
How to Utilize Attack Surface Management and Vulnerability Intelligence for ‘Vulnerability Mapping’
The concept of vulnerability is a persistent shadow that haunts the digital realm; it is an element that opens the door to a potential breach, compromising the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of a system. It resembles a crack in the digital armor, an Achilles’ heel that cyber adversaries seek to exploit. Identifying and addressing vulnerabilities are critical in maintaining the security of systems and data, and this is where the concept of ‘vulnerability mapping’ enters the scene.
In this article, we will explore the concept of vulnerability mapping in-depth, shedding light on its importance and how you can utilize Attack Surface Management (ASM) and Vulnerability Intelligence of SOCRadar XTI for vulnerability mapping.
By the end of this journey, you will have a clearer understanding of how to navigate the ever-present shadows of security vulnerabilities and fortify your digital fortress.
What is Vulnerability Mapping and Why is it Important?
Vulnerability mapping is akin to reconnaissance during a digital intrusion, representing the second phase of the attack cycle, following information gathering. It is the process of systematically charting and cataloging the weaknesses and gaps within a system. Vulnerabilities can manifest in a myriad of forms, making it essential to have a comprehensive understanding of each category.
However, the digital landscape is far from static. Unit 42, in a recent research, revealed a dynamic reality where over 45% of an organization’s high-risk, cloud-hosted exposures in a given month appear on new services not present in the previous month. This ever-changing attack surface poses a challenge in prioritizing vulnerabilities effectively.
Poor vulnerability and attack surface management can have grave consequences without a proper way to comprehensively map vulnerabilities throughout your digital assets. This includes an increased risk of data breaches, ransomware, and various other cyber threats, even potentially leading to supply chain compromises.
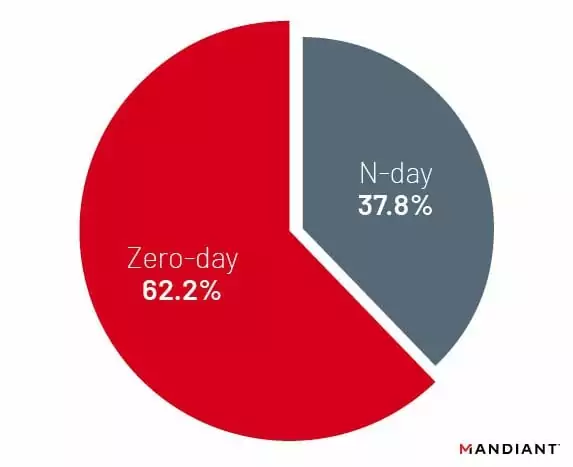
The importance of attack surface management becomes evident when considering the historical trends. While zero-day vulnerabilities have outpaced N-day vulnerabilities, N-day vulnerabilities – vulnerabilities that are first exploited after patches were released – are typically exploited for longer periods of time. Attack surface management plays a crucial role in protecting your assets against these identified vulnerabilities.
Mandiant’s analysis of 246 vulnerabilities disclosed in 2021 and 2022, tracked as exploited in the wild, highlights the significance. Among these vulnerabilities, 153 were exploited as zero-days, compared to 93 vulnerabilities first exploited as N-days.
When zero-day attacks commence, vendors swiftly develop patches to address identified vulnerabilities. Once a patch or update is available, the exploit loses its effectiveness, marking the end of the ‘zero-day’ threat. However, as many users do not patch immediately, the vulnerability persists, granting threat actors a window for vulnerability mapping to exploit unpatched systems and devices ahead of organizations; in such cases, ASM emerges as a critical line of defense.
To better comprehend the significance of vulnerability mapping, let’s delve into an example. Envision a scenario in which an attacker aims to compromise a target system. During the initial stages of reconnaissance, the attacker identifies that a server is running on version X. This is when vulnerability mapping takes center stage.
