
January 2025 Patch Tuesday Highlights: 8 Zero-Days, 159 CVEs Fixed; SAP & Fortinet Updates
[Update] January 16, 2025: “Growing Risk from CVE-2024-55591 as FortiGate Exploits Resurface”
Microsoft has released its January 2025 Patch Tuesday updates, delivering critical fixes. This month’s release tackles 159 CVEs, including eight zero-days, three of which are actively exploited. Key products impacted include Windows Telephony Service, Windows Digital Media, and MSMQ, among others.
Notably, the update addresses vulnerabilities across various categories:
- 58 Remote Code Execution (RCE) Vulnerabilities
- 40 Elevation of Privilege (EoP) Vulnerabilities
- 22 Information Disclosure Vulnerabilities
- 20 Denial of Service (DoS) Vulnerabilities
- 14 Security Feature Bypass
- 5 Spoofing Vulnerabilities
The spotlight this month is on RCE vulnerabilities, which make up the largest share, followed closely by EoP vulnerabilities that pose serious risks if exploited.
In this blog, we will explore the specifics of the January 2025 updates, including the most critical vulnerabilities, their potential impact, and the essential patches you need to apply to secure your systems.
Zero-Days in January 2025 Patch Tuesday: 3 Actively Exploited, 5 Disclosed
Microsoft’s January 2025 Patch Tuesday addresses eight zero-day vulnerabilities, with three actively exploited, posing immediate risks. These vulnerabilities impact critical components like Windows Hyper-V, Microsoft Access, Windows App Installer, and Windows Themes. The actively exploited zero-days are particularly concerning, enabling privilege escalation and potentially compromising systems.
Below, we provide an overview of the disclosed and exploited zero-days to help organizations understand the risks and prioritize updates.
Zero-Day Vulnerabilities in Windows Hyper-V Exploited for Privilege Escalation
Windows Hyper-V NT Kernel Integration VSP Elevation of Privilege Vulnerabilities – CVE-2025-21333 , CVE-2025-21334, CVE-2025-21335 (CVSS 7.8)
These three vulnerabilities affect the Hyper-V Virtualization Service Provider (VSP) component, which facilitates communication between the Hyper-V hypervisor and the Windows NT kernel. Exploitation of these flaws allows attackers to escalate privileges to SYSTEM on a vulnerable host.
Notably, Microsoft has confirmed active exploitation of all three vulnerabilities, underscoring the urgency for patching systems running Hyper-V.
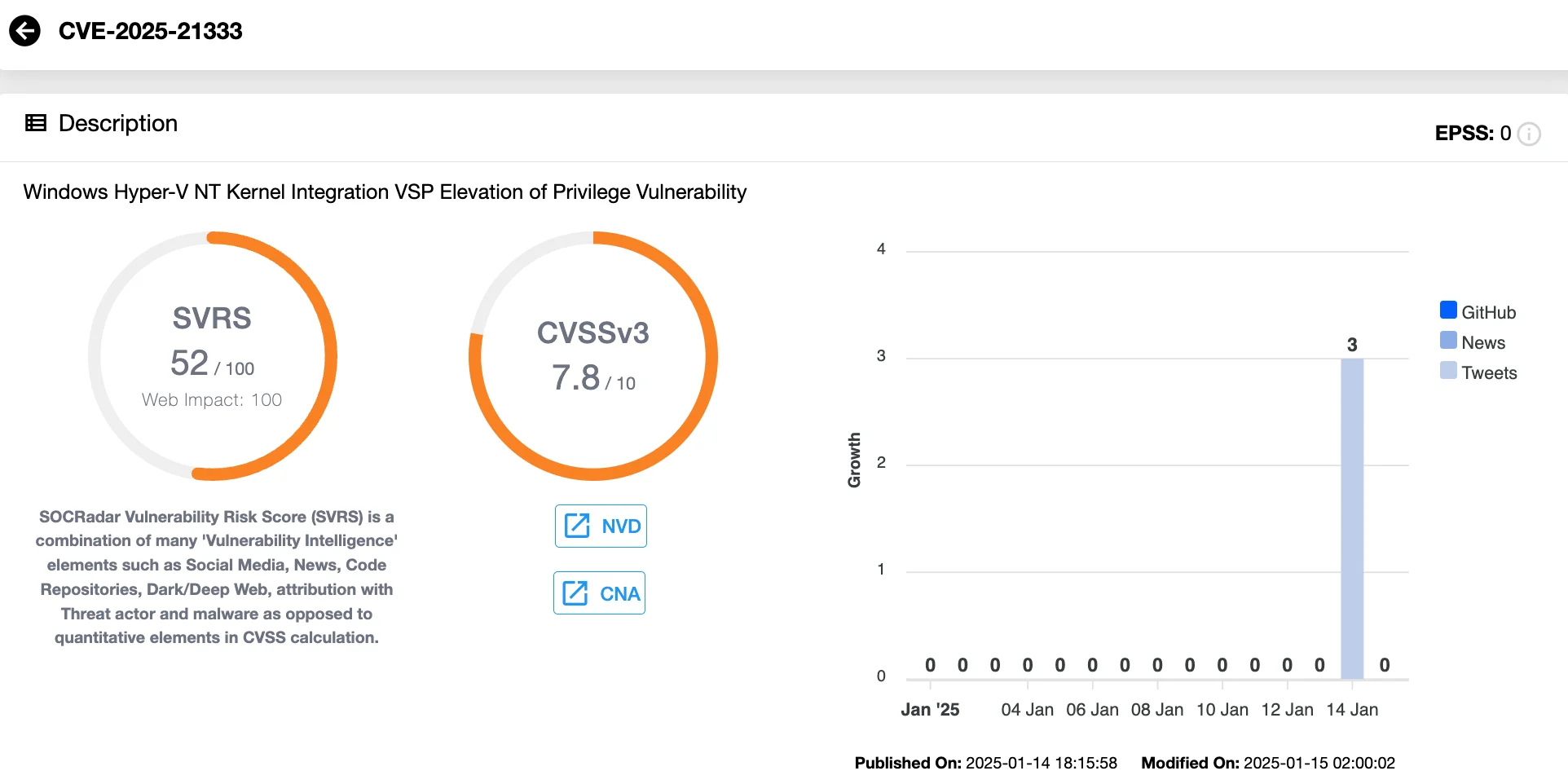
