
Lampion Banking Malware Reappears in WeTransfer Phishing Attacks
Lampion malware operators use the free file-sharing platform WeTransfer to perform phishing attacks. This way, attackers can avoid security alerts since they are tricking users into downloading from a trustworthy service.
Threat actors used hacked business accounts to email recipients links to documents they wanted them to download from WeTransfer. The attackers present these documents as Proof of Payment.
Following the link, users end up downloading a fake VBS loader (virtual basic script) ZIP file.
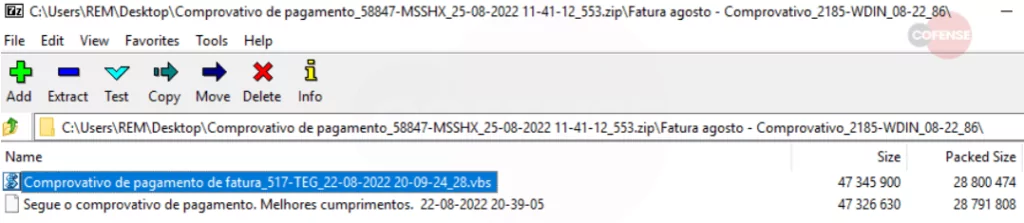
The attack begins once the user executes the script file, and a WScript process starts, which generates four additional VBS files with random names.
One of them can run the fourth script, starting yet another WScript process to retrieve DLL files stored in ZIP files with hardcoded passwords. The URLs used to download these DLLs have references to AWS instances. The DLL payloads are loaded into memory.

At last, Lampion is executed in stealth. The malware can start stealing data using techniques such as overlay attacks and injections on compromised systems.
More About Lampion Malware
Since at least 2019, the Lampion trojan has been active, focusing mainly on Spanish-speaking targets and hosting its malicious ZIPs on hijacked servers.
For the first time, Lampion was observed utilizing cloud services like Google Drive and pCloud to host the malware in 2021.

Cyware found a hostname link to Bazaar and LockBit operations in March 2022, when it reported an increase in the trojan’s distribution.
Additionally, Cyware noted that the creators of Lampion were constantly working on updating their malware with additional layers and trash code to make it more difficult to detect.
According to Cofense analysis, Lampion is an active and sneaky threat. Therefore, users should consider the risk of emails that request that they download files, even from reliable cloud services.
Recommendations
There are several security tips to prevent malware phishing attacks or mitigate them:
- Use antivirus software and scan for threats.
- Keep sensitive data out of reach, and encrypt it where you can.
- Before clicking any link or downloading a file, ensure it is safe.
- Look for indicators of compromise, a complete list from a previous campaign can be found here.



































