
Lazarus Exploits Google Chrome Zero-Day to Steal Cryptocurrency in ‘DeTankZone’ Campaign (CVE-2024-4947)
Earlier in 2024, the North Korean Lazarus APT group exploited a critical zero-day vulnerability in Google Chrome, tracked as CVE-2024-4947. This flaw was used in a deceptive campaign involving an imitated version of a DeFi game to target individuals in the cryptocurrency sector. Though the attack was discovered in May 2024, it had been active since February.
Google has previously addressed this vulnerability with security updates, but the incident highlights the persistent threat of advanced cyber actors targeting vulnerable systems. In this blog post, we will outline the details of CVE-2024-4947 and how Lazarus used it in their malicious campaign.
What is CVE-2024-4947?
CVE-2024-4947 (CVSS 8.8) is a critical vulnerability in Google Chrome, residing in the browser’s V8 JavaScript engine. It is categorized as a type confusion vulnerability within Chrome’s Just-In-Time (JIT) compiler, Maglev, and could lead to Remote Code Execution (RCE).
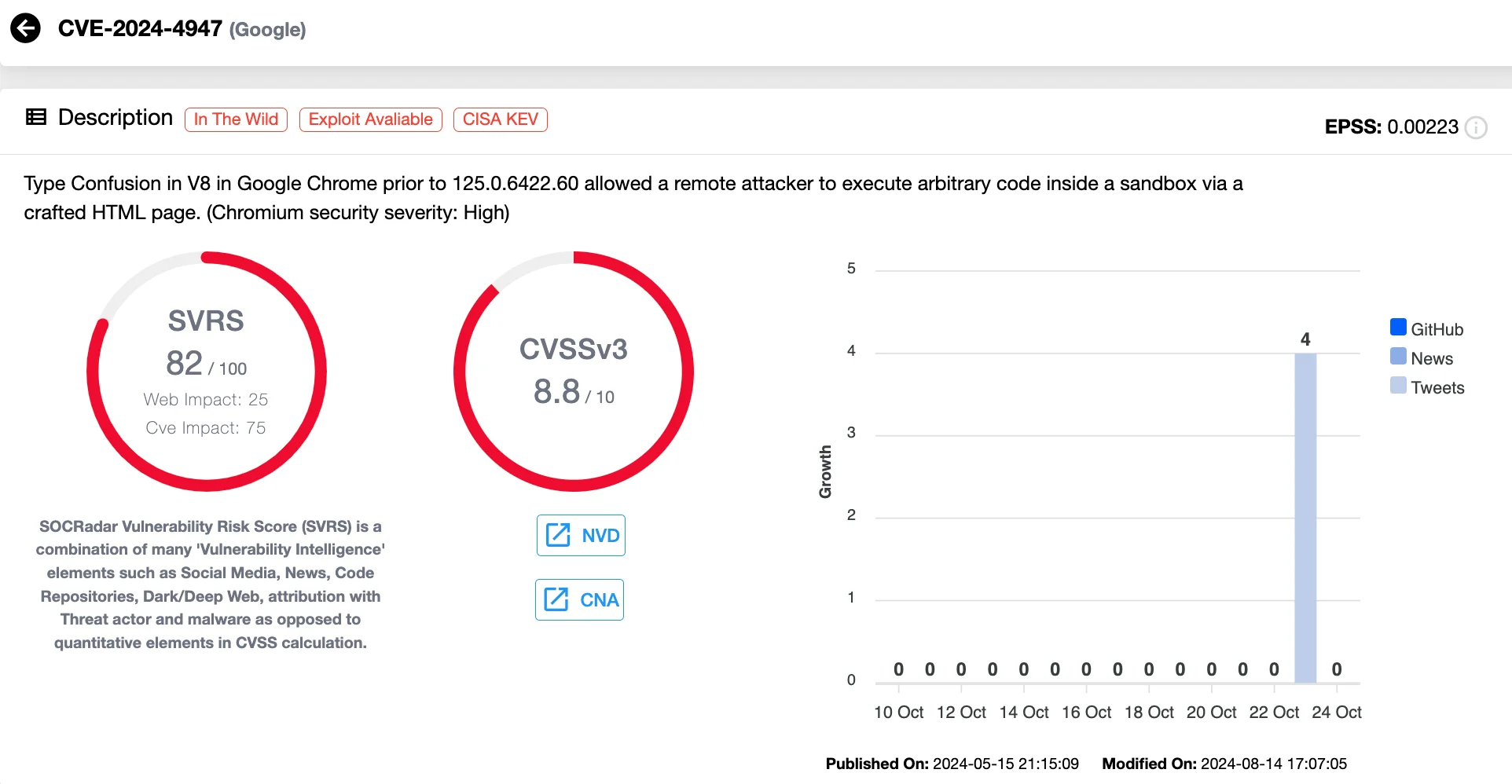
Details of CVE-2024-4947 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Exploiting CVE-2024-4947 enables attackers to steal valuable information like cookies, authentication tokens, browsing history, and saved passwords. In more advanced cases, they can bypass Chrome’s V8 sandbox with an additional exploit, gaining more control over the compromised system.