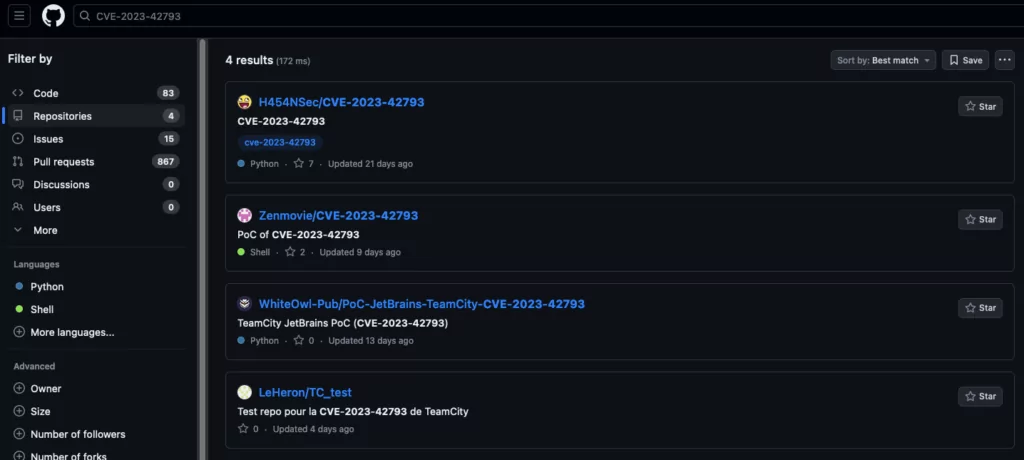
With the version information in hand, the attacker can leverage open resources on the internet to discover vulnerabilities associated with the targeted version, and even access readily available Proof-of-Concept exploits (PoCs) for those identified vulnerabilities within various online communities.
Microsoft’s 2022 Digital Defense Report emphasizes that hackers often outpace security teams in developing exploits, typically making them available within just 14 days of a vulnerability’s disclosure.
Mandiant’s findings shed light on the timing of exploitation. It is most likely to occur within the first month following the initial patch. Additionally, for vulnerabilities disclosed in 2021 and 2022, 51 percent eventually had publicly available code, with 54 percent of those featuring code on the same day as the first known exploitation or before. A compelling trend emerges when comparing vulnerabilities with and without exploit code. Among those with exploit code, 41 percent were first exploited as zero-days. In contrast, 84 percent of vulnerabilities without available code were exploited as zero-days. This underscores that while most actors exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities do not rely on public exploit code, the availability of code slightly increases the likelihood of post-patch exploitation.

The attacker then proceeds to perform banner grabbing, collecting information about the target server, including its software, service, and configuration details. Once armed with a clear understanding of the target’s specifics, the attack process becomes streamlined, and the likelihood of a successful breach increases.
In the dynamic landscape of digital threats, where attackers act swiftly, prioritizing exploitable vulnerabilities in patch management efforts is essential. This is where SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence module, accompanied by the SOCRadar Vulnerability Risk Score (SVRS), proves invaluable. The SVRS helps gain a better understanding of which vulnerabilities demand immediate action, as it rates vulnerabilities from 0 to 100 by their susceptibility to exploitation, utilizing data from diverse sources such as social media, news, and the dark web. The module simplifies the prioritization of actions and patch management while seamlessly aligning with vulnerability mapping’s mission to efficiently identify security risks, contributing to a robust cybersecurity strategy.
In summary, vulnerability mapping provides malicious actors with a means to efficiently and precisely identify and exploit vulnerabilities. Meanwhile, it also plays a pivotal role in cybersecurity, offering a structured, efficient, and a rather simplified approach to assessing and addressing security risks. It serves as an early warning system, allowing organizations to:
- Identify threats and weaknesses in their IT security infrastructure.
- Take prompt remediation actions to safeguard sensitive systems and data.
- Ensure compliance with cybersecurity regulations.
- Prioritize resource allocation by focusing on the most critical vulnerabilities, especially exploitable ones.
- Make informed decisions about risk acceptance and mitigation.
