | T1566.002 – Spearphishing Link |
| T1190 – Exploit Public-Facing Application | |
| T1078 – Valid Accounts | |
| T1110 – Brute Force | |
| Execution | T1059.003 – Windows Command Shell |
| T1059.001 – PowerShell | |
| Defense Evasion | T1027.001 – Binary Padding |
| T1112 – Modify Registry | |
| T1036.005 – Match Legitimate Name or Location | |
| T1070.004 – File Deletion | |
| T1620 – Reflective Code Loading | |
| Discovery | T1016.001 – Internet Connection Discovery |
| T1082 – System Information Discovery | |
| T1012 – Query Registry | |
| T1049 – System Network Connections Discovery | |
| Exfiltration | T1537 – Transfer Data to Cloud Account |
| T1020 – Automated Exfiltration | |
| T1029 – Scheduled Transfer | |
| T1041 – Exfiltration Over C2 Channel | |
| T1567 – Exfiltration Over Web Service | |
| Impact | T1489 – Service Stop |
| T1490 – Inhibit System Recovery | |
| T1486 – Data Encrypted for Impact | |
| Persistence | T1547.009 – Shortcut Modification |
| T1547.001 – Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder | |
| Privilege Escalation | T1078 – Valid Accounts |
| T1547.001 – Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder |
Latest IoCs for Mallox Ransomware in SOCRadar Platform
| Type | Value | Date |
| IP | 203.154.255.114 | 2024-02-16 |
| IP | 195.3.146.183 | 2024-02-16 |
| IP | 80.66.75.66 | 2024-02-16 |
| IP | 91.215.85.142 | 2024-02-16 |
| HASH | 88eef50d85157f2e0552aab07cac7e7ec21680f5 | 2023-12-18 |
| HASH | a8886c9417b648944d2afd6b6c4941588d670e3c | 2023-12-18 |
| HASH | 9d182e17f88e26cb0928e8d07d6544c2d17e99f5 | 2023-12-18 |
| HASH | 60784ab7fec3f23066a996f3347b721a09eb677b63dbc5e1bb2bfc920fa3f13d | 2023-12-18 |
| HASH | 5d9cc0bc652b1d21858d2e4ddd35303cd9aeb2a3 | 2023-12-18 |
| HASH | 0e45e8a5b25c756f743445f0317c6352d3c8040a | 2023-12-18 |
| HASH | db3fd39fc826e87fa70840e86d5c12eef0fe0566 | 2023-12-18 |
| HASH | 2a6f632ab771e7da8c551111e2df786979fd895d | 2023-12-18 |
| HASH | 643918830b87691422d6d7bd669c408679411303 | 2023-12-18 |
| HASH | 246e7f798c3bfba81639384a58fa94174a08be80 | 2023-12-18 |
| HASH | b8bd3cc96bfea60525d611e38b4de30c59d82d1df54a873fc9998533945063ff | 2023-12-18 |
| HASH | b7a5068f9d696d6767bfddaea222649ff3541af306f93bce23c0aa6edd892534 | 2023-12-18 |
| HASH | fa450286a4aa25579c8da7684051e7cdda3ba249ff03da71689e5138fd9f5c73 | 2023-12-18 |
| HASH | 64e560f40df031149c745ecaf44ce379aa44373d80a0ee3c4bd0abf7955df88e | 2023-12-18 |
| HASH | 142f2b232fa96e71379894d1bb6cb242c0f33886c1802922163901e70fdc3320 | 2023-12-18 |
| HASH | 9b24ee3dd5f50e65ea15aaa3946e76281c4f9d519524dc659f2bcdfb62241316 | 2023-12-18 |
| HASH | 3fa79012dfdac626a19017ed6974316df13bc6ff | 2023-12-18 |
| HASH | 273e40d0925af9ad6ca6d1c6a9d8e669a3bdc376 | 2023-12-18 |
| HASH | 33c24486f41c3948fbd761e6f55210807af59a1f | 2023-12-18 |
| HASH | 5d0b9521cca0c911d49162e7f416a1463fbaefae | 2023-12-18 |
| HOSTNAME | updt.ps | 2023-12-18 |
| HASH | fb05a6fafc28194d011a909d946b3efa64cdb4cf | 2023-12-18 |
| HASH | ee15c76e07051c10059a14e03d18a6358966e290 | 2023-12-18 |
| HASH | 11d7779e77531eb27831e65c32798405746ccea1 | 2023-12-18 |
| HASH | df29d5c4a750663440ce76d6804ce88e03faeef9591ec0b3b9ca348a6c930b7f | 2023-11-06 |
| HASH | ba1d4e9366de6b9a16fb2ef143d66b3d | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | be3537fdcf8dc04150a3ae4ad6daf9f7 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | b6c220e70880dfefdba9decd189f5a42 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | c3c590f44df548ce324bfdaac6ec33a6 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | c447bbb8f60df97e6e4bd5d8c68728ed | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | be971d880e75cd48a669ea9e45f6f022 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | b1b42fa300d8f43c6deb98754caf0934 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 992efe1fbf140f13f22f3094e867277d | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 99bfaaacebf1b34fdebd4e7ce4070a36 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 98184e867f9eb64612ce3797c259efb5 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | a5328247106299a6ac54794c345a0380 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 