Vulnerability card of CVE-2025-21333 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Disclosed Zero-Days in Microsoft Access, Windows App Package Installer, Windows Themes
Microsoft Access Remote Code Execution Vulnerabilities – CVE-2025-21366, CVE-2025-21395, CVE-2025-21186 (CVSS 7.8)
These vulnerabilities in Microsoft Access, the company’s database management system, could allow attackers to execute malicious code. To mitigate risks, Microsoft has restricted access to potentially dangerous file extensions such as .accdb, .accde, .accdw, .accdt, .accda, .accdr, .accdu.
Although exploitation of these flaws is deemed less likely, organizations should apply patches to eliminate risks.
Windows App Package Installer Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability – CVE-2025-21275 (CVSS 7.8)
This vulnerability in the Windows App Package Installer could grant SYSTEM privileges to attackers who successfully exploit it. While exploitation is considered less likely, the potential for privilege escalation makes this an important vulnerability to address.
Windows Themes Spoofing Vulnerability – CVE-2025-21308 (CVSS 6.5)
As a spoofing vulnerability in Windows Themes, it could lead to the exposure of sensitive information if a user is tricked into loading a malicious file. The vulnerability could also leak NTLM hashes if proper security settings are not in place. Organizations are advised to restrict NTLM traffic to mitigate this risk.
Critical Vulnerabilities Addressed in January 2025 Patch Tuesday
Microsoft’s January 2025 Patch Tuesday updates address several critical vulnerabilities, categorized as high severity based on their potential impact. These vulnerabilities span across multiple Microsoft products and could lead to Remote Code Execution (RCE), privilege escalation, or information disclosure if exploited.
Remote Code Execution (RCE) Vulnerabilities
- CVE-2025-21298 (CVSS 9.8) – Windows OLE Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
An attacker could exploit CVE-2025-21298 by sending a specially crafted email to a victim using an affected version of Microsoft Outlook. The attack could be triggered either by the victim opening the email or by Outlook displaying a preview, potentially allowing the attacker to execute remote code on the victim’s machine.
- CVE-2025-21307 (CVSS 9.8) – Windows Reliable Multicast Transport Driver (RMCAST) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
An unauthenticated attacker could exploit CVE-2025-21307 by sending specially crafted packets to a Windows PGM open socket on the server, requiring no user interaction.