- Contribute to overall risk analysis and management, ensuring a proactive defense against potential cyber threats.
Once vulnerabilities are identified through mapping, the next logical step is to develop attack vectors based on the findings. This is where cybersecurity experts, ethical hackers, and threat analysts come into play, using this information to enhance security measures and mitigate risks.
How Can ASM and Vulnerability Intelligence Help in Vulnerability Mapping?
SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) and Vulnerability Intelligence modules can significantly aid in vulnerability mapping by providing a holistic view of an organization’s digital assets, identifying emerging threats, and offering comprehensive information about vulnerabilities.
Here is a guide on how you can effectively harness these modules in vulnerability mapping and what you can access with each module:
With Attack Surface Management:
- Digital Asset Discovery: The ASM module can automatically discover and catalog an organization’s digital assets, including web applications, services, and network resources. This asset inventory is a critical first step in vulnerability mapping, as it establishes a foundation for understanding what needs to be protected.
- Real-time Monitoring: ASM continuously monitors the organization’s digital footprint, identifying changes and new assets. This is essential for keeping the vulnerability map up to date as new assets are added and old ones are decommissioned or modified.
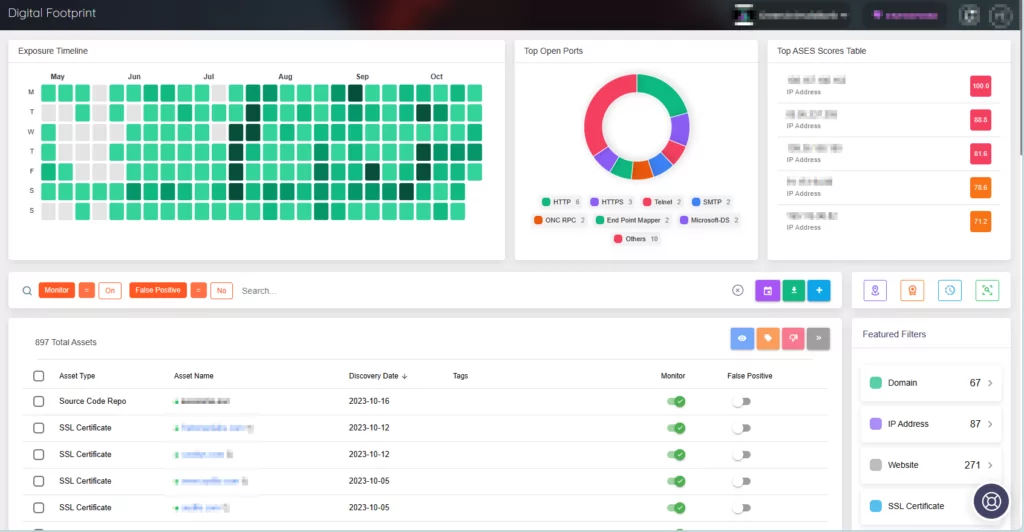
- Threat Tracking: ASM also tracks emerging security threats that could affect the organization’s assets. When new vulnerabilities are discovered, or when existing assets become exposed to new risks, this information is crucial for prioritizing which vulnerabilities should be addressed first.
Through ASM, you can also check if a vulnerability has been included in CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog or exploited in ransomware operations. CISA has also recently included a label to specify vulnerabilities exploited by ransomware attacks in its KEV catalog, aligning with the purpose of our previously introduced ransomware check feature.