Google initially addressed the vulnerability in its Chrome update version 125.0.6422.60/.61 in May 2024. However, the threat of similar attacks remains a concern for users who have not updated their browsers.
How Did Lazarus Exploit CVE-2024-4947? Details of the DeTankZone Campaign
The Lazarus Group exploited CVE-2024-4947 in a deceptive campaign, targeting individuals within the cryptocurrency sector. This sophisticated operation revolved around a fake DeFi game, which Lazarus rebranded as “DeTankZone.”
The reason researchers initially began investigating this activity stemmed from the discovery of the Manuscrypt malware on a victim’s machine. Manuscrypt, a backdoor malware that Lazarus has used in previous campaigns, was detected on a personal computer in Russia. This raised red flags, prompting further analysis that led to the identification of the broader campaign.
Campaign Overview
Lazarus orchestrated their attack through a malicious website, detankzone[.]com, which promoted the game. Unbeknownst to visitors, the website concealed harmful code designed to exploit the Chrome zero-day vulnerability, CVE-2024-4947.
The game was created using stolen source code from a legitimate project, DeFiTankLand. Lazarus rebranded and repurposed this legitimate game, using it as bait to lure unsuspecting victims.

Imitation website, providing a malicious version of the game (SL)
Anyone who visited the site was unknowingly exposed to a hidden script that triggered the Chrome vulnerability, allowing Lazarus to execute arbitrary code. According to the researchers, simply visiting the website was enough to carry out the exploit, and the game only served as a distraction.
To ensure wide reach, the hackers launched promotions via ads on social media, spear-phishing emails, and direct messages through platforms like LinkedIn.
While this covers the initial stage of the attack, by the time security researchers uncovered it, the backend infrastructure for the game had already been taken down. Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) related to the attack have been listed at the end of this blog post.
Who is Lazarus?
Lazarus Group, a North Korean state-sponsored hacking collective, is notorious for carrying out sophisticated cyber campaigns that frequently target financial institutions, including cryptocurrency exchanges.
Known for using advanced social engineering, exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities, and deploying advanced malware, Lazarus has been responsible for numerous high-profile cyberattacks. In the DeTankZone campaign, they combined these tactics with the exploitation of CVE-2024-4947 to conduct cryptocurrency theft.