86424c9f1797d280c0fe30ab813eb1da | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 7f144e43bd054a6e6ca7294d31274d85 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 74156c103d01abd8d9963c6032c1bb83 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 6ea65106bdd4ab1148028f83956336d1 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 6845db47108d6324b9fcad6707cfcff6 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 67fd732ee69588cb09b316346bc61ee1 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 6707a7a43ffa0c0e8743bed3ea2c13ef | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 6290ac7c78fdadb4e8ea5bed199ace9b | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | a57ea2a7451b3a071617031c19bebcf5 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 9df3e8466b99e4e6ef640d1296975e90 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 94547b455c5926ab4e3104371a4448a4 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | b1b42fa300d8f43c6deb98754caf0934 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | b6c220e70880dfefdba9decd189f5a42 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | aead1b9f42f5abc33901dde0a89ed70f | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | be3537fdcf8dc04150a3ae4ad6daf9f7 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | be971d880e75cd48a669ea9e45f6f022 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | ba1d4e9366de6b9a16fb2ef143d66b3d | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | ab56a34389bd5444a16d7979dfad76f0 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 8c1a1dce9fbaec99a4587fd758c11aed | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 5403c42e93344acfeb24875af453fef1 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | ebf81ebf55d6387f97e5cd7aff1a7f90 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 98184e867f9eb64612ce3797c259efb5 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 7f144e43bd054a6e6ca7294d31274d85 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | a5328247106299a6ac54794c345a0380 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | aead1b9f42f5abc33901dde0a89ed70f | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 9df3e8466b99e4e6ef640d1296975e90 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 94547b455c5926ab4e3104371a4448a4 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 8c1a1dce9fbaec99a4587fd758c11aed | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 6e0ff5cdd9085463451709a8e462470f | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 6bd93817967cdb61e0d7951382390fa0 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 67fd732ee69588cb09b316346bc61ee1 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 67296fcb1243fc10145bf137e4c379c5 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 5e45cb878abb96168f90c0efa96475c3 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | cb1ba70812eda56152bd1e2186acabe9 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 2f82436e491b17c67a3ea0419f0b61de | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 23b7b0e6737283bdd1b75f61990adbdb | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | e39bf90a383548311753a116c346b47a0d63ad9d | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 930b5fe5ceeffd3c84be48932b8c94ae4760da5b | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 60212fddfb3d5ed6b7bdc0ee08aa6e98faed2a8c | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | e135c9c231bc82dcc7d4aa90616e8caa | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 358d3a87ed243e4c9e95e41525d8a839 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 1b30d16d3e632130ced6dc8b403d4275 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 0c8aa6e8c22fa6a6ee5d575ac336994c08451d6b | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 43b24f5108ff16c56e836082da80128fe516d8af | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 4791db1e3ba5215a8eec0c9c913e56512d6e64f8 | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 3d434b7cc9589c43d986bf0e1cadb956391b5f9a | 2023-11-04 |
| HASH | 4d54af1bbf7357964db5d5be67523a7c | 2023-11-04 |




