- CVE-2025-21362 (CVSS 8.4) – Microsoft Excel Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
- CVE-2025-21354 (CVSS 8.4) – Microsoft Excel Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
- CVE-2025-21309 (CVSS 8.1) – Windows Remote Desktop Services Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
- CVE-2025-21297 (CVSS 8.1) – Windows Remote Desktop Services Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
- CVE-2025-21295 (CVSS 8.1) – SPNEGO Extended Negotiation (NEGOEX) Security Mechanism Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
- CVE-2025-21296 (CVSS 7.5) – BranchCache Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
Information Disclosure Vulnerabilities
- CVE-2025-21380 (CVSS 8.8) – Azure Marketplace SaaS Resources Information Disclosure Vulnerability
- CVE-2025-21385 (CVSS 8.8) – Microsoft Purview Information Disclosure Vulnerability
Elevation of Privilege Vulnerabilities
- CVE-2025-21311 (CVSS 9.8) – Windows NTLM V1 Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
This critical vulnerability allows attackers to easily escalate privileges, granting unauthorized access to sensitive data and critical resources. With low attack complexity and high reliability, it enables repeatable exploitation of the vulnerable component with minimal effort, posing a severe security risk.
Proactively Secure Your Systems with SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence
In a world where zero-day vulnerabilities and evolving threats are constant challenges, organizations must make sure to protect their critical assets. Vulnerabilities like those addressed in the January 2025 Patch Tuesday can be exploited quickly, leaving unpatched systems exposed to significant risks.
SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence provides real-time insights into newly discovered vulnerabilities, their potential impacts, and actionable mitigation strategies. It helps you prioritize threats based on severity and exploitability, ensuring your security team focuses on what matters most.
Discover the latest vulnerabilities, access detailed insights and updates (Vulnerability Intelligence module)
With advanced data analysis and contextual threat intelligence, SOCRadar identifies vulnerabilities relevant to your environment. Automated alerts keep you informed, while detailed reports help you understand risks and act decisively. Stay ahead of attackers by integrating SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence into your security strategy.
Trouble Installing January Windows Updates? Citrix SRA Could Be the Cause
With the January 2025 Patch Tuesday updates, Microsoft also released cumulative updates for Windows 11 and Windows 10, including KB5050009 and KB5049981. However, these specific updates may fail to install if the users’ devices are running Citrix Session Recording Agent (SRA).
According to reports, the problem arises because the update cannot modify specific drivers while SRA is running. Microsoft points out that this issue is exclusive to organizations using Citrix SRA version 2411, and it does not affect home users.
Citrix provided an interim fix to the issue:
- Prior to installing the updates, stop the Session Recording Monitoring Service.
- After the updates have been successfully installed, re-enable the service.
Consult Citrix’s official support article for further instructions. For now, impacted organizations are advised to use the workaround while Microsoft and Citrix work together to develop a final solution.
Vulnerabilities More Likely to Be Exploited
Beyond the zero-day and critical vulnerabilities addressed this month, Microsoft has flagged additional vulnerabilities as more likely to be exploited. This includes some critical vulnerabilities already mentioned, such as CVE-2025-21298, CVE-2025-21362, CVE-2025-21354, and CVE-2025-21309. Below is the full list of these high-risk vulnerabilities from the January 2025 Patch Tuesday update:
- CVE-2025-21298 (CVSS 9.8) – Windows OLE
- CVE-2025-21292 (CVSS 8.8) – Microsoft Windows Search Component
- CVE-2025-21309 (CVSS 8.1) – Windows Remote Desktop Services
- CVE-2025-21354 (CVSS 7.8) – Microsoft Office Excel
- CVE-2025-21362 (CVSS 7.8) – Microsoft Office Excel
- CVE-2025-21364 (CVSS 7.8) – Microsoft Office Excel
- CVE-2025-21365 (CVSS 7.8) – Microsoft Office
- CVE-2025-21315 (CVSS 7.8) – Microsoft Brokering File System
- CVE-2025-21299 (CVSS 7.1) – Windows Kerberos
- CVE-2025-21314 (CVSS 6.5) – Windows SmartScreen
- CVE-2025-21189 (CVSS 4.3) – Windows MapUrlToZone
- CVE-2025-21219 (CVSS 4.3) – Windows MapUrlToZone
- CVE-2025-21268 (CVSS 4.3) – Windows MapUrlToZone
- CVE-2025-21269 (CVSS 4.3) – Windows MapUrlToZone
- CVE-2025-21328 (CVSS 4.3) – Windows MapUrlToZone
- CVE-2025-21329 (CVSS 4.3) – Windows MapUrlToZone
- CVE-2025-21210 (CVSS 4.2) – Windows Virtual Trusted Platform Module
Timely patching of these vulnerabilities is critical to mitigate the risks associated with potential exploitation. Make sure your systems are updated without delay.