You can explore Lazarus Group’s previous campaigns, techniques, and targets on SOCRadar’s Dark Web Profile.
If you want to stay informed about cyber threat actors like Lazarus, SOCRadar’s Threat Actor Intelligence is an invaluable resource. It offers detailed insights into various threat actors and malware, highlighting their latest campaigns, Indicators of Compromise (IOCs), and Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs).
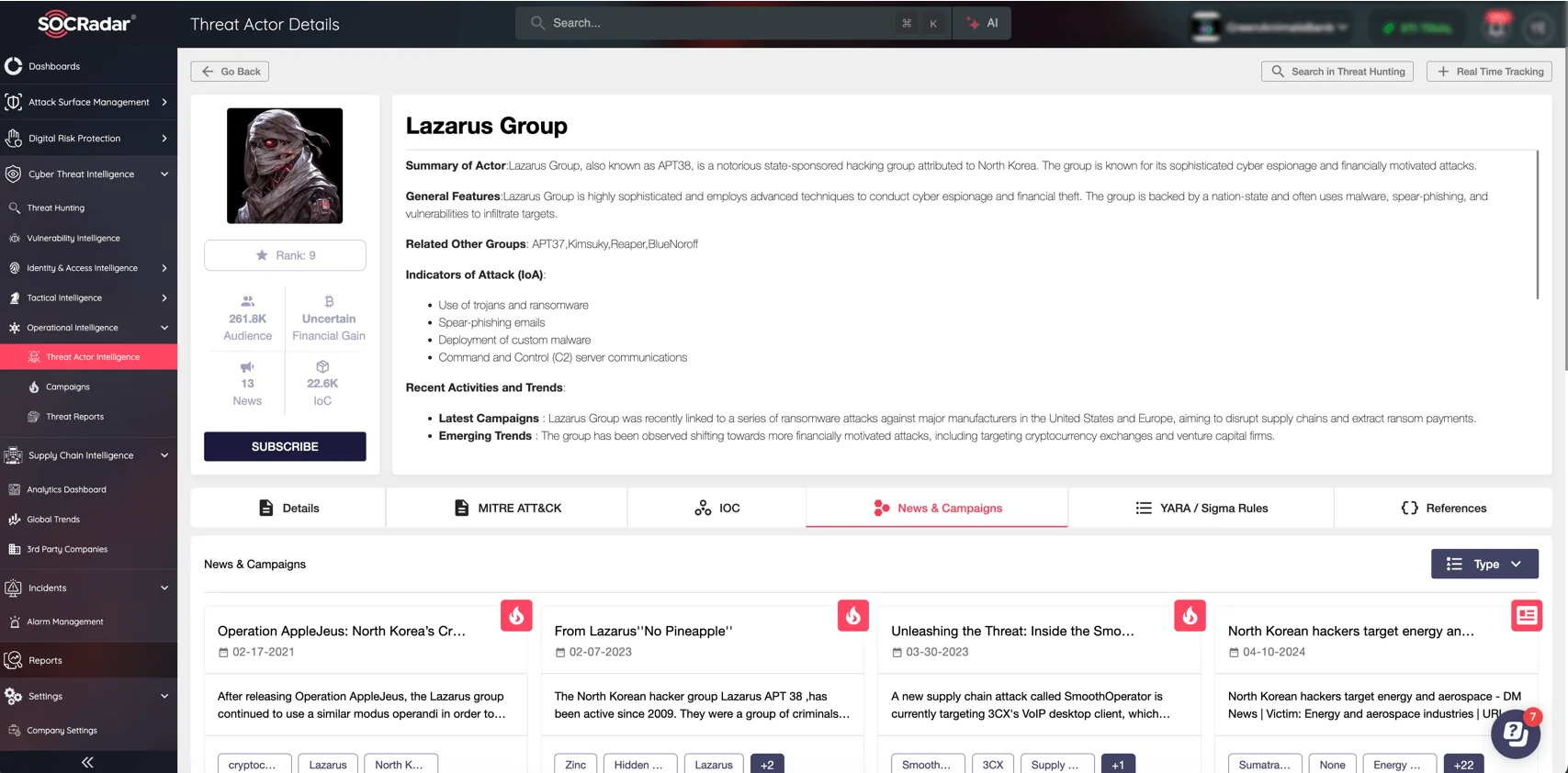
Details of Lazarus Group (SOCRadar Threat Actor Intelligence)
With the intelligence available on SOCRadar XTI, you can strengthen your defenses by understanding who the attackers are, what methods they use, and how they might target your organization.
Latest Chrome Release Fixes 3 High-Severity Flaws
Having covered the latest details surrounding CVE-2024-4947, it’s also important to note that Google has recently patched new security vulnerabilities in Chrome.
The new flaws are identified as CVE-2024-10229, CVE-2024-10230, and CVE-2024-10231, discovered in the browser’s Extensions and V8 JavaScript engine. These flaws, if exploited, could allow attackers to execute arbitrary code, gain unauthorized access to user data, or compromise systems through malicious browser extensions.
Google addressed these vulnerabilities with the release of Chrome versions 130.0.6723.69/.70 for Windows, Mac, and Linux. Users are strongly encouraged to update their browsers to mitigate these risks. For more detailed information, you can refer to the official Chrome advisory.
With new vulnerabilities emerging daily, the key to protecting your organization is knowing where you’re most at risk. SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence helps you identify and prioritize vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them.
SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence feature, available under the CTI module
By offering real-time alerts and actionable insights, the Vulnerability Intelligence module ensures you stay informed about the latest threats. This way, you can focus on the most critical risks, patch faster, and keep your systems secure.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) for Lazarus’ Exploitation of CVE-2024-4947
Following are the IOCs related to Lazarus’ exploitation of CVE-2024-4947, as listed on Securelist.
Exploit Hashes:
- MD5: B2DC7AEC2C6D2FFA28219AC288E4750C
- SHA1: E5DA4AB6366C5690DFD1BB386C7FE0C78F6ED54F
- SHA256: 7353AB9670133468081305BD442F7691CF2F2C1136F09D9508400546C417833A
Game:
- MD5: 8312E556C4EEC999204368D69BA91BF4
- SHA1: 7F28AD5EE9966410B15CA85B7FACB70088A17C5F
- SHA256: 59A37D7D2BF4CFFE31407EDD286A811D9600B68FE757829E30DA4394AB65A4CC
Domains:
- detankzone[.]com
- ccwaterfall[.]com




