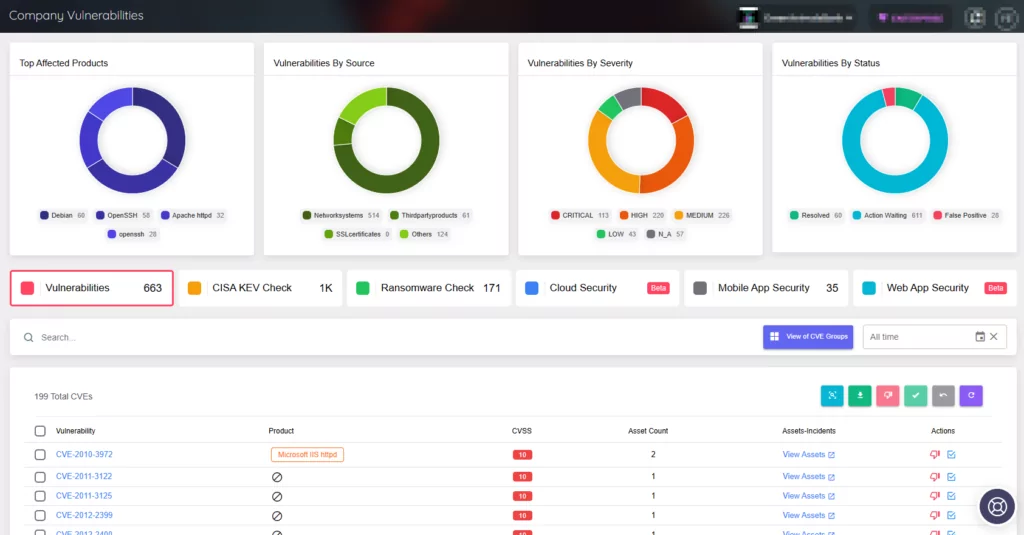
With Vulnerability Intelligence:
- Comprehensive Vulnerability Information: The Vulnerability Intelligence module provides detailed and up-to-date information about known vulnerabilities, including their severity, potential impact, exploit activity, and available patches or mitigations. This information is invaluable for assessing the risk associated with each vulnerability.
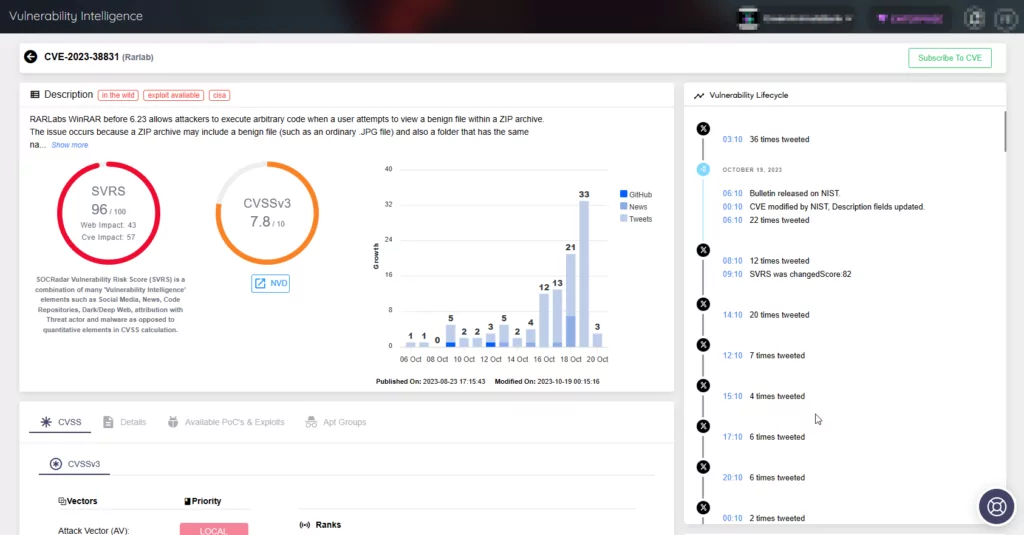
- Likelihood of Exploitation: On the platform, the vulnerability cards also include the SOCRadar Vulnerability Risk Score (SVRS). SVRS combines various elements from Vulnerability Intelligence, including data from social media, news, code repositories, the dark/deep web, attribution with threat actors, and malware. This approach differs from the quantitative elements used in CVSS calculations; SVRS enables organizations to attain a more accurate assessment of a vulnerability’s severity and its likelihood of exploitation.