For a detailed overview of the vulnerabilities addressed this month, refer to Microsoft’s Release Note.
Updates Beyond Microsoft: SAP and Fortinet Address Critical Vulnerabilities
In addition to Microsoft’s Patch Tuesday updates, other vendors, including SAP and Fortinet, have released critical security updates addressing vulnerabilities that demand immediate attention.
SAP’s January 2025 Security Updates
SAP’s Security Patch Day for January includes 14 new Security Notes, two of which are marked critical:
- Security Note #3537476 – CVE-2025-0070 (CVSS 9.9) – Improper Authentication in SAP NetWeaver ABAP Server and ABAP Platform.
- Security Note #3550708 – CVE-2025-0066 (CVSS 9.9) – Information Disclosure in SAP NetWeaver AS for ABAP and ABAP Platform (Internet Communication Framework).
Organizations using affected SAP products are urged to apply these patches immediately to address potential exploitation risks. For a full list of addressed SAP vulnerabilities, refer to their official Security Notes page.
Fortinet Zero-Day Under Exploitation: CVE-2024-55591
Fortinet addressed several critical vulnerabilities, including CVE-2024-55591 (CVSS 9.6), a zero-day authentication bypass flaw actively exploited to compromise firewalls and enterprise networks.
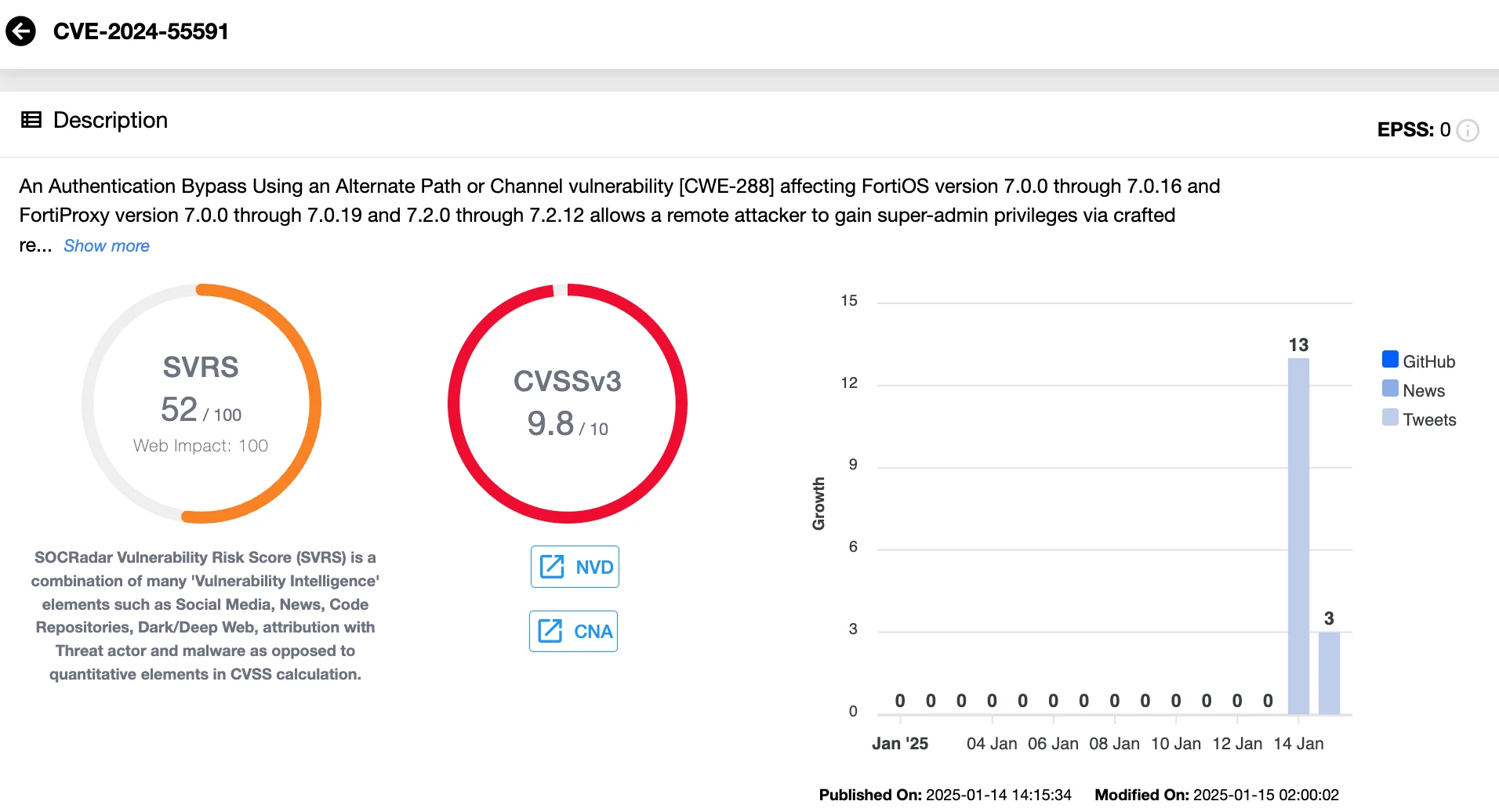
Vulnerability card of CVE-2025-55591 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
This vulnerability impacts FortiOS (versions 7.0.0 to 7.0.16), FortiProxy (versions 7.0.0 to 7.0.19), and other related products. Exploitation enables attackers to gain super-admin privileges and modify firewall configurations, add rogue user accounts, and breach internal networks via SSL VPNs.
Researchers detailed the timeline of the mass exploitation campaign, highlighting phases that began with vulnerability scanning in mid-November 2024, followed by reconnaissance, SSL VPN configuration, and ultimately lateral movement through compromised networks in December.
The campaign detailed by researchers is linked to Fortinet’s recently disclosed zero-day vulnerability (CVE-2024-55591) based on matching Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) and similar tactics observed across affected systems.
Fortinet also patched another critical vulnerability, CVE-2023-37936 (CVSS 9.6), an RCE flaw in FortiSwitch caused by hardcoded cryptographic keys. Immediate updates are recommended to mitigate these risks.
For the latest Fortinet advisories and patches, visit their PSIRT page.
Growing Risk from CVE-2024-55591 as FortiGate Exploits Resurface
CVE-2024-55591 has gained significant attention, with increased discussions on platforms like Telegram, signaling growing interest from potential attackers. According to SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence module, the timeline for this vulnerability shows a notable rise in discussions, indicating that it could become a target for cybercriminals.

Lifecycle information for CVE-2024-55591 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Additionally, in response to the vulnerability, researchers have developed a detection script available on GitHub. The script attempts to establish a WebSocket connection from a pre-authenticated perspective to the FortiOS management interface, checking for signs of exploitation by reviewing the system’s response.
Recent dark web activity further raises alarms as a threat actor named ‘Belsen Group’ leaked configurations from over 15,000 compromised devices. This breach, tied to CVE-2022-40684 (a previous FortiGate vulnerability), exposed sensitive data like usernames and VPN credentials, highlighting the risk of unpatched systems. Despite patches, many organizations remain vulnerable.
The discovery of CVE-2024-55591 reiterates the ongoing risks with Fortinet devices, as threat actors may exploit this new vulnerability using similar tactics.
Gain Complete Visibility with SOCRadar Attack Surface Management (ASM)
Modern organizations operate in an ever-expanding digital landscape, increasing their exposure to cyber risks. Unmanaged or unknown assets can create entry points for attackers, as seen in breaches exploiting misconfigurations or outdated systems.
SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) module provides comprehensive visibility into your organization’s digital footprint. It identifies exposed assets, monitors for vulnerabilities, and assesses risk levels to minimize attack surfaces effectively.
Monitor your digital assets and vulnerabilities with SOCRadar XTI (Attack Surface Management module)
Using real-time scanning and enriched threat intelligence, SOCRadar ASM maps your external-facing assets, highlights weaknesses, and alerts you to potential risks. By continuously monitoring your attack surface, it enables you to proactively secure your digital environment and mitigate threats before they escalate.



