Combining ASM and Vulnerability Intelligence:
- Risk Assessment and Prioritization: By combining the asset information from the ASM module with vulnerability data from the Vulnerability Intelligence module, organizations can assess the specific vulnerabilities that affect their assets. This enables organizations to create a risk profile based on factors like asset criticality, potential impact, and the availability of patches, allowing for the effective prioritization of remediation efforts and ensuring that organizations’ limited resources are allocated to the most critical security issues.
- Alerts and Reporting: With the aid of both modules, SOCRadar provides alerts and reports to organizations, making them aware of newly discovered vulnerabilities or changes in their attack surface. This allows for proactive vulnerability mapping and risk management.
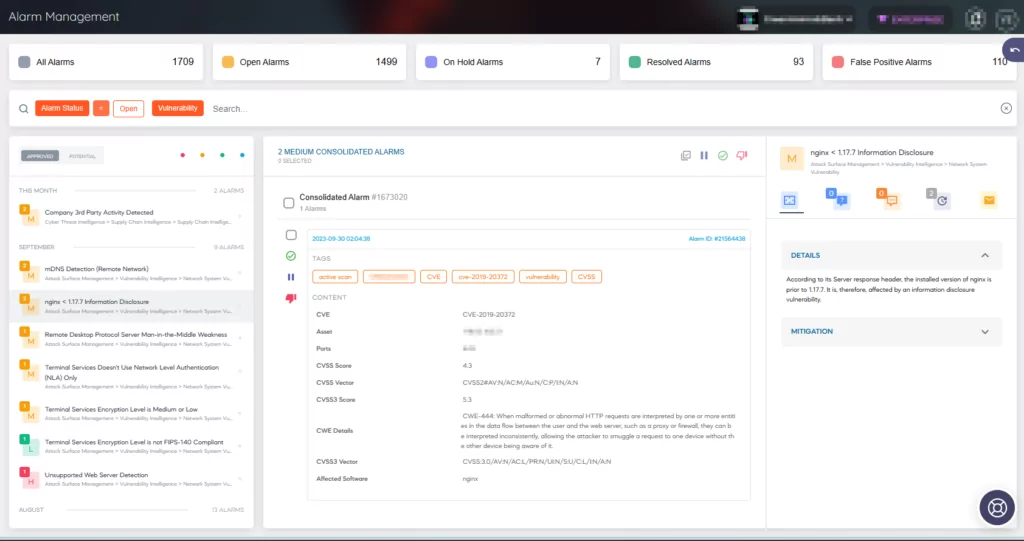
You can also access alarms via the ASM module by clicking on a discovered vulnerability. This action reveals the affected assets and provides direct links to the associated incidents, as shown below:
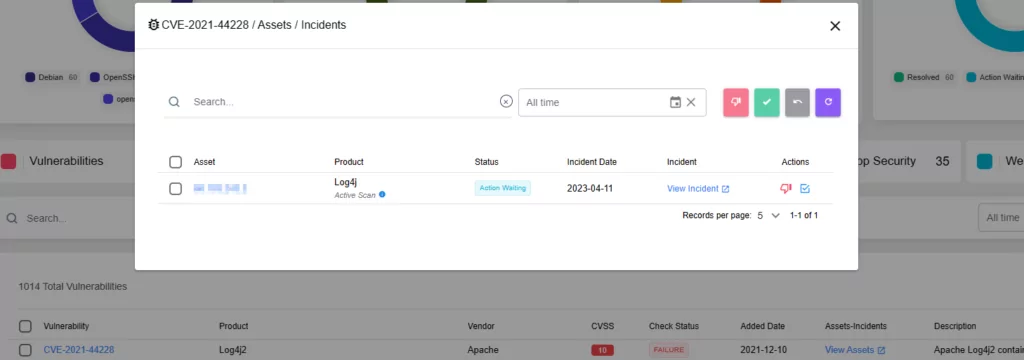
Additionally, when you navigate through the Digital Footprint page and explore assets categorized by type, you can access in-depth information regarding their exposure and open incidents.
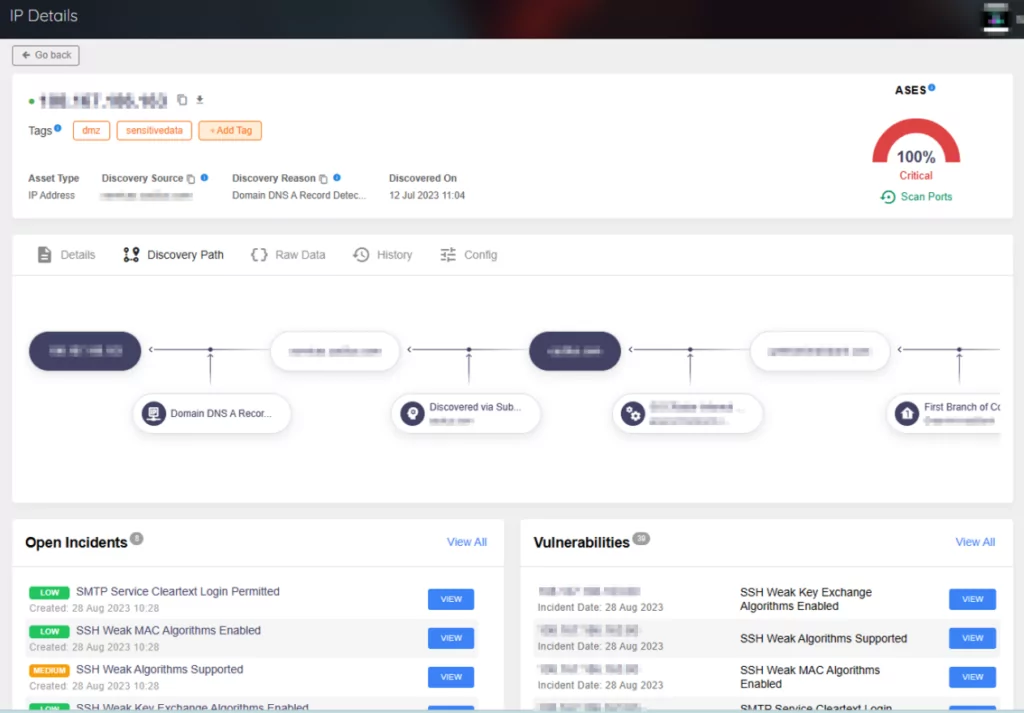
In summary, SOCRadar’s ASM and Vulnerability Intelligence modules work together to help organizations establish a detailed and up-to-date view, not just for vulnerability mapping. They assist in identifying assets, monitoring and prioritizing emerging threats, and providing comprehensive information about vulnerabilities, ultimately enabling organizations to make informed decisions about vulnerability remediation and risk management.
Conclusion
In essence, vulnerability mapping is akin to creating a roadmap through the complex terrain of cybersecurity, guiding organizations and individuals to navigate potential risks proactively.
In a broader context, vulnerability mapping serves as an essential component of risk analysis. It allows organizations and individuals to evaluate and understand the risks associated with their systems based on the vulnerabilities they have identified. This is where ASM and Vulnerability Intelligence become invaluable partners in safeguarding digital assets and fortifying security defenses.
The holistic view, comprehensive information, and risk assessment capabilities provided by ASM and Vulnerability Intelligence solutions, such as SOCRadar’s, empower organizations to proactively address vulnerabilities and stay resilient in the face of evolving digital threats.
Additional References:
- What is Vulnerability Assessment? Definitions & Best… | BeyondTrust
- What Is Vulnerability Assessment? Benefits, Tools, and Process | HackerOne
- Why Mapping Vulnerability is Key to Robust Cybersecurity | TrueFort
- What is a Zero-Day Exploit? | IBM
- What is a zero-day exploit? The most dangerous attacks, explained | PCWorld




